Cough, not always, but most often, is a manifestation of illness in a child. And it is not the cough reflex itself, which is protective in nature, that needs to be treated, but its cause – an infectious disease, allergy, or helminthic infestation.
Medicines for children are specially produced in children's form, not only in the form of tablets. Children can be treated for cough with syrups, suspensions, to which sweeteners are added to mask the bitter taste of the medicine, which makes it easier to take the drug.
What is a cough
Coughing is just a protective reaction of the body. It occurs when irritants and pathogens enter the respiratory organs. The appearance of a dry cough can be associated with viruses, bacteria and allergens. They enter the respiratory tract, settle on the mucous membrane and provoke excessive mucus secretion. Bronchospasms occur because the body tries to cleanse itself.
Due to intense coughing attacks, microorganisms do not settle on the walls of the bronchi, but are excreted along with sputum. This allows you to avoid serious diseases - bronchitis, pneumonia and pleurisy.
If the cough reflex is impaired for some reason, mucus accumulates in the respiratory organs and is an excellent breeding ground for bacteria. In this case, bacteria multiply quickly and the person begins to get sick.
In young children who often lie down, coughing may be caused by a runny nose. Snot flows into the nasopharynx, irritating it and causing a cough. This unpleasant problem can be eliminated only after the runny nose is cured.
Coughing in children may be a response to inhaling too dry or polluted air.
Cough with a cold
The choice of medications for colds depends on the age of the child. In the instructions for use, be sure to look at what age the medicine can be given, how to treat a child, and in what dosage to give the cough medicine.
For a dry cough, give Erespal, Sinekod - drugs that suppress the cough reflex. A child's wet cough should be treated differently than a dry cough. In this case, mucolytics, expectorants that promote the removal of sputum are required.
For a wet runny nose, vasoconstrictors may be required, for example, Otrivin. After all, if the nose is stuffy, then mucus flows into the airways, causing irritation and coughing.
Causes of cough in a child
There are many reasons for a child’s severe cough. This includes systemic diseases and the conditions in which the baby is located. Intense cough attacks in children can be provoked by:
- Colds.
- Bronchitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Pleurisy.
- Whooping cough.
- Allergy.
- Bronchopneumonia.
- Laryngitis.
- Pharyngitis.
- Tonsillitis.
- Rhinitis.
A child may cough constantly if someone smokes in the house. Passive smokers inhale no less harmful smoke than those who smoke. It has already been proven that children who constantly inhale cigarette smoke are more prone to respiratory diseases.
The cause of a child's cough can also be too dry air in the room. In this case, the mucous membrane dries out and becomes irritated, which leads to the urge to cough. This phenomenon is especially common in winter, when the heating radiators are turned on.
Children under 6 years of age often suffer from respiratory infections. This is due to incompletely formed immunity. Children who attend preschool institutions are more susceptible to colds.
In children under 5 years of age, whooping cough and parawhooping cough are often diagnosed. These infectious diseases occur with severe coughing attacks, which become more intense day by day. A characteristic feature of whooping cough is the whistling sounds made by the patient when trying to inhale. At the end of each coughing attack, viscous glassy sputum is coughed up.
The entry of a foreign body into the respiratory organs is also accompanied by a debilitating paroxysmal cough. In this case, whistling sounds are observed in the chest, and the skin becomes bluish. If a foreign body enters the bronchi, respiratory failure occurs. If the child is not given timely assistance, everything may end in suffocation.
To prevent whooping cough, it is recommended to vaccinate children promptly. Even if a vaccinated child gets sick, the disease is mild and rarely causes complications.
General principles of treatment
A cough that lasts up to 3 weeks is called acute. A frequent cough that lasts more than 8 weeks is called chronic. Quite often, coughing persists for a month, after suffering from respiratory diseases and pneumonia.
To speed up recovery, you must follow these recommendations:
- The home should be maintained at normal humidity and temperature. The humidity level should be about 55%, and the temperature in the children's room should not exceed 21 degrees.
