Tyrosol is a drug that is used in the treatment of thyrotoxicosis due to its property of inhibiting the production of thyroid hormones.
The effects of thiamazole in the thyroid gland are characterized by a decrease in basal metabolism, acceleration of the excretion of iodides, as well as an increase in the reciprocal activation of the synthesis and secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone by the pituitary gland, which may be accompanied by the development of thyroid hyperplasia.
A single dose of thiamazole continues to act for almost 24 hours.
pharmachologic effect
The effect of the active component Tyrosol on the thyroid gland inhibits the production of hormones by blocking enzymes, in particular peroxidase, which is involved in the iodination of tyrosine. Taking the drug accelerates the removal of iodides from the thyroid gland and reduces basal metabolism.
In parallel, the use of Tyrosol increases the activation of the synthesis and secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone by the pituitary gland. This can sometimes be accompanied by a slight increase in the volume of the thyroid gland. The drug is very effective in the symptomatic treatment of thyrotoxicosis. A single dose of Tyrosol guarantees its effect for at least 24 hours.
Patient reviews
I became very ill with ARVI, and, unfortunately, it turned into complications on the thyroid gland. I developed a fever and severe neck pain. I went to the endocrinologist, and he prescribed me Tyrosol along with Dexamethasone. Tyrosol is a very serious and powerful remedy that really helps. It is strictly not recommended to take it on your own. The slightest mistake with the dosage will cause problems and side effects, but this is perhaps its only drawback. I recommend.
infection2008
I'll tell you the story of my illness. About a year ago I gave birth, and six months later I started having strange pain in my throat, it became very difficult to turn my neck, and my neck itself seemed to get bigger. An incomprehensible increase in temperature appeared for no reason at all!
My initial thoughts were of a cold, but there were no other symptoms and after a few days I saw a GP.
He referred me to an endocrinologist, and I passed the necessary tests. Eventually I was diagnosed with thyrotoxicosis. I was prescribed the medicine Tyrozol and after a course of treatment I felt much better. After that, I was switched to other, gentler medications. There were no side effects. I recommend the drug. AlisonRose
Indications for use
According to the instructions, Tyrozol is used:
- with thyrotoxicosis;
- in preparation for radioactive iodine therapy;
- in preparation for surgery for thyrotoxicosis;
- for the purpose of preventing thyrotoxicosis when taking iodine-containing drugs for latent thyrotoxicosis, a history of thyrotoxicosis, autonomous adenomas;
- as a treatment during the latent period of radioactive iodine;
- as long-term maintenance therapy for thyrotoxicosis, when, due to the general condition of the patient or for other reasons, radical treatment cannot be performed.
Drug interactions
According to the instructions, increased effects of the drug Tyrozol may occur:
- When used simultaneously with gentamicin, with lithium drugs, with amiodarone, with beta-blockers, with reserpine.
- With insufficient amount of iodine.
With the therapy, the risk of leukopenia:
- Decreases if the drug is taken together with folic acid.
- It increases if you take this drug simultaneously with metamizole sodium and sulfonamides.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- glucose-galactose malabsorption, galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency;
- hypersensitivity to thiourea derivatives and any ingredients of the drug;
- granulocytopenia (including history);
- development of agranulocytosis during previous therapy with thiamazole or carbimazole;
- therapy with thiamazole and levothyroxine during pregnancy;
- age up to 3 years.
Tyrosol is used with caution in the following cases:
- severe increase in goiter, leading to narrowing of the trachea (the drug is used only for short-term treatment in the preoperative period);
- liver failure.
Contraindications for use
The drug has many contraindications and limitations. If you have and are experiencing similar problems, then the use of Tyrozol is strictly contraindicated.
Hypersensitivity to the active ingredients and substances of the drug, as well as allergic reactions to them.- Agranulocytosis is a pathological disease that entails a significant decrease in the level of leukocytes. If you have such a disease, use of the drug is prohibited.
- If the child is less than three years old, then the use of Tyrozol is contraindicated for him.
- Cholestasis is a pathological process in which the formation, secretion and flow of bile into the duodenum is disrupted. During this process, the use of Tyrosol is prohibited.
- If there is a problem such as granulocytopenia - a decrease in the content of granulocytes in the blood, the medicine is not used.
- In addition, the medicine cannot be used if the patient has lactase deficiency - too little lactose.
If you have at least one of the above problems, then the use of Tyrozol is strictly contraindicated.
Prescription during pregnancy and lactation
Untreated hyperthyroidism during pregnancy can cause serious complications, including fetal malformations and premature birth. In turn, hypothyroidism, formed as a result of the administration of inadequate doses of Tyrozol, can lead to miscarriage.
