- Causes of cracked tongue
- Symptoms
- Treatment of cracked tongue
- Traditional treatment
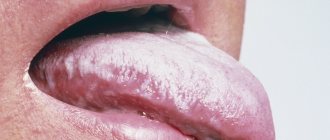
Cracks in the tongue are a sign of a malfunction in the functioning of the human body. It is not in vain that doctors judge the presence of diseases by the condition and appearance of this organ. A clean and pink tongue occurs only in healthy people; a change in color, the appearance of plaque and, especially, cracks, indicate the presence of all kinds of disorders and serious diseases.
Why do cracks appear on the tongue?
In some cases, a person has cracks since birth. The child has a “folded” tongue, it is also called “scrotal”. The cracks are located symmetrically, across and lengthwise, and do not cause any discomfort. With this option, treatment is not necessary. Such cases should be distinguished from disorders requiring intervention. Glossitis of the tongue is a disease that causes discomfort. The reasons why the tongue is cracked are:
- lack of vitamin PP, iron, some other nutrients, B vitamins;
- anemia;
- allergies to medications, toothpaste, mouth rinses;
- stress, fatigue;
- damage to the mucosa;
- uncomfortable dentures;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- complications caused by other diseases.
Mechanical injuries easily occur due to a lack of vitamins. A person accidentally bites his tongue, causing a crack to form. The following types of glossitis are distinguished:
- Deep - at the bottom of the mouth. If left untreated, the problem gradually spreads to the chin and neck.
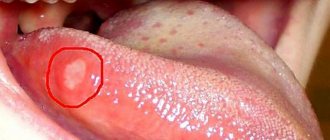
- Desquamative, also known as “geographical language.” Typical for pregnant women, patients with stomach diseases, parasites, and metabolic disorders. Accompanied by a burning sensation. The organ is dotted with lines reminiscent of continents.
- Diamond-shaped. Occurs in patients with gastritis with low acidity. Diamond-shaped glossitis manifests itself in the form of a thickening of the tongue; an area similar to a geometric figure is formed near the root.
- Villous, in which inflammation of the papillae on the tongue is noted. They grow and become keratinized, after which the papillae resemble villi. Causes: candidiasis, constant injury to the papillae, smoking.
- Folded, scrotal – not dangerous, but may require aesthetic surgery if the folds are deep.
- Gunterovsky. The tongue is smoothed on top, looks too even, shines, and has a crimson color. The papillae are retracted. This glossitis occurs due to a deficiency of vitamins, folic acid, and B12.
- Interstitial, occurring as a complication of syphilis. Part of the muscle tissue of the tongue is replaced by connective tissue, and the organ looks riddled with scars. If syphilis is not treated, there will be no muscle tissue left in the organ, and glossitis can develop into cancer.
- Alcohol coding - prices, methods and consequences. How to get rid of alcoholism
- Ninth month of pregnancy
- Salmon steak: recipes with photos
Why is my tongue cracked and what to do about it?
Cracks in the tongue indicate a disruption in the functioning of the body. The causes of this phenomenon are different, therefore the treatment is individual in each case. Photos of the lesions are unattractive, but they allow you to determine whether you have such a tongue feature.
A clean tongue, not covered with a heavy coating, without lesions and especially cracks, speaks of the good health of its owner. External changes in this organ are a signal for the need to visit a doctor and undergo an examination.
Localization of cracks in the tongue
Inflammation of the papillae on the tongue, cracks, spots and other unpleasant symptoms can be located in different ways. The location of the lesions makes it possible to determine why they appeared, and sometimes to make a diagnosis based on the tongue. Additional diagnostic measures are not excluded, but are mandatory. Inflammation is a symptom to contact a specialist.
Over the entire surface of the tongue
If there are many cracks in the organ, they are small, arranged in a disorderly manner - this may indicate diseases of the large intestine, and in a chronic form. When damage is accompanied by dry mouth and constant thirst, consultation with an endocrinologist is required.
On the tip
Inflammation on the tongue, localized in the area of its tip, often appears due to mechanical injuries, burns from hot food, and stomatitis. Sometimes the cause is disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. A weakened immune system facilitates the formation of cracks, which are caused by slightly biting the tip of the organ.
