Roles of the lymphatic system
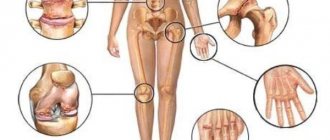
DIAGRAM OF THE HUMAN LYMPHATIC SYSTEM.
MOVEMENT OF LYMPH FROM THE PERIPHERY TO THE HEART The described phenomenon occurs with HIV due to direct damage to the human immune system by the virus. The lymph nodes are affected immediately, since the viral particles are divided in them. The infection mainly affects lymphocytes (T-helper cells). These cells are responsible for regulating the strength of the immune response.
Human lymph nodes with HIV infection do not undergo changes immediately after infection, but after some time. Typically this period is several months. The time for symptoms to appear depends on the strength of the immune system response and the viral load that the patient’s body has to fight.
Causes of enlarged lymph nodes
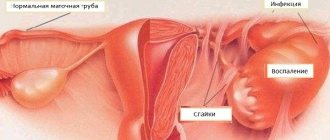
The lymphatic system in the human body is a collection of corresponding vessels and nodes that “stand guard” to cleanse the body of various harmful microorganisms (toxins, infection carriers, foreign bodies). The vascular system accumulates everything that the body does not need and moves “garbage” to the lymph nodes, where it is all destroyed with the help of cells of the lymphatic system.
The most common type of inflammation of the lymph nodes, which forces the attention of not only the patient, but also those around him, which forces the patient to consult a doctor
It is for this reason that when a virus or bacteria enters the body, the lymph nodes become inflamed. A similar reaction in practical medicine is called reactive lymphadenitis.
Fact! The course of some diseases is accompanied by local enlargement of nodes. For example, with ailments of the ENT organs, the patient’s submandibular, cervical and postauricular lymphatic angles are more often affected.
HIV affects the entire body as a whole, therefore, during infection, the viral load is distributed across all components of the system. This enlargement of lymph nodes during HIV infection is called generalized lymphadenopathy.
However, with the development of the disease in question, a weakening of the immune system and the development of local inflammation are observed. The latter can move to the lymph nodes, and they enlarge. This phenomenon is equated to lymphadenitis in acute or chronic form.
Lymphadenopathy in HIV is also observed due to the active growth of altered cells in the cavity of the nodes. The AIDS virus infects lymphocytes - these are the ones we are talking about. Atypical, malignant cells accumulate during the development of the infectious process - a tumor forms in the lymph nodes. This phenomenon is called lymphoma.
To summarize, it is worth saying that medical practice demonstrates the following probable causes of swelling of nodes:
- infection (bacterial, viral, fungal type);
- proliferation of parasitic microorganisms;
- systemic or autoimmune diseases;
- oncological diseases of the system.
Thus, lymph nodes can become enlarged and inflamed when the number of foreign objects in the lymphatic tissue increases dramatically. In response to this, the human body finds an additional resource in the emergency production of new cells of the immune system. The lymph nodes will inevitably increase in size.
Attention! Only if the enlargement of the nodes is not accompanied by redness and pain on palpation can we talk about lymphadenopathy. Otherwise, the symptom (manifestation of lymphadenitis) is highly likely caused by other inflammatory ailments that have joined the infection due to the lack of appropriate treatment at the initial stage of development of HIV infection.
Treatment
Treatment of lymphadenitis is complex, carried out therapeutically or surgically, additionally - folk remedies
It is important not only to prevent further spread of the inflammatory process throughout the body, but also to eliminate the primary foci of infection that led to the development of submandibular lymphadenitis.
Therapeutic treatment
It consists of prescribing to patients:
- Burov's fluid, which has an astringent, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect;
- saline solution as an antiseptic for rinsing the mouth, for example, when inflammation occurs against the background of chronic tonsillitis;
- antibiotics (cephalexin, clindamycin, amoxiclav, cefuroxime. These drugs have a number of contraindications, so they must be used in strict consultation with the attending physician.