A characteristic feature of thiamazole is its penetration through the placental barrier, after which a drug concentration similar to that of the mother is observed in the fetal blood. For this reason, the prescription of Tyrosol during pregnancy can be justified only in extreme cases, after a full assessment of the benefits/risks of its use for the mother/fetus, in minimal effective daily dosages (up to 10 mg) and without parallel use of levothyroxine sodium.
Taking high doses of thiamazole by a pregnant woman can lead to the formation of hypothyroidism and goiter in the fetus, as well as to a decrease in the child’s body weight at birth.
During breastfeeding, therapy for thyrotoxicosis in the mother can be continued in minimal dosages, since the concentration of thiamazole in breast milk corresponds to its content in the mother’s blood and can cause the development of hypothyroidism in the newborn. Taking Tyrosol by nursing women requires monitoring the functionality of the thyroid gland in newborns.
Overdose
In the case of prolonged use of thiamazole in high dosages, the formation of clinical and subclinical hypothyroidism , as well as the growth of the thyroid gland due to an increase in TSH levels, is possible. These negative effects can be avoided by additionally prescribing the patient levothyroxine sodium or reducing the dose of thiamazole until the thyroid gland reaches a state of euthyroidism . thiamazole therapy is discontinued, there is an independent restoration of normal thyroid function.
When taking ultra-high doses of thiamazole of myelotoxic phenomena may be observed . Therefore, taking the drug in such doses is allowed only if there are special indications ( thyrotoxic crisis , very severe course of the disease).
As a treatment for overdose conditions with thiamazole, discontinuation of ongoing treatment with its use, cleansing of the gastrointestinal tract and further relief of negative symptoms with the help of adequate medications are indicated. If necessary, transfer the patient to take an antithyroid drug from another group.
Dosage and method of administration
As indicated in the instructions for use, Tyrozol is taken orally after meals. The tablets should be taken without chewing, with a sufficient amount of liquid.
The daily dose is prescribed in 1 dose or divided into 2-3 single doses. At the beginning of treatment, single doses are taken throughout the day at strictly defined times. The maintenance dose should be taken in one dose after breakfast.
- For thyrotoxicosis, depending on the severity of the disease, the drug is prescribed at a dose of 20-40 mg/day for 3-6 weeks. After normalization of thyroid function (usually after 3-8 weeks), they switch to a maintenance dose of 5-20 mg/day. From this time on, additional intake of levothyroxine sodium is recommended.
- In preparation for surgical treatment of thyrotoxicosis, 20-40 mg/day is prescribed until a euthyroid state is achieved. From this time on, additional intake of levothyroxine sodium is recommended. In order to reduce the time required to prepare for surgery, beta-blockers and iodine preparations are additionally prescribed.
- In preparation for treatment with radioactive iodine, 20-40 mg/day is prescribed until a euthyroid state is achieved.
- When treating during the latent period of radioactive iodine action, depending on the severity of the disease, 5-20 mg/day is prescribed until the onset of radioactive iodine action (4-6 months).
- For long-term thyreostatic maintenance therapy, Tyrozol is prescribed in doses of 1.25-2.5-10 mg/day with additional levothyroxine sodium in small doses. When treating thyrotoxicosis, the duration of therapy is from 1.5 to 2 years.
- In order to prevent thyrotoxicosis when prescribing iodine preparations (including cases of use of iodine-containing radiocontrast agents) in the presence of latent thyrotoxicosis, autonomous adenomas or a history of thyrotoxicosis, Tyrozol is prescribed at a dose of 10-20 mg/day and potassium perchlorate 1 g/day for 8-10 days before taking iodine-containing products.
For children aged 3 to 17 years, Tyrozol is prescribed at an initial dose of 0.3-0.5 mg/kg body weight in 2-3 equal divided doses daily. The maximum recommended dose for children weighing more than 80 kg is 40 mg/day. Maintenance dose – 0.2-0.3 mg/kg/day. If necessary, sodium levothyroxine is additionally prescribed.
Not recommended for use in children aged 0 to 3 years.
During pregnancy, the drug is prescribed in minimal doses: single - 2.5 mg, daily - 10 mg.
In case of liver failure, the drug is prescribed in the minimum effective dose under close medical supervision.
When preparing patients with thyrotoxicosis for surgery, treatment with the drug is carried out until a euthyroid state is achieved within 3-4 weeks before the planned day of surgery (in some cases longer) and ends the day before it.
Tyrosol: instructions for use, side effects, analogues, price
The drug Tyrozol is a film-coated tablet containing 10 mg or 5 mg of thiamazole.