In the middle
The cracks in the middle part of the lingual surface are most clearly captured in the photo; they are the deepest. In the center of the organ, folded, diamond-shaped glossitis appears more noticeably. Malfunctions of the immune system lead to dry mouth: the mucous membrane dries out and cracks form.
On the side surfaces
The hidden cause of cracks in the tongue along the edges may be diseases of the liver and gall bladder. Damage on the lateral surface is a common symptom of anemia, thyroid pathologies, and gastrointestinal disorders. There are also tooth marks on the edges; they appear due to the fact that the organ swells and is easily injured.
Symptoms
When depressions form on the surface of the tongue, the patient comes with the following complaints:
- feeling of pain when eating food, and sometimes even when talking;
- burning sensation in the affected area;
- swelling and swelling of the tongue;
- violation of taste perception;
- dry mouth occurs.
A common cause of cracks in the tongue is glossitis - its inflammation. In this case, symptoms arise, including hyperemia of the mucous membrane, the formation of blisters on the back of the tongue and swelling, and increased salivation occurs (hypersalivation). In case of infection, signs of intoxication of the body and hyperthermia are possible.
Symptoms that may accompany a cracked tongue
If injuries occur, the patient is concerned about:
- pain when talking, while eating;
- swelling, redness;
- blisters, ulcers throughout the mucous membrane;
- increased salivation, or vice versa, dry mouth;
- white coating on the tongue;
- burning in the mouth;
- temperature increase.
- Signs of pneumonia in an adult
- Pizza in the microwave - recipes with photos
- How to reduce jpg file size
Why is my tongue cracked? Main reasons
There are many reasons why folds form on the tongue. To identify the source of problems, it is necessary to examine not only a dentist, but also highly qualified general practitioners.
Diseases that lead to cracks in the tongue:
- diseases of the stomach and intestines;
- helminthic lesions;
- vitamin deficiency;
- hormonal imbalances;
- blood diseases;
- thrush;
- central nervous system dysfunction;
- low quality of removable dentures and tooth-replacing structures.
Often, based on the condition of the oral cavity, one can assume that a patient has HIV, as evidenced by pathological changes in the mouth. Among these signs are long-term non-healing, painful, sometimes bleeding, progressive damage to the mucous membrane.
Cracks, accompanied by swelling and redness, may occur as a response to the allergic effects of certain toothpastes and elixirs. However, the most common source of changes in the tongue are traumatic lesions: scratches from fish bones, biting, burns from hot drinks. All this, against the background of a weakened immune response and vitamin deficiency, leads to slow healing of wounds and the formation of bleeding cracks.
From birth
Sometimes cracks are congenital. Such manifestations do not bring unpleasant sensations to a person and do not require treatment. The main reason for the formation of changes on the back is considered to be “folded tongue syndrome.”
Children and adults who have been diagnosed with a “scrotal tongue” from birth do not complain, do not feel discomfort, sometimes they only mention that plaque accumulates excessively on its surface. The cracks lie both along the tongue and transversely, and are located symmetrically relative to the center line.
Appeared in adulthood
The occurrence of cracks in an adult indicates gross disturbances in the functioning of the body. The main reasons leading to the formation of lesions on the tongue comprise two large groups.
- Local causes are a reflection of dental health.
- Diseases of internal organs.
An inflammatory disease of the tongue is called glossitis. It is this that is the main source of cracks and sweetness. A white coating is deposited around them. In addition to structural changes, the patient complains of a burning sensation, which intensifies when eating hot or irritating foods.
The disease occurs due to frequent biting of the tongue or an allergy to dental hygiene products, which manifests itself in the form of pimples.
There are several types of glossitis:
- diamond-shaped - occurs due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and is manifested by redness of a diamond-shaped area on the tongue, while the disease can be observed for years and have a chronic course, without bringing any discomfort to the person;
- desquamative - the disease initially manifests itself in small lesions that increase over time, the pain is moderate, but if left untreated the disease progresses and causes severe discomfort;
- folded - longitudinal and vertical cracks form on the back of the tongue, which cause attacks of severe pain.
Localization
Cracks in the tongue can have different locations, due to which not only the appearance of this organ changes, but also characteristic symptoms arise, while each type of localization corresponds to certain internal causes.
