Serum sickness is a condition of the body that is a form of allergic reaction. It develops in some people after the parenteral (injection) introduction of a certain type of drug - immune serum of animal origin - into the body for therapeutic or prophylactic purposes.
What is serum sickness?
Serum sickness is a systemic allergic reaction that develops with sensitization to foreign proteins due to their entry into the body with serum, vaccines, medications, and blood components.
It is characterized by the fact that predominantly inflammatory damage to blood vessels and connective tissue occurs. Serum sickness is a special case of type III hypersensitivity.
The mechanism of development of serum sickness is the formation of circulating immune complexes (type III allergic reactions according to the classification of Coombs and Jell). If a drug is administered to a child for the first time, the baby’s body regards it as foreign and promotes the production of specific antibodies, which are classified as immunoglobulins.
At this time, there may be no clinical manifestations, but if there is a subsequent supply of this medication, then antibodies and antigens contribute to the formation of immune complexes. They circulate in the body, attach to blood walls, and increase their permeability. Neutrophils that reach immune complexes contribute to the occurrence of inflammatory reactions such as vasculitis. Because of this, internal organs are affected: kidneys, heart, pulmonary arteries.
Serum sickness was first described in the works of the Austrian immunologists Pirquet and Schick in one thousand nine hundred and five. Patients receiving drugs that were made from horse serum had similar clinical symptoms - fever, skin rashes like urticaria, pain in the joints and nearby lymph nodes (relative to the site where the injection was given).
At the time of these scientists, if patients were injected with anti-rabies horse serum (for rabies), serum sickness developed in 95 - 100% of cases. Due to the fact that the technology of its production was gradually improved and certain precautions were observed when administering this serum, the probability of the occurrence of this disease decreased to 15 - 20%. But, nevertheless, this figure is unacceptably high, because of this, the indications for its use are constantly being revised.
Pathogenesis
Serum sickness is characterized by an immunocomplex type of allergic reactions. In this case, in response to the first administration of a vaccine or serum, specific antibodies are synthesized in the body, which, upon repeated contact with the allergen, form circulating immune complexes that are fixed on the inner wall of blood vessels. Subsequently, the pathological process leads to the activation of complement; its components (C3a, C4a and C5a) cause an increase in vascular permeability, attract neutrophils to circulating immune complexes, resulting in the development of an inflammatory process similar to systemic vasculitis. The most common lesions are the vessels of the kidneys (renal glomeruli with the development of glomerulonephritis), as well as the coronary and pulmonary arteries.
Causes of serum sickness
Serum sickness develops when:
- intravenous administration of the drug. Most often it occurs after the child has received an intravenous injection. Serum sickness can also develop if the baby is given a drug intramuscularly or subcutaneously, but the frequency of its occurrence and symptoms will be less pronounced.
Serum sickness almost never occurs with oral administration of the drug;
- reuse of medications. With each new administration of the drug and the prescription of course therapy, the risk of this disease increases.
If a child has an allergic reaction to any drug, be sure to tell the pediatrician about it! Because more serious complications may develop with repeated use of medications;
- large quantities of medicine. Depending on the amount of medication administered, the risk of this disease increases or decreases. When using large dosages of drugs, the development of this disease increases;
- poor quality of the drug. If the drug has a high level of purification and has passed quality control, then serum sickness occurs less frequently;
- hereditary predisposition. People who have a hereditary predisposition and a tendency to other allergic diseases are more likely to suffer from serum sickness.
Origin and development of the disease
The main function of the body's immune system is to protect against the entry of foreign proteins, microorganisms and toxins, that is, to maintain homeostasis. The immune system is able to recognize an antigen (a foreign substance that has entered the body) and destroy it. Immediately after the antigens enter, antibodies begin to form.
The process of interaction between antibodies and antigens aimed at their destruction is called an immune reaction.
Serums and some pharmaceutical preparations containing animal and plant proteins can be perceived by the immune system as antigens, resulting in an allergic reaction, that is, an excessive immune response, if there is increased sensitivity.
The way the drug is administered to the patient is of great importance. With intravenous injections, the pathological process is detected more often than with intramuscular or intranasal injections.
What are the stages in the development of serum sickness?
- Incubation period. Its duration is seven to fourteen days. During this time, immune complexes are formed and inflammatory processes are launched. If the drug is reintroduced to the child, the duration of this period is shortened and takes from several seconds to one day, in this case the allergy occurs in the form of an anaphylactic reaction.
- Prodromal period. At this time, the first symptoms of the disease appear, but there is no obvious clinical manifestation yet.
- Acute period. Its duration is five to seven days.
Principles of treatment
The management of patients with serum sickness depends on the severity of the pathological process.
