Allergic dermatitis in children develops in response to exposure to a particular allergen. The formation of this disease can be a harbinger of more serious illnesses that also have an allergic component in the mechanism of their development (bronchial asthma and others). For complete treatment, you need to contact an experienced pediatrician, allergist or dermatologist.
The development of allergic dermatitis in a child can be a harbinger of more serious diseases.
How does dermatitis manifest in children?
Manifestation of dermatitis in children
The child’s adaptive reactions during this period are immune defense and skin. Especially insidious for a child during this period are allergies and reactions that are caused by the presence of a provoking microorganism, which leads to the child developing a number of skin diseases. Among the diseases of this spectrum, due attention should be paid to such as dermatitis in a child.
What is dermatitis? This term refers to a set of diseases in which there is the presence of inflammatory damage to the skin and an increase in the degree of sensitivity of the body to existing irritants. In this case, children in the age group from birth to 4 years are at significant risk; they develop infantile dermatitis.
Neglect of the disease and lack of timely treatment leads to complications and complication of the treatment procedure. A relapse of the disease is possible, triggered by a secondary virus entering the child’s body.
What should a mother do if her child has allergic dermatitis?
If you notice a rash in your child, you need to call a pediatrician at home to fully verify the diagnosis and rule out other diseases, such as chicken pox, measles, measles rubella, scarlet fever, meningococcal infection
If the diagnosis leaves no doubt, then all possible sources of the rash need to be analyzed. It is worth thinking about what could provoke such a reaction. Perhaps you yourself (if the baby is breastfed) or your baby have consumed some new foods that can cause allergies. Maybe you used a new washing powder or cosmetics, or maybe an animal came into the house to whose fur an allergic reaction occurred. If, through a thorough analysis, you were able to establish the root cause of the allergy, then it should be eliminated as quickly as possible.
Before giving your child any medications on your own, you should remember that in a child with diathesis they can cause severe allergies, including angioedema and anaphylactic shock. Therefore, never give medications to a child with allergic dermatitis without a doctor's prescription.
Features of the flow
Typically, practical medicine considers the occurrence of dermatitis in childhood as a congenital disease. This is what creates certain difficulties in the area of how to treat dermatitis in a child and what is the main factor in the development of such a disorder. It is extremely rare that inflammatory skin diseases are isolated. When visiting a specialist, a sign of dermatitis and concomitant pathology are simultaneously detected. The most common in children are also hereditary diseases of the allergic type. Identification of various types of food allergies, hay fever, allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, bronchial asthma only confirms the diagnosis of congenital dermatitis in children, the treatment of which is directly related to certain difficulties. The disease is chronic, with frequent relapses, and is combined with other disorders of the functioning of organs and systems.
Today, pediatricians consider three types of childhood dermatitis:
Before the first six months of life, it occurs in 45% of babies, mainly on the child’s bottom and cheeks
- From birth, perhaps from 3 to 4 months, when they begin to introduce complementary foods into the diet or use infant formula until the age of three - infant.
- The period from the beginning of 4 years to 7 years of childhood-type atopic inflammation of the skin.
- After the age of seven and until the age of 12-14, doctors diagnose adolescent skin disease.
Another feature of the pathology is that the peak of the disease occurs in the first year of life. Before the first six months of life, it occurs in 45% of babies, mainly on the child’s bottom and cheeks. Upon reaching the first year of life, about 60-67% of children are already susceptible to allergic manifestations. By the age of five, dermatitis on the buttocks, in the folds of the buttocks, limbs or on the face can be found in 18–20% of all children examined. There is a very clear trend towards a decrease in susceptibility to dermatitis towards older preschool age, which is associated with an increase in the immune functions of the child’s body. So, what is the possibility of pathology occurring?
Treatment methods
The main goal of therapy for atopic dermatitis in children is to desensitize the body, limit provoking factors, eliminate symptoms and prevent the development of serious complications or exacerbations of the pathology. Complex therapy should include taking medications (the use of local and systemic drugs), following a special diet, as well as traditional medicine.