The active ingredient is used to treat thyroid diseases, but is not suitable for all forms of pathology.
The composition of the drug is supplemented with minor components: colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, sodium carboxymethyl starch, corn starch, cellulose, lactose monohydrate.
The drug shell is light yellow in color.
The INN name (international nonproprietary name) of the drug coincides with its active substance.
Other medicines are produced with this component and become substitutes for Tyrosol.
pharmachologic effect
Tyrosol tablets are positioned in the instructions for use as an antithyroid medication that disrupts the process of formation and release of thyroid hormones.
The pharmacological effect of the drug is due to the main substance included in its composition.
Thyrozol tablets block peroxidase, an enzyme that takes part in the iodization of the thyroid gland and promotes the formation of the hormones T3 and T4.
As a result of the use of the medication, symptomatic treatment of thyrotoxicosis is performed.
This effect will not work if the development of the disease and the release of hormones occurred due to the destruction of gland tissue due to thyroiditis or the use of radioactive iodine.
When treated with Tyrozol, the following properties are achieved:
- the level of T3 and T4 in the blood is normalized,
- the excretion of iodides from the thyroid gland is accelerated,
- reciprocal activation of TSH synthesis increases,
- does not affect the release of synthesized thyronones from thyroid follicles.
After consuming the medication, the active component is quickly absorbed, reaching its maximum in the blood within 30-90 minutes.
After 3-6 hours, the amount of the active component in the body is reduced by half.
Indications for use
The abstract describes the indications for use, which are limited to the list:
- thyrotoxicosis,
- preparation for surgical treatment for thyrotoxicosis,
- preparation for treatment with radioactive iodine,
- prevention of drug toxicosis due to excessive use of iodine preparations.
The speed of action of the medication is different for each patient.
This is due to the fact that a latent period of varying duration occurs at the beginning of using the medication, after which a noticeable result occurs and the symptoms of thyrotoxicosis disappear.
Contraindications
For the drug Tyrozol, contraindications are limited to the list:
- high sensitivity to the active substance,
- agranulocytosis, leukopenia, provoked by drugs containing thiamazole,
- granulocytopenia, including after normalization of indicators,
- cholestasis,
- treatment with Tyrosol with Levothyroxine during pregnancy,
- child's age up to 3 years.
Due to the presence of lactose in the medication, taking tablets is not recommended for patients who are intolerant to this substance.
With extreme caution and only under the supervision of a doctor, the medicine is prescribed for excessive enlargement of the thyroid gland to a very large size with narrowing of the trachea; usually such therapy is short-term.
In case of liver diseases or liver failure, the effect of the drug and the effect on the organ may be negative, so you should first consult with your doctor.
Directions for use and dosage
The manufacturer recommends taking Tyrozol after meals with sufficient liquid. Depending on the patient’s wishes, the daily volume of the drug can be taken immediately or divided into 2-3 times.
At the initial stages of treatment, the tablets should be taken at the time strictly prescribed by the doctor. The maintenance dose should be taken at one time.
Depending on the nature of the pathology and the characteristics of the patient’s body, an individual dosage of the medication is prescribed:
- for the treatment of thyrotoxicosis from 20 to 40 mg for up to two months, and after normalization of gland function from 5 to 20 mg (additional levothyroxine sodium is prescribed for maintenance),
- before surgical treatment 40 mg until a euthyroid metabolic state is achieved,
- before treatment with radioactive iodine from 20 to 40 mg until a temporary favorable state is achieved,
- during the latent period during treatment with iodine from 5 to 20 mg,
- with long-term use of Tyrozol, it is recommended to drink from 1 to 10 mg, treatment must be adjusted by additional prescription of levothyroxine drugs (use period up to 2 years),
- for latent thyrotoxicosis and for prophylaxis, 10 to 20 mg with potassium prechlorate.
For children, the dosage is calculated according to body weight: up to 0.5 mg/kg in 2-3 doses.
The period for how long you can take Tyrozol is determined by your doctor individually. The period of use of the drug can range from one week to several years.
Use of the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Failure to treat thyroid pathology during pregnancy can lead to unpleasant consequences.
Therefore, if necessary, this drug can be used.
It is important to evaluate the benefits and risks, since the active component can penetrate the placental barrier.
Tyrosol during pregnancy is prescribed in a dose not exceeding 10 mg per day.
The active substance of the drug passes into breast milk. For maternal hyperthyroidism, the medication can be used, but in a minimal adequate dose.
The medicine penetrates into the child’s body, so it is necessary to regularly monitor the functioning of the baby’s thyroid gland.
At the first symptoms of hypothyroidism or poisoning, you should consult a doctor.