Surgery
Prescribed for rotting lymph nodes. The operation is performed by making an incision in the lymph node capsule, inserting a drainage catheter, and removing accumulated pus.
Folk remedies
Not recommended for use without consultation with your doctor. Although some recipes can be quite effective when the disease develops at the initial stage of the disease or when the symptoms have already significantly subsided.
It is recommended to apply gauze bandages to the inflamed nodes at night by wetting them in an alcoholic tincture of Echinacea. For oral administration, you can dilute the composition in water (30 drops per 0.5 glass of water), take 2-3 times a day. It is also recommended to drink warm blueberry drink, ginger tea, beet juice, and garlic infusion.
Treatment with folk remedies is ineffective and dangerous when the nodes are filled with purulent contents. Even in the case of short-term relief of symptoms and achievement of the desired relief, the inflammatory process is able to continue its development again. If you suspect an illness, it is not advisable to self-medicate; it is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible, undergo the proposed examination procedures, and then the course of prescribed treatment.
Lymphadenopathy in HIV: why lymph nodes hurt
As a rule, the lymph nodes of an HIV-infected person are always enlarged. What about pain, do the patient’s lymph nodes hurt with HIV? As mentioned earlier, at the beginning of the development of the disease in question, namely with the onset of the first symptoms, the patient experiences lymphadenopathy. If, after some time, the patient becomes infected with other infectious, bacterial or fungal diseases, the human immune system cannot withstand the overload - lymphadenitis develops, which is accompanied not only by enlargement of the lymph nodes, but also by their inflammation. This process reveals itself as pain. Consequently, if the patient has the human immunodeficiency virus in the body, the lymph nodes on the body not only swell, but can also hurt.
Typically, the clinical picture of swelling of the nodes looks like this: the patient notices an impressive “bump” on the body. It is pliable to palpation, mobile and often painless. Typically, such growths are localized in different areas. We will discuss below exactly which lymph nodes enlarge on the patient’s body first.
Manifestations of lymphadenopathy are expressed in swelling of nodes up to 1-2 cm (diameter indicator). In rare cases, changes in the size of lymph nodes exceed this indicator. “Bumps” are usually dense, not connected to nearby tissues, but often represent conglomerates - formations in the form of fused nodes of a certain group. In this case, even in the absence of inflammation, slight pain may occur when you press on the area.
How long does generalized lymphadenopathy last? This period can last for several months or years with regular remissions and relapses that occur with AIDS in the lymphatic system. As the disease progresses, bacterial lymphadenitis or oncology may appear.
When HIV progresses in the patient’s body, the lymph nodes enlarge - this is a normal reaction of the body. Therefore, regardless of which part of the lymphatic system suffered the main blow, this symptom does not require special therapy. In case of immunodeficiency, HIV and related diseases are treated.
Pathologies of the submandibular lymph nodes
Hyperplasia of the submandibular lymph node occurs when the body is unable to eliminate harmful agents. In this case, bacteria or viruses attack the immune system and concentrate in it, provoking the development of the inflammatory process. Based on which glands are enlarged, the doctor can guess the etiology of this condition.
Causes of violation of the submandibular lymph nodes:
- diseases of the upper respiratory tract (laryngitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, etc.);
- pathologies of the oral cavity, dental diseases for which you need to see a dentist (caries, tooth abscess);
- infectious process (mumps, scarlet fever, chickenpox);
- blood diseases, for example, leukemia, lymphoma;
- inflammation of the salivary glands caused by tooth extraction;
- tumors of malignant and benign nature (cancer, arthenoma);
- tuberculosis;
- infected wound in the jaw area;
- purulent abscess;
- disorders of the immune system (HIV, systemic lupus erythematosus);
- diseases caused by parasites (toxoplasmosis).