Goals of treatment for atopic dermatitis in children
Pharmacy drugs
To relieve the symptoms of atopic dermatitis, the child may be prescribed the following groups of drugs:
Goals of external therapy for atopic dermatitis in children
- antihistamines – have antipruritic properties. Such products as “Zodak”, “Cetrin” and “Finistil” are used;
- antibiotics - prescribed in cases where the disease is accompanied by a bacterial infection (Differin, Levomikol, Bactroban and others);
- antimycotics and antivirals are required when diagnosing additional infections. If a viral infection occurs, the doctor may prescribe Gossypol or Alpizarin, and if a fungal infection develops, Nizoral, Pimafucin, Candide, etc. are used;
- immunomodulators - used for atopic dermatitis, if signs of immune deficiency have been added to the symptoms of the pathology. These are potent drugs, so only the attending physician should select them;
- drugs to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Glucocorticosteroids are steroid hormones designed to eliminate pronounced symptoms of dermatitis. They are used in rare cases due to the large number of contraindications and side effects.
Drugs for atopic dermatitis in children
To speed up the regenerative functions of the body and restore affected areas of the skin, the doctor may prescribe special ointments that stimulate regeneration. The most effective drug is Panthenol.
Nutrition
Komarovsky works hard on the topic of treating atopic dermatitis in children . He recommends organizing nutrition when the child's diagnosis is confirmed (see nutrition for seborrheic dermatitis). This will speed up the healing process and prevent recurrence of the disease.
Diet for a child with atopic dermatitis in children
To do this, you should follow a few simple nutritional rules:
- do not overfeed the child, because this will lead to disruption of metabolic functions, which is fraught not only with obesity, but also with the development of skin diseases;
- Reduce the fat content of breast milk if possible. To do this, a nursing mother must also follow a special diet, do not overeat fatty foods and drink enough fluids;
- When feeding a baby, you need to make a small hole in the nipple, thereby slowing down this process. This manipulation promotes normal digestion of food.
Features of diet therapy for atopic dermatitis in children
Komarovsky also advises maintaining the room temperature no more than 20C. This will reduce the level of sweating in the child.
Folk remedies
If the disease was diagnosed in a child over 3 years old, then many parents use traditional medicine as therapy, which are in no way inferior in effectiveness to synthetic drugs. But before using them, you should definitely consult with your doctor.
Table. Traditional medicine for atopic dermatitis in children.
The use of homeopathic remedies helps normalize the gastrointestinal tract, and also restores the child’s immune and nervous system.
Additional recommendations
Many doctors recommend hyperbaric oxygenation , reflexology and phototherapy methods to complement traditional treatment methods. This will speed up the recovery process, strengthen the child’s body and reduce the likelihood of re-development of the pathology.
Hyperbaric oxygenation (pressure chamber) for atopic dermatitis in children
Often, when diagnosing atopic dermatitis, children require the help of not only a dermatologist, but also a psychologist.
What types of dermatitis in children are there?
The development and course of dermatitis in children is highly individual
It is necessary to determine in detail the types of dermatitis in children. Taking into account the fact that dermatitis in children is a combination of diseases of an allergic nature, the following types are distinguished, differing in different etiologies, localization of the affected area, course and clinical picture.
Atopic is a secondary disease of a viral nature, which manifests itself as the presence of hypersensitivity to allergic pathogens, as well as irritants that are nonspecific in nature. In the medical field, these diseases are also referred to as neurodermatitis and atopic eczema. The disease is observed in early childhood and completely subsides at the age of 5 years.
The causes are hereditary factors, underdevelopment of the digestive system, the mother’s diet during gestation and other factors. The symptoms of the disease vary, most often in the presence of the disease there is redness of the skin and rashes on the skin folds. Dermatitis appears on the face, body, limbs and other parts of the body.
Dermatitis appears on the face, body, limbs and other parts of the body
Seborrheic variety is the presence of inflammatory processes in the scalp area. The causative agent is a fungus that infects the skin and thereby causes the manifestation of the disease. In pediatrics, seborrheic dermatitis in children under 1 year of age is called gneiss. Most often, gneiss is characteristic of newborns.
What does dermatitis look like in children? This question worries parents and teachers who work with children, observe and record their condition and development. This type of disease is characterized by the presence of crusty neoplasms of a yellowish color, including redness of the affected areas of the skin.
Most often, gneiss formations are characteristic of the parotid region; they appear on the head, neck, chest, and groin of the child.
Diaper dermatitis in children. The name diaper itself speaks for itself. With the advent of diapers and their widespread use in newborns, cases of this type of dermatitis in children have become more frequent. With the advent of diapers, the number of washes, including money for purchasing SMS, has decreased, but everything needs a reasonable approach, and modern parents, due to saving money, save money not only on powder, but also on their own children, trying to make the most of one diaper for a whole day, which, in turn, affects the child’s health.
