Vaginal itching is usually the result of exposure to irritants and infections. Both girls and women can suffer from this problem. Itching in the intimate area can also be a symptom of certain skin conditions or sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
Sometimes the problem can develop due to stress or vulvar cancer. This condition can be uncomfortable and sometimes painful.
Causes
Urethritis
This is a condition where the urethra, which carries urine from the bladder to the outside, becomes inflamed and irritated.
Urethritis can affect people of all ages regardless of race or gender. Therefore, both women and men are equally at risk of inflammation.
General symptoms
- Discomfort during urination
- Burning or irritation when opening the urethra
- More frequent urge to urinate
- Abnormal vaginal discharge (typical of infection)
- Itching or burning near the opening of the penis
- Presence of blood in semen after ejaculation (in men) or urine during urination
- Discharge from the vagina in women or the penis in men.
What causes urethritis?
Urethritis is caused by bacterial or viral infections. Bacteria that can cause bladder and kidney infections can also infect the lining of the urethra.
Bacteria found naturally in the genital area can also cause urethritis if they enter the urinary tract. These bacteria include:
- Gonococcus (Neisseria gonorrhoeae)
- Chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis)
- Mycoplasma genitalium.
These pathogenic microorganisms are the primary biological agents that cause disease. These include bacteria that cause gonorrhea and chlamydia, and parasites that cause trichomoniasis.
The same microorganisms that cause STIs can also cause urethritis. These viruses include human papillomavirus (HPV), herpes simplex virus (HSV), and cytomegalovirus (CMV).
Urethritis is not the same as urinary tract infections (UTIs). While it is an inflammation of the urethra, UTIs are infections that affect the urinary tract, i.e. are located deeper.
Yeast infections
Fungi are usually found on the skin, but can also live in the vagina and, under certain conditions, lead to infection. These conditions include the following set of factors (many of which are considered risk factors):
- Oily skin
- Sometimes the use of oil-based products can affect the growth of candida
- Using birth control pills
- Stay in tropical warm temperatures
- Hormonal changes
- Stress
- Diabetes.
The main fungus that causes this infection is the genus Candida (Candida sp).
If left undiagnosed, a vaginal yeast infection can become a problem that interferes with quality of life and lead to uncomfortable symptoms, including itching, burning and a curdled discharge.
According to research, it is a common condition, affecting 3 out of 4 women. Infection often occurs after taking a course of antibiotics because they destroy the good bacteria that the body needs along with strains of “bad bacteria.”
Skin diseases
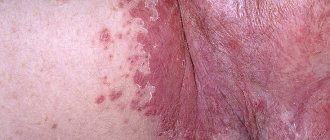
Most skin conditions, such as eczema and psoriasis, can cause redness and itching in the genital area. Eczema (atopic dermatitis) is a chronic skin condition characterized by a rash.
Eczema tends to occur in people with asthma or allergies. The rash is usually reddish in color with an itchy, scaly texture.
Psoriasis is another common skin condition that causes scaly, itchy red patches to form on the scalp and joints. Sometimes these symptoms can occur in the genitals, including the vagina.
Vaginal irritation or reaction to substances
The most common form of irritation occurs as a result of direct contact of chemicals with the skin of the genitals, resulting in vaginal itching.
Allergies to ingredients found in various foods can occur because it is unknown how the body's systems will react to certain substances.
The irritants cause an allergic reaction, which is accompanied by an itchy rash on various parts of the body, including the intimate area. Common chemical irritants include: bubble baths, feminine sprays, creams and ointments. Additionally, detergents, fabric products, and scented toilet paper may also fall into this category.
Vaginitis
This term is used to refer to swelling or infection of the vagina and vulva.
Women of all ages are susceptible to this problem. If you have a yeast infection, your risk of vaginitis increases, as candida is the most common cause.
Other potential causes include:
- Prickly heat
- Problem with a vaginal product such as a tampon.
Girls who have not reached puberty are also at risk.
Symptoms
- Inflammation, redness and swelling of the genitals
- Discharge with odor
- Irritation and itching
- Burning during urination.
For proper treatment, a clinical examination is required.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Most STIs that are transmitted during unprotected sex are characterized by rashes accompanied by itching.