If a person has caught a cold, the following pathological signs occur: the formation becomes dense to the touch and slightly increases in diameter, while maintaining mobility during palpation, pain occurs (often migrating to the ear or shoulder). When you turn your head, the immune system sometimes hurts. Other symptoms are often observed (decreased or absent appetite, slight chills, sleep disturbances). The development of a purulent process in the submandibular lymph node is accompanied by severe pain, even without affecting the affected area. The patient's body temperature rises, the skin in the affected area becomes red.
Lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis are different pathologies, the latter of which is accompanied by an inflammatory process. With lymphadenopathy, the formation increases in size, remains separate from adjacent tissues, and does not hurt on palpation. The skin over it has a normal color. Lymphadenitis develops when a node is damaged by bacterial waste products. In this case, the gland becomes painful, often merges with neighboring tissues, takes on a dense consistency, and sometimes conglomerates are observed. The skin over it becomes hot to the touch and red in color.
An enlarged lymph node located under the jaw indicates various abnormal processes. Based on the location of the inflamed formation, it is possible to guess what pathology is occurring in the body.
Where are the lymph nodes inflamed during HIV?
How quickly and exactly which lymph nodes enlarge with HIV depends on the ability of the patient’s immunity to resist the disease. If the patient’s immune function is compromised, lymphadenopathy can be observed at the very beginning of the development of the pathology and occur against the background of the disease and other associated infections, regularly appearing and disappearing.
The photo shows inflamed lymph nodes
In some cases, the swelling of the nodes is insignificant, they are almost invisible to humans. However, if you carefully examine the patient’s body, you can clearly state the fact that the main group of lymph nodes is enlarged.
The following lymph nodes are usually deformed:
- parotid;
- under the jaw;
- cervical;
- on the back of the head;
- under and above the collarbone;
- elbows;
- salivary
As a rule, these nodes are not easy to palpate. When infection occurs, they turn into denser formations, but retain their elasticity. Redness and pain are observed exclusively in the case of inflammation of the lymph nodes with HIV at the time of additional infections.
The nodes in the upper part of the body swell more often. These include lymph nodes in the neck, at the location of the salivary glands, submandibular, elbow, etc. Sick pregnant women may experience generalized lymphadenopathy. This is especially true in case of infection with the herpes virus.
Attention! If a patient notices a significant increase in the inguinal nodes of the lymphatic system, he needs to consult a venereologist, since such a symptom is highly likely to indicate an STD.
Many people are interested in how much the tissues in the neck and other places where nodes are localized are deformed and whether the changes will be noticeable to other people. The size of enlarged lymph nodes depends on the patient’s immunity, but significant swelling of the nodes is observed only in the last stages of HIV. If the course of the disease is also accompanied by associated inflammatory processes, “bumps” in the neck, back of the head, and jaw will be noticeable to others.
Under such circumstances, infected people have to “camouflage” deformed lymph nodes on the neck and other visible areas with the help of clothing and accessories.
Important! A single significant swelling of the cervical, submandibular, salivary lymph nodes is not a clear symptom of HIV. This can be observed in a number of alternative diseases, for example, damage to the eyelids and conjunctiva of the eye.
Principles of treatment of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes
The first rule to follow when detecting any changes in the condition of the lymph nodes, regardless of their location, is to do nothing until examined by a doctor and the cause of this situation is determined.
Inept and incorrect actions can only cause harm and aggravate the problem. What to do if the submandibular lymph node in the neck is painful, enlarged and swollen, regardless of the left or right under the jaw, how to cure it and what preventive measures to take, the doctor will tell you after receiving the results of tests and examinations.
A mild form of lymphadenitis does not require serious treatment. It is enough just to get rid of the illness that caused it and the lymph nodes themselves will return to their previous state.
Tuberculosis of lymph nodes in HIV
People infected with HIV have a weakened immune system, which is why these representatives of humanity are most susceptible to various diseases, including tuberculosis.
When the bacterium enters the patient’s respiratory tract, the primary focus of the disease is formed. Infection of the lymph is observed, the latter spreading the harmful organism throughout the entire system, affecting the nodes.
