In this article we will look at the causes of fever without symptoms. What could this pathology mean?
An increase in temperature is a very common occurrence. However, it is usually accompanied by certain accompanying symptoms that may indicate the development of a particular disease. In the absence of these, it is very difficult to determine the disease, so patients are often worried about this.
Pathogenesis of development - the difference between fever and hyperthermia and the reasons for their appearance
The hypothalamus is responsible for temperature control at the level of reflexes.
Located in the diencephalon, it controls endocrine function and the ANS. In the area of the brain, there are centers that regulate temperature, the feeling of hunger, the desire to drink, sleep, stay awake, and physiological processes. The reasons for the high temperature lie in pyrogens. Protein substances can be external - waste products of pathogenic microbes and secondary - internal proteins produced by the human body.
In case of pathology in the body, exogenous pyrogens stimulate the cells of the body to synthesize endogenous pyrogens, they transmit an impulse to thermoreceptors. The hypothalamus makes adjustments to temperature homeostasis in order to launch the body's barrier functions at full capacity. An imbalance of heat production leads to fever without cold symptoms in an adult.
If changes in the state of the body are recorded only by a thermometer, the phenomenon can occur without the participation of a part of the brain. The hypothalamus does not receive a request to launch the body's barrier functions and protect against infection. The rise in temperature is explained by a violation of heat transfer due to the fact that it is hot outside or indoors, physical activity, or overheating.
With hyperthermia and fever, the following occurs:
- phagocytosis - cells absorb hostile pathogenic microorganisms;
- the intensity of the liver and kidneys increases, toxic compounds and decay products are bound and removed;
- the intensity of the action of antibodies increases.
Fluctuations in temperature in a child and an adult are a protective measure and a signal from the body that it needs help. Even if the symptoms are not particularly bothersome, the consequences can be serious, sometimes irreversible. The causes of fever can only be established after diagnosis, so do not delay
Causes of high fever in adults without symptoms
An increase in temperature or fever is observed in almost all acute infectious diseases, as well as during exacerbation of certain chronic diseases. And in the absence of catarrhal symptoms, doctors can determine the cause of the patient’s high body temperature by isolating the pathogen either directly from the local source of infection or from the blood.
It is much more difficult to determine the cause of a temperature without signs of a cold if the disease arose as a result of exposure to opportunistic microbes (bacteria, fungi, mycoplasma) on the body - against the background of a decrease in general or local immunity. Then it is necessary to conduct a detailed laboratory study of not only blood, but also urine, bile, sputum and mucus.
Causes of fever without symptoms may be associated with the following diseases:
- Endocrine diseases, for example, thyrotoxicosis;
- Systemic inflammation: Crohn's disease, rheumatism, polyarthritis, periarthritis nodosa, etc.;
- Oncological diseases: tumors of the stomach, liver, kidneys, bronchi or lungs, lymphoma, leukemia;
- Diseases of fungal, parasitic or viral etiology: syphilis, toxoplasmosis, candidiasis, malaria;
- Infectious diseases: HIV infection, Lyme disease, relapsing and typhus, tuberculosis;
- Inflammatory diseases of bacterial origin: sepsis, inflammation of the uterine appendages, prostatitis, meningitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, pneumonia, endocarditis, etc.
In all situations, an increase in temperature without signs of a cold indicates that the body is trying to fight something. For example, the so-called low-grade fever is often accompanied by anemia - a low level of hemoglobin in the blood.
General rules of treatment
For high fevers without other symptoms, a wait-and-see approach is recommended. As can be seen from the description of the possible causes of this phenomenon, with most common diseases in children that begin with a high temperature, symptoms will still appear, just a little later.
Waiting tactics means that the child does not need to be given antibiotics or any other drugs right away, because the cause of the fever is still unknown. Knowing that nine out of ten children in this situation have one of the viral infections, base your child’s care on the general rules for treating viral illnesses.
The room where the baby is lying must be ventilated and washed - wet cleaning and an open window are mandatory actions that need to be done immediately after the doctor sees the baby. If the doctor does not take the child to the hospital, suspecting something serious, then the treatment will fall on the shoulders of the parents.
You need to create conditions in the room that will help the baby’s immune system cope with the disease faster.
In addition to clean air, you should pay attention to the temperature - the room should not be hotter than 21-22 degrees. If the family has a device such as a humidifier, it should be turned on and ensure that the humidity in the room is at 50-70%
Such environmental parameters will help to avoid complications of viral diseases associated with drying out of the nasopharynx and mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract.