Use for liver and kidney dysfunction
The active substance of the drug is excreted in the bile and passes through the kidneys. If the function of the paired organ is impaired, the period of drug elimination may increase. In this case, it is necessary to adjust the dose.
If liver function is impaired, the medicine is prescribed in the minimum dose that will be effective.
During the admission period, careful medical supervision is carried out.
Side effects of Tyrosol
Reviews of the use of Tyrozol say that the drug often causes side effects, and it cannot be taken for a long time.
With constant use, the medication destroys the thyroid gland, as a result of which the patient requires lifelong use of hormones and medications that create the illusion that the thyroid gland is working.
Side effects of Tyrosol are reduced to the following manifestations:
- distortion of blood components,
- severe hypoglycemia,
- changes in taste sensations, neuritis,
- enlargement of the salivary glands, vomiting, from the digestive tract - all signs of dyspeptic disorders,
- arthralgia,
- allergic manifestations,
- weakness,
- temperature increase.
Patients often have questions about whether it is possible to gain weight or gain weight from Tyrozol.
Weight gain is considered an adverse reaction. Therefore, you will not be able to lose weight on Tyrosol, despite the fact that it causes a decrease in blood sugar.
Overdose
With prolonged and excessive use of the drug, an enlargement of the thyroid gland is possible due to the large production of TSH.
Proper administration of the drug in combination with additional medications will help to avoid this condition.
It is permissible to use high doses of the drug only in severe forms of the disease and thyrotoxic crisis.
Interaction of Tyrosol with other drugs
- When used after x-ray examinations with an iodine-based contrast agent, a decrease in effectiveness occurs. It is necessary to increase the dose over time.
- Agents that remove iodine from the body enhance the effectiveness of the drug.
- When using the medication, it is necessary to adjust the doses of warfarin, aminophylline and cardiac glycosides.
- Lithium and beta-blockers increase the concentration of thiamazole.
- Sulfonamides and drugs based on sodium metamizole increase the likelihood of complications from the circulatory system.
- Gentamicin increases the effectiveness of the drug.
- Tyrosol and alcohol are incompatible. This combination causes serious toxic damage to the body.
Analogs
Tyrozol analogues are absolute and relative. The first include medications that contain the same active ingredient: Mercazolil, Timazol, Metizol.
For diseases of the thyroid gland, medications with a different composition are also prescribed: Propranolol, Metaprolol, Dexamethasone, L-thyroxine and others.
It is necessary to choose an alternative remedy after examination together with an experienced specialist.
What's better?
To answer the question which Tyrozol analogues are better or worse, let’s look at the table for a brief statement of the pros and cons of these drugs:
- Tyrosol
- Mercazolil
- Propycyl
- Euthyrox, Thyroxine, L-Thyroxine
- Prednisolone
Pros Cons
| Active substance | ||
| Thiamazole | An affordable drug that can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as for the treatment of children | Has many side effects, causes weight gain, affects menstruation |
Pros Cons
| Active substance | ||
| Thiamazole | Inexpensive drug | If you choose between Tyrosol and Mercazolil, then preference should be given to the first, the analogue is often prescribed in excessive doses, which causes serious adverse reactions, and is not allowed for use during pregnancy and lactation |
Pros Cons
| Active substance | ||
| Propylthiouracil | Short elimination period, minimal penetration through the placenta and low concentration in breast milk (if you choose Tyrozol or Propycil to prescribe to expectant mothers, then preference is given to the latter) | The need to constantly replenish the dose of the drug, and therefore 3-4 single doses are taken during the day |
Pros Cons
| Active substance | ||
| Levothyroxine sodium | Replenishes thyroid hormone deficiency | You cannot choose what to buy: Thyrozol or Eutirox, since these drugs are diametrically opposed, but can be used together (Thyroxine and L-Thyroxine can be compared in a similar way) |
Pros Cons
| Active substance | ||
| Prednisolone | Has anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, anti-shock effects | Tyrosol and Prednisolone can be used together; Prednisolone alone will not have a positive effect on diffuse toxic goiter, as a result of which its use will be useless |
Terms of sale in pharmacies
The drug is available only with a prescription.
To purchase medication, you must visit an endocrinologist and receive individual recommendations on the volume of the drug to be purchased.
Price
The cost of Tyrozol in different regions may vary.
A package containing 50 5 mg tablets costs $3, and 50 10 mg capsules cost more than $6.
Terms and conditions of storage of the drug Tyrozol
The medication should be stored out of the reach of children and away from direct sunlight.
The shelf life is 4 years from the date of issue.