These include:
- Chlamydia
- Genital warts
- Gonorrhea
- Genital herpes
- Trichomoniasis.
Common symptoms that may occur along with itching in the intimate area include abnormal growths, green or yellow vaginal discharge, discomfort or pain when urinating.
Enterobiasis
Enterobiasis refers to an infection in which tiny white worms less than 1.5 cm in size (pinworms) infect the intestines and lay eggs around the anus. The condition is highly contagious.
The infection is common among children aged 5 to 10 years and people who have regular, close contact with them.
How can you become infected with pinworms?
Infestations are caused by unintentionally consuming (or inhaling) helminth eggs.
The infection begins the moment the eggs enter the body of a healthy person. They remain in the intestines until they hatch and mature. Adult females move into the large intestine and exit through the anus.
Pinworms lay eggs in the folds of skin around the anus, which often causes itching in the area. When scratching the affected area, eggs can be transmitted using fingers and nails to the vagina. Also, females can sometimes crawl onto the intimate area, causing itching with their mucus.
Children most often carry these eggs because they like to play with toys or other objects.
Risk factors
- Children attending nursery, kindergarten or primary school
- Family members or guardians of infected children and adults
- Persons who live in dormitories or other overcrowded accommodations
- Children or adults who do not wash their hands regularly and thoroughly before eating
- Children who have a habit of putting their fingers in their mouth.
Symptoms
- Frequent and severe itching of the anal area
- Restless sleep due to itching and discomfort in the anus
- Pain, rash, or other skin irritation around the anus
- The presence of pinworms in the area of the child’s intestinal opening
- The presence of helminths in the stool.
Menopause
Vaginal itching caused by menopause is due to a decrease in estrogen levels, which leads to atrophy (changes in tissue) of the vagina.
According to the American Academy of Family Physicians, the vaginal epithelium, or mucosa, typically undergoes changes in response to circulating estrogen levels throughout the cycle.
One of the expected changes is the thinning of the mucous membrane, which can lead to excessive dryness, which can potentially cause itching and irritation.
Vulvar cancer
Vulvar cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the outer part of the female genitalia (labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and vaginal opening).
It is not easy to determine the progression of the disease, but regular symptoms such as itching, abnormal bleeding or pain in the vulva may indicate this. Although they do not always mean the presence of cancer.
Stress
Stress, as seen in people with emotional instability, can trigger itching. This is due to the fact that it can affect some vital processes of the body, which can lead to problems with the skin, blood, etc.
Notably, both physical and emotional stress can cause vaginal itching and irritation. Stress is often associated with a weakened immune system, making a person more susceptible to infections.
Although stress can be difficult to control, it is possible through some means, including therapy, exercise, and medication.
Why might women have itchy skin in their intimate areas?
There are many reasons for this phenomenon, but they can all be divided into two groups. The first includes those that are not associated with diseases. These include:
- Lack of hygiene.
- Reaction of the skin and mucous membranes to the material of underwear.
- Allergy to pads and tampons.
- The predominance of spicy and savory dishes in the diet.
- Hormonal disorders caused by taking certain medications, pregnancy.
- Itching in an intimate place after antibiotics (they kill beneficial microflora, which is immediately used by pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms).
- Too rough sex.
- Hygiene products that are not suitable for the skin (soap, shower gel).
- Frequent stress.
If the causes of itching in intimate places in women are exactly the same, treatment with medications is not required.
How can you tell if your genitals are itching not because of an illness? To do this, a woman must follow some steps:
- Start washing yourself not occasionally, but every day. It is advisable to use intimate hygiene products for this. If they are not available, you can replace them with baby soap. It does not contain chemical ingredients such as dyes, flavors, fragrances. All that manufacturers put there is chamomile or string extracts. In cases of increased skin sensitivity, you can wash yourself without soap at all, using only a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate or chamomile decoction. In medical practice, there are cases where women have an allergy to chlorinated water with itching of the genitals.
- Change washing powder.
- Replace underwear, for example, synthetics with cotton, thongs with classic briefs.
- Start using a different brand of pads and tampons.
You can also reconsider your diet, daily routine, and priorities in intimacy.