The child should drink a lot and eat little. Do not try to feed your child at any cost. If he himself asks to eat, you can give him light food that will be quickly digested without requiring a large amount of energy expenditure for the digestion process. Such foods include fruit salad, porridge, vegetable puree, and steamed cutlet. It is better not to give cakes and fatty meats.
The temperature should be reduced only when it begins to threaten the condition. Fever is a protective mechanism necessary for the child’s immune system. Therefore, antipyretic drugs should be given only after the thermometer “crosses” the mark of 38.5 in infants and children under 2 years of age, and 39.0 in children 2 years of age and older. To reduce fever, it is better to use paracetamol-based drugs. For children of different ages, you can choose either syrup, tablets, or rectal suppositories.
You shouldn't try to treat something that doesn't exist. You can often hear that parents, when a high temperature appears, begin to give their child inhalations and put cupping. And they do this not because he has a cough. Mothers try to prevent this cough and think that they are “playing ahead.” The only thing that is really worth doing, if you really want to treat something with something, is to instill homemade saline solution into the nasal passages as often as possible (to prevent them from drying out), and also gargle with the same saline solution.
If new symptoms appear, you should definitely notify your doctor. As prescribed by the doctor, it is necessary to do general blood and urine tests, as well as an immunological blood test, which will show the presence of antibodies to certain viruses.
Fever, why does it occur?
In all other situations, an increase in body temperature above normal indicates that the body is trying to fight something. In most cases, these are foreign agents in the body - bacteria, viruses, protozoa, or a consequence of physical impact on the body (burn, frostbite, foreign body).
At elevated temperatures, the existence of infectious and toxic agents in the body becomes difficult; most infections die at a temperature of about 38 degrees.
All fevers can be divided into three groups:
- Subfebrile, in which the temperature rises from 37 to 38 degrees;
- Febrile - temperature rises from 38 to 39 degrees;
- Hectic - an increase in temperature from 40 degrees and above.
But any organism, like a mechanism, is not perfect and can malfunction. In the case of fever, we can observe this when the body, due to the individual characteristics of the immune system, reacts too violently to various infections, and the temperature rises too high, for most people it is 38.5.
Symptoms
Most known childhood diseases have their own diagnostic signs, in addition to the presence of fever. Many childhood infections are characterized by various rashes. Catarrhal symptoms indicate colds.
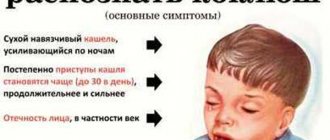
Common signs of a sharp rise in temperature to high numbers in a child are (symptoms of intoxication):
- Lethargy;
- Weakness;
- Apathy;
- Bad mood;
- Upon skin contact, a feeling of heat;
- Vomiting, nausea;
- Refusal to eat.
If such an external condition is confirmed by measuring the temperature with a thermometer, we should talk about the body’s fight against an infectious agent.
Pneumonia
A rise in temperature to 39 is more realistic, in the case of pneumonia (pneumonia). The factors of this pathology are:
- Hypothermia;
- Chronical bronchitis;
- Previous respiratory diseases.
Very often, a sharp rise in temperature will be accompanied by all the signs of intoxication, while examination of the throat will not yield any results. The child may have difficulty breathing.
Pyelonephritis
Infectious diseases of the urinary organs often occur in childhood. Pediatricians distinguish pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. With the latter, the immune system is involved in the process. The temperature rises to 39-40 C, signs of intoxication are characteristic. There may be an initial course without symptoms. After some time, the following temperatures will be added:
- Symptoms of urinary dysfunction;
- Kidney pain;
- Glomerulonephritis is often characterized by elevated blood pressure.
Meningitis
Meningitis, an acute infectious disease transmitted by airborne droplets from patients with catarrhal form or carriers. A temperature reaction without symptoms is rare. Usually accompanied by a massive headache, vomiting of central origin, which does not bring relief, and classic meningeal symptoms:
- Rigidity of the neck muscles;
- Backache;
- When trying to apply pressure in the suprapubic region, pull up the legs;
- When one leg bends at the joints, the other bends and back pain occurs;
- When the baby is lifted up, the legs are pulled up.
Bacteremia
Bacteremia is characterized by the presence in the blood of pathogenic microbes that have entered there from the primary focus of the abscess in the thickness of the skin or internal organs. A temperature of 39-40 is typical, followed by loss of consciousness, stuporous states and convulsions. Requires immediate hospitalization.
Neuroses
Sometimes children find it difficult to cope with the daily stress of school and experience nervous system overstrain, accompanied by high fever. In this case, the child should be put to rest, and soothing tea can be given.