Tuberculosis of the lymph nodes in HIV is diagnosed in the case of the pulmonary form of the disease or as an independent pathology. With the onset of the disease, the clinical symptoms are very vague and resemble signs of lymphadenopathy, because the lymph nodes swell slightly, and there is no pain on palpation.
After some time, the patient may complain of:
- high temperature (up to 39 degrees);
- pale skin;
- excessive fatigue;
- sweating activity.
Following the appearance of the above-described signs, a further enlargement of the lymph nodes is observed, they resemble clusters of growths, and pain is felt upon palpation. Then pus fistulas can form, which, when ruptured, lead to a drop in temperature - this makes the diagnosis of tuberculosis difficult.
Attention! To make an accurate diagnosis, the usual Mantoux test and sputum analysis will not be enough. In this case, a biopsy or tomography of the affected area is prescribed.
Treatment methods: drug therapy
After determining the causes of the disease and identifying the source of infection, drug treatment is prescribed. It is necessary if the lymph nodes in the neck hurt and the patient’s health condition worsens. How to treat is determined by the doctor; self-medication is excluded, as it can lead to serious consequences.
With the help of painkillers (Ibuprofen, Ibufen) it is possible to alleviate the patient's condition. To stop the inflammatory process, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed:
- Medron.
- Prednisolone.
- Deltason.
Antibiotics Amoxiclav or Amiksin are indicated in the presence of infection in the upper respiratory tract:
- pharyngitis;
- tonsillitis;
- sinusitis (acute, chronic);
- acute and chronic otitis.
When treating specific lymphadenitis caused by syphilis, the antibiotic Benzylpenicillin is prescribed. It is administered 2–4 times a day intramuscularly.
Medicines containing vitamins help restore the immune system. Identification at an early stage of the primary disease that causes enlarged lymph nodes facilitates the treatment of lymphadenitis. In addition to medications, the patient may be prescribed physiotherapeutic treatment:
- UHF therapy, provided that he has normal body temperature;
- laser therapy - exposure of the problem area to light waves of a certain length;
- galvanization - the effect on the body of a weak current of no more than 50 milliamps.
Lymphoma and malignant tumors
Malignant formation of lymph nodes (lymphoma) is manifested by a number of additional signs:
- itchy rash;
- increased sweating at night;
- weight loss;
- enlarged liver, spleen;
- constant increase in body temperature (up to 38 degrees).
When the pathological process affects the patient’s central nervous system, regular seizures of epilepsy are observed. Lymphoma or malignant tumors with HIV can develop in the patient’s brain, which causes severe headaches in the latter. Attention! Not in all cases, migraine during the development of the disease in question indicates the development of malignant pathologies in the lymph nodes. The phenomenon can be caused by a common acute respiratory viral infection, a surge in pressure, meningitis, or intoxication of the body, for example, with pneumonia. When the headache does not subside for several days, despite taking traditional analgesics, you need to consult a specialist. To confirm the fact of the formation of malignant pathologies in the lymph nodes of a patient with HIV infection, in addition to a routine examination, they resort to a general blood test and biopsy. If the node is located in a place inaccessible for inspection, radiation diagnostics (tomography) is recommended. To identify metastases in the bone marrow system, bone marrow tissue is examined.
A malignant tumor in the lymph nodes is diagnosed in approximately 1/3 of infected people. Lymphomas are usually detected at the last stage of the disease, at the same time the appearance of fistulas and ulcers is observed. In case of refusal to carry out medical therapy, formations may form earlier. Tumors formed in the lymph nodes progress very rapidly - the patient dies in about a year. This fact is explained by the impossibility of overcoming the disease, which, forming an impressive “barrier” to the absorption of antiviral therapy, leads the patient to death.
Diagnostics
A complete examination of the patient is necessary to determine the exact reason why the lymph nodes in the neck hurt so much. Adult patients should see a therapist; for lymphadenitis in children, they should see a pediatrician.
