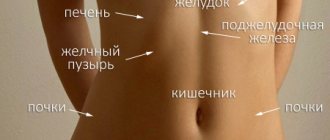
Specific pain in the lower abdomen, that is, a condition where the lower abdomen periodically hurts and sometimes aches, usually occurs in the intestines, stomach or urinary tract.
Symptoms often vary in severity, from really mild to extremely severe and intense pain combined with spasms and cramps.
Why does it hurt in the lower abdomen? There are certain reasons for these painful sensations. It is worth paying attention to some of the most well-known reasons, which we will talk about in this article.
Causes
In gynecological practice, one type of pain syndrome can manifest itself in over a dozen pathologies. They are similar in clinical manifestations, sometimes causing the need to take an analgesic to improve the condition.
The most common cause of lower abdominal discomfort in women is related to menstruation. The painful period is complicated by the pressure of the bladder on the uterus. Potentially aggravating the patient's condition:
- being in a stressful environment
- empty stomach cramps
- drinking alcohol or strong coffee on an empty stomach
- intimacy
- lifting weights
- insomnia caused by unpleasant sensations
Discomfort is felt with intestinal overcrowding, constipation and subsequent complications (for example, colon diverticulosis). Abdominal pain in women in the 2-3 trimester of pregnancy is explained by stretching of the abdominal muscles. Factors that provoke pain in the lower abdomen include pathologies of the genitourinary system, pelvic organs, and malignant neoplasms.
Pathology of the genital organs
These include inflammation of the uterus, ovaries, vagina, and fallopian tubes. Particularly dangerous conditions are included in the definition of “acute abdomen”.
The following pathologies cause pain and serious health consequences:
- Ovarian cyst. Intra-abdominal rupture of this neoplasm is accompanied by unbearable pain, often with loss of consciousness. Until emergency hospitalization, it is advisable to limit physical activity, which will help stop bleeding.
- Torsion of the uterine appendages. Diagnosed exclusively in women of reproductive age. Changing their position on the capillary base, torsions destabilize blood flow and cause acute pain with variable intensity. Accompanied by vomiting and nausea. Often, a dermoid active teratoma of the ovary is subsequently discovered. Dermoid consists of compacted connective tissue of a round shape with a mucous consistency inside. It is an indication for cystectomy, in the worst case – for wedge resection or oophorectomy.
- Chronic adnexitis, genital prolapse, preserved ovary syndrome. They cause dull, recurrent pain symptoms.
- Benign neoplasms in the muscular lining of the uterus: endometriosis of all histological varieties, fibroids. Compression of adjacent internal organs and pathological processes of the cyst itself cause symptoms of fibromyoma. Non-cancerous myometrial tumors cause the formation of secondary dysmenorrhea. With it, pain becomes systematic. Otherwise, the pain becomes unbearable, causing loss of ability to work and the need for emergency hospitalization.
In addition to pain in the lower abdomen, the above pathologies are accompanied by discharge, elevated body temperature, and fatigue. The diagnosis is confirmed by blood and urine tests: high levels of leukocyte volume indicate the presence of inflammatory processes.
Pregnancy and its complications
Pain is contrary to the full health of mother and child during pregnancy. It is necessary to differentiate your own sensations, determine the irradiation of discomfort that may arise during the development of:
- Ectopic pregnancy. If the pain is strong, cramping, up to loss of consciousness, with localization at a specific point and minor discharge. This condition is characterized by a sharp drop in blood pressure. There is a risk of rupture of the fallopian tube from 7 to 12 weeks, when pain spreads under the ribs or to the anus.
- Threatened miscarriage. If the pain is aching in nature, radiating to the lower back, lasts for several hours, accompanied by bloody discharge. In case of sudden attacks, the patient must be hospitalized immediately. Premature termination can be triggered by stressful situations, various types of trauma, physical activity, and fetal diseases.
- Flatulence, constipation or megacolon, if frequent pain in the lower abdomen is preceded by an incorrect diet. The diagnosis is confirmed by nausea or heartburn, vein thrombosis in the rectal areas. Such conditions prevent the full development of pregnancy, so it is recommended to carefully optimize the diet.
- Placental abruption. If the pain is very strong, increasing, and does not allow you to take a vertical position of the body. The lower abdomen is tense, and the risk of intrauterine hypoxia and subsequent death of the child is high. In this case, immediate medical attention is required.
- One of the pathologies from the “acute abdomen” group (pancreatitis, appendicitis) with the need for immediate medical intervention.
Diagnosis of abdominal pain
If you experience the slightest discomfort in the abdominal area, which lasts for several hours in a row and is not associated with menstruation, you should visit a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination. In no case is it recommended to relieve pain with analgesics and other drugs, or to perform significant physical activity, otherwise the disease will inevitably begin to progress. A medical examination usually consists of the following:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- taking a vaginal smear;
- CTG, ECG.
After identifying the disease, the doctor prescribes a specific treatment, which may include medications, injections, hardware and massage procedures. It is also necessary to follow the prescribed regimen to prevent deterioration of the body’s current condition and the development of complications.
Types of pain and their symptoms
When contacting a specialist, you need to describe to him in as much detail as possible the nature of the pain that has arisen and the symptoms accompanying it. Reproduction of the clinical picture simplifies the diagnosis process.
Pulsating
They have a cramping character upon palpation and are a consequence of various deviations in the development of hollow organs and the subsequent increased load on them. They accompany an ovarian abscess, when the formed purulent masses are the source of painful pulsation.
Permanent
They are observed long-term – from 4 months and longer. They provoke neurological disorders. Mycoplasmosis or chlamydia are often detected. In medical practice, the origin of symptoms is associated with psychogenic factors.