When assessing symptoms, it is necessary to perceive the entire complex of signs. A separate symptom found in a child may indicate a completely different pathology. Seizures may be a sign of new-onset epilepsy, and difficulty breathing may be a symptom of a primary attack of bronchial asthma.
Increased body temperature without signs of a cold
A fast pace of life and numerous stresses are the daily reality of modern man. Sometimes the day is scheduled according to hours, which are sorely lacking; you have to sacrifice sleep, cut down on the time allotted for rest. There is no place for sick leave in the schedule, so illnesses are carried on the feet, despite the risk of complications.
Elevated body temperature without signs of a cold is a symptom that is not always given due attention, although it can indicate various pathologies.
What does a person think about when he sees high numbers on the thermometer scale? Probably the first thought that comes to mind is a possible cold - but is this correct if there are no other symptoms? Fever without signs of a cold in an adult may be the only complaint or accompanied by manifestations that are not characteristic of acute respiratory diseases. Fever is present in the clinical picture:
- Thermoneurotic syndrome.
- Leukemia.
- Systemic lesions of connective tissue (collagenosis).
Before talking about the characteristics of the above diseases, it is worth emphasizing the difference between their course and the common cold.
Colds include acute respiratory infections, the development of which is observed against the background of hypothermia. Onset is sudden or after a short prodromal period; in the absence of complications, recovery occurs within a few days. Symptoms of a cold make it possible to clearly identify the affected area (nasal cavity with rhinitis, pharyngeal mucosa with pharyngitis), and fever is a protective reaction that stops 2-3 days after the onset of complaints.
An increase in temperature as a manifestation of thermoneurosis, leukemia or systemic connective tissue diseases can be observed for several weeks without other symptoms or, conversely, be accompanied by a number of characteristic signs, reach high numbers or remain at the level of low-grade indicators (from 37.2 to 37.9 ° C ).
Thermoneurosis
Thermoneurosis (thermoneurotic syndrome, thermoneurotic fever) is a type of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. The temperature without signs of a cold in a child or an adult rises as a result of stress (stressful study or work), and can be combined with weakness, a feeling of heaviness and “fog” in the head. The disease is characterized by periodic low-grade fever - it is provoked, in addition to psycho-emotional stress, by acute pathologies (ARVI).
Complaints from patients with thermoneurosis:
- unmotivated weakness;
- drowsiness during the day and insomnia at night;
- dizziness, feeling of lack of air;
- stabbing, aching pain in the left side of the chest.
Thermoneurotic syndrome is also considered among the manifestations of overtraining, that is, disruption of adaptation and overstrain of regulatory processes in athletes. Depletion of the body's functional capabilities or disproportionate loads, especially in the presence of emotional experiences and pathological changes in the endocrine system, lead to fatigue. Patients are concerned about general malaise, low-grade fever, and muscle pain. Temperature fluctuations in this case differ from physiological norms. The morning temperature without cold symptoms in an adult may be higher than the evening temperature; There are likely to be sharp jumps in indicators during the day without objective reasons or persistent low-grade fever for several weeks.
Leukemias are tumor diseases of hematopoietic tissue. Acute and chronic myeloid leukemia are among the forms that predominate in adult patients, while acute lymphoblastic leukemia is more common in childhood. Due to nonspecific complaints and varied clinical symptoms, it may be difficult to make a diagnosis.
Fever is one of the initial symptoms; sometimes accompanied by night sweats, weakness, enlarged lymph nodes, enlarged liver and spleen (hepatosplenomegaly). Increased bleeding of the mucous membranes and the appearance of bruises on the skin are also characteristic. There are variants of a benign course (for example, in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia), when patients complain only of increased body temperature or do not complain at all, and pathological changes are detected after laboratory tests. If an adult has a fever without signs of a cold, a general blood test is necessary for differential diagnosis.
Collagenoses
Collagenoses are diseases caused by inflammatory damage to connective tissue of autoimmune origin. These include systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, polymyalgia rheumatica, etc.
Systemic lupus erythematosus is one of the most severe types of collagenosis.
It occurs more often in women aged 20 to 40 years. The onset of the disease in some cases is characterized by fever without signs of a cold. In this case, indicators vary from subfebrile to hyperpyretic (above 41 °C). Additional symptoms usually appear after a few weeks. Systemic lupus erythematosus is included in the list of pathologies that should be included in the diagnostic search in the presence of fever of unknown origin.
In addition to fever, you may experience:
- Fatigue.