- Persons suffering from a mild form of the disease can receive treatment on an outpatient basis. It involves taking antihistamines and corticosteroids in a short course.
- Patients with moderate and severe forms of serum sickness are hospitalized in a hospital. They are prescribed bed rest, a hypoallergenic diet, higher doses of hormones, antihistamines, and symptomatic therapy. In case of protracted course of the disease, hemosorption methods are used.
Forms of serum sickness
Depending on the intensity of clinical manifestations, there are 4 forms of serum sickness.
- Mild form , which is characterized by an increase in body temperature to 38°C, the appearance of angioedema, a slight increase in lymph nodes, and skin changes in the form of an urticarial rash. The general condition of the child is not affected.
- Moderate severity, it is characterized by the fact that the child develops redness, swelling, itching, and an urticarial rash around the place where the antigen was injected, as well as enlarged regional lymph nodes. There is an increase in body temperature to 38 – 39°C. One in two children develop headaches, joint pain, and tachycardia.
- A severe form, which is characterized by the appearance of a morbilliform and hemorrhagic rash, shortness of breath, a drop in blood pressure, and an increase in body temperature (in some cases up to 40°C). Joint pain and swelling may occur. Often children with this form develop synovitis and neuralgia. The general blood test will show the following changes: leukopenia, moderate lymphocytosis, thrombocytopenia, decreased blood clotting, increased ESR.
- Anaphylactic form. It occurs when serum is reintroduced to a child. In this case, there is a sharp increase in body temperature, a drop in pressure, first there is stunning, and then excitement and convulsions. It is also characterized by the occurrence of cyanosis, shortness of breath, and in some cases, death.
Depending on the form of serum sickness, the body’s reactivity and proper treatment, its duration will vary. If a child has a mild course of the disease, he can recover in one week. In severe cases, recovery most often occurs within one to two weeks. The occurrence of relapses most often occurs due to the subsequent introduction of an allergen or the manifestation of autoallergic processes.
Diagnosis of the disease
As a rule, making a diagnosis of serum sickness is not difficult.
The clinical picture is quite characteristic; moreover, the onset of symptoms is preceded by the administration of a drug that contains protein molecules.
If skin rashes are severe, it is necessary to make a differential diagnosis with certain infectious diseases, for example, scarlet fever and measles.
A severe form of the disease can be difficult to distinguish from sepsis based on its clinical picture. A blood test and examination of its sterility can help make a correct diagnosis.
Symptoms of serum sickness
Serum sickness symptoms can vary. After the incubation period has passed, and in most cases it does not manifest itself in any way, its first signs begin to appear. During the prodromal period, “minor symptoms” occur. The skin becomes slightly reddened, and is also characterized by the appearance of a rash in the place where the medicine was administered, and enlargement of the lymph nodes.
In the acute period, characteristic signs are:
- elevated body temperature. It most often increases to 38 ºС, but in some children up to 39 – 40 ºС. This reaction of the body also causes stiffness and pain in the joints;
- presence of rashes. Subsequently, the appearance of an urticarial rash is characteristic, which is accompanied by severe itching. Due to the fact that the rashes are polymorphic, they can be confused with allergic and infectious diseases. At the onset of the first symptoms of serum sickness, it resembles measles, scarlet fever, and urticaria. A distinctive feature is that if the child has serum sickness, then the rash will be at the injection site;
- presence of articular manifestations. When rashes appear, the temperature immediately decreases, but the stiffness of movements increases, a feeling of pain and swelling in the knee, ankle, and wrist joints is added;
- circulatory disorder. It occurs when rashes appear. The patient develops swelling on the face, the lymph nodes become enlarged, and they become slightly painful when touched. Some children have an enlarged spleen;
- the appearance of heart disease. With serum sickness, myocarditis, ischemia, heart attacks, etc. can be diagnosed. These manifestations occur due to damage to the heart muscle. The child complains of chest pain, shortness of breath with previous exertion, and a feeling of palpitations;
- the occurrence of digestive disorders. In severe cases, the digestive system is affected and diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, and abdominal pain develop;
- the occurrence of diseases of the urinary system. This occurs due to damage to the tissues of the kidney vessels by immune complexes, resulting in a chronic inflammatory process - glomerulonephritis. Over time, the disease progresses, causing renal failure and edema syndrome to develop;
- the presence of lesions from other organs and systems. If the process spreads further, serious illnesses occur. For example, if it affects the lungs, it is characterized by the appearance of emphysema and pulmonary edema. If the liver is damaged, hepatitis occurs, and if the nervous system is damaged, neuritis and meningoencephalitis occur.