- cracks on the sides - the main sources of cracks on the sides are changes in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract that occur due to impaired absorption. In addition, folds on the lateral surface are formed as a result of iron deficiency anemia and diseases of the thyroid gland;
- crack in the middle - occurs with rhomboid glossitis and “geographical” tongue, burdened by folding. The disease occurs when immunity is low, and dryness of the tongue develops, due to which deep folds develop on its surface;
- a crack at the tip is a lesion resulting from mechanical trauma to the tongue resulting from burns, biting and the occurrence of stomatitis ulcers.
Deep cracks
Cracks that exceed more than 5-6 mm in depth are considered deep. The reasons leading to their occurrence are the same as for lesions of small and medium depth. They are more complicated and bring suffering to their owner.
Read also: Why is the tongue yellow?
The disease is called “geographic language” because of its similarity to a world map. The disease occurs:
- In women during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- In children.
- During the period of hormonal changes in adolescents.
When depressions form on the surface of the tongue, the patient comes with the following complaints:
- feeling of pain when eating food, and sometimes even when talking;
- burning sensation in the affected area;
- swelling and swelling of the tongue;
- violation of taste perception;
- dry mouth occurs.
A common cause of cracks in the tongue is glossitis - its inflammation. In this case, symptoms arise, including hyperemia of the mucous membrane, the formation of blisters on the back of the tongue and swelling, and increased salivation occurs (hypersalivation). In case of infection, signs of intoxication of the body and hyperthermia are possible.
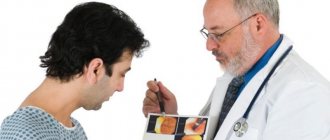
Which doctor should I contact?
The answer to the question of which doctor treats glossitis is simple. When painful changes appear in the mouth, patients turn to the dentist. This specialist will help alleviate the condition, but there is a high chance that damage to the taste organ is only a symptom of changes in the body. It is not always possible to determine the disease by the tongue; additional studies are prescribed. Consultations with a hematologist, endocrinologist and gastroenterologist may be required, diagnostics including:
- external examination of damage, swelling;
- epithelial scraping examination;
- blood analysis;
- identification of concomitant chronic or acute diseases.
Local reasons
Regarding inflammation of the surface of the tongue, two similar phenomena should be distinguished: glossitis and glossalgia. The causes of cracks in the tongue due to glossitis can be:
- Lack of vitamins in the body.
- Anemia.
- Infection of the body with helminths (worms).
- Severe poisoning.
- Mechanical tissue damage (for example, due to bite or prosthetics).
- Diseases of the stomach, liver or intestines.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Allergy.
Unlike glossitis, glossalgia is characterized by the appearance of pain in the tongue area in the absence of obvious causes. In addition, all the causes characteristic of glossitis can also accompany glossalgia.
Human phobias are considered the main cause of glossalgia. In other words, the fear of acquiring an incurable disease, such as cancer, causes stress and, as a result, painful sensations up to the appearance of visible organ defects. Such an illness requires psychotherapeutic diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms of glossalgia usually include:
- Pain, burning or tingling sensation in the tongue.
- Perceptible fatigue of the organ after a long conversation.
- Difficulty and discomfort when moving the tongue.
- Swelling and pathological changes in the papillae of the organ.
- Cracks on the surface of the tongue.
- Feeling dry.
In this case, the above symptoms occur periodically depending on the mental state of the patient. They may suddenly disappear and appear again after a while. The main difference between glossitis and glossalgia is a change in the sensitivity of the organ when eating food. If a person eats non-spicy food, the painful symptoms of glossalgia decrease, unlike the symptoms of glossitis, which worsen while eating.
Glossitis, as a consequence of local inflammation of tissues and disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, has the following symptoms:
- Spots, bumps and cracks on the tongue in adults and children.
- Burning sensation and pain.
- The appearance of plaque.
How and with what to treat cracks in the tongue
Whatever disease causes cracks in the tongue, damage to the oral cavity requires symptomatic treatment. Patients are prescribed:
- analgesics (for pain relief), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- steroid medications, for severe inflammation: Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone;
- for pain in the tongue, applications with anesthetics are used: “Trimecaine”, “Lidocaine”, “Pyromecaine”;
- a drug that stimulates epithelial restoration, for example “Dalargin”;
- antimicrobial agents (antibiotics), for bacterial and fungal complications;
- calcium pantothenate;
- vitamins;
- antihistamines;
- decoctions, infusions, rinses with antiseptics;
- solcoseryl paste;
- exclusion of hot, spicy foods and other irritants.
