Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Resorcinol is a phenol . The Pharmacopoeia defines it as 1,3- Dioxybenzene , formula Resorcinol C6H602.
Phenols form compounds with polysaccharides of the wall of microorganisms, disrupt its properties and have an antiseptic effect. They cause the death of vegetative forms and have no effect on spores.
The drug in small concentrations (0.25–2%) has an epithelializing effect and is prescribed as part of lotions to weeping lesions - it stimulates regenerative processes and eliminates inflammation. High concentrations (for example, 5–10% ointment) have a keratolytic and cauterizing effect, and 30–50% concentration of resorcinol has a pronounced cauterizing effect.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic studies have not been conducted.
What is pityriasis versicolor?
Tinea versicolor
(
pityriasis versicolor
, solar fungus, Latin tinea versicolor, pityriasis versicolor) is an infectious (fungal) skin disease, which is characterized by damage only to the stratum corneum of the epidermis, the absence of inflammatory phenomena and very low contagiousness (infectivity).
The disease, which is widespread, is more common in countries with high temperatures and humidity (tropics, subtropics), where the incidence rate of lichen versicolor reaches 40%. While in countries with a temperate climate (including Ukraine) the incidence rate reaches 5-10%. Both men and women are affected, but lichen versicolor is twice as common in women. The peak incidence is observed at a young age (18-25 years), however, both children and older people are affected.
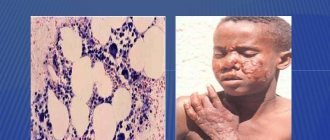
The causative agent of pityriasis versicolor belongs to yeast-like fungi of the genus Malassezia (former name Pityrosporum orbiculare). The most common pathogen in humans is Malassezia furfur. Most often, the fungus prefers the scalp, upper parts of the body and folds. Most people carry Malassezia fungi (90%) in areas of the skin that are rich in sebaceous glands and do not cause disease. These people, as well as people with clinical manifestations of pityriasis versicolor, are sources of infection for others. Transmission of the pathogen can occur through close contact with a patient or carrier, through sharing household items or underwear (bed linen), infection is possible through beach sand, sun loungers, bedding, towels, sponges, etc. Sun rays and salty sea water help its spread, as they dry out the skin, lead to the formation of microcracks and the penetration of microorganisms into the surface layers of the skin. In the development of the disease, increased sweating, the chemical composition of sweat, skin pH, and concomitant diseases (endocrine system disorders, gastrointestinal pathology, diseases of the pulmonary system and blood, immunodeficiency states) are of no small importance. There is evidence of a genetic predisposition to the development of pityriasis versicolor.
Instructions for Resorcinol (Method and dosage)
A solution of Resorcinol alcohol (in Latin Solutio Resorcini spirituosa) is applied externally to the affected areas of the skin using a cotton swab. The ointment is applied at night. The dosage regimen is individual and depends on the disease.
For red acne, use a 1% alcohol solution. For oily seborrhea , rub a 1–2% alcohol solution into the scalp. For the treatment of dermatitis and eczema, 1–2% solutions are used.
For vulgar acne, for the purpose of exfoliation - 10-15% ointment. For seborrheic eczema, this drug is used in combination with sulfur.
For local treatment of genital warts , a powder of a pure product is used as a chemical coagulant. The antiseptic properties determine the use of Resorcinol in medicine, as an independent remedy, but more often as part of other drugs. Thus, Resorcinol is included in rectal suppositories (in combination with zinc oxide, bismuth subnitrate and tannin ) and Fukortsin solution. It is part of Andriasyan ointment and Castellani liquid, which are used to treat mycoses and pyoderma .
To cleanse the skin, especially with signs of liquid seborrhea, water-alcohol talkers are used, which also contain salicylic and boric acids.
Lotions with a keratolytic effect are known, containing resorcinol, salicylic acid and allantoin . For hygiene of the scalp during dandruff and desquamation, Squafan S shampoo (France) has been developed, in which salicylic acid and resorcinol in high concentrations make it possible to remove persistent areas of desquamation.
Another use of resorcinol in medicine is resorcinol-formaldehyde paste, which is used by dentists to fill canals with incomplete pulp extirpation. The resorcinol-formalin treatment method was proposed in 1912 and was widely used in Soviet times - it turned out to be cheap.
Currently, it is rarely used and among professionals symbolizes poor quality treatment. The fact is that resorcinol-formalin paste is dangerous for the body due to toxicity. Cysts appear on the roots of the tooth, the gums atrophy, the tooth becomes fragile, and its color changes. Progressive dentists abandoned this treatment method more than 20 years ago.
Instructions for use of Resorcinol
According to the instructions, Resorcinol is used externally in the form of a 2% alcohol solution or 5-10% ointment. For acne, the drug is applied in a small amount at night with the addition of special resorcinol alcohol (alcohol is especially necessary for rosacea).
When Resorcinol is applied to uncleaned skin, it may become red or purple in color.