- Muscle weakness.
- Headache.
- Decreased appetite, nausea.
- Loss of body weight.
- Pain in joints, muscles.
- Heart rhythm disturbances.
- Erythema in the form of a “butterfly” on the face, etc.
The variety of manifestations is explained by damage to the kidneys, respiratory and gastrointestinal tract, musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular, and nervous systems. Patients develop nephritis, pericarditis, myocarditis, and a skin rash. Changes in the blood picture are characterized by anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Author: Torsunova Tatyana
https://prostudnik.ru/proyavleniya/temperatura/bez-simptomov.html
Features of treatment
Only a specialist can prescribe therapy for children after conducting a series of diagnostic measures. It will be aimed at eliminating the disease that is revealed during the examination.
Usually prescribed:
- Antipyretic substances;
- antibiotics;
- antiviral drugs;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- electrolytes;
- immunostimulants, etc.
The main treatment will be aimed at eliminating the disease that caused the fever. But there are peculiarities when children take antipyretic drugs.
If the child does not tolerate the fever well, or he is growing, the doctor will prescribe Panadol syrup and suppositories, Cefekon D or Nurofen suspension.
They help eliminate hyperthermia, relieve pain, and make the baby feel better. These drugs are especially relevant during teething.
If we are talking about a baby, then a temperature of thirty-eight degrees without the development of severe symptoms is a rather alarming condition.
The baby needs to be diagnosed and treated before the doctor arrives. A specialist will most often prescribe Efferalgan to relieve febrile symptoms.
Temperature and nothing else – School of Dr. Komarovsky
When urgent medical attention is needed
There are situations when the patient suddenly loses activity, he develops changes in the skin or other disorders, in this case it is worth remembering when the temperature at night and during the day leads to an immediate call to the ambulance team.
The child needs immediate hospitalization if:
- an increase in temperature without additional symptoms leading to the child’s refusal to eat;
- twitching of the chin is a harbinger of seizures;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- sleep disturbance, lack of response to toys;
- a sharp increase in temperature in an adult;
- pale skin color.
Symptoms of fever without a cold in children are carried out in parallel with the fight against the symptom, but this is done under the supervision of doctors.
For adults whose fever systematically increases and there are no other symptoms, no runny nose, prolonged cough or other signals of a cold, adhere to the following algorithm of actions:
- During illness, physical activity should be reduced.
- Carry out aromatherapy, calm down.
- Periodically apply a compress of cloth soaked in a solution of water and vinegar (1:1) to the forehead. Changes should be carried out frequently (every quarter of an hour).
- Drink tea with the addition of medicinal berries (raspberries, lingonberries, cranberries), herbal infusions (linden).
If the temperature does not go down, it is recommended to take an antipyretic drug
But the temperature often rises in the evening, and this is also an alarm signal, since it is important to avoid possible night complications, such as stenosis
If you have not achieved the required result, if the thermometer readings are rapidly increasing, if your consciousness is confused, you should call an ambulance. The question of placement in a hospital is decided by the attending physician.
Temperature 38 without symptoms: causes
A temperature of 38 without symptoms can occur quite often. And the reasons for this temperature are not always the same. This temperature may signal that lacunar or follicular tonsillitis is beginning (with catarrhal tonsillitis, the temperature rises slightly).
If a temperature above 38 degrees without symptoms lasts for 3 or more days, then this may be a manifestation of:
- Rheumatism;
- Heart attack;
- Inflammation of the kidneys (characterized by severe stabbing pain in the lower back);
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia, accompanied by surges in blood pressure;
- Pneumonia.
The most unpleasant syndrome is the persistence of an elevated temperature for several weeks and even months. This is most likely:
- A sign of tumor development in the body;
- Serious endocrine disorders;
- Leukemia;
- Diffuse changes in the liver or lungs.
The only thing that all these cases have in common is that in any case, the increase in temperature is due to the body’s resistance, which means that the immune system is fighting.
Why does a high temperature appear without symptoms of a cold?