Source: https://kvd9spb.ru/endokrinnaya-sistema/naskolko-effektiven-tirozol-detalno-ob-ispolzovanii-preparata
Side effects
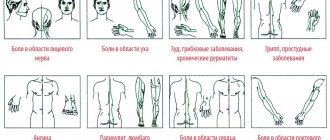
When taking Tyrozol tablets orally, patients experienced some side effects:
- Connective tissue and musculoskeletal system: often - arthralgia (slowly progressive) without clinical symptoms of arthritis;
- Skin and subcutaneous tissues: very often - itching, rashes, redness of the skin; very rarely - baldness, generalized skin rash, lupus-like syndrome;
- Gastrointestinal tract, liver and biliary tract: very rarely - vomiting, toxic hepatitis, enlarged salivary glands, cholestatic jaundice;
- Blood and lymphatic systems: uncommon – agranulocytosis; very rarely - thrombocytopenia, generalized lymphadenopathy, pancytopenia;
- Nervous system: rarely - dizziness, reversible change in taste sensations; very rarely – polyneuropathy, neuritis;
- Endocrine system: very rarely - Hirata disease (autoimmune insulin syndrome) with hypoglycemic conditions;
- Other reactions: rarely - weakness, fever, weight gain.
special instructions
Before you start using the drug, read the special instructions:
- If the course of treatment is stopped early, a relapse of the disease is possible.
- Rarely, after the end of treatment, late hypothyroidism may occur, which is not associated with taking the drug, but with inflammatory and destructive processes in the thyroid tissue.
- In case of severe goiter, Tyrozol is prescribed in combination with sodium levothyroxine to avoid further narrowing of the tracheal lumen.
- During the treatment period, monitoring of the peripheral blood picture is necessary.
- The drug may reduce the sensitivity of thyroid tissue to radiation therapy.
- If you experience a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, increased body temperature, signs of stomatitis or furunculosis during treatment, the drug should be discontinued and consult a doctor immediately.
- The drug is discontinued if hemorrhages or bleeding of unknown origin, generalized skin rash and itching, persistent nausea or vomiting, or jaundice occur. severe abdominal pain, severe weakness.
With alcohol
Despite the absence in the official instructions of contraindications to drinking alcohol during treatment with Tyrozol, such a combination a priori cannot lead to any positive aspects and, on the contrary, most likely, due to synergy , will cause an increase in the severity of side effects of therapy, and possibly even more severe ones reactions. In this regard, Tyrosol and alcohol are incompatible in the treatment of thyroid diseases.
Interaction with other drugs
When using the drug, it is necessary to take into account interactions with other medications:
- Gentamicin enhances the antithyroid effect of thiamazole.
- Lack of iodine enhances the effect of thiamazole.
- Lithium preparations, beta-blockers, reserpine, amiodarone increase the effect of thiamazole (dosage adjustment is required).
- Leukogen and folic acid, when used simultaneously with thiamazole, reduce the risk of developing leukopenia.
- When prescribing the drug after using iodine-containing radiocontrast agents in a high dose, the effect of thiamazole may be weakened.
- When used simultaneously with sulfonamides, metamizole sodium and myelotoxic drugs, the risk of developing leukopenia increases.
- There are no data on the effect of other drugs on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the drug. However, it should be borne in mind that with thyrotoxicosis, the metabolism and elimination of substances is accelerated. Therefore, in some cases it is necessary to adjust the dose of other drugs.
- In patients taking Tyrozol for thyrotoxicosis, after achieving a euthyroid state (normalization of thyroid hormone levels in the blood serum), it may be necessary to reduce the doses of cardiac glycosides (digoxin and digitoxin), aminophylline, as well as increase the doses of warfarin and other anticoagulants - derivatives coumarin and indanedione (pharmacodynamic interaction).
TYROZOL
Drug: TYROZOL®
Active substance: thiamazole ATC code: H03BB02 KFG: Antithyroid drug ICD-10 codes (indications): E05 KFU code: 04/15/04 Reg. number: P No. 014893/01 Registration date: 07/31/08 Owner of reg. ID: MERCK KGaA {Germany}
DOSAGE FORM, COMPOSITION AND PACKAGING
Light yellow , film-coated tablets at the fracture it looks like a white or almost white mass.
| 1 tab. | |
| thiamazole | 5 mg |
Excipients: colloidal silicon dioxide, sodium carboxymethyl starch, magnesium stearate, hypromellose 2910/15, talc, cellulose (powder), corn starch, lactose monohydrate, yellow iron oxide, dimethicone 100, macrogol 400, titanium dioxide.