The drug has strong antiseptic properties, so its contact with mucous membranes, the digestive system and the respiratory tract is unacceptable. If Resorcinol gets into the eyes, it is necessary to rinse the mucous membranes with copious amounts of water, and in case of poisoning of the digestive organs, it is necessary to immediately perform a gastric lavage.
Resorcinol should not be used in combination with salicylic acid, magnesium oxide and sodium bicarbonate. The medicinal properties of the drug disappear when interacting with yellow mercury oxide, phenyl salicylate and antipyrine.
In accordance with the instructions, Resorcinol in the form of an ointment must be diluted in a solution of ethyl alcohol and water, and ethyl ether can also be added.
Reviews
Reviews mainly concern the use of Resorcinol for acne vulgaris: 10-15% ointment, drying the stratum corneum, acts as an exfoliant and helps get rid of acne. It is noted that for acne, a good result is given by talkers - powder of the main substance, chloramphenicol, boric and salicylic acid, and a composition containing only resorcinol is ineffective, in addition, it can cause irritation and dryness of the skin. Resorcinol alcohol is used to cauterize individual rashes.
This substance, in combination with sulfur and salicylic acid, helps to cope with open and closed comedones.
Chemical properties
Resorcinol has the properties of phenols. With alkalis it forms salts - phenolates, with dimethyl sulfate it gives resorcinol monomethyl ether and resorcinol dimethyl ether [3].
When reacting with ammonia, it forms 3-aminophenol.
The mutual influence of the two OH groups makes it easy for resorcinol to enter into electrophilic substitution reactions, mainly at position 4(6), and more difficult at position 2. Thus, when interacting with halogens, it forms 2,4,6-trihalogen-substituted.
When nitric acid acts on resorcinol, resazurin is formed [4], when interacting with concentrated nitric acid (d = 1.4 g/cm3) and concentrated sulfuric acid, 2,4,6-trinitroresorcinol is formed. With picric acid gives picrate, m.p. 89-90 °C.
Resorcinol easily enters into azo coupling reactions, for example, with diazotized sulfanilic acid it produces resorcinol yellow dye.
It condenses with phthalic anhydride in the presence of zinc chloride (175-196°C) to form fluorescein.
With glacial acetic acid in the presence of zinc chloride at 145 °C it forms acetophenones.
Restores feling liquid and ammonia solution of silver chloride.
Color reaction to resorcinol: upon interaction with FeCl3, a dark purple color appears, turning into black.
If stored improperly, resorcinol turns pinkish-orange due to easy oxidation.
How to diagnose lichen versicolor?
Only a specialist - a dermatologist - can make a correct diagnosis. What matters is clinical experience (the ability to suspect a disease during a visual examination and prescribe the necessary examination) and the use of diagnostic methods (samples, microscopic examination, etc.). To confirm the diagnosis (lichen versicolor), an iodine diagnostic test is performed - the Balser test
.
The affected skin is lubricated with alcohol tincture of iodine (or aniline dye) and immediately wiped with alcohol. If you really have lichen versicolor, the spots become dark brown in color and stand out sharply against the background of slightly yellowed healthy skin. This occurs due to the fact that the surface layer of skin loosened by the fungus quickly absorbs iodine. We do not recommend performing this test yourself, since without the appropriate experience you cannot adequately interpret the result. In addition, if you scrape the stains with your fingernail, the loosened horny masses are removed in the form of shavings - a symptom of “shavings”
.
In cases where the doctor has doubts about the diagnosis, a microscopic examination of skin flakes
to detect the pathogen, as well as a bacteriological examination using
Sabouraud's medium
to cultivate (grow in special conditions) colonies of the pathogen, followed by microscopic examination.
To diagnose pityriasis versicolor, especially localized on the scalp, you can use the luminescent method
: in the rays
of a Wood's lamp,
the spots acquire a golden-yellow, reddish-brown or brown glow.
Electron microscopic examination
of the skin in the area of spots with disturbed pigmentation usually reveals a decrease in the number and disturbance in the location of melanosomes (pigment cells).
What signs indicate the presence of pityriasis versicolor?
From the moment of infection to the appearance of the first clinical manifestations, it can take from two weeks to several months or even years. The duration of this period depends on the state of the immune system and a number of factors that have already been discussed above.
The disease begins with the appearance of a small (3-5 mm) pink spot that does not rise above the surface of the skin. The first spot may appear on the skin of the chest, upper back, neck, and shoulders. Often the manifestation of the disease is found on the scalp, especially in children. Hair, however, is not affected by this disease. Over time, the spots become more numerous, they quickly spread over the listed areas of the skin, begin to merge into bizarre patterns, or remain isolated from each other. Inflammatory phenomena and subjective sensations (itching, pain) are absent; peeling similar to bran may be observed. The color of the spots may vary: light pink, yellow, coffee, light brown. Against the background of tanned skin, areas affected by lichen usually stand out sharply in a lighter color compared to the rest of the skin. Lichen versicolor has a chronic course and is characterized by frequent relapses; the disease can manifest itself for years. Impaired skin pigmentation not only causes a cosmetic defect, but can also often lead to a psycho-emotional breakdown, impaired social adaptation, and a decrease in quality of life.