If there is a sharp increase in temperature to 38-39°C without cold symptoms, then there may be some kind of infection in the body. A sharp exacerbation or complication of diseases that were present in the baby before and were not cured is also possible. To determine the presence of a specific disease, you need to donate blood for analysis and conduct a series of clinical studies. If a high temperature of 38-39°C appears due to an infection entering the body, then you should donate not blood for analysis, but also urine, mucus, sputum and even bile. When making a primary diagnosis, when there is a high temperature without cold symptoms, experts assume the presence of a fever of unknown etymology. Some reasons for an increase in temperature in the region of 38-39 degrees without signs of colds may be: - Disturbance in the functioning of the thyroid gland; — Systemic disease with lupus erythematosus; — Crohn's disease; — Liver and kidney diseases; — Tumor pathologies of the lungs; — Rheumatoid arthritis; — Bronchial tumors (malignant or benign); — Malaria; — Typhoid fever; — Tuberculosis disease; - Inflammatory processes caused by bacterial infection. Such processes are caused by pneumonia, endocarditis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, osteomyelitis and adnexitis. With low hemoglobin, the temperature can reach 38-39°C and affect the external condition of the baby. If a child is often exposed to stress, shock, or depressive notes, then it is possible to have a temperature of 38-39 degrees without signs of a cold. This is the so-called adrenaline hyperthermia. In some children, hyperthermia without signs of a cold up to 39 degrees can develop due to prolonged use of antibiotics. Before giving your baby any medication, be sure to read the instructions for it and study the possible side effects of the body. Depending on the cause of the temperature process and the age of the baby, a qualified specialist will prescribe the necessary treatment.
Why does a temperature of 39.5 °C appear without symptoms?
High body temperature is the main sign of the development of inflammatory processes in the human body2,4. All other symptoms may occur later, a few days after the onset of hyperthermia. In any case, it is worth contacting specialists so that they can make an accurate diagnosis and select effective treatment.
If the infectious process is localized in the throat or sinuses, a temperature of 39.5 °C becomes the only clear sign of the development of the disease; the disease proceeds without symptoms, especially if the infection occurs in a child2. Young children do not always tell their parents about a sore throat or swelling in the nose or forehead. Therefore, only a specialist can determine the true causes of the rise in temperature, using the capabilities of modern diagnostics.
A persistent increase in body temperature without symptoms of the underlying disease may indicate the progression of a latent infectious process2,4. In people with weakened immune systems, many diseases of a viral and bacterial nature occur with mild symptoms.
Re-promotion
There are situations when high fever returns after the disease has begun to recede. This means only one thing - the infection has not been completely defeated.
On a note! Most often, such a rise occurs with young children, since they do not yet know how to clear their nose and cough well enough. Because of this, the disease can “lurk” and then flare up with renewed vigor.
Therefore, from the very beginning of the disease, during treatment you need to use nasal drops, for example, Nazivin or AquaMaris (in children, use a nasal aspirator to suck out mucus from the nose)
And also pay special attention to expectoration of sputum. If the baby is too lazy to cough, you can easily stimulate the release of sputum: the child is placed on his stomach and lightly tapped on the back (between the shoulder blades) with the pads of the fingers, ensuring that the sputum comes out naturally
The first thing to do if a repeated rise occurs is not to panic and act according to the symptoms. First, you should make sure that ARVI has not developed into one of the possible complications. Only a doctor can determine this. Therefore, repeated high temperature is a reason to seek medical help (even urgent).
Possible reasons
Doctors say: the temperature of 39 degrees does not always rise due to the onset of the disease. The absence of symptoms often makes a quick diagnosis difficult. But there are always indirect signs that help parents determine the cause.
⇒Overheating
Fever in a young child may occur due to general overheating of the body. To do this, it is not at all necessary to leave the stroller under the scorching sun. The reason is simply wrapping the baby up.
Main signs of overheating:
• Hyperthermia, • Redness of the skin, • Sweat on the palms, neck, and back of the head.
Temperature without symptoms due to overheating rises in the evening and lasts 1-2 days. If you notice that your baby is hot, immediately remove his wet clothes. Replace it with a dry, cooler one. Wash your child, be sure to give him water. When the condition normalizes, the fever will disappear on its own.
⇒Stomatitis
It appears in the form of ulcers on the oral mucosa. The disease is typical for children in the first year of life. Moms may not notice changes in their mouth until a fever occurs. With stomatitis, it reaches 38-39 degrees and lasts 4-6 days.
Signs of stomatitis: • The baby refuses to eat, • Constantly tries to put his hands in his mouth, • Becomes capricious and irritable.
A medical examination helps identify stomatitis. The pediatrician prescribes a simple treatment, as a result of which the children fully recover within 7-10 days.
⇒Growing teeth
The baby's first teeth are often accompanied by a high temperature (up to 39 degrees) without symptoms. In children 6 months. – 2 years old, very sensitive gums. Teething causes inflammation, causing discomfort and causing hyperthermia
Parents should pay attention to the following symptoms: • Excessive drooling, • Redness, swelling of the gums, • Restless condition of the child, • Refusal of the breast or solid foods
⇒Viral infections
Some infectious diseases begin without symptoms. Only high thermometer readings indicate that the virus has entered the child’s body. Common viral diseases (flu, ARVI) begin this way.