The doctor, examining the patient, determines the nature of the inflammatory process. To clarify the sources of infection, the patient is prescribed a consultation with an ENT doctor and a dentist. To diagnose tumors, the patient undergoes an ultrasound of the lymph nodes. Using ultrasound, the structure and size of the nodes are examined. If necessary, a puncture of the node tissue is performed.
After the examination, the patient is given a blood test. An increase in the white blood cell count indicates that the body is infected. In complex forms of lymphadenitis, the inflammatory process spreads to various tissues located near the lymph node.
A complete diagnosis of cervical lymphadenitis includes:
- Ultrasound;
- puncture biopsy;
- computed tomography;
- blood analysis.
During the diagnosis, the size of the lymph nodes, their location and consistency are determined. Timely diagnosis and proper therapy help avoid serious complications such as thrombophlebitis and sepsis. You should see a doctor immediately if there is thickening of the lymph nodes and pain in their area.
In most cases, the cause of the disease can only be determined by a doctor upon examination. However, it often happens that the presence of inflammation of the nodes coincides with respiratory symptoms: sore throat, cough, runny nose, and high fever. In such cases, there is no doubt that lymphadenitis is caused by an acute respiratory disease.
Which specialist is best to contact if the lymph nodes in the neck hurt? This is usually the prerogative of an otolaryngologist. He can send you for additional tests - a blood test, ultrasound, research on the genomes of microorganisms, or to other specialists, for example, to an infectious disease specialist, oncologist, hematologist, dentist, pulmonologist.
How does a doctor make a diagnosis of “inflammation of the lymph nodes”? What is it based on? Making a diagnosis begins with a thorough examination of the patient. In addition, the doctor may ask questions regarding his well-being, etc. We have already given sample questions to which a complete and truthful answer should be given above.
Next, the doctor will carefully examine the patient’s entire medical history. To make a correct diagnosis, it is important to find out what the person was previously ill with and how these diseases developed. Next, a blood test will be ordered. It is he who can shed light on the true causes of lymphadenitis. It is important for the doctor to exclude a tumor, as well as to find the true source of infection.
For this purpose, the patient is prescribed an x-ray or a more modern version of hardware diagnostics - computed tomography. It, unlike x-rays, is quite expensive. But it will help the attending physician get better quality images than a simple x-ray. They will most fully provide the true picture of the disease. This will allow you to prescribe the most adequate and effective treatment.
It also happens that, despite the fact that the doctor has used all diagnostic methods, he still finds it difficult to make an accurate diagnosis. In this case, a lymph node biopsy will be required. This procedure is not the most pleasant, but it will provide comprehensive information about the condition of the lymph node and the type of infection that affected it.
Diagnosis and treatment of lymphadenopathy
Primary diagnosis - palpation
In the case when a patient has persistent lymphadenopathy (3 months or more) and there is no way to find the cause of this phenomenon, it is worth seriously thinking about the likelihood of HIV infection. The first step is to take a medical history of a potential patient and find out whether there have been casual sexual relationships, blood transfusions, surgical interventions, or artificial insemination. Diagnosis and treatment of lymphadenopathy always begins with laboratory tests. There are special laboratories for this purpose. If a positive result is obtained, repeat tests are performed. If the second test also determines the presence of antibodies to HIV in the blood, then the diagnosis is confirmed. When HIV infection itself becomes the cause of lymphadenopathy, direct treatment of the lymph nodes is not carried out - treatment of the underlying disease is carried out in the following areas:
- antiretroviral therapy;
- increasing immunity.
In cases where the cells of the immune system are weakened, additional diseases may develop, which are treated with standard methods.
Antiretroviral therapy
This therapy is the main treatment for HIV.
The following groups of drugs used are distinguished:
- nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors – Abacavir, Stavudine, Phosphazide;
- non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors – Delavirdine, Rilpivirine;
- protease inhibitors – Amprenavir, Darunavir, Fosamprenavir.
