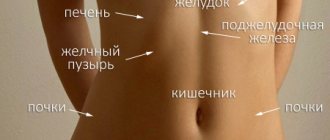
Causes of abdominal dropsy
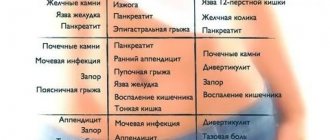
Dropsy of the abdomen (or ascites) is a concentration of free fluid in the abdominal cavity, usually occurring as a result of severe and inadequately treated liver diseases, for example, cirrhosis. Ascites is manifested by a significantly increased volume of the abdomen. It may occur suddenly or develop gradually over several months. Whatever the period of development of the pathology, it will certainly be accompanied by a feeling of bursting heaviness and pain in the abdomen, and flatulence. If the dropsy of the abdomen acquires impressive dimensions, the patient will begin to observe:
- difficulty bending the body,
- shortness of breath when walking,
- swelling of the legs.
With a large amount of ascitic fluid, additional symptoms appear such as:
- umbilical and inguinal hernias,
- varicose veins of the leg, and hemorrhoidal veins,
- diaphragm shift up,
- heart displacement,
- increased pressure in the jugular vein.
Ascitic fluid is like a plasma ultrafiltrate, since its components are in dynamic equilibrium with plasma components. Within an hour, 40-80% of ascitic fluid is exchanged with plasma.
Portal hypertension and associated portal vein congestion are considered serious factors predisposing to the development of ascites. Increased sinusoidal hydrostatic pressure during intrahepatic portal hypertension causes increased extravasation of protein-rich filtrate through the walls of the sinusoids into the spaces of Disse. The intrahepatic outflow block causes an increase in lymph production in the presence of liver cirrhosis. According to pathological and clinical observations, with cirrhosis of the liver, the number of subcapsular, intrahepatic and efferent lymphatic vessels significantly increases, however, their walls are thinner, and the lumen is filled with lymph. The enhanced functioning of the lymphatic system helps to unload the venous network, but subsequently dynamic lymph circulation insufficiency develops, which means there is a risk of fluid leaking from the surface of the liver into the abdominal cavity.
Diagnostics
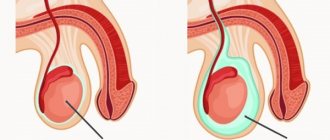
The success of hydrocele treatment depends on the success and timeliness of the diagnosis. Timely diagnosis can increase the chances of successful treatment of hydrocele in men.
To make a preliminary diagnosis, the following diagnostics are carried out:
- physical examination and imaging to detect hidden pathologies;
- consultation with a specialist to rule out tuberculosis;
- consultation with a surgeon to exclude an inguinal-scrotal hernia.
Additional diagnostic tests:
- Ultrasound – the cause of appearance and size assessment;
- sonogram – clarification of the size and contours, the presence of a tumor, the condition of the lymph nodes and appendages;
- CT and MRI in the presence of a tumor;
- PCR tests;
- laboratory tests for UAC and OAM;
- spermogram;
- tumor markers hCG and AFP;
- other laboratory tests.
At the stage of diagnosing the disease, it is important to distinguish between inguinal hernias, testicular tumors and dropsy. Ultrasound is used for this. A complete analysis of morphological studies allows us to confirm the final diagnosis.
How to treat dropsy of the abdomen?
Treatment of abdominal dropsy in a hospital involves adherence to a regimen and diet with dietary sodium limited to 2 g per day. Usually, under these conditions, within a week it is possible to outline the tactics for further management of the patient and determine whether he needs diuretics. Diuretics are not indicated if the patient has lost more than 2 kg of body weight during this time.
If weight loss is up to 2 kg over the next week, spironolactone (potassium-sparing diuretic) is prescribed, and only in the absence of positive diuresis are sodium-sparing diuretics used. Saluretics (loop diuretics) reduce the reabsorption of sodium and chlorine ions at the level of the ascending segment of the loop of Henle and the proximal segment of the distal tubule of the kidneys; at the same time, to a lesser extent, but also the reabsorption of potassium is inhibited.
General principles of diuretic therapy.
- prescribing the smallest dose of diuretics at the beginning of therapy in order to minimize the likelihood of side effects;
- ensuring a slow increase in diuresis without the risk of losing large amounts of potassium and other vital metabolites.
The following indicators are monitored:
- body mass;
- abdominal circumference;
- daily urine volume;
- neuropsychic status;
- blood serum parameters (creatine, sodium, potassium).