- Smoking should be limited in the home where there are children. To smoke, adults can go outside or onto the balcony. It is worth remembering that toxic cigarette smoke reduces immunity.
- Sudden changes in temperature should be avoided. In winter, before going outside, it is recommended to stand in the entrance for a few minutes.
- A mixed, severe cough can be caused by allergens. Such substances can be pollen, animal hair and fluff. For some people, certain medications and foods cause coughing. When cleaning your home, you should use personal protective equipment to prevent respiratory irritation from household chemicals. For allergy sufferers, it is better to replace strong-smelling substances with soda or regular laundry soap.
It is important to remember that spicy and highly seasoned foods can irritate the throat and cause coughing. To prevent this phenomenon, you should avoid canned and spicy foods at least for the duration of treatment.
If your child is prone to allergies, you should not keep an aquarium with fish in the children's room. Few parents know that dry food is a strong allergen.
Prolonged dry cough
This cough can be acute (up to three weeks) or chronic (a period of about 8 weeks or more). A cough in a child that appears more than 3-4 times over the course of a year without acute symptoms of infection (fever, general weakness, runny nose, painful syndromes in the throat, etc.) is also considered chronic.
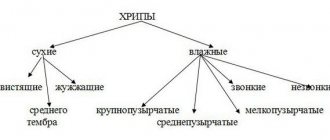
A cough can be divided into a productive (wet) cough (with sputum production) and a non-productive cough without sputum (dry). Sputum production is a sign that the bronchi are irritated by pathogenic microbes, which provoke high secretion. A dry cough may indicate an allergic reaction and foreign microparticles entering the nasopharynx. But do not forget that if a child has a prolonged dry cough without fever, this does not always mean that there is no viral infection. In children of the first years of life, a nonproductive cough is often associated with increased viscosity of sputum and poor development of the muscular system of the bronchi. However, sputum still forms. Modern medicine believes that it must be removed. In such cases, pediatricians prescribe expectorants in the form of syrups or tablets that thin mucus and stimulate the formation of a productive cough.
Prolonged dry cough is a disease in which there is no formation of sputum in the nasopharynx or lungs for a long time.
Causes of prolonged cough
- Viral diseases - very often after an infection, a child coughs for several weeks with a dry cough, which worsens at night.
- Bronchial spasms - a dry cough at night may indicate spasm of the bronchial tubes, which are caused by inflammation.
- Allergic processes - frequent sneezing - is the main symptom of allergic rhinitis.
- Irritation from smoke, dust, chemicals, which are very often present in the work environment.
- Asthma - A chronic dry cough can be a sign of mild asthma.
- Blockage of the airways by foreign objects: food or medications.
Treatment of long-term dry cough
A dry cough with fever over a long period of time often brings many problems; for treatment you need to follow a few simple recommendations:
- Complete the treatment of viral and bacterial diseases;
- Spend more time outdoors;
- Drink plenty of fluids throughout the day;
- Avoid contact with allergens and ingredients.
Methods for treating cough in children
Treatment of cough should begin with determining the exact cause of the ailment. The treatment regimen is different in each case. Sometimes you can get rid of coughing only after humidifying the air in the room.
Drug therapy
For coughs of various etiologies, the doctor prescribes medications that facilitate the discharge of sputum. Medicines for children are often produced in the form of syrups and lozenges. After a complete examination and clarification of the diagnosis, the child may be prescribed the following medications:
- Ambroxol.
- Licorice syrup.
- Lazolvan.
- Doctor Theiss syrup.
- Pertussin.
- Mukaltin.
- ACC.
- Potion with marshmallow.
All these drugs help to thin out and facilitate the removal of sputum. They must be used according to the instructions or taken in the dosages prescribed by the doctor. For children under 3 years of age, the dose of medications is calculated by the doctor based on weight and diagnosis.
Dr. Komarovsky believes that mucolytics and expectorants cannot be given in all cases. Medicines based on ambroxol increase the production of sputum, which should normally be coughed up. But few people take into account that young children cannot cough normally, as a result of which children experience congestion in the respiratory organs.
In some European countries, mucolytics are prescribed only after the child is 4 years old. Prescribing such drugs before 2 years of age is generally prohibited in these countries.
Lollipops and lozenges of plant origin will help cure a child’s cough. They can only be prescribed to children over 3 years of age who already understand how to dissolve lollipops. Such drugs are quite effective for coughs caused by laryngitis and pharyngitis; they soften the mucous membrane and reduce its irritation. The child should dissolve lozenges and lollipops only in the presence of adults to avoid accidents.
For coughs caused by allergies, antihistamines are prescribed. Such drugs will help eliminate allergy symptoms in a few minutes. Most often, children are prescribed medications of the latest generations:
- Tavegil.
- Citrine.
- Claritin.
- Zodak.
Time-tested drugs, Loratadine, can also be prescribed. Diazolin and Suprastin. It is worth considering that such medications have more contraindications and side effects.
If coughing attacks are accompanied by obstruction, then it is advisable to give the sick child drugs to expand the lumen of the bronchi. Such drugs include Berodual and Ventolin; inhalations are used with these drugs.
Bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia, whooping cough and other infectious diseases of the respiratory organs are treated with antibacterial drugs. Broad-spectrum antibiotics from the penicillin or cephalosporin group are most often prescribed. If you are allergic to antibiotics from these drug groups, macrolides may be prescribed. When treated with antibiotics, it is necessary to simultaneously take probiotics, which will help prevent dysbiosis.
For infectious diseases, children may be prescribed vitamin preparations and immunomodulatory agents that will help strengthen the immune system.
Non-drug therapy
Therapeutic inhalations will help quickly relieve cough. For diseases of the lower respiratory organs, it is recommended to carry out procedures using a nebulizer. This medical device converts medicinal solutions into a fine mixture, which settles on the mucous membrane and has a therapeutic effect.
Mucolytics and alkaline solutions can be used for inhalation. The doctor may prescribe inhalations with Ambroxol, Ambrobene, Berodual or alkaline mineral water. If a child coughs heavily and cannot stop, you can inhale it with saline solution. When performing inhalations, it is important to choose the right mask; it should fit tightly to the face.
If your child is constantly coughing, you can put mustard plasters on your child. It is worth considering that for young children, mustard compresses are applied with the reverse side or through a layer of gauze. Mustard plasters warm soft tissues well, improve blood circulation and metabolism. Thanks to such procedures, you can get rid of bronchospasms very quickly.
For children 11 months and younger, 1 mustard plaster is placed on the back, avoiding the heart area. Children over 2 years old can apply mustard compresses to the back and chest. The procedure lasts 2-3 minutes, after which the mustard plasters are removed, the skin is wiped with a clean napkin and lubricated with baby cream.
Rubbing will also help to quickly clear up a cough. The following drugs can be used to treat children:
- Pulmex baby.
- Doctor Mom.
- Dr. Theiss.
- Eucabalus.
- Turpentine ointment.
If turpentine ointment is used to rub a child, it must first be mixed in half with baby cream. This will prevent burns and skin irritation. The child should be rubbed at night and then put to bed.
If, despite the treatment, the cough intensifies and the child’s condition worsens, it is necessary to show the patient to a doctor. The cause of this malaise may be complications of the disease.
Folk remedies
There are many folk recipes that can be used to treat cough in children. It is recommended to discuss non-traditional methods with your doctor:
- A liter of full-fat milk is poured into a saucepan, half a glass of washed oats is added and simmered over low heat for an hour. Give the child 1/3 cup of milk decoction twice a day, always warm.
- Ginger root is peeled, crushed and boiled in half a liter of milk for an hour. The finished broth is filtered and given to the child a tablespoon, 4 times a day.
- The radish is peeled, cut into pieces and placed in a jar, smearing the layers with honey. An hour later, give the sick baby the resulting syrup, a teaspoon 5 times a day.
If a child constantly coughs, it is recommended to rub it with goat or badger fat. You need to rub not only the chest and back, but also the legs.
Traditional methods of treatment
At home, inhalation of medications or infusions of medicinal plants helps well. The expectorant effect is different from coltsfoot and elecampane.
A good remedy can be prepared by taking the roots of elecampane, licorice, and marshmallow in equal proportions. Two tablespoons of the mixture are poured with cold boiled water, taken in the amount of 2 glasses, and left for 8 hours.
You should drink half a glass of water infusion 3 times a day.
Read more about inhalations in the article Inhalations for coughs.
Warming up the chest
Warming compresses prescribed by a doctor for persistent dry cough without fever can be used to treat children from an early age.
A simple and safe compress can be prepared as follows:
- heat sunflower oil in a water bath;
- saturate a napkin with it;
- squeeze well, wrap the child’s body without touching the heart area;
- wrap in wax paper;
- wrap in a warm scarf.
The wrap is done at night. Be sure to give a warm diaphoretic drink. You can brew raspberry leaves or berries, linden blossom, strawberry leaves.
A child 7-8 years old can treat a cough with a warm massage with eucalyptus oil, which achieves a double effect. The child's blood circulation in the chest area improves, and oil vapors penetrate the respiratory tract, providing a medicinal effect.
Mustard plasters or medicinal cups help with coughs.
The restriction for medical cups is age under 5 years, as well as insufficient weight, undeveloped subcutaneous fat tissue. Even if a child is older than 5 years old, but is underweight, he cannot be treated with glass jars; this can severely injure the skin and cause a local burn at the site where the jar is attached.
Doctors' advice
When coughing of any etiology, it is useful for the patient to give a lot of warm drink. It moisturizes the mucous membrane, helps thin out mucus and facilitates its removal from the respiratory tract. It is correct to give your child warm tea, jelly, decoctions of medicinal herbs and compotes. You can offer mineral water after releasing the gas from it. But you shouldn’t give concentrated juices, they irritate the throat and provoke coughing attacks.
The room of a sick child must be constantly ventilated. In the warm season, the window can be open all the time, but you need to make sure that the baby does not sit in a draft.
If you have a cough of unknown etiology, you should see a doctor immediately. Coughing can be caused by stress or heart problems.
Prevention
Doctors advise not to neglect the prevention of respiratory diseases in order to avoid serious complications:
- The house needs to maintain normal humidity, about 50%.
- During an outbreak of respiratory diseases, you should refrain from visiting crowded places.
- During cold season, you need to rinse your nose with saline solution when you get home.
- At the first signs of illness, you should see a doctor.
When treating cough in children, you must strictly follow all the pediatrician's recommendations . If the prescribed treatment does not produce results within 3-4 days, you should inform your doctor.
Inhalations for dry cough
Treatment of dry cough in children often consists of inhalation procedures that act at the very source of inflammation, allowing to relieve inflammation and thin the mucus. Inhalation can be carried out using improvised means - using steam in a pan, or using a nebulizer. The second method is more effective and can be used for children from 6 months.
Cough inhalations using a nebulizer allow the medicine to penetrate into the deep parts of the respiratory system, thereby softening the cough, reducing the viscosity of mucus, and speeding up the recovery period. If a nebulizer is used for inhalation, the following drugs can be used:
- Ambrobene.
- Lazolvan.
- Berodual.
- Pulmicort.
- Rotokan.
- Furacilin.
- Miramistin.
Only pure drug solutions can be used for nebulizer therapy. Any of the drugs must be diluted with 9% sodium chloride in proportions 1:1 or 1:2. It is recommended to perform inhalation procedures 2–4 times a day, for 5–7 minutes. Treatment may take from 5 to 10 days. Thanks to inhalation procedures, the recovery period will come much faster, and the risk of complications will be minimized.