Depending on the form and course of serum sickness, the symptoms of the disease will change. If the child has a mild course, only disturbances in health, slight fever, and rash may occur. In half of children, the disease occurs this way, and with proper treatment, the baby recovers quickly. If a child has a moderate or severe course of the disease, the symptoms are more pronounced and other organs and systems are affected. In these cases, severe neurological complications and death are possible.
Complications
The most dangerous complication of a pathological reaction to serum is anaphylactic shock, which most often develops if the serum is reintroduced to the patient.
The main symptoms of anaphylactic shock include:
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- the appearance of seizures;
- fainting with involuntary urination and defecation.
Anaphylactic shock is a dangerous condition that threatens the patient’s life. Therefore, when it develops, immediate hospitalization is necessary.
After the patient is brought out of the state of shock, he should be hospitalized, since within 3-5 days a repeated sharp decrease in pressure is possible to alarming values.
It is fraught with the development of complications such as: myocarditis and endocarditis, nephritis, meningitis, etc. Therefore, you should not self-medicate and try to relieve the symptoms of the disease yourself. This can lead to unpredictable consequences. In severe cases of the disease, hospitalization is indicated.
Death from serum sickness is extremely rare. In the majority of reported cases, patients died due to anaphylactic shock, the development of which was not promptly provided emergency care.
The most informative methods for diagnosing serum sickness
Diagnosis of serum sickness is carried out using:
- collecting anamnesis. In this case, it is necessary to identify allergic diseases or a tendency to their occurrence. You also need to find out whether the serum or vaccine was administered on the eve of the onset of symptoms of the disease;
- inspection. The diagnosis is made by an allergist after examining the child. He pays attention to where the rash is located, what it looks like and how it spreads on the skin;
- laboratory research. In the prodromal period, the blood test will show: leukocytosis and a slight increase in ESR, and at the height of the disease - leukopenia, relative lymphocytosis, high ESR. In some children, platelets and blood sugar levels decrease. There may also be an increase in the concentration of C-reactive protein, a decrease in the concentration of components C3 and C4 of the complement system, an increase in transaminases and the concentration of circulating immune complexes. In a general urine test, a child is characterized by the appearance of protein, microhematuria, and hyaline casts. These changes occur due to the fact that the glomeruli of the kidneys are affected;
- histological examination of skin biopsy (carried out only in doubtful cases).
Diagnostics
After any signs of serum sickness occur, contact an allergist. To establish an accurate diagnosis, a blood test is taken, which determines the amount of immunoglobulin E, eosinophils and other standard indicators.
Diagnosis is based on the characteristic acute manifestations inherent in the disease. It can be similar to some infectious diseases, so differentiation must be made.
Polymerase chain reaction and serological methods are highly informative. These diagnostic tests provide an answer about the amount of antibodies. If, through the tests described above, the assumption of the development of serum sickness has been confirmed, X-ray, ultrasound and other examinations are prescribed.
Treatment of serum sickness in children
The chosen treatment method depends on what form of serum sickness the child has. But it is mandatory to discontinue the medication that caused the allergic reaction. To quickly remove the antigen and get rid of the effect of this drug, it is necessary to prescribe infusion therapy, sorbents and a cleansing enema.
The main thing in the treatment of serum sickness is also the appointment:
- antiallergic drugs to reduce itching (Zodak, Erius);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They are used to reduce body temperature and joint damage. These include: Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Voltaren;
- glucocorticosteroids. If the heart, blood vessels, and nervous system are affected, because they have anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- symptomatic therapy. If necessary, diuretics, painkillers and other medications are prescribed.
Causes and mechanisms of development
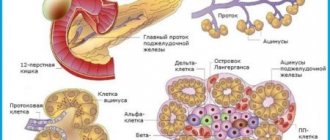
Even insulin injections can lead to serum sickness, since this drug contains proteins of animal origin.
The immediate cause of the development of this type of drug allergy is the introduction of certain drugs into the body:
- heterologous protein preparations (antitoxic serums against botulism, diphtheria, staphylococcal infection, tetanus);
- homologous protein drugs (antilymphocyte sera, immunoglobulins, whole plasma);
- vaccines and toxoids;
- poisons of snakes and insects;
- medications containing animal proteins (insulin).
This pathology is based on the deposition of circulating immune complexes in the vascular wall and tissues, which causes impaired vascular permeability and inflammation. These changes are a complication of serum therapy.
Normally, a few days after the administration of serum, antibodies begin to be produced in the blood, which bind the antigen and form circulating immune complexes. They persist for a long time in the bloodstream and are slowly eliminated by the phagocyte system. As the titer of protective antibodies increases, larger complexes are formed, which are deposited in tissues and then destroyed. This activates the complement system. The immune complexes are then bound by red blood cells, delivered to the liver and excreted from the body. In serum sickness, disruptions can occur at various levels of this process.