The dose of diuretics is selected under the control of the patient’s weight. In the absence of positive diuresis in a patient on bed rest and a salt-free diet, aldactone is prescribed, maintenance doses of which are prescribed for months and years.
The lack of effect when using anti-potassium diuretics is an indication for the use of thiazide diuretics (furosemide, Lasix) in combination with aldactone or potassium chloride. It is advisable to prescribe triamterene for metabolic alkalosis caused by other diuretics. If diuresis is below optimal, then the dose of saluretics is increased or stronger or other drugs from the same groups are prescribed.
Combination therapy for abdominal dropsy is usually supplemented with drugs to improve liver cell metabolism and protein agents. In clinical practice, it is better to use native concentrated plasma and a 20% albumin solution. Therapy with protein drugs helps to increase the albumin content and colloid osmotic pressure of plasma.
Tense ascites is a condition when the patient’s abdomen is tense due to ascites and requires rapid unloading to reduce the risk of complications: rupture of the umbilical hernia, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Therapeutic tactics for tense ascites involve paracentesis with the evacuation of large volumes of fluid, followed by the prescription of a diet. Evacuation of liquid in an amount of 4-6 liters is considered safe. If necessary, albumin or colloidal solutions are subsequently administered intravenously.
Ascites is called refractory (persistent) when there is no positive effect on the sodium-restricted diet and high doses of diuretics. The causes of persistent abdominal hydrops are the addition of hepatorenal syndrome, Budd-Chiari syndrome, liver cancer, and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis to liver cirrhosis. Usually, the presence of refractory ascites can be judged after 4 weeks from the start of treatment, if it meets all standards.
If ascites cannot be treated according to a program agreed upon with the physician, provided that the patient strictly follows all instructions, then other methods are used to control the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, in particular abdominal paracentesis. It is carried out to prevent strangulation of the hernia, bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract, and intractable shortness of breath. Subsequently, therapeutic paracentesis is performed. It is important, simultaneously with the removal of ascitic fluid, to administer a 10-20% albumin solution intravenously at a rate of 6-8 g for each liter of fluid removed. This is necessary to replenish circulating blood volume and maintain effective blood flow. Contraindications to paracentesis include infections, bleeding, and hepatic coma.
Treatment of abdominal dropsy sometimes requires surgical intervention.
In recent years, the operation of applying a peritoneojugular shunt with a Le Veen valve has proven its effectiveness in cases that are not amenable to conservative treatment of abdominal hydrops , in particular in various forms of portal hypertension. The operation involves subcutaneous implantation of a special valve connecting the abdominal cavity and the internal jugular vein using plastic tubes. Due to the pressure difference, a dosed flow of ascitic fluid into the venous bed is ensured, and retrograde blood flow into the abdominal cavity is impossible. The operation is not indicated for severe liver failure due to high operative mortality, as well as when there is a history of bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus.
For patients with persistent or recurrent ascites, the importance of paracentesis and peritoneojugular shunt is approximately the same. Both forms of treatment are not satisfactory. Operations of applying lymphovenous anastomosis between the thoracic lymphatic duct and the jugular vein with drainage of the duct are also not widespread.
Today, a new approach to the surgical treatment of ascites is being studied - transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting (TIPS). For ascites against the background of hepatorenal syndrome, vasopressin infusion and TIPS are indicated.
An alternative operation for patients with persistent abdominal hydrops is liver transplantation. It should be considered first when ascites appears. Its urgency is determined by the development of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. With the development of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, the issue of liver transplantation must be addressed urgently.
What diseases can it be associated with?
The pathogenesis of ascites, in particular in liver cirrhosis, is determined by several factors:
- portal hypertension,
- hormonal and neurohumoral imbalance,
- disturbances of water-electrolyte balance.
The presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity easily results in the development of:
- umbilical, inguinal, diaphragmatic hernia,
- esophageal reflux,
- erosions and bleeding in the esophagus and intestines,
- varicose veins of hemorrhoidal and calf veins.
Hypokalemia is the most common complication of abdominal dropsy and develops due to excessive removal of potassium from the body. The likelihood of hypokalemia is reduced with additional oral potassium or antikaliuretic drugs. Hyperkalemia is characterized by general weakness, signs of heart failure, and arrhythmia.
Increased excretion of potassium, sodium and chlorides when prescribing large doses of thiazide diuretics and excessive diuresis can lead to the development of metabolic alkalosis or worsening respiratory alkalosis.
Massive diuresis and too rapid removal of effusion from the abdominal cavity can cause renal circulatory failure.