If the cause of itching is hormonal imbalances, it is still worth visiting a gynecologist. The doctor will select corrective agents that will improve the woman’s general condition and relieve the unpleasant symptom. If you treat itching only with “grandmother’s” methods, you can only achieve short-term improvement by driving the problem inside.
If all these methods do not help, there is a high probability that the cause of the itching in the intimate area is a disease. In such a situation, consulting a doctor is necessary at least to find out what kind of illness is causing the annoying symptom. Without this, treatment is impossible.
In men, itching in the intimate area can occur for the same reasons, with the exception of pregnancy and pads.
Treatment
Treatment may be aimed at relieving symptoms or treating the cause (infection).
- Vaginal yeast infections are usually treated with antifungal medications, including ointments, suppositories, or oral medications.
- STDs can be treated with antibiotics or antiviral medications. Patients are advised to take medications regularly and avoid sexual intercourse until the infection clears up.
- If itching in the intimate area is associated with menopause, you should first contact a gynecologist or endocrinologist. The problem can be treated with estrogen cream, pills or a vaginal ring.
- Other types of vaginal itching and irritation usually go away on their own.
- Steroid creams or lotions may also be used to reduce inflammation and discomfort and to help prevent other infections.
More importantly, you should consult your doctor before starting any treatment. The duration of symptoms and the age of the patients must be taken into account.
Why does unpleasant itching occur?
The vaginal mucosa is populated by various bacteria that ensure the normal functioning of the genital organs, protection against infections and prevent inflammation. The ratio of “beneficial” and “harmful” microflora is normally maintained at a certain level, which depends on the age and physiological state of the woman. When the correct balance is disturbed, normal processes in the mucous membrane are disrupted, and various infections begin to develop. They make themselves known by the appearance of itching, burning or other discomfort in the intimate area. For example, fungal flora may be activated, causing thrush, which makes the external genitals itch.
Important! A woman should regard any deviations from the normal state of health as a signal of possible problems in the body. It’s better to play it safe and visit a gynecologist one more time than to develop an infection and undergo an expensive and lengthy course of treatment.
As a rule, the symptoms of various infections are similar. Most often, itching appears, which may indicate various pathological processes. In addition to itching, a woman may complain of:
- Burning.
- Changes in the nature and abundance of discharge.
- Feeling of discomfort.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Dryness.
- Redness.
- The appearance of rashes.
Home Remedies
Sea salt bath
- Cold compress
- Rinse with diluted apple cider vinegar
- Garlic
- Bath with salt.
However, if your doctor has diagnosed certain infections or skin conditions that cause itching, you should only follow the doctor's recommendations.
WARNING: Some ingredients can sometimes worsen itching, causing further irritation. For example, garlic.
Symptoms of irritation
The following manifestations are possible:
- feeling of severe itching and burning in the genital area,
- pain and burning when urinating,
- discharge with different smell, consistency, coloring,
- rashes on the mucous membrane, in the pubic area, labia,
- vaginal dryness, foreign body sensation,
- pain in the perineum, lower abdomen.
Effective care tips
If the itching is caused by irritants or you suspect that the problem is caused by skin products (such as perfumes, antiperspirants, deodorants, or certain cleansing products), you can try the following:
- Washing the body with plain water without any soap
- If a person is used to hot water baths, you can try using warm or cold water
- Rinse your hair with shampoo after or before showering to avoid getting it on your skin.
- Stop rubbing your labia and surrounding areas after going to the toilet
- Wear breathable, non-synthetic underwear and clothing, especially during pregnancy.
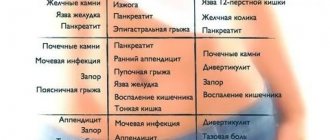
Causes of itching in female intimate areas
To eliminate the source of the unpleasant phenomenon, let’s figure out what causes it. Irritation of intimate areas can be caused by:
- Candidiasis (thrush) - a disease provoked by the yeast-like fungi Candida albicans due to changed pH conditions in the vagina. The disease is not contagious, often goes away during menstruation on its own, or when the microflora of the intimate areas normalizes.
- Trichomoniasis is caused by the protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, transmitted during sexual intercourse through household contact. This infectious sexually transmitted disease is curable.
- Gonorrheal vaginitis - the disease is provoked by gonococci and is sexually transmitted.