10 pieces. - blisters (2) - cardboard packs. 10 pieces. - blisters (4) - cardboard packs. 10 pieces. - blisters (5) - cardboard packs. 10 pieces. - blisters (10) - cardboard packs. 25 pcs. - blisters (2) - cardboard packs. 25 pcs. - blisters (4) - cardboard packs. 25 pcs. - blisters (5) - cardboard packs. 25 pcs. - blisters (10) - cardboard packs.
film-coated tablets , round, biconvex, scored on one side; at the fracture it looks like a white or almost white mass.
| 1 tab. | |
| thiamazole | 10 mg |
Excipients: colloidal silicon dioxide, sodium carboxymethyl starch, magnesium stearate, hypromellose 2910/15, talc, cellulose (powder), corn starch, lactose monohydrate, yellow iron oxide, red iron oxide, dimethicone 100, macrogol 400, titanium dioxide.
10 pieces. - blisters (2) - cardboard packs. 10 pieces. - blisters (4) - cardboard packs. 10 pieces. - blisters (5) - cardboard packs. 10 pieces. - blisters (10) - cardboard packs. 25 pcs. - blisters (2) - cardboard packs. 25 pcs. - blisters (4) - cardboard packs. 25 pcs. - blisters (5) - cardboard packs. 25 pcs. - blisters (10) - cardboard packs.
TYROZOL INSTRUCTIONS FOR SPECIALISTS. The description of the drug is approved by the manufacturer.
PHARMACHOLOGIC EFFECT
Antithyroid drug. It disrupts the synthesis of thyroid hormones by blocking the enzyme peroxidase, which is involved in the iodination of thyronine in the thyroid gland with the formation of triiodo- and tetraiodothyronine.
The drug is effective in the symptomatic treatment of thyrotoxicosis (except for cases of disease development due to the release of hormones after the destruction of thyroid cells during treatment with radioactive iodine or thyroiditis).
Tyrosol® does not affect the release of synthesized thyronines from the thyroid follicles. This explains the latent period of varying duration, which may precede normalization of T3 and T4 levels in the blood plasma and improvement of the clinical picture.
The drug reduces basal metabolism, accelerates the excretion of iodides from the thyroid gland, increases reciprocal activation of the synthesis and secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone by the pituitary gland, which may be accompanied by some hyperplasia of the thyroid gland.
The duration of action of the drug after a single dose is about 24 hours.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Suction
After taking the drug orally, thiamazole is quickly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Cmax is achieved within 0.4-1.2 hours.
Distribution
Practically does not bind to plasma proteins. Cumulates in the thyroid gland.
Metabolism
Slowly metabolized in the thyroid gland, as well as in the kidneys and liver.
Removal
Small amounts of thiamazole are found in breast milk. T1/2 is about 3-6 hours. Thiamazole is excreted in the urine (within 24 hours, 70% of the drug, with 7-12% unchanged) and bile.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In patients with liver failure, T1/2 increases.
The pharmacokinetic parameters of the drug do not depend on the functional state of the thyroid gland.
INDICATIONS
- thyrotoxicosis;
— preparation for surgical treatment of thyrotoxicosis;
— preparation for treatment of thyrotoxicosis with radioactive iodine;
- therapy during the latent period of radioactive iodine action (carried out before the onset of radioactive iodine action /for 4-6 months/);
- in exceptional cases, long-term maintenance therapy for thyrotoxicosis, when due to the general condition or for individual reasons it is impossible to perform radical treatment;
- prevention of thyrotoxicosis when prescribing iodine preparations (including cases of use of iodine-containing radiocontrast agents) in the presence of latent thyrotoxicosis, autonomous adenomas or a history of thyrotoxicosis.
DOSING REGIME
The tablets should be taken after meals, without chewing, with a sufficient amount of liquid. The daily dose is prescribed in 1 dose or divided into 2-3 single doses. At the beginning of treatment, single doses are taken throughout the day at strictly defined times. The maintenance dose should be taken in one dose after breakfast.
For thyrotoxicosis, depending on the severity of the disease, 20-40 mg/day is prescribed for 3-6 weeks. After normalization of thyroid function (usually after 3-8 weeks), they switch to a maintenance dose of 5-20 mg/day. From this time on, additional levothyroxine is recommended.
In preparation for surgical treatment of thyrotoxicosis, 20-40 mg/day is prescribed until a euthyroid state is achieved. From this time on, additional levothyroxine is recommended. In order to reduce the time required to prepare for surgery, beta-blockers and iodine preparations are additionally prescribed.
In preparation for treatment with radioactive iodine, 20-40 mg/day is prescribed until a euthyroid state is achieved. It should be borne in mind that thiamazole and thiourea derivatives may reduce the sensitivity of thyroid tissue to radiation therapy.