Paroxysmal
The duration of the discomfort is at least an hour, the character ranges from cutting-pulling to sharp-aching. The condition indicates a potential ectopic pregnancy, ovarian rupture, inflammation of the appendages (adnexitis), and torsion of the cyst. Pain in the lower back. Refers to pain that requires immediate hospitalization.
Localized in a specific place in the lower abdomen
The reasons for the localization of pain in the left lower abdomen indicate diseases of the left kidney or left side of the intestine, as well as the internal genital organs:
- Diverticulitis. If detected late, it causes perforation of the sigmoid colon.
- Urolithiasis caused by the passage of stones through the urinary tract.
- Adnexitis.
- Worm infestation.
- Inflammation of the sigmoid colon.
- Inguinal hernia strangulation.
- Tubal pregnancy.
- Granulomatous enteritis.
- Ulcerative colitis.
A comprehensive examination of the entire abdominal cavity will allow the pathology to be correctly diagnosed. If the epicenter of pain is in the lower right side, there is a high probability of appendicitis. Etiology may also include: ulcerative right-sided colitis, cholecystitis, terminal ileitis, pyelonephritis, cancer, salpingitis. Less commonly – intestinal herpes, endometrial polyp, inflammation of the right ureter.
Gives to the lower back
Pelvic pain affects the sacrum, lower back, and often shifts to the vaginal area. Acute pain in the lumbar region with high fever and general weakness of the body occurs with appendicitis, megacolon, pyelonphritis, cholecystitis, rupture of an ovarian cyst or inflammation of the urethra. This condition of a woman can be caused by multiple reasons:
- gynecological
- psychogenic
- proctological
- urological
- vascular
- neurological nature
Chronic pain in the lower abdomen radiating to the lumbar region indicates the presence of a hidden disease, which must be stopped as soon as possible.
Give to the anus area
Such pain in a woman is not considered physiologically normal. They often manifest as rupture of the fallopian tube, ectopic pregnancy, and inflammation of the pelvic organs. The listed diseases require prompt medical intervention.
Natural pain
Includes the period of ovulation, menstruation, and also after childbirth (approximately 5-7 days). Some women are susceptible to psycho-emotional factors. As a consequence, the stomach may hurt, which is a neurological manifestation of vegetative-vascular syndrome.
Associated symptoms
Along with pain in the lower abdomen, the following may occur:
- Diarrhea, vomiting, fever, which occurs with inflammation of the appendages.
- Curdled vaginal discharge - with candidiasis, sexually transmitted diseases, long-term use of antibiotics or contraceptives. Lack of timely treatment can provoke cervical erosion.
- High temperature is a sign of hyperthermia, characteristic of ulcerative processes, dysentery, diverticulitis, cholecystitis, even venereal diseases. An increase in temperature above 38°C is an indicator of septic infection of the body. The condition occurs with peritonitis, apoplexy of an ovarian cyst, rupture of the abdominal aorta or fallopian tubes.
Hypothermia within 34-35°C is a harbinger of internal bleeding, an indication for prompt medical intervention.
Bladder diseases
The most common bladder disease in women is cystitis, characterized by inflammation of the bladder that causes cutting pain before, during and after urination. In this case, the urge to empty the bladder becomes quite strong, but when visiting the toilet, a very small amount of urine is released.
Against the background of cystitis or general infectious diseases, urethritis - inflammation of the urethra, and pyelonephritis - inflammation of the renal pelvis can develop. Against the background of these diseases, various problems with urination may occur, there may be an increase in temperature, weakness and aching pain in the lower abdomen.
Which doctor should I contact?
If a woman’s condition requires an independent visit to the clinic, it is recommended to begin her treatment in the therapist’s office. If necessary, the specialist will refer you to specialist doctors: a gynecologist, urologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist.
If the patient’s health is at risk and an ambulance has already been called, before its arrival the woman is advised to:
- Take a horizontal position in a quiet, ventilated area
- Place a heating pad with ice on your stomach for a maximum of 15-20 minutes. Warming up the sore spot is strictly prohibited.
- Do not take any medications on your own, except for No-shpa (maximum – 2 tablets)
- Connect an intravenous drip (if possible) with sodium chloride solution if there are obvious symptoms of internal bleeding. These include a blue tint to the face, rapid pulse, fainting
Before being examined by a doctor, you should not eat or drink. If necessary, moistening the lips and tongue with water is allowed.
Treatment
The scope of therapeutic intervention is determined by the type of diagnosis identified and the individual characteristics of the body. The doctor takes into account the day of the monthly cycle, which determines the use of antispasmodics.
The gynecologist selects gentle healing practices for the female body. Hormone therapy, antibiotics, analgesics, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Additionally, vitamin therapy is carried out. Surgical intervention is carried out only if there are indications (for peritonitis, rupture of the fallopian tube), and in case of ineffectiveness of conservative methods.
Pregnancy
During this period, every woman is very worried if pain appears, as it may indicate a threat to the baby. There are two types of pain:
- obstetrics;
- not obstetric.
Obstetric pain includes those that are a consequence of placental abruption, indicating an ectopic pregnancy or the risk of losing a child. In these cases, the pain will be cramping. In addition, bloody discharge may be present.
The presence of an ectopic pregnancy indicates the need for surgical intervention, which is aimed at removing the embryo along with the fallopian tube. This is the only treatment for this case.
Premature placental abruption can be caused by abdominal trauma or physical strain. May be present: bleeding, nausea and vomiting, weakness and pallor, the stomach becomes bloated.
Non-obstetric pain usually occurs from excessive strain on the abdominal muscles. Also causes are sprains of the ligaments that support the uterus.