- Chlamydia is a pathology caused by intracellular bacteria chlamydia (Chlamydiae), transmitted through sexual contact.
- Herpes, caused by a virus of the same name, one of the types that lives in the human body.
- Treponema pallidum is a bacterium called Treponema pallidu, which causes the sexually transmitted disease syphilis.
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Koch bacillus, Mycobacteriaceae), which is the source of tuberculous vaginitis.
- Mycoplasma is a microorganism transmitted both sexually and domestically (much less frequently).
- Ureaplasma - the bacteria Ureaplasma urealyticum, which causes colpitis, is classified as a venereal disease.
- Helminthic infestations - pinworms, crawling from the rectum to the vagina and living there, are often found in small girls.
- Psychological factors (nervous itching) - prolonged stress, depression, increased nervous tension, diseases of the nervous system and other ailments.
- Hormonal changes in the body during the period of the first regula, pregnancy, menopause, due to the use of hormonal drugs, diseases of the endocrine system, operations, and other reasons of this kind.
- Chronic inflammation of the appendages, diseases of the genital organs, changing the local pH of the vagina and the entire intimate area.
- Deramatological ailments, increased sensitivity of mucous membranes due to taking medications.
- Allergic reactions to synthetic underwear, pads, personal hygiene products, and male sperm (rare, but it does happen).
- Diabetes mellitus, disorders of the kidneys, liver, bladder, blood pathologies.
- Insufficient or excessive hygiene of the genital organs, as a result of which the natural acid-base balance and microflora of the environment are disrupted.
A huge number of causes of itching require different symptoms and treatment measures. To get rid of the pathology, treatment is carried out for a disease that causes itching and burning in the female intimate area. For diagnosis and help in treatment, they turn to doctors: a gynecologist, an infectious disease specialist, a venereologist, a dermatologist, a therapist and other specialists.
Prevention Tips
To prevent vaginal itching you can:
- Maintain good hygiene
- Use warm water and a gentle cleanser to wash the intimate area
- Avoid scented soaps, lotions and bubble baths
- Avoid using feminine hygiene products such as sprays
- Change wet clothes immediately after swimming or exercising
- Wear cotton underwear and change it every day
- Eat yogurt with live cultures to reduce the chance of fungal contamination
- Use condoms during sexual intercourse
- After visiting the toilet, wipe the genital area strictly from front to back.
Itching and burning in the intimate area in women - how to treat and how to get rid of it
How to relieve symptoms of discomfort and itching at home:
- Keep your intimate area clean. Do water procedures at least three times a day. Ideally, after every urination.
- Carry out a careful selection of genital care products. Do an analysis of the sensations after using new remedies, because it is quite possible that it was this that provoked the bad sensations.
- Wear only good underwear. Preferably made of cotton. It should be comfortable and not interfere with movement.
- Make baths using medicinal herbs.
- Using antiseptics, such as chlorhexidine, using a syringe or a regular baby bulb, rinse the vagina.
- Use skin soothing products after shaving. If you don’t have them on hand, you can take regular talc.
- Review your diet. Fermented milk products will help populate the microflora with beneficial bacteria. Spicy foods and alcohol should not be present in your diet.
- To protect yourself from even more irritation and itching, you need to abstain from sexual intercourse temporarily.
- To relieve itching, you can use potassium permanganate. Mix a teaspoon of potassium permanganate in 5 liters of water and pour the prepared solution into the bath. Sit in this water for about 15 minutes.
- You can use laundry soap. This product has a high pH level, which will help kill fungi in an acidic environment. You need to wash yourself with it, or do vaginal douching. To do this, cut or grate soap is dissolved in boiled water, no higher than room temperature. It is preferable to take natural soap, without any fragrance additives. After the procedure, lie in a horizontal position for about 15 minutes, and then wash with non-hard water. As soon as the foam stops flowing, the procedure can be considered complete.
All these tips will only bring temporary results. Be sure to visit your doctor for regular checkups and seek timely help. Also, strengthen your immune system. Don't neglect this.
And, be healthy!
Treatment at home
In addition to the treatment prescribed by the doctor, traditional medicine is used as an auxiliary therapy. Itching caused by sexually transmitted pathogens is treated with medications. Relieve symptoms of irritation in the labia area by washing and irrigating with herbal preparations.