Contact dermatitis in children. This variety is localized at the site of skin contact with an irritant from the external environment. Such an irritant can be a metal object, cosmetics, or seams on clothing.
This type of allergic reaction does not require treatment with medications; you need to isolate the irritant and use a specialized cream base to alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
In addition to the above classification, there is viral dermatitis, septic.
The formation of viral dermatitis is facilitated by the penetration of infection into the body. The disease may be secondary or may be independent. Sometimes the cause can be an enterovirus, that is, a combination of several viruses.
Fungal dermatitis in children is a disease of secondary origin, located on smooth skin and in the area where hair is located. Often it becomes a complication of existing diseases or is provoked by allergies, which introduces certain difficulties in its diagnosis.
Septic dermatitis or erythema are processes of a pathological nature occurring in the body, accompanied by the presence of red spots on the skin. It develops when a pathogen enters the body - an infection caused by a microorganism. In this case, the pathogen must be in the patient’s blood.
Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis is a rare complication. A response to the causative agent of the disease is produced by tissue structures of a granulomatous type, while immune complexes and collagen derivatives are formed in the blood fluid.
According to age criteria there are:
- dermatitis in preschool children;
- dermatitis in children under one year of age;
- dermatitis in adolescents.
Each of the above types of disease has its own characteristics. It is necessary to highlight the characteristics of each type of dermatitis in children. It is not recommended to prescribe treatment for dermatitis on your own. Your starting point in treating the disease is an appointment, examination and consultation with a specialist.
Septic dermatitis or erythema is accompanied by the presence of red spots on the skin
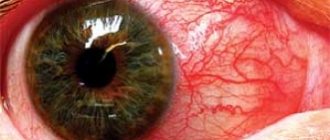
How to determine dermatitis on the face? It's very simple - look in the mirror. This disease is dangerous because it develops gradually and proceeds unnoticed by the patient until it enters the indicated phase. Symptoms observed:
- instant formation on the face of minor redness and irritated areas of the skin;
- the presence of a rash in the mouth, near the nose, forehead and cheeks;
- peeling of the skin combined with itching;
- increased sensitivity of the skin layer, pain;
- migraines and pain in joint tissue, extremely rarely, there is a sharp increase in temperature.
Reasons for the development of the disease
As a rule, allergic dermatitis develops under the following conditions:
CONTACT ALLERGY. This condition occurs when a child is allergic to the skin, so it is recommended to carefully select clothes and toys for a child prone to allergic reactions. In addition, for a baby up to one year old, it is advisable to use hypoallergenic care products.
FOOD ALLERGY. The food route for the development of allergic dermatitis is the most common, especially in infants, when the nursing mother does not comply with the diet. In addition to the fact that the diet is disrupted, early and improper complementary feeding becomes a provocateur of the disease.
Potential allergens for the child and mother are cow's milk, eggs, various types of fish, exotic vegetables and fruits, and chocolate.
The famous pediatrician Dr. Komarovsky recommends not giving some of these foods (chocolate, strawberries) to children under one year of age. Other foods should be introduced into the child’s diet carefully, following certain rules:
- It is not recommended to introduce complementary foods consisting of several products more than once every 7 days, which makes it possible to monitor negative reactions to the introduction of a new product. In case of an acute reaction of the baby, a week-long break is recommended, after which a replacement should be made with products with low allergenicity.
- You can return to the product that caused the allergic reaction no earlier than after 8-9 weeks.
- Unfamiliar foods should be given to the baby at the very end of the feeding procedure and it is not advisable to mix them with others.
Komarovsky recommends that you never overfeed your baby. This can provoke disruption of the digestive system and, as a result, the development of allergies. In addition, even when breastfeeding, the mother must follow a diet.
RESPIRATORY ALLERGY. This form of the disease occurs when allergens (animal hair, dust, aerosols, perfumes, etc.) penetrate through inhalation. In this case, the occurrence of allergic dermatitis requires immediate measures. Frequent wet cleaning and limited contact with pets are recommended.
In addition, there are secondary factors that provoke exacerbation of dermatitis in a child under 1 year of age. These include:
- parental smoking (passive and active);
- unbalanced diet of the mother when feeding a child up to one year;
- nervous stress;
- chemical additives and flavorings in food products;
- increased physical activity, accompanied by increased sweating;
- seasonal factors, when immunity is most weakened.