When treating during the latent period of radioactive iodine action, depending on the severity of the disease, 5-20 mg/day is prescribed until the onset of radioactive iodine action (4-6 months).
For long-term thyreostatic maintenance therapy, Tyrozol® is prescribed in doses of 1.25-2.5-10 mg/day with additional levothyroxine in small doses.
In order to prevent thyrotoxicosis when prescribing iodine preparations (including cases of use of iodine-containing radiocontrast agents) in the presence of latent thyrotoxicosis, autonomous adenomas or a history of thyrotoxicosis, Tyrozol® is prescribed at a dose of 10-20 mg/day and potassium perchlorate 1 g/day for 8-10 days before taking iodine-containing products.
For children, Tyrozol® is prescribed at an initial dose of 0.3-0.5 mg/kg body weight daily. Maintenance dose - 0.2-0.3 mg/kg/day. If necessary, additional levothyroxine is prescribed.
During pregnancy , the drug is prescribed in minimal doses: single - 2.5 mg, daily - 10 mg.
For liver failure, the minimum effective dose of the drug is prescribed.
The duration of use of Tyrosol® in the treatment of thyrotoxicosis is from 1.5 to 2 years.
When preparing patients with thyrotoxicosis for surgery, treatment with the drug is carried out until a euthyroid state is achieved within 3-4 weeks before the planned day of surgery (in some cases - longer) and ends the day before it. In all cases, the duration of treatment with the drug is determined by the doctor.
SIDE EFFECT
Sometimes - allergic skin reactions (itching, redness, rashes), vomiting, arthralgia, dizziness, weakness.
Rarely - an increase in temperature, a change in taste sensations (they are reversible).
In approximately 0.3-0.6% of cases, agranulocytosis occurs (symptoms may appear even weeks and months after the start of treatment and lead to the need to discontinue the drug).
In isolated cases - cholestatic jaundice, toxic hepatitis, arthralgia (usually develop slowly and gradually, several months after the start of treatment; there were no clinical signs of arthritis).
In some cases - generalized lymphadenopathy, acute enlargement of the salivary glands, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, neuritis, polyneuropathy, lupus-like reaction, autoimmune syndrome with hypoglycemia.
Increase in body weight.
Subclinical and clinical hypothyroidism can develop when taking the drug in high doses. The thyroid gland may also begin to enlarge, which is associated with an increase in TSH levels in the blood.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- agranulocytosis during previous therapy with carbimazole or thiamazole;
- granulocytopenia (including history);
- cholestasis before starting treatment;
- therapy with thiamazole in combination with levothyroxine during pregnancy;
- hypersensitivity to thiamazole or thiourea derivatives.
Relative contraindication: history of allergic skin reactions to thiourea derivatives.
The drug should be used with caution in case of very large goiter with narrowing of the trachea (only short-term treatment during preparation for surgery), and in case of liver failure.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION
Untreated hyperfunction of the thyroid gland during pregnancy can lead to serious complications: premature birth, fetal malformations.
Thiamazole penetrates the placental barrier and reaches the same concentration in the fetal blood as in the mother. Since the effect of thiamazole on the fetus cannot be completely excluded, during pregnancy the drug should be used only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus at the minimum effective dose and without additional use of levothyroxine.
Thiamazole in high doses can cause goiter, hypothyroidism and low birth weight in the fetus.
During lactation, treatment of thyrotoxicosis with Tyrozol® can be continued if necessary. Since thiamazole is excreted in breast milk and can reach a concentration in it corresponding to the level of thiamazole in the mother's blood, the newborn may develop hypothyroidism. Therefore, if it is necessary to continue treatment of thyrotoxicosis during breastfeeding, Tyrozol® should be used in low doses (up to 10 mg/day) without additional levothyroxine.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS
For patients with a significant enlargement of the thyroid gland, narrowing the lumen of the trachea, Tyrozol® is prescribed for a short time in combination with levothyroxine, because with prolonged use, an increase in goiter and even greater compression of the trachea is possible. It is necessary to carefully monitor the patient (monitoring TSH levels and tracheal lumen).
During treatment with the drug, regular monitoring of peripheral blood patterns is necessary.
If during treatment with the drug a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, increased body temperature, signs of stomatitis or furunculosis (possible symptoms of agranulocytosis) suddenly appear, you should stop taking the drug and consult a doctor immediately.
If subcutaneous hemorrhages or bleeding of unknown origin, generalized skin rash and itching, persistent nausea or vomiting, jaundice, severe epigastric pain and severe weakness appear during treatment, discontinuation of the drug is required.
If treatment is stopped early, a relapse of the disease is possible.