In addition to fever, the following conditions are noted: • body aches, • pallor, • lack of appetite, • headache, • redness, • painful sensations in the eyes.
If you suspect a virus, you need to provide the baby with rest, give more fluids, and call a doctor. He will prescribe antiviral drugs. Medicines based on paracetamol or ibuprofen will help cope with hyperthermia.
⇒Reaction to vaccination
Normally, the temperature after the administration of vaccines does not rise above 38 degrees and lasts no more than a day. Pediatricians advise reducing fever that occurs as a result of vaccination. To prevent such a reaction from occurring, it is recommended to give the child antihistamines 1-2 days before the vaccination.
⇒Stress
The child's immature nervous system responds with the appearance of hyperthermia to some external stimuli. These include: • Change of environment (adaptation period in kindergarten), • Sharp loud sounds, bright light.
In older children, a temperature of 39 degrees in the absence of other symptoms appears against the background of psychological discomfort. Strong excitement contributes to this. For example, before going to school or important competitions. Children are also sensitive to family scandals.
Since this is a nervous condition, it is necessary to calm the child. Give him water, wash him, try to put him to sleep. Minimize irritants. Keep calm yourself, too, children feel everything very well.
⇒Children's diseases
Rubella and chickenpox begin with the child’s temperature rising to 39 degrees. Only after 2-3 days a characteristic rash appears on the body. If the institution your child visits is quarantined for viral diseases, monitor his condition.
If a rash appears, call a doctor. You cannot go to the clinic yourself during this period. The diseases are highly contagious and are quickly transmitted through the air, so the sick person must be isolated from peers and adults who have not had “childhood” diseases.
Possible causes of asymptomatic fever
The main factors for asymptomatic fever are:
- Diseases caused by infection with pathogenic microorganisms, which are viruses, fungi, bacteria and parasites. In this case, it is advisable to begin treatment immediately, without waiting for the appearance of accompanying symptoms of this pathology and focusing on the nature of the temperature increase. When febrile fever occurs, when the temperature rises to 38-39 degrees, intoxication occurs with waste products of infectious agents. In this case, the development of diseases such as ARVI, influenza, and catarrhal tonsillitis is possible. Why else can a fever appear without cold symptoms?
- In an adult with various purulent inflammations, as well as with tuberculosis, as a rule, an abrupt occurrence of high temperature is observed.
- Its smooth decrease over several days may indicate the development of pathologies such as malaria and motor neuron disease. In addition, such phenomena are often observed in cases of dysfunction of the organs of the excretory system.
- Stable preservation of high temperature can be the main symptom of typhus and some others.
- Tumor formations. In this case, the use of antipyretic drugs does not have any effect, since the patient's febrile state is associated with pathological changes in the tissues of the affected organ.
- Injuries. Fever without cold symptoms in an adult in this case may be due to inflamed wounds, fractures, or after surgical interventions.
- Porphyria.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Hemolysis and blood diseases.
- Heart attack.
- Kidney inflammation. The temperature in this condition usually rises to 37-38 degrees and often this is the only sign of the disease. In case of pyelonephritis, it is not recommended to lower the temperature, since its increase indicates the fight against the disease with natural forces.
- Allergy. The increase in temperature without symptoms in an adult with allergic reactions is insignificant and intermittent.
- Inflammation and various systemic diseases, for example, autoimmune - lupus, periarthritis nodosa, scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, polyarthritis, allergic vasculitis, Crohn's disease.
- Development of meningococcal infection in an adult. The temperature without symptoms rises to almost 40 degrees, and it is practically impossible to bring it down, or it does go down, but for a very short period of time. Characteristic symptoms do not appear immediately. When this disease occurs, it is important to hospitalize the patient in a timely manner.
- Infectious endocarditis. The disease develops after a sore throat or flu. The temperature rises significantly, sometimes up to 40 degrees.
- Disruption of the hypothalamus. The causes of occurrence, as well as methods of treatment of this pathology are currently unknown. In this case, sedatives are most often used to reduce the temperature and eliminate symptoms.
- Mental disorders. For example, febrile schizophrenia is often accompanied by a characteristic febrile syndrome.
- Malaria. Fever may be accompanied by severe headache, severe trembling, coldness of the extremities, and delirium. Periodically, an adult’s high temperature decreases noticeably, and this occurs with a certain cyclicity of several hours or days.
