The intestines are part of the complex human digestive system. The main function is to digest food to an enzymatic state and further absorption into the circulatory system. A variety of factors can disrupt the natural process. Intestinal infections, worms, frequent intoxications are just part of the negativity that can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system and provoke the appearance of a dangerous disease - inflammation of the intestines. Its symptoms are noticeable immediately, and when they appear, you should consult a doctor.
Intestinal inflammation: causes of the disease
Intestinal inflammation in official medicine is referred to as colitis. There are several factors that provoke the disease:
- eating disorder;
- genetic factor;
- age-related changes;
- infections;
- helminths;
- dysbacteriosis;
- alcohol abuse;
- long-term use of medications;
- weakened immune system;
- nervous stress;
- frequent evening overeating;
- an abundance of fatty, spicy, salty foods.
These are precisely the reasons that reduce the intestinal’s own protective functions, causing intestinal inflammation. The mucous membrane of the intestinal walls becomes inflamed. The disease in the initial period may occur without any obvious signs at all. But the main reason is the wrong lifestyle that a person leads.
Important! Simple heartburn may indicate the onset of the disease.
In order to identify intestinal inflammation in the early stages and carry out timely treatment, you need to know how it manifests itself. The disease is simply treatable at an early stage. Then colitis becomes chronic. This causes frequent excruciating pain, forcing a person to go on a lifelong diet and take many medications.
The concept of pathology and causes
Inflammation of the abdomen is a combination of several diseases. This process is characterized by damage to the mucous membrane of the intestinal tract. In terms of frequency, this disease ranks second among all diseases of the digestive system. It occurs equally in both men and women. Moreover, the disease is often diagnosed in children of preschool and school age.
The cause of inflammation of the large and small intestine in adults and children may be hidden in the following problems:
- infections. The inflammatory process occurs due to the ingress of bacterial, viral and protozoan agents in the form of E. coli, salmonella, shigella, rotavirus, amoebic dysentery;
- parasitic infestation;
- autoimmune processes. This condition is characterized by the perception by the immune system of mucosal cells as foreign. Against this background, the body produces antibodies to them, as a result of which destruction of the mucous membrane is observed;
- hereditary predisposition;
- poor nutrition. This may include overeating, consumption of fatty, fried, smoked, fried and spicy foods;
- insufficient blood flow in the choroid plexuses of the organ. Against the background of this phenomenon, atherosclerotic changes and narrowing of the arterial bed are observed;
- disruption of flora in the digestive tract.
The development of the inflammatory process is directly related to the death of cellular structures in the mucous membrane due to the influence of an unfavorable factor. In the damaged area, blood flow increases, severe pain and impaired enzyme function appear.
Classification of the disease
This pathology has several types. But the development of the disease occurs almost the same. Under the influence of these irritating factors, mucosal cell death occurs. Blood supply increases, inflammatory ulcers appear in place of dead cells, which quickly progress, and the first pain appears.
This leads to the fact that the synthesis of enzymes is disrupted, nutrients are not absorbed into the blood, and many internal organs are at risk.
There are several types of disease depending on the location of the inflammatory processes:
- colitis - inflammation of the large intestine;
- enteritis - inflammation of the small intestine;
- inflammatory process in the duodenum - duodenitis.
When intestinal inflammation is diagnosed, treatment is determined by the form of the disease, which gives a prognosis for its further development:
- Acute form - if the inflammatory process lasted no more than a month.
- Chronic form - when development occurred for about six months.
- Infectious. The disease is caused by pathogenic bacteria, most often Escherichia coli.
- Non-infectious. The cause may be hereditary factors, genetics, poor diet, and helminths.
- Ischemic colitis is caused by impaired blood supply to the intestines.
- Pseudomembranous colitis appears after long-term use of antibiotics against the background of the development of dysbacteriosis.
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis has not been fully studied; it occurs most often in people of working age. Mostly these are women, residents of large cities.
Diseases of the stomach and intestines
Ulcerative disorders
Ulcerative disorders are complex diseases of the stomach and duodenum. In practice, this is associated with deep damage to the mucous membrane. This process is called an ulcer.
Doctors have found that gastric ulcers mainly occur in people over 40 years of age. Duodenal ulcer affects the organisms of young people. But there are also cases where the disorder manifests itself in young children.
There are many reasons for the development of peptic ulcers, and they all lead to the formation of acute gastritis, because the protective barrier weakens, and the mucous membrane, in turn, becomes vulnerable. The role of heredity and human genetic resources is very important, so a set of preventive measures will be relevant when there have been repeated manifestations of inflammation in your family.
The stomach cavity is home to a large number of harmful bacteria that can provoke the development of inflammation of the mucous membrane, resulting in ulcerative formations. This happens especially often under stress, lack of proper nutrition and the existence of predisposed heredity. The above facts have long been proven by scientists who were awarded the Nobel Prize. Their discoveries became the basis for the progress of medicine.