Vaginal irrigation (douching) for thrush, burning and itching due to hormonal imbalance, allergies:
- Prepare a solution for douching by taking a tablespoon of table salt and baking soda (without a slide). The components are dissolved in a liter of hot boiled water. They wait until the water cools down to body temperature and carry out the procedure using an Esmarch mug or a rubber bulb with a volume of 200-300 ml. After irrigation, you need to lie down for 20 minutes.
- Chamomile decoction: brew 10 grams of chamomile flowers in a thermos in 400 ml of boiling water. Wait half an hour, filter the composition, and use it for irrigation at a temperature of 34°-36°C. The decoction is also used to wash intimate areas.
- Oak bark decoction: 20 grams of oak bark are boiled for 15 minutes in 500 ml of boiling water. Leave for an hour, filter, and use as directed.
- Mix 10 grams of marigold flowers, sage grass, and birch buds. Brew in 600 ml of boiling water in a thermos for an hour. The cooled, strained composition is used for douching and washing the external intimate areas. Normalizes vaginal microflora. Used for treatment using a composition for washing in case of itching during pregnancy in an intimate place.
- From marigolds - brew two tablespoons of marigold flowers in two glasses of boiling water for 20 minutes. Used for irrigation of intimate female areas.
- Prepare a composition for douching from the herb St. John's wort, as in “From marigolds”. Used for washing the vagina and external genital areas.
- For thrush: apply for a week of irrigation with strained whey twice a day, douching with apple cider vinegar (40 ml of 7% vinegar per liter of water).
If itching is a consequence of inflammation of the appendages, salpingoophoritis, endometritis:
- Herbal mixture with eucalyptus: mix the ingredients in a ratio of 3:2:2:3:2 - nettle leaves, crushed bergenia roots, birch leaves, crushed calamus roots. Using a water bath, prepare a tablespoon of the mixture in a quarter liter of boiling water for 35 minutes. Drink chilled, strained tea, without sweetening, a quarter glass before meals four times a day for 2 weeks.
Contraindications: do not use if you have low blood pressure, tachycardia, allergies, a tendency to constipation and increased blood clotting.
- With an immunomodulatory effect: make a mixture by taking 10 grams of each component - crushed root of Leuzea safflower, small-fruited maklea herb, herbal part of hairy tenacity, calendula flowers. Two tablespoons of the mixture are infused for 2 hours in a thermos in 400 ml of boiling water. The strained warm mixture is consumed 50 ml between meals four to five times throughout the day. Last dose no later than three hours before bedtime.
Not recommended: in case of liver disease, kidney disease, epilepsy, increased nervous excitability, asthma, hyperkinesis, angina pectoris, pregnancy.
- With a bifidogenic effect: prepare a collection of equal parts - leaves of wintergreen round-leaved, poop grass, lemon balm leaves, burdock leaves, plantain, shepherd's purse grass. Two tablespoons of the mixture (tablespoons) are steamed for 20 minutes. The collection is infused for another hour. Strained tea is drunk half a glass between meals four times a day. Do not use for eczema.
- Strengthening the immune system: infuse a tablespoon of chopped walnut leaf in a glass of boiling water in a thermos for 40 minutes. Add 40 drops of 80% alcohol tincture of propolis to 50 ml of pure infusion. Take four times a day.
Do not use: for hypertension, thrombophlebitis, varicose veins, thrombocytosis, pregnancy and breastfeeding, do not give to children under 14 years of age.
Local baths have a calming effect on female intimate areas; gentle treatment with herbal compounds relieves swelling of the mucous membranes and itching:
- Composition with nettle and chamomile: boil 100 grams of the herbal part of nettle and 100 grams of calendula flowers for 5 minutes in 6 liters of boiling water. They insist for an hour. Filter the composition. Used for a sitz bath. Sit down so that the genitals are completely covered with the broth, ensuring that the broth penetrates into the vagina.
- With oak bark and pine needles: boil 100 grams of crushed oak bark and half a kilogram of chopped pine or spruce needles in 10 liters of water for 10 minutes. Leave for 2 hours, filter. Use warm for local baths.