In addition, the development of dermatitis is facilitated by the unfavorable environmental situation in the patient’s region of residence.
Complex of reasons
In order to effectively eliminate any organic disorder, including cure dermatitis, it is necessary to accurately determine why the child suffers from such a pathology:
The main trigger factor for the development of atopic dermatitis is a violation of the barrier, protective function of the skin.
- The main reasons, according to modern medicine, are that there is a genetic predisposition to allergic symptoms.
- The influence of unfavorable environmental factors.
- The influence of heredity is a very serious reason. When the father and mother show hypersensitivity to various allergens, the child has an 80-85% risk of getting dermatitis. Violations in one of them can lead to an inflammatory process on the skin of infants in 42 - 45% of cases.
- To determine exactly how to treat a child, it is necessary to find out whether the source is a food intolerance factor. It is from the first days of birth until 4–6 months that the baby is affected by the mother’s incorrect diet during gestation and lactation.
- Very serious reasons for the early onset and severe course of the disease are possible overfeeding of the baby, breastfeeding is minimized or completely excluded by the mother, early introduction of complementary foods.
- In order to plan how to cure dermatitis in childhood, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of the influence of health problems in women. This is a natural or artificial termination of pregnancy, exacerbation of the chronic course of pathologies, maternal and intrauterine infections, acute or chronic hypoxia of the newborn.
- It is also necessary to identify causes such as metabolic imbalance, digestive dysfunction, infectious and viral diseases that the baby suffers from at the same time.
Diet for allergic dermatitis
Diet plays a very important role in this disease. Certain foods are considered allergens that may cause or worsen a reaction. Therefore, whole milk, chocolate, currants, raspberries, strawberries, and citrus fruits should be excluded from the patient’s diet. It is not recommended to consume nuts, honey, spices, sauces, mayonnaise, mushrooms, wheat, chicken and other products. The diet should be especially strict during the period of exacerbation of the disease.
It is important to reduce the amount of potatoes, pork, peaches, red fruits and vegetables, rice, bananas, and corn in the diet. It is recommended to consume fermented milk products, zucchini, lamb, radishes, herbs, green and yellow vegetables and fruits, plums, almonds. Preference should be given to hypoallergenic porridges prepared without milk and cereal soups. The diet must be developed individually by a doctor.
We recommend reading about the diet for atopic dermatitis in adults.
What are the symptoms of dermatitis?
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis in children
The pathology is quite complex, its exacerbation causes a lot of unpleasant sensations. Therapy should be comprehensive, its methodology is based on the study of symptoms, a consultation of doctors, which includes a dermatologist, allergist, nutritionist, gastroenterologist, psychoneurologist, ENT. Symptoms and treatment are completely interrelated; atopic dermatitis is characterized by:
- The appearance of severe itching, burning, rashes of various types.
- Eczema affects numerous parts of the body - primarily on the face, in the groin; clearly defined dermatitis on the arms, head, buttocks, and thighs appears a little later.
- Symptoms of the disease in preschool and early school age increase, rashes appear in the groin, armpits, and on the skin of the folds of the upper and lower extremities. Skin dermatitis appears near the mouth, in the eyelids and neck, accompanied by keratinization of the skin and very painful microcracks.
- A prolonged course is associated with wetting of the rash sites, the formation of crusts, peeling, pustular formations, swelling and the release of exudate, which may smell bad. The appearance of serous discharge in 4 places is especially common - on the bends of the elbows, knees, armpits, and groin.
- Insomnia, nervousness, general malaise.
Symptoms
It is important to determine whether the skin irritation is mild or severe. This is usually quite easy to do. One of the first signs of diaper rash is redness in the area that is usually covered by the diaper. In mild cases there may be a faint pinkish tint. Other symptoms include the following:
Mild diaper rash
Mild diaper rash is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Pink or red spots
- A few scattered pimples
- Slight flaking and dryness
- Burning sensation when urinating
Severe diaper rash
Severe diaper rash is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Extensive redness
- Soreness in this area
- Tips
- Ulceration
- Blisters
- Dry, cracked skin
- The baby is clearly upset
How activated charcoal helps cope with illness
Regardless of its origin, skin dermatitis and its varieties are treatable. A universal remedy for the treatment of diseases of this type is talkative for children. Activated carbon provides significant assistance in the treatment of the disease. Activated carbon has proven itself in the treatment of a whole range of diseases; allergies, which intensify with the onset of warm days, are no exception.