Folk remedies also reduce inflammation, swelling, and have a wound-healing effect. Herbal preparations, infusions, and decoctions are used to rinse the mouth. Here are some recipes:
- A decoction of oak bark with the addition of honey. Four tablespoons of crushed bark are poured with cold water (take 4 cups) and put on fire. When the composition boils, remove from the stove, leave for half an hour, filter, and add honey to the warm infusion. Rinse your mouth and throat up to 5 times a day.
- Compress made from cottage cheese and sour cream. Wrap the mixture in gauze, apply it to your tongue, and do this before breakfast.
- Herbal collection: pour sage, raspberries, mallow and coltsfoot (all 20 g), pour 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for about 2 hours, rinse your mouth and throat.
- Rinse your mouth with potato juice (squeeze fresh).
If damage is localized in the area of the tip of the tongue, it is recommended to take daily baths with herbs and infusions. The affected part is immersed directly in a cup with infusion. During treatment, a strict diet is followed. Spicy, salty, smoked foods, scalding teas, and alcohol should be eliminated from the diet. Anything that dries or damages the lingual epithelium is excluded.
Preventive measures
Photo: You need to brush not only your teeth, but also your tongue!
Despite the fact that there are many reasons for the appearance of cracks, their formation can be prevented by following simple preventive measures:
- do not neglect regular preventive visits to the dentist;
- pay special attention to high-quality teeth cleaning;
- stop drinking alcohol and smoking;
- avoid foods that irritate the surface of the tongue: hot, spicy;
- balance your diet. Include more foods that contain large amounts of essential vitamins and minerals. Protein foods should always be on the menu. Consume as little sweets as possible, which are an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria;
- ensure adequate fluid intake;
- Treat common diseases in a timely manner.
The formation of cracks in the tongue is not always accompanied by discomfort. But even so, they can be very dangerous.
Careful monitoring of the surface of the tongue will help identify serious pathological changes in the early stages of development and avoid complications.
In the next video we will be told about what other problems our language can “tell” us:
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags language
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Tongue cracks - causes - treatment
Let's look at the causes of cracks in the tongue. Why does my tongue crack? If the tongue is cracked and hurts, the reasons may be: 1. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract 2. Lack of vitamins, especially A. group B, PP 3. Blood diseases 4. Hormonal changes in the body. 5. Damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue from sharp edges of teeth and dentures. Dissimilar metals of prostheses.
All of the above factors are also causes of glossalgia. One of the symptoms of glossalgia is cracks in the tongue, which are accompanied by pain and a burning sensation. The following sign will help to accurately determine whether cracks are a manifestation of glossalgia: if the pain decreases while eating non-spicy food, then this is a symptom of glossalgia. With all other diseases of the oral cavity, pain increases during eating.
Often the cause of cracks in the tongue is dental prosthetics: crowns made of dissimilar metals can create electric microcurrents in the mouth, irritating the mucous membrane. Also, plastic or metal crowns can cause allergies and cracks will appear on the tongue. Such pathologies quickly disappear after the corresponding causes are eliminated.
Treatment of cracked tongue. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease. Sanitation of the oral cavity, change of dentures, and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. If the disease has developed due to nervousness, medications are prescribed to relieve anxiety and depression. Hypnosis and auto-training help well. In the treatment of glossalgia, drugs that normalize cerebral circulation, as well as improve blood circulation in oral tissues, are also used. For severe pain, painkillers are used. Very often, when treating cracks in the tongue, medicinal leeches are used - they are placed directly on the tongue. Vitamin complexes are prescribed, including vitamins A, B1, B2, B12, C, PP
Cracks in the tongue - treatment with folk remedies - how to cure a cracked tongue.
Folk treatment for cracked tongue with lard. If the cause of cracks in the tongue is glossalgia, and the pain when eating decreases, then a thin slice of unsalted lard placed on the tongue will help. For glossalgia, it is useful to chew carrots - the pain decreases, and cracks in the tongue heal faster.