The appearance or worsening of endocrine ophthalmopathy is not a side effect of adequate treatment with Tyrozol.®
In rare cases, after completion of treatment, late hypothyroidism may occur, which is not a side effect of the drug, but is associated with inflammatory and destructive processes in the thyroid tissue that occur as part of the underlying disease.
OVERDOSE
Symptoms: chronic overdose of Tyrozol® leads to an enlargement of the thyroid gland and the development of hypothyroidism. Taking Tyrosol in very high doses (about 120 mg/day) can lead to the development of myelotoxic effects.
Treatment: in case of chronic overdose of Tyrosol®, discontinuation of the drug is necessary. Replacement therapy with levothyroxine is carried out if this is justified by the severity of hypothyroidism. As a rule, after stopping Tyrozol, spontaneous restoration of thyroid function is observed. In case of overdose, you should discontinue the drug, rinse the stomach, take activated charcoal, and carry out symptomatic therapy.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
When prescribing the drug after using iodine-containing radiocontrast agents in a high dose, the effect of Tyrosol® may be weakened.
Lack of iodine enhances the effect of Tyrosol®.
In patients taking Tyrozol® for thyrotoxicosis, after achieving a euthyroid state (normalization of thyroid hormone levels in the blood serum), it may be necessary to reduce the doses of cardiac glycosides (digoxin and digitoxin), aminophylline, as well as increase the doses of warfarin and other anticoagulants - coumarin and indanedione derivatives (pharmacodynamic interaction).
Lithium preparations, beta-blockers, reserpine, amiodarone increase the effect of thiamazole (dosage adjustment is required).
When used simultaneously with sulfonamides and metamizole sodium, the risk of developing leukopenia increases.
Leukogen and folic acid, when used simultaneously with thiamazole, reduce the risk of developing leukopenia.
Gentamicin enhances the antithyroid effect of thiamazole.
There are no data on the effect of other drugs on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the drug. However, it should be borne in mind that with thyrotoxicosis, the metabolism and elimination of substances is accelerated. Therefore, in some cases it is necessary to adjust the dose of other drugs.
CONDITIONS OF VACATION FROM PHARMACIES
The drug is available with a prescription.
CONDITIONS AND DURATION OF STORAGE
The drug should be stored in a dry place, out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Shelf life: 4 years.
Reviews
We invite you to read the reviews of people who have used the drug Tyrosol:
- Anna. My mother-in-law is currently taking this drug. A couple of years ago I started to lose a lot of weight. The cause could not be determined for a long time. And then it turned out that the thyroid gland and the well-known hormone TSH were to blame. The result of the treatment was not long in coming. Soon the mother-in-law again became a living, blooming woman. She still drinks it to this day. The only thing you need to periodically monitor TSH so as not to overdo it with taking Tyrozol.
- Sofia. The only medicine prescribed by endocrinologists for thyrotoxicosis and thyrotoxicosis. It is worth noting that it will not solve the problem forever, but will rather relieve an acute crisis and maintain the level of the TSH hormone at normal levels. The main thing is the correct dosage. And here is an ambush. This hormone constantly fluctuates, and yesterday’s dose may become either insufficient or excessive... Therefore, it is extremely important to regularly check the TSH level and donate blood. If you adjust the correct dosage and adhere to general recommendations, diet and lifestyle, you can enter a state of remission for a long time. But, alas, tyrosol cannot be completely abolished. After withdrawal, a large percentage of the hormone drop returns.
Analogs
Level 4 ATX code matches:
Tyrosol analogues can be divided into two groups, these are hormonal drugs that include thyroid hormones or their synthetic analogues (mainly levothyroxine sodium ): L-Thyroxine , Bagotirox , Eutirox , L-Tyroc , Thyro-4 , Triiodothyronine and drugs , affecting the synthesis and/or metabolism of thyroid hormones: Mercazolil , Iodomarin , Iodbalance , Microiodide , Thiamazol , Metizol , Propicil .
Propicil or Tyrosol?
Considering these two analogue drugs, it is worth noting that although they contain different active ingredients ( thiamazole for Tyrosol and propylthiouracil for Propicil ), they have a fairly similar mechanism of action in relation to the functionality of the thyroid gland. You can also trace similar contraindications and side effects of both drugs. Often, for example, if the patient has a personal hypersensitivity to one of the active ingredients of the drugs ( thiamazole or propylthiouracil ), one drug is replaced with another.
Judging by the reviews of patients, in the case of the use of Propicil , the positive dynamics of the treatment develops faster in comparison with Tyrozol, therapy with which, in turn, more often leads to long-term remission of the disease. In connection with all of the above, it is worth leaving the choice between these drugs at the discretion of the doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.