Summer is a time when the air is saturated with a large number of allergens: dust particles, nectar from flowers, wool and poplar fluff. It’s great if you don’t have an allergic reaction to the above allergens, and if you do, your salvation is to take activated carbon.
Activated carbon is prescribed primarily to cleanse the body of existing pathogens.
How does activated carbon work? Activated carbon is prescribed primarily to cleanse the body of existing pathogens. When you have another allergy attack, it is so important to have these tablets on hand. Activated carbon removes waste and toxins from the body. As a result of thorough cleansing measures, the body activates its defense mechanisms with renewed vigor, helping to improve immunity, releasing immune units and using them in the fight against infection.
Principles of therapy for atopic dermatitis
Before developing an individual therapy system, the attending physician conducts a complete diagnosis of the patient. The main goal of the treatment plan is to change the course of the disease, reduce the severity of exacerbation, and control possible relapses for a long period.
Basic concept of therapy:
- Corticosteroid medications in combination with skin softening medications. Relevant in case of severe dermatitis to quickly eliminate it.
- Antibiotics are prescribed externally to eliminate the development of skin infections. Miramistin, chlorhexidine, fucaseptol, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green 1-2%, fucorcin has an excellent effect. The use of ointments is no less important. Applying ointments of Bactroban, Fucidin, Levosin, Levomicol up to 2 times a day helps to avoid suppuration.
- Antihistamines that reduce the severity of an allergic reaction. It is acceptable to prescribe Cetrin, Eodac, Zyrtec, Erius. The minimum course is at least 4 months.
- Painkillers, sedatives and sedatives - tavegil, suprastin, cromoglycic acid and ketotifen, traditional calcium chloride solution.
- Increasing signs of pyoderma require the use of systemic antibacterial agents. Before treatment with antibiotics, tests should be carried out to determine the susceptibility of microorganisms.
- General strengthening and vitamin complexes, decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs, folk remedies should be used strictly individually.
To effectively treat dermatitis, it is necessary to establish the exact cause
It is important for therapy to eliminate factors that lead to exacerbations. The exclusion of contact, food, inhalation, and chemical irritants and a strictly selected diet will reduce the risk of developing pathology. Physiotherapeutic procedures, mud treatment, balneotherapy are indicated. Parents should not take their child’s diagnosis as a death sentence; however, even the most thorough treatment can completely cure no more than 25–32% of young patients; for the rest, dermatitis accompanies their entire lives.
Diagnostics
Criteria for diagnosis have been developed. They are divided into mandatory and auxiliary.
Required:
- Itching of the skin of varying degrees of intensity.
- In the infantile phase, there is a symmetrical lesion located on the face and on the inner surfaces of the limbs.
- In adolescence, lichenification processes dominate, with peeling on the face, torso, knees, wrists, and elbows.
- Genetically determined tendency to atopy (allergy in close relatives). The disease has a chronic course, periods of remission alternate with exacerbations.
- Pronounced resistance to treatment.
Minor:
- manifestation of symptoms up to 2 years;
- xerosis - increased dryness of the skin;
- increase in IgE in blood serum;
- the addition of frequent infectious skin lesions;
- palmar ichthyosis;
- cheilitis;
- suborbital fold;
- change in skin color in the form of white stripes (dermatographism) under mechanical influence;
- painful cracks behind the ears;
- the occurrence of pathological changes on the skin of the hands and feet.
The diagnosis is made when three major and more than three minor criteria are present.
Laboratory methods
Laboratory tests are not specific; they only serve as an auxiliary method in making a diagnosis.
- HIV test (many skin manifestations of HIV infection are similar to severe atopic dermatitis).
- Blood analysis. Eosinophilia, an increase in basophils and a decrease in lymphocytes are observed.
- Blood chemistry. This test evaluates the functional state of many organs and body systems in a child. If there are disturbances in the liver, the level of transaminases (ALT, AST), bilirubin increases in the blood serum; Creatinine and uric acid levels will help determine the condition of the kidneys.
- Determination of immunoglobulin classes in blood serum, especially IgE by enzyme immunoassay (ELISA).
- The appearance in the blood of specific antibodies to a significant allergen.
In pediatrics, skin tests are performed outside the period of exacerbation and are allowed in children from 4 years of age.
The methods of conducting these tests are different: with violation of the integrity of the skin (puncture, scarification) and without damaging the skin (application). These tests are considered one of the most reliable methods for determining the factor causing an allergy.