Home treatment with oak bark. You can treat cracks in the tongue at home with a decoction of oak bark: 2 tbsp. spoons of crushed oak bark, pour 500 g of cold water, boil over low heat for 15-20 minutes, rinse the mouth 5-6 times a day. In the traditional treatment of cracks, a little honey is added to the bark decoction.
Traditional treatment of cracked tongue with sage. Sage disinfects the oral cavity well and tightens cracks in the tongue. If the tongue is cracked, you need 1 tbsp. l. pour 1 cup of boiling water over sage leaves and leave for 2 hours - rinse your mouth with the infusion.
Treatment of cracks in the tongue - recipes and reviews from the newspaper “Vestnik ZOZH”
Cracks in the tongue - treatment with curd compresses. A compress helps heal cracks in the tongue: mix cottage cheese with sour cream, wrap in gauze and place on the tongue. The compress can be left overnight. Compresses with sea buckthorn oil also help well. (HLS 2001, No. 20, p. 18,).
How to cure cracked tongue with water. 20 years ago, a woman constantly had a burning sensation in her tongue and palate; doctors could not make an accurate diagnosis; no treatment helped. One day she met a doctor from Armenia and told about her illness. The doctor asked how much water the patient drinks, it turned out that only two glasses a day, the rest was tea, compotes, coffee. The doctor said that the patient must drink 7-8 glasses of clean water a day. Do not have snacks between meals. Drink water 30 minutes before meals and 2 hours after meals. This remedy helped the woman get rid of glossalgia quite quickly, but she still drinks 6 glasses of water every day. (HLS 2010, No. 17, p. 30).
Read also: Language education
Traditional treatment for cracked tongue with garlic. For many years, the woman suffered day and night from an unbearable burning sensation of her tongue. She went to doctors, but they could not help her. Glossalgia was cured with garlic. She finely chopped a clove of garlic, placed it on her tongue, rolled the mass with her tongue to avoid burns, and bit lightly. I kept the garlic in my mouth for about 10 minutes. This should be done 2-3 times a day after meals. Then you need to put a gauze soaked in sea buckthorn oil on your tongue. Garlic kills all germs, and sea buckthorn oil heals all cracks in the tongue. (review from Healthy Lifestyle 2009, No. 18, p. 30).
If your tongue is cracking, use tea tree oil. The woman had a sore mouth for more than a year. First the tongue turned red, then the palate, the disease either subsided or reappeared. The tongue was covered with deep cracks. The woman could not eat spicy food and could no longer feel its taste. She was in the hospital. I lost 14 kg. At home I decided to treat myself. Several times a day I rinsed my mouth alternately with infusions of sage and celandine, but this only helped for a while. She was advised to treat glossalgia with tea tree oil. During the day she rinsed her mouth with an infusion of herbs, and in the evening she lubricated her tongue with tea tree oil. It stings a lot, the mucous membranes go numb, but it’s bearable. This treatment helped, but not immediately, but after 2 months. (HLS 2009, No. 23, p. 30).
What is glossalgia - Causes of glossalgia.
Glossalgia is translated from Greek simply as pain in the tongue. With this disease, capillary blood circulation in the mucous membrane of the tongue is disrupted, and blood stagnation occurs. The causes of this disease are different. Among patients with glossalgia, 75% have pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. But for the disease to begin, this pathology alone is not enough. Blood circulation is regulated by the nervous system, and if there is a problem in the functioning of the nervous system, especially the hypothalamus, glossalgia can develop. But this requires a push, stress, mental trauma. Often the cause of the disease is carcinogenic phobia - fear of cancer. If a person convinces himself that a wound on the tongue is cancer, then glossalgia will be very difficult to cure. Often the trigger was a carelessly spoken word, or the following situation: a friend died of cancer, and the patient once drank from the same mug with him. That is, glossalgia develops on a nervous basis. Such patients need psychotherapeutic help.
Symptoms of glossalgia
1, Burning, tingling, raw tongue. 2, Tongue fatigue after speaking. 3. When moving the tongue - discomfort, pain 4. Reduction of pain while eating 5. Swelling, atrophy or hypertrophy of the papillae of the tongue 6. Dry mouth 7. Cracks 8. The disease either subsides or appears again for no apparent reason
What is glossitis?