Diuretics in rare cases can cause toxic and allergic complications - deafness, skin rash, gynecomastia, kidney damage, vasculitis, pancreatitis, agranulocytosis.
Hyponatremia is observed in 20-30% of patients with cirrhosis with ascites and is rarely clinically significant. The incidence of hyponatremia increases in parallel with the severity of liver cirrhosis. This complication negatively affects the quality of life of patients, since they require fluid restriction to restore serum sodium levels.
Types of rashes and locations on the child’s body
The rash occurs due to various reasons. It occurs with allergic reactions, infectious diseases, improper skin care, poisoning of various etiologies, insect bites, penetration of parasites into the body, mechanical stress, fungal infections, allergies. Depending on the cause of occurrence, there are different types of rashes on the body:
- spots of red, pink or white;
- pimples with clear liquid inside;
- pus-filled blisters or pustules;
- subcutaneous bumps;
- dry flaky spots;
- small bumps or papules;
- blue or red stars resembling subcutaneous hemorrhages.
What medications are used to treat dropsy of the abdomen?
Natriuretics:
- hypothiazide,
- chlorothiazide,
- furosemide (Lasix),
- brinaldix,
- ethacrynic acid (uregit).
Kaliuretics:
- spironolactone (aldactone, veroshpiron),
- triamterene,
- amiloride
The dose of diuretics is selected under the control of the patient’s weight. In patients with dropsy without peripheral edema, diuretics are prescribed in such a dose that the body weight loss is 500-750 grams per day; body weight loss of less than 300 grams per day is an indicator of ineffectiveness of therapy.
In the absence of positive diuresis in a patient on bed rest and a salt-free diet, aldactone is prescribed at a dose of 150-200 mg/day, after 7-10 days the dose is reduced to 100-150 mg/day, followed by maintenance doses (75-100 mg/day) over the course of months and years.
The lack of effect when using anti-potassium diuretic drugs is an indication for the prescription of thiazide diuretics (furosemide, Lasix) at a dose of 40 mg/day. Its administration is combined with aldactone 100 mg/day or potassium chloride 4-6 g/day. Once a pronounced diuretic effect is achieved and ascites disappears, they switch to aldactone in maintenance doses of 75 mg/day and furosemide in a dose of 40-20 mg once every 10-14 days.
Getting rid of hydrocele with herbs
Dropsy of the testicles in men can be cured with the help of an infusion of medicinal herbs. To prepare it, you need to mix dried sweet clover flowers and coltsfoot herb in equal proportions. For one serving you need to take a tablespoon of a mixture of these herbs, pour a glass of boiling water over it, cover with a lid and leave for up to half an hour. When the herbal mixture is infused, it must be filtered through thick gauze and the resulting liquid should be taken orally, 60 ml (4 full tablespoons) up to 5 times a day. Both components of the herbal infusion have anti-edematous properties, and, complementing each other, they contribute to the successful removal of excess fluid from the male scrotum. The course of treatment with sweet clover and coltsfoot should continue until complete recovery.
For the treatment of hydrocele with folk remedies, a medicine prepared from calendula ointment and any baby cream, taken in a 1:1 ratio, is suitable. A mixture of two components should be generously applied to the swollen scrotum every evening before going to bed, covered on top with a piece of sterile bandage folded in several layers, and then put on thick underwear made of natural fabric. The procedure must be repeated daily until the dropsy disappears completely.
To get rid of hydrocele, men use the following method: take 1 liter of high-quality white wine, add 100 g of agrimony herb into it, boil for five minutes, let cool to room temperature and filter through a thick sieve. Gauze, folded in several layers, is moistened in wine infusion and applied to the sore spot for half an hour. The number of procedures is 1-2 times a day. Compresses help remove excess fluid from the testicles.
The initial stage of testicular hydrocele can be successfully treated with chamomile flowers. Fresh flowers of the plant are best suited for this purpose. You need to make a paste out of them by passing them through a meat grinder. Crushed chamomile, wrapped in gauze, is applied to the swollen testicles for 20 minutes. The procedure should be repeated 2-3 times a day. Usually, with this folk treatment it is possible to completely get rid of small dropsy in 10 days.
Treatment of abdominal dropsy during pregnancy
Treatment of abdominal hydrops during pregnancy is carried out under the supervision of an experienced gastroenterologist who is aware of the woman’s situation. It is appropriate to collaborate with professionals from other medical fields, an obstetrician-gynecologist in particular. The treatment strategy for dropsy in a pregnant woman differs little from the standard one. The mechanisms and factors for the development of abdominal dropsy are taken into account. Based on the medical history of the disease, doctors can recommend that a woman terminate her pregnancy, but in the absence of indications for this, the most effective drug therapy that is safe for the fetus and mother is chosen. Having overcome dropsy of the abdomen, doctors see the need to treat the woman further for the disease that caused the dropsy.