The main factor in the occurrence of ulcerative formations in the duodenum is an increase in the level of acidity in the stomach and lumen. The parts of the small intestine contain alkaline content, which is why gastric juice irritates the walls of the hollow organ.
The signs of the clinical picture of the disorder are varied, and their manifestation can significantly complicate not only treatment, but also diagnostic procedures. Symptoms directly correlate with the age of the patients, the duration of the disease, the level of exacerbation of remission and various types of complications. But the key sign of the disorder is the manifestation of severe abdominal pain. In some cases, prompt medical attention is even required (including in men with constipation).
If an ulcer develops in the stomach, then the pain accumulates in the upper part of the digestive organ under the xiphoid process. Only with the help of a multifunctional examination can one determine the degree of development of the disorder and select the optimal treatment. If you do not take any action, the pathology will only progress.
The intensity of pain in the human body is quite diverse. Dull and aching pain abruptly gives way to intense secretion, and sometimes the sensations and signs become so unbearable that they cannot be tolerated. In practice, you can drink 250 ml of warm milk, take a position on your left side, apply a heating pad to your stomach, and pull your legs towards the abdominal cavity. If the above mentioned actions do not help, you can resort to medications that have an analgesic effect.
Gastric ulcer has certain patterns of progression. The following are listed which influence the form of the disease itself. As a rule, pain appears 15 minutes after a meal. This is due to the fact that the food mass injures the ulcerative defect. This is especially true for errors in the diet: food with spices, overeating, fatty and salty foods. Additional signs: heartburn, belching, sour taste in the mouth, vomiting symptoms - can characterize the pathological disorder in more detail.
In practical medicine, patients often experience stool disturbances, since the disease is localized in parts of the colon, in the lower abdomen. Constipation should be dealt with comprehensively and systematically.
Intestinal diseases have similar clinical manifestations as stomach disorders, but duodenal ulcer has its own characteristics. The pain has a “hungry” nature and makes itself felt only 4 hours after a meal; during this period of time, food enters directly into the intestines and irritates the mucous membrane. There are also night pains, which are relieved with milk and medications. Symptoms of intestinal disease appear in increasing progression, and peptic ulcers often transform into serious complications that can lead to hospitalization and the need for surgical intervention.
Intestinal diseases are much more common than stomach disorders. In most cases, this concerns inflammatory processes and their complications. For example, gastritis is a digestive disease of the 21st century, since a nervous lifestyle contributes to the development of colon irritation syndrome, and in children under 1 year of age, the intestines are sensitive to external influences and dysbiosis.
Chronic enteritis
Chronic enteritis is formed as a result of nutritional disorders, systematic consumption of spicy foods, poor quality nutrition and abuse of spices and seasonings. Alcoholism and drug intoxication also influence the development of the disorder. In addition, the pathological illness is characterized by Sternberg syndrome, that is, pain in the mesentery of the small intestine, and signs of Obraztsov’s disorder, the process of rumbling in the parts of the cecum. Treatment of these disorders is carried out only after a detailed diagnosis.
In men, chronic enteritis is accompanied by a feeling of pressure, distension and rumbling in the abdominal cavity; increased gas formation and nausea often occur, and manifestations of the disease are observed a couple of minutes after a meal. The thing is that the digestion of dietary fiber in the intestinal lumen is impaired, and patients experience disruptions in peristalsis and absorption of nutrients. In acute forms of the disease, weakness and frequent dizziness are felt.
Chronic enteritis is a consequence of the influence of ionizing radiation on the body. This condition usually occurs after radiation therapy of tumor formations.
Treatment of enteritis is based on complex effects. Often, gastroenterologists prescribe the patient to follow diet No. 4: the menu includes a large amount of protein foods (up to 150 g) and fatty structures, which are quickly absorbed by the body, and the consumption of lamb and pork is completely excluded. The daily diet also includes carbohydrates, their daily amount reaches 500 g. Treatment should be targeted, and physical effects on the body will be relevant: walks in the fresh air, swimming, gymnastic exercise “bicycle”.
Colitis
Chronic colitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the large intestine and is accompanied by a large number of dystrophic and atrophic changes. As a result, a sick person develops specific complaints: painful contractions are combined with flatulence, diarrhea and constipation, frequent loose stools occur 5 to 10 times every 24 hours. The disorder is characterized by the following symptoms: bitterness in the mouth, nausea, complete refusal to eat, wave-like attacks.
There are many reasons for the development of colitis. Medicine divides these factors into two groups: infectious, the activity of Salmonella and Cygella, and non-infectious, impaired diet, poor symptoms. Dysbacteriosis also contributes to the formation of the disease, because pathogenic intestinal microflora activates a disorder of the absorption organ.
Chronic colitis can occur due to gastrointestinal diseases, such as dyspepsia, pancreatitis. Side effects come from medications in the form of antibiotics and anthroglycosides; their active ingredients often provoke allergic reactions in the body. Treatment of the disease has the following structure:
- fractional meals. Meals are taken at least 6-7 times a day;
- following a fasting diet. The menu should consist of wheat bread, low-fat soups, barley, semolina porridge, white fish, soