- Moderate oligohydramnios is diagnosed with minor deviations from standard values. It is mainly detected in the early stages, so the problem is solved quickly and without consequences for the fetus: dietary nutrition is prescribed, adjustments are made to the mother’s lifestyle. In this case, there are no pronounced symptoms, the woman feels normal.
- Pronounced form. Observation in a hospital is required to avoid possible consequences. The woman is bothered by pain in the lower abdomen, and when the fetus moves, her health worsens. You may notice a decrease in the circumference of the pregnant belly due to a reduction in the size of the uterus. Bleeding after the birth process is possible, the gynecologist-obstetrician prescribes a caesarean section.
- Relative form. Observed in the last trimester. The reason lies in the aging of the placenta. Don’t worry, it can be treated, but you need to be prepared for the strict control of the supervising gynecologist.
To make an appropriate diagnosis, measure the volume of the abdomen and the height of the uterine fundus. If there are deviations, the patient is sent for an ultrasound examination, then treatment and other auxiliary procedures are prescribed.
What does oligohydramnios mean during pregnancy?
Amniotic fluid or amniotic fluid is the natural habitat of the fetus, which is responsible for its life support. The correct development of the baby depends on the quantity and quality of intrauterine fluid, which allows him to be born healthy.
Amniotic fluid forms in the uterus 12 days after implantation of the fertilized egg. A bladder consisting of durable membranes forms in the uterus. They ensure the tightness of the amniotic sac and are called chorion and amnion.
The amount of fluid increases as the gestational age increases. So, with the onset of the 38th gestational week, 1-1.5 liters of amniotic fluid is observed. But closer to 40 weeks, the water level drops to 0.6 l. Compliance with these indicators plays an important role, therefore, during a routine ultrasound, the volume of fluid in the uterus must be measured. For measurement, a specific indicator is used - the amniotic fluid index.
On a note! On the eve of labor, the bladder ruptures on its own, which in obstetrics is called “water breaking.”
The physiological volume of amniotic fluid is variable and differs from woman to woman. If the indicator drops below the critical level (below 500 ml), this phenomenon is called oligohydramnios. The deviation is more often observed in the last trimester and may well provoke the development of fetal pathology.
A pregnancy disorder such as fetal oligohydramnios is associated with inadequate functioning of the placenta. Although previously this pathology was associated only with a violation of the water-salt balance in women. But regardless of the cause of oligohydramnios, the risk of developmental delay, heart defects and even fetal death increases.
Is there oligohydramnios?
What are the symptoms of lack of amniotic fluid? If a woman herself notices that she is developing oligohydramnios, then this indicates only one thing - the reasons are very serious. The thing is that usually pregnant women do not know that they have oligohydramnios. Only when there is too little amniotic fluid for fetal development. But at the same time, with moderate oligohydramnios, a woman only shows meager signs, to which pregnant women usually do not attach much importance.
As a rule, if the volume of water in the uterus becomes small, then the movements of the developing baby are painful for the mother - the child hits and pushes hard. In pregnant women, a moderate degree of amniotic fluid deficiency is more common; mothers rarely notice it. This form of amniotic fluid deficiency does not pose a threat to the life of the child or the pregnant woman.
In gynecology, an obstetrician can track indirect symptoms of the development of oligohydramnios: parts of the child’s body are easy to palpate, the size of the uterus does not correspond to the period. It is especially important to track the level of the uterine fundus - if it is 2 centimeters lower than the due date, then the cause may be a lack of amniotic fluid. At the same time, it could be fetal malnutrition, or its incorrect location in the uterus.
There are no methods that can accurately diagnose oligohydramnios without ultrasound.
Sometimes a woman may experience abdominal pain - this is one of the symptoms of a small amount of amniotic fluid, but an ultrasound examination is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
Classification of oligohydramnios during pregnancy
Oligohydramnios can be transient (temporary) and chronic:
- Acute (transient) oligohydramnios occurs suddenly under the influence of a certain factor. For example, temporary oligohydramnios develops against the background of acute respiratory infections, sore throat, or food poisoning. This form of oligohydramnios is benign and often goes away on its own after the woman recovers.
- Chronic oligohydramnios develops slowly and progresses with increasing gestational age. Sometimes it is possible to notice the deviation only in the third trimester, when treatment for oligohydramnios during pregnancy no longer brings results. At the initial diagnosis, a woman undergoes a comprehensive examination to find out the cause of the pathology.
Oligohydramnios is also classified according to the period of development:
- Early oligohydramnios develops between 16 and 20 gestational weeks. Oligohydramnios in early pregnancy is easily detected during an ultrasound. The main reason is the inferiority of the chorion. It is the most unfavorable type of oligohydramnios, since it occurs at the time of fetal formation and often provokes congenital malformations. If the diagnosis of oligohydramnios is confirmed, screening is required to identify chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus.
- Late oligohydramnios occurs after the 26th gestational week. This is a more favorable form of pathology, since the fetus is already fully developed and the risk of chromosomal diseases is minimal. However, oligohydramnios during late pregnancy requires vigilant monitoring of the baby’s condition, especially during childbirth.
Depending on the condition of the fetal membrane, oligohydramnios is divided into two subtypes:
- Primary - a decrease in the amount of water without signs of damage to the amniotic sac. The cause of the pathology is abnormal development of the fetus, chromosomal abnormalities, and inferiority of the placenta.
- Secondary - lack of water caused by trauma to the shell. As a result of damage to the wall of the fetal bladder, slight leakage of water occurs.
Oligohydramnios: treatment
Let us remember that oligohydramnios is not a disease, but a symptom. The doctor must find the cause of this process and prescribe a therapy that eliminates the cause of the lack of amniotic fluid. This is also influenced by the duration of pregnancy, the severity of oligohydramnios, etc.
During treatment against the causes of oligohydramnios, you need to visit your doctor regularly. During the sessions, the pregnant woman is examined by ultrasound, CTG, and Doppler so that measures can be taken if there is a deterioration.
Alas, if oligohydramnios is detected early, and its causes are incompatible with the life of the fetus, then the doctor decides to terminate the pregnancy.
If ultrasound has determined the aging of the placenta, doctors carry out therapy that is designed to combat fetoplacental insufficiency. Moderate oligohydramnios does not require hospitalization.
Whereas in case of severe water shortage, treatment is carried out in a hospital. Oligohydramnios in combination with fetal hypoxia is a common reason for delivery through cesarean section.
With oligohydramnios at the end of pregnancy, doctors evaluate the condition of the fetus to decide how to treat and what to do. If the pregnancy is already coming to an end, the child is normal, then there is no need for treatment - the woman is sent straight to the maternity hospital.
But remember, if you identify any of the above-described symptoms of oligohydramnios, you must definitely come to an appointment with a gynecologist. Traditional medicine can only harm the fetus!
Causes of oligohydramnios during pregnancy
The factors for the development of oligohydramnios have not been fully studied. But a study of similar cases in obstetric practice showed the following possible causes of this pathology:
- Underdevelopment and decreased functionality of the amniotic sac.
- Severe pathologies of the fetus (underdevelopment of the kidneys, deformities, chromosomal abnormalities).
- Hypertension. A severe and prolonged hypertensive crisis provokes placental dysfunction, which leads to oligohydramnios.
- Infectious diseases. Bacterial flora, when released into the amniotic fluid, complicates the functioning of the placenta.
- Improper blood flow in multiple pregnancies.
- Post-term pregnancy.
- Metabolic disorders in women, in particular severe obesity.
Causes
Many pregnant women, and especially those who are carrying a child for the first time, often ask questions about what oligohydramnios is during pregnancy, and what the causes and consequences are.
In medicine (gynecology, obstetrics), there are
ten main reasons why expectant mothers have a lack of amniotic fluid:
- Infectious diseases of the genital organs (ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, etc.).
- Chronic diseases of a pregnant woman (for example, diseases of the urinary system or cardiovascular pathologies).
- Severe congenital pathologies of the baby’s kidneys (lack of amniotic fluid manifests itself in the first weeks of pregnancy).
- Bad habits of a pregnant woman (smoking, drugs, etc.).
- Pathologies of the placenta (abnormal development of the placenta, premature aging, fetoplacental insufficiency).
- Late detection of pronounced hystosis.
- Acute viral and bacterial diseases of the mother (influenza, ARVI, etc.).
- Idiopathic amniotic insufficiency.
- Late labor with long delay.
- Carrying twins or triplets.
Some doctors also believe that the reasons for the lack of amniotic fluid may be: obesity with metabolic disorders, previous TORCH infections (rubella, herpes, toxoplasmosis), damage to the membranes, diabetes, etc.
Symptoms of oligohydramnios during pregnancy
Confirmation of oligohydramnios is based on characteristic symptoms. So, the signs of oligohydramnios during pregnancy are as follows:
- Discomfort caused by fetal movement.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of pain during menstruation.
- Morning sickness and increased dry mouth.
- Weakness, body aches, apathy.
- Restless sleep.
- Refusal of food.
Symptoms
Some expectant mothers do not pay attention to the symptoms of a lack of amniotic fluid, without knowing what oligohydramnios in pregnant women is and how it is dangerous.
But this physiological disorder can lead to dangerous consequences, so you need to know all the symptoms of oligohydramnios and immediately consult a doctor when you first notice them.
Self-medication in this case will be dangerous not only for the mother, but also for the child.
Did you know? According to statistics, oligohydramnios occurs in 4% of pregnant women.
Oligohydramnios during pregnancy can be moderate or severe. In the first case, the symptoms practically do not make themselves felt. A moderate lack of amniotic fluid is determined only after an ultrasound examination.
If the mother’s lack of amniotic fluid is severe, the following symptoms :
- Abdominal pain when the fetus moves.
- The uterus decreases in size (the size of the abdomen decreases, and this can be observed even visually; during an obstetric examination, a decrease in the height of the uterine fundus is noted).
- Loss of strength and poor health (nausea, weakness, dry mouth).
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen with periodic aching and nagging pain.
Find out what to do if during pregnancy you experience pain in the tailbone, lower back, or toothache.
Only a doctor can confirm the lack of amniotic fluid. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor for further examination and treatment.
How to determine oligohydramnios during pregnancy
A gynecologist may suspect oligohydramnios in a woman during a routine examination. This pathology is indicated by:
- Insufficient fetal activity.
- Discrepancy between the height of the uterine fundus and the gestational age.
- Abdominal circumference is less than the established norms.
- The basic criterion for oligohydramnios is the amniotic fluid index, which is included in the list of indicators determined by ultrasound.
However, to confirm chronic oligohydramnios, all parameters are studied over a period of 1-2 months. If oligohydramnios progresses, the diagnosis is finally confirmed.
After this, the woman unscheduled undergoes additional screening:
- Donates blood for infections.
- Does a glucose tolerance test.
- Donates blood for indicators of developmental defects.
- An additional ultrasound is performed.
- Sent for amniocentesis with karyotyping to exclude genetic pathologies of the fetus.
Based on the research results, the doctor decides what to do in case of oligohydramnios during pregnancy: terminate the pregnancy or continue with subsequent treatment and observation.
Examinations and tests
Lack of amniotic fluid in pregnant women is diagnosed based on dynamic observations of the woman: the degree of fetal activity, the amniotic fluid index, abdominal circumference and the height of the uterine fundus.
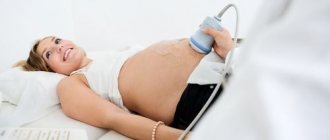
If doctors identify any suspicions, the pregnant woman is prescribed an ultrasound.
However, diagnosis using ultrasound should be based on repeated studies .
A one-time ultrasound can only indicate that a woman has some abnormalities during this particular period of pregnancy. They may be associated with previous viral diseases, and subsequently disappear independently and irrevocably. If ultrasound is performed continuously over 1-3 months, and there is always a lack of amniotic fluid, then this indicates the presence of severe oligohydramnios.
Currently, many doctors diagnose oligohydramnios on the basis of a single ultrasound, which in itself can only mean a statement of fact. In this case, active drug treatment is not prescribed. Pregnant women can be prescribed a course of treatment based on harmless vitamin complexes.
If ultrasound repeatedly shows severe insufficiency of amniotic fluid, then pregnant women are additionally prescribed Doppler ultrasound of the placental vessels (duplex ultrasound scanning of blood vessels) or fetal CTG (cardiotocography, which helps evaluate the characteristics of fetal heart contractions). If the results of the two above diagnostic methods are normal, this means that there are no serious abnormalities, and the oligohydramnios was only temporary, functional in nature.
In case of poor data from CTG and Doppler studies, doctors prescribe additional examinations and tests: studies for anti-Rhesus bodies, the presence of infection in the blood, glucose levels, etc. It is imperative to do a targeted ultrasound, which gives a detailed picture of everything that is happening. If possible, karyotyping and amniocentesis are also prescribed. The last two diagnostic methods allow us to identify chromosomal and genetic abnormalities of the child.
Did you know? Down syndrome and trisomy 8 and 13 in the fetus cause oligohydramnios in almost 100% of cases.
Sometimes a gynecologist may suspect that a woman has amnionic hydrorhea (leakage of amniotic fluid). In such cases, water smears are prescribed. In late pregnancy, a lack of amniotic fluid can be detected by amnioscopy, a procedure that is safe for both mother and fetus.
Amniotic fluid index: norms
The optimal method for determining oligohydramnios is ultrasound. During the study, the amniotic fluid index (AFI) is calculated, and the length of the vertical pouch is measured. Using these two quantities, the water level is determined. If the index is below normal, oligohydramnios is confirmed.
- A vertical pocket is a free sector of amniotic fluid between the baby and the anterior wall of the peritoneum. At the time of measurement, there should be no fragments of the placenta or parts of the fetal body. Normally, the length of the pocket is from 5 to 8 cm.
- IAF - for measurement, the abdomen is conventionally divided by two perpendicular lines passing through the navel. As a result, 4 even squares are visualized. Then the height of the pocket is determined in each of them. At the end, these values are added and the IAF is obtained.
Moderate oligohydramnios during pregnancy
With moderate oligohydramnios, the length of the pocket varies between 2 and 5 cm. In this case, the AFI should be as follows:
This degree of oligohydramnios is insignificant and is often an echographic sign without clinical manifestations. Moderate oligohydramnios requires mandatory CTG, as well as Doppler ultrasound, to exclude defects in the fetus. The woman will be prescribed short-term multivitamins and medications to improve the functioning of the placenta.
Severe oligohydramnios during pregnancy
Severe oligohydramnios is an obvious pathology, indicating significant disturbances in the functioning of the placenta and the development of the baby. The diagnostic criterion for the anomaly is that the length of the vertical pocket does not exceed 2 cm, and the AFI is equal to the following values:
After the diagnosis is confirmed, the woman is sent for examination. Its goal is to exclude chromosomal abnormalities and assess the functional viability of the placenta. If the cause of the pathology turns out to be a woman’s illness (diabetes, gestosis) or phytoplacental insufficiency, the pregnancy is maintained and the woman’s condition is corrected. If chromosomal defects in the fetus are detected, the woman is advised to terminate the pregnancy.
Amniotic fluid: norms and diagnosis of oligohydramnios
Amniotic fluid is the natural habitat for the baby in the womb during gestation. In order for two united cells to develop into a little person, the environment for growth and development must be special, providing the most comfortable and favorable conditions.
A considerable part of these functions is performed by amniotic fluid:
- provide and maintain the required level of temperature and pressure;
- are a nutrient medium containing fats, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins and other substances necessary for the development and growth of the fetus;
- perform a protective function in different directions: protects the fetus and umbilical cord from damage, protects the placenta and blood vessels from the effects of active movements of the baby, limits external noise exposure, protects the fetus from infections, prevents the possibility of fusion of the baby’s skin with the walls of the fetal bladder;
- provide the child with the opportunity to move easily and actively;
- “help” the baby to take the correct position in the womb before birth;
- promote the opening of the uterus during childbirth and facilitate the passage of the birth canal.
The amount of amniotic fluid is not the same throughout pregnancy.
In parallel with how the baby and the pregnant woman’s belly grow, the amount of water also increases: at the 12th week it is about 65 ml, at the 32nd week of pregnancy - about 600 ml, and before childbirth - an average of 1000 ml.
But this is the norm; we also wrote about polyhydramnios. What is oligohydramnios?
Oligohydramnios is a pregnancy anomaly in which there is a reduced volume of amniotic fluid. It occurs in no more than 4-5% of pregnant women, and can appear before the 20th week (early oligohydramnios) or in the II-III trimester (late oligohydramnios). Depending on the degree of decrease in the level of amniotic fluid, there are:
- moderate oligohydramnios – a decrease in amniotic fluid within 500-700 ml;
- pronounced oligohydramnios – a decrease in the required amount of water by 3 or more times.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Different degrees of severity of oligohydramnios manifest themselves in different ways, and accordingly, may require different diagnostic methods. If minor deviations may not have any external manifestations and do not in any way affect the mother’s well-being, then severe oligohydramnios makes itself felt with the following symptoms:
- nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness and weakness;
- constant feeling of dry mouth;
- pain during intrauterine activity of the baby.
In addition to the symptomatic detection of oligohydramnios, there are more reliable diagnostic methods:
- objective examination - the doctor evaluates the ratio of the pregnant woman’s abdominal circumference and the height of the uterus, as well as their correspondence to the timing of pregnancy;
- Ultrasound - a specialist assesses the presence of a “free pocket” between the baby and the front wall of the mother’s abdomen (in case of oligohydramnios, it is less than 2 cm), calculates the amniotic fluid index, correlating the readings with a special table of norms for weeks of pregnancy.
When diagnosing oligohydramnios, additional tests are prescribed to determine the condition of the fetus and the degree of oligohydramnios:
- Dopplerography;
- tests for bacterial and sexually transmitted infections;
- fetal cardiotocography.
But in order to effectively and timely provide assistance to a pregnant woman and her baby, you need to understand why oligohydramnios developed and what its risks are.
How to treat oligohydramnios during pregnancy
Moderate oligohydramnios often does not require treatment. It does not progress and in most cases is temporary. In this case, there is no danger for the mother and fetus, so the woman is not given recommendations on a healthy lifestyle.
The situation is completely different with severe oligohydramnios. There is no clear treatment plan for the pathology, so the doctor selects an individual strategy for each case. Unfortunately, the outcome is not always favorable. Some women have a miscarriage or the fetus is born with deformities, while others have babies born weak and in need of resuscitation.
A common method of treating oligohydramnios is to inject saline into the amniotic sac through the cervix. This procedure allows you to delay the aging of the placenta or its detachment, as well as the premature death of the umbilical cord. But such measures are effective only if the fetus has no signs of developmental pathology.
If screening shows developmental abnormalities before the 26th gestational week, the pregnancy is terminated. If treatment for oligohydramnios does not bring improvement, and the pregnancy is already long (at least 28 weeks), premature labor is stimulated.
What to remember
- Oligohydramnios during pregnancy is a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid.
- For the mother, infertility threatens termination of pregnancy. Dangerous consequences for the child - weight loss, disturbances in nervous and brain activity, pain after birth, congenital anomalies.
- The main causes of oligohydramnios are hypertension, placental pathologies, multiple pregnancies, congenital fetal defects, and inflammatory diseases.
- Using the amniotic fluid index table you can determine whether you have infertility. Compare the ultrasound result with the lower limit of the index.
- With moderate infertility, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, and with severe infertility, the expectant mother is hospitalized.
- Since the causes and consequences of oligohydramnios during pregnancy are explained by irregular ultrasound diagnostics, which detect pathology too late, the best prevention is a timely visit to the doctor.
Oligohydramnios during pregnancy: consequences for the child and woman
Oligohydramnios in the 1st or 2nd trimester can cause multiple defects in the fetus or miscarriage. In the second half of pregnancy, pathology complicates the growth and development of the baby and often provokes premature onset of labor.
What are the risks of oligohydramnios during pregnancy for a woman:
- Insufficiency of amniotic fluid leads to pain in the uterus.
- The risk of miscarriage increases.
- During childbirth, insufficient labor activity is observed, and incomplete dilatation of the cervix occurs.
- Often it is necessary to resort to stimulation of contractions, and the bladder is opened artificially.
The effect of oligohydramnios on the fetus:
- The baby cannot grow and development is delayed.
- The fetus develops clubfoot, a skeletal deformity.
- Increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities or deformities.
- The baby cannot be born naturally, so a caesarean section is performed.
- Perinatal mortality of the baby is possible.
What dangers does a lack of amniotic fluid pose?
To discuss the likely complications of this phenomenon, its causes should be reliably determined. Only after this will experts be able to judge what consequences this may have.
According to statistics, only 4% of pregnant women in our country experience insufficient amniotic fluid.
Amniotic fluid performs important functions:
- protects the baby from external influences;
- does not allow fusion of the fetus and the membranes;
- provides the necessary space for activity;
- prevents damage to the umbilical cord and placenta during embryo movement.
If the amount of amniotic fluid is less than normal, this primarily threatens aesthetic problems for the baby. Possible tugging and atrophy of the limbs, compression of the skull and other deformities.
In addition, taking a comprehensive look at the causes and consequences, we can say that a low content of amniotic fluid will lead to the following problems:
- developmental delay;
- hypoxia;
- birth injuries;
- difficult and prolonged labor;
- onset of labor ahead of schedule.
But the most terrible consequence of dangerous oligohydramnios can be intrauterine fetal death. The likelihood of a sad ending increases with the gestation period. This way, in the early stages, specialists have a better chance of avoiding adverse consequences.
Oligohydramnios during pregnancy - prevention
The only way to prevent oligohydramnios is to eliminate the factors that provoke this pathology both at the stage of pregnancy planning and after conception. To do this, you need to detect these factors (if they exist) and eliminate them in time.
- Thus, metabolic disorders in a woman, including water imbalance, decreased metabolism due to endocrine disorders, and poor nutrition are deviations from the norm that need to be corrected at the stage of pregnancy planning.
- And during pregnancy, you need to avoid intoxication with alcohol, nicotine, medications and chemical elements. This leads to slower placental blood flow and oligohydramnios.
- For prevention, a woman is also recommended to have good nutrition, moderate physical activity, regular visits to the doctor and undergo all routine examinations.
Prevention
To date, there are no specific recommendations that would guarantee the absence of oligohydramnios during pregnancy. To reduce the likelihood of the disease to a minimum, expectant mothers should eat a healthy and balanced diet, lead a healthy lifestyle and strictly follow all doctor’s instructions.
Special gymnastics is very useful for pregnant women
It is recommended to undergo prescribed examinations in a timely manner and take the necessary tests, and to refrain from excessive physical activity, however, special gymnastics for pregnant women and feasible physical activity will be very useful.
In addition, preventive measures include planning pregnancy, minimizing unprotected sex, and avoiding casual sex. It is necessary to prepare for conception in advance: identify and cure all chronic diseases and be sure to register with the antenatal clinic. Following these tips can significantly reduce the risk of oligohydramnios.
Oligohydramnios during pregnancy - reviews of outcomes
In most cases, women report slight oligohydramnios in the second half of pregnancy, which went away successfully after short-term treatment. Women carried the baby to term normally and gave birth naturally.
Some ladies say that they were prescribed vitamins and a metabolic complex (Curantil with Actovegin), while other women did without treatment.
The described cases indicate the prevalence of transient physiological oligohydramnios, which does not threaten either the woman or the fetus.
Only in rare cases is there information about early oligohydramnios (before 26-28 gestational weeks), when examination showed impaired fetal development. In these cases, the pregnancy ended in artificial termination.
As you can see, the dangerous consequences of oligohydramnios during pregnancy are rare, and it is not always possible to prevent them. But in most cases, minor oligohydramnios goes away on its own, leaving no sad consequences.
What to do?
With moderate oligohydramnios, when the amount of amniotic fluid is almost at the upper limits of normal, it is enough to optimize the woman’s diet and include foods rich in vitamins and minerals in the diet. It is imperative to visit a doctor to monitor the dynamics of amniotic fluid restoration and timely detect and stop possible deterioration.
With severe polyhydramnios, home treatment will not be enough. The condition requires constant monitoring by a doctor and therapeutic measures in a clinical setting. With a significant deficiency of amniotic fluid, there is a possibility of developing pathology of the hearth, for example, disturbances in the formation of limbs, bone tissue, intrauterine fetal hypoxia, and developmental disorders of the central nervous system.