VIDEO: Get rid of leg swelling in 5 minutes
Source
Dropsy on the hands is not only a cosmetic problem. It provokes unpleasant sensations. Against its background, other disorders are often observed that worsen a person’s condition. It is necessary to identify the exact cause of the appearance of a cosmetic defect in order to get rid of it. This can only be done when going to the hospital. Self-treatment will only worsen the situation.
To get rid of pathology, it is necessary to identify its cause.
Which doctors should you contact if you have abdominal dropsy?
- Gastroenterologist
- Hepatologist
Detection of a significant amount of free fluid in the abdominal cavity (more than 1.5 liters) does not cause difficulties and is performed using conventional clinical methods. Percussion for patients with dropsy will show a dull sound over the lateral areas of the abdomen and intestinal tympanitis in the center. Moving the patient to the left side will provoke the movement of a dull sound downwards, and it will become noticeable over the left half of the abdominal cavity, the tympanic sound will be in the area of the right flank.
Changing the position of the patient will not demonstrate changes in percussion if there is encysted fluid due to adhesive peritonitis of tuberculous etiology or an ovarian cyst.
If a small volume of abdominal dropsy is suspected, percussion is used with the patient standing - it will demonstrate a dull or dull sound in the lower abdomen, which will disappear when the torso is moved to a horizontal position. For small volumes of ascites, it is advisable to use a palpation technique called “fluid fluctuation” - the doctor applies intermittent pushes on the surface of the abdomen with his right hand, and the palm of his left hand feels a wave transmitted to the opposite wall of the abdomen.
Small amounts of fluid in the abdominal cavity will be shown by both ultrasound and CT scans.
To more accurately determine the amount of ascitic fluid, 5 ml of a 5% solution of bromsulfalein is injected intraperitoneally, by determining the concentration of which in the ascitic fluid extracted after 2 hours, it is possible to calculate the total volume of ascitic fluid.
To clarify the nature of abdominal hydrops, Doppler ultrasound is used. This method allows you to evaluate blood flow through the portal, hepatic and splenic veins. Sometimes it is important to resort to laparoscopy and biopsy of the liver or peritoneum. In the last decade, in all patients with newly diagnosed ascites, especially if a tumor process or spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is suspected, diagnostic paracentesis is considered mandatory - under local anesthesia, a puncture is made in the lower right corner of the abdomen and up to 50 ml of fluid is extracted, its cytological and biochemical tests are performed research, culture. Direct culture of ascitic fluid eliminates false-negative results during microscopy due to the low content of microbial cells in ascitic fluid.
Essential for diagnosis is the assessment of the nature of the peritoneal fluid, determination of the content of protein, albumin, leukocytes and erythrocytes in it. Determination of the gradient between the content of albumin in the blood serum and ascitic fluid serves to determine the causes of abdominal hydrops.
Treatment of other diseases starting with the letter - c
| Treatment of varicose veins |
| Treatment of varicocele |
| Treatment of vasculitis |
| Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia |
| Treatment of vesiculitis |
| Treatment of chickenpox |
| Treatment of papilloma virus |
| Treatment of Epstein-Barr virus |
| Treatment of vitiligo |
| Treatment of hydrocele |
| Treatment of Volyn fever |
| Treatment of vulvitis |
| Treatment of knee dislocation |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.
Symptoms in children
Having understood the causes of dropsy of the brain, it is necessary to talk about the symptoms of this disease. Given the danger of the diagnosis, every parent should take the signs listed below very seriously.
So, let's look at the most common symptoms in children:
- the child’s head quickly grows and becomes like a ball;
- frequent and profuse regurgitation;
- developmental delay;
- pale skin;
- eye displacement, strabismus, decreased vision;
- convulsions and trembling of the limbs, chin;
- irritable behavior;
- throwing back the head;
- there is no pulsation in the fontanel; it rises significantly above the skull.
It is important to take into account that in older children, the head will not enlarge due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. This is explained by the fused bones of the skull. But the absence of a visual change in the child’s head, unfortunately, does not exclude the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid. If he has severe headaches, weakness, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision and hearing, then he should consult a doctor. In this case, the diagnosis can be confirmed or refuted only by performing a tomography.