Glossitis is a disease associated with inflammation of the tongue caused by a viral, bacterial or fungal infection. The difference from glossalgia is that with glossitis, an inflammatory process occurs in the tissues of the tongue. The cause of glossitis is an infection; the cause of glossalgia is not clear and often lies in the head (occurs on a nervous basis).
Causes of glossitis
The cause of glossitis is weak immunity, when, when the tongue is injured, an infection enters the wound and inflammation begins. The cause of inflammation can be viruses and microorganisms, such as streptococci, staphylococci, fungi. Tongue injury can be caused by a burn to the oral cavity with hot food, dentures, sharp fragments of teeth, prolonged peeling of seeds, chemical additives in food or toothpaste. Glossitis is often a symptom of diseases such as anemia, erythema, lichen and syphilis.
Symptoms of glossitis
1. The tongue increases in size and swells 2. Salivation increases 3. Pain in the tongue occurs when eating and speaking 4. The sense of taste is lost 5. The color of the tongue becomes bright red with a viral infection, with a fungal infection it becomes covered with a white coating 6. With viral infection, blisters may appear on the tongue, after opening which painful erosions form 7. Signs of intoxication - fever, swelling of the lymph nodes, weakness 8. Sometimes cracks occur
Glossitis of the tongue - treatment with folk remedies - how to treat glossitis.
Glossitis of the tongue - treatment by rinsing. Folk remedies for treating glossitis use rinsing the mouth with an infusion of chamomile flowers (1 tablespoon per 1 glass of boiling water - leave for 1 hour). Rinse after each meal and at night. Chamomile relieves inflammation and pain. For rinsing with glossitis, you can also use a decoction of oak bark, an infusion of St. John's wort, celandine, sage or galangal rhizomes. All these infusions are good for treating ulcers and cracks. Often a solution of furatsilin, potassium permanganate, and baking soda is used in rinses.
Traditional treatment for glossitis with potatoes at home. Potato juice can help against inflammation and pain. Grate the potatoes and squeeze out the juice, wrap the potato mixture in gauze, and make a compress on the tongue. Rinse your mouth with the squeezed juice. After rinsing or compressing, do not eat or drink anything for 30 minutes.
Horseradish in folk remedies for treating glossitis. Take 50 ml of horseradish juice and 150 ml of water. If it is difficult to squeeze out the juice, then simply steep the grated horseradish in cold water. Rinse your mouth; if it stings too much, you can dilute it with water.
Glossitis is a traditional treatment with oil applications. Rosehip oil or peach oil is recommended to be used as applications - this will speed up the healing process and reduce pain. Apply oil to the painful area. Repeat the procedure several times a day. You can apply sea buckthorn oil. To do this, apply oil to a cotton swab, apply it to the crack, hold for several minutes
Traditional treatment for glossitis with propolis or honey. For glossitis, it is useful to chew or hold a piece of propolis in your mouth. Honey is also useful - you need to lubricate the cracks with honey or apply a swab with honey.
Treatment of glossitis at home - recipes "Bulletin of Healthy Lifestyle"
Treatment of glossitis with peroxide. The woman felt a burning sensation in her tongue, but did not attach any importance to it and decided that she had been burned by the tea. The next day the pain intensified, then she examined her tongue and found that from the larynx to the middle it was covered with a white coating, so dense that it was impossible to scrape it off, and from the middle to the tip it was purple-scarlet and swollen. She called a doctor she knew, described the symptom, and the doctor confirmed that it was glossitis. The woman made a cotton swab, dipped it in hydrogen peroxide and began to vigorously wipe her tongue. The burning intensified to such an extent that tears appeared. An hour later, she diluted peroxide in warm water (1 teaspoon per 1 glass of water), took the solution into her mouth, and kept it in her mouth for a long time. After another hour, I soaked cotton swabs in peroxide and covered my tongue with them, holding it for 10 minutes. In the morning, the woman discovered that there was no trace left of the plaque and swelling, only a burning sensation remained. To consolidate the effect, she repeated all the procedures. On the third day, all symptoms of glossitis completely disappeared. (HLS 2007, No. 9, p. 10)