It should be remembered that medications in this group cannot cure HIV infection or protect against infection. Medicines only reduce the ability of viral cells to multiply, which helps to improve a person’s standard of living and improve overall well-being.
The use of special medications to treat an infected patient has its pros and cons.
Among the advantages:
- prolongation of the patient's life;
- maintaining a stable quality of life without symptoms of the disease;
- improvement of living conditions;
- prevention of the development of secondary disease;
- reducing the risk of infection transmission.
The disadvantages boil down to the following characteristics:
- constant use of medications;
- high toxicity of drugs with a risk of side effects:
- inflated cost of medicines, especially drugs with less toxicity;
- the need to regularly change antiretroviral drugs due to the development of resistance to therapy in the virus.
Fact! Antiretroviral therapy can increase the patient's life expectancy. There are currently known cases of HIV-infected people living to a ripe old age.
Boosting immunity
The next step in treating HIV is to boost immunity by:
- the use of immune drugs, such as Imunofar, Cycloferon, etc.;
- normalization of the daily routine;
- moderate physical activity;
- giving up bad habits;
- regular walks in the fresh air;
- balanced nutrition;
- use of vitamin-mineral complexes;
- traditional medicine using decoctions of medicinal herbs.
For enlarged (inflamed) lymph nodes, it is possible to prescribe topical anti-inflammatory ointments, as well as surgical intervention. Removal of lymph nodes is performed in extreme cases, when they greatly interfere with the patient’s daily life.
Treatment
At the initial stage, you can get by with drug treatment.
The key to successful therapy is the correct identification of the cause that provoked inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes. Depending on the stage of development of the pathology and its etiology, you can do the following:
- Drug therapy. Based on the diagnostic results, the following may be prescribed as prescribed by a doctor:
- Antibacterial drugs: ampicillin, amoxiclav, ceftriaxone, sumamed and amoxicillin. Their use is effective in the presence of purulent exudate in the glands, infections whose pathogens are bacteria, and in the prevention of complications. Their choice is determined by the clinical picture of health and the age category of the patient, as well as the stage of development of the pathology.
- Antiviral agents: Kagocel, rimantadine, anaferon. Prescribed for viral etiology. Under their influence, the process of bacterial reproduction is suspended and the process of producing its own interferon is stimulated.
- Antitumor: aromazine, thioguanine, methotrexate. Block the development of cancer cells.
- Immunosuppressors: tacrolimus, cyclosporine A. Prescribed for autoimmune pathologies, which makes it possible to artificially suspend the activity of the immune system.
- Also, as an auxiliary therapy, gargling with antiseptic solutions can be prescribed, among which Burov's solution is the most popular. As an additional treatment, local drugs are used in the form of ointments: troxevasin, heparin, Veshnevsky.
- Surgical treatment. Prescribed in the presence of an abscess, oncology or complications of lymphadenitis. To eliminate it, surgical cleaning of the cavity after its removal is required. In case of a large amount of pus, after opening the abscess, a drainage is installed to ensure the outflow of the contents. After surgery, to prevent relapse and complications, a course of antibacterial therapy with certain physical procedures is prescribed. In case of oncology, nodes can be removed for additional examination or if metastases form in them.
- Traditional therapy. It can only act as an auxiliary treatment. The use of alternative remedies helps relieve acute symptoms. For these purposes, only in consultation with a doctor, the following can be used: Herbal decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs: birch, wormwood, pine needles, thyme and St. John's wort.
- Warming compresses made from rosin, gauze soaked in herbal decoctions, heated sea salt.
- Applications made from fresh dandelion juice.
- Chicory root lotions on an inflamed lymph node.
Important! The choice of therapeutic course, its type, duration and use of auxiliary means of traditional medicine is determined exclusively by the attending physician. Self-medication of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes is strictly prohibited.