- Endocarditis. This disease occurs against the background of inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, provoked by the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the body. The main signs of such a pathology are pain in the heart, profuse fetid sweating, and intoxication of the body. The fever is constant or hectic in nature.
- Various blood diseases, for example, lymphoma, leukemia. In addition to an increase in body temperature, phenomena such as skin rash, sudden weight loss, and intoxication are often observed.
Why does an adult have a fever without symptoms?
Should I give an antipyretic at 38?
No parent can calmly watch as his child is overcome by symptoms of a disease that make him suffer. Therefore, you need to decide to urgently see a doctor, and before being examined by a specialist, do everything to help the baby.
The general practice is this: the temperature is not brought down to 38.5 in 4-year-old children; above that, it requires reduction with antipyretics. But that’s why it’s a general practice, and every child is individual! In short, when a child does not tolerate heat well, then it is necessary to reduce the temperature below the specified threshold, but if it tolerates it normally, is active, not drowsy and does not have chronic diseases that can be negatively affected by hyperthermia, then such a fever is up to 38.5℃ no need to reduce.
In addition to antipyretic drugs, there are several options that will alleviate the child’s condition:
- Medicines do not always bring the temperature back to normal. Medicines will help the child alleviate the condition and feel comfortable, but they do not eliminate the cause of the disease. Lowering the temperature by a couple of degrees does not relieve the feverish state. After all, elevated temperature is a manifestation of the body’s fight against an infectious virus, since in a normal environment pathogenic microbes can exist and develop.
- The antipyretic drug should be appropriate. To do this, it is better to consult a doctor, since at different ages children’s bodies perceive medications differently. To avoid problems with the gastrointestinal tract, you should carefully choose medications to reduce fever.
- You cannot give several types of antipyretics at the same time. Mixing medications is strictly prohibited, as this may cause an overdose of the drug contents in the body.
- You must carefully follow the instructions for using the drug. The dosage must be correctly calculated, which is based on the baby’s weight. Medicines for children often have a measuring stick in the package that will help you correctly determine the right dose.
Why is a temperature of 39.5 °C dangerous?
An increase in temperature to 38.5 °C and above can be dangerous for the body, especially if hyperthermia occurs in early childhood, when the thermoregulation mechanism is imperfect and the immune system functions differently than in an adult1,3. The risk of complications increases as the temperature approaches the critical level. Severe hyperthermia can disrupt the functioning of the brain and nervous system, provoke the development of cardiovascular diseases, seizures, and respiratory arrest, especially in people with chronic pathologies, a tendency to blood clots and shortness of breath1,3,5.
It is also worth remembering the risk of dehydration as your body temperature rises. In addition to taking antipyretics, it is necessary to expand the drinking regime1 in order to promptly replenish the lack of fluid.
Increase in temperature due to overheating of the baby in the sun
The child reacts to the slightest changes in the external environment, since the system responsible for thermoregulation has not yet fully adapted. Hyperthermia can develop due to the onset of summer heat, and a baby can overheat at any time of the year, since many mothers wrap their children up excessively. In this case, the temperature can reach 38-38.5 degrees, the baby begins to worry, be capricious, and cry. In this situation, you only need to do a few simple steps. If a child overheats outside, you need to place him in the shade or take him home. The room needs to be well ventilated. Then you need to change the child into light clothes and wipe the skin with a towel soaked in cool water. It is also worth providing your baby with plenty of fluids, and soon the signs of overheating will disappear.
A 6-month-old child has a fever without signs of a cold.
Tatyana Timofeeva
Actually, there is no need to shoot down 38.2. How will it exceed 38.5? Dilute a couple of tablespoons of vinegar (not essence!!!!) in 1 liter of cool water and wipe the baby. Especially in places where arteries are close (neck, groin, armpits_) Do not cover. You can use a light sheet. Give children's paracetamol (Panadol). If the temperature suddenly rises sharply, fill the bathtub with water (summer temperature) and put the child in the water, rinse him with cool water for about 5 minutes.
Marina Petranova
let him drink more, 38.2 is a high temperature, unlikely due to overheating. I sprayed mine with Tantum at 9 months, it was fine. Erespal is more for an allergic cough. If it rises to 38, it’s better to call an ambulance, let another doctor take a look. If I were you, I’d play it safe; the children’s temperature rises very quickly and convulsions can begin, and a nurse is still not a doctor (I’m a nurse myself), but I always listen to doctors, especially if children are sick.
%-) %-)
Mariska
We are 1.3 the other day, the same thing, no signs of a cold, but the temperature was 38.7 and in the evening it rose to 39.3. I lowered the temperature with an etheralgan candle and wiped it with a cool solution of water and alcohol. The next day there are no signs of temperature or anything, it's just overheating.
Gorishka
We also had it at six months - the temperature stayed at 37 - 37.2 for about 4 days. It turned out that the thymus gland was enlarged... consult your pediatrician, maybe he can prescribe an ultrasound....
Temperature 37 without symptoms: causes
A runny nose, fever, and sore throat are all common symptoms of a common cold. But what to do if the temperature is 37 without symptoms? For what reasons does this occur and how to deal with it, let's figure it out.
Causes of fever without visible symptoms:
- The onset of pregnancy in women.
- Weakening of the immune system.
- The presence of any sluggish infection in the body.
- Pre-cold condition.
- Depletion of human energy reserves.
- General fatigue, depression or post-stress state.
- Sexually transmitted diseases (syphilis, AIDS).
Basically, a temperature of 37 without symptoms in an adult is due to the fact that there is some reason that caused such a condition, but it has not completely overcome the person’s defenses.
Doctor Komarovsky about temperature without symptoms
Dr. Komarovsky advises parents to remain calm if the temperature rises sharply and there are no other signs of illness. In most cases, this symptom is observed in the summer, when it is hot outside. To reduce the body temperature, it is necessary to dress the child in light clothing or completely undress. He needs to ensure peace (stop running, jumping, etc.). The patient should be placed in a pre-ventilated room.
To make breathing easier, you should do wet cleaning. In a stuffy room, it is necessary to ensure air circulation. If comfortable conditions are created, then after 10-15 minutes the thermometer will drop.
Due to the fact that not all diseases immediately manifest as deterioration in well-being, parents should carefully monitor the patient’s condition. If the child continues to have a fever and redness of the epidermis appears (or does not go away), this may be evidence that the body has been exposed to a viral infection. Pale skin and general weakness are also symptoms of the disease.
In most cases, Dr. Komarovsky does not recommend giving a patient an antipyretic if the thermometer shows a temperature no higher than 39°C (but there are exceptions). You should not wait for other symptoms to appear, but consult a doctor immediately. People who do not have medical education are not always able to recognize subtle signs of illness. Therefore, they may not even imagine that it could be, for example, a helminthic infestation.
Self-medicate, i.e. The patient should be given an antipyretic drug when it has exceeded the safe limit. Other medications, such as antibiotics, should be prescribed by a doctor after diagnostic testing. But, if during illness the patient has a temperature in the range of 37.5-38.5 ° C, he is lethargic, refuses and shows apathy towards everything around him, he can be given an antipyretic drug. Refusal to drink is also a reason for the child to take medicine. All children are individual, so they tolerate increased body temperature differently.
Evgeniy Olegovich recommends that parents have Ibuprofen and Paracetamol in their home medicine cabinet. These medications can reduce the temperature to a safe level. If a child has a temperature of 39°C without symptoms, he is provided with peace and comfort, and antipyretic drugs do not help, you must call an ambulance. Refusing medical care is dangerous for the health and life of the patient.
What temperature is considered normal?
In a healthy person, body temperature can vary during the day within the range of 35.5°C-37.4°C. At the same time, the place where it is measured is important, because the normal value of 36.5°C is usually determined in the armpit. When measuring the temperature in the mouth, the thermometer will show 37°C, and in the ear and rectum - up to 37.5°C. However, an increase in indicators to 38°C is always alarming. This reaction can be provoked by various factors that have a negative impact on the human body.
Giving help
Parents can provide first aid if the temperature rises to 39°C on their own before a doctor comes to the house. Help consists of providing the patient with plenty of warm drinks, a regularly ventilated room, and taking antipyretic medications.
Before giving your child antipyretics, it is better to consult a specialist about the dosage, taking into account the age and body weight of the patient. After about 60 minutes, the medicine will begin to work and the baby will feel better.
Providing plenty of warm fluids is important as this will ensure that the body does not become dehydrated. After all, the body of children aged 9 years needs fluid necessary for the functioning of all organ systems
Warm water, tea, herbal infusion or compote are ideal for drinking. It is not necessary to force your baby to eat; he will ask for it himself when he has an appetite.
It is strictly not recommended to provide your baby with a hot bed, wrapping him in a warm blanket and wearing hot clothes. Intense sweating requires changing from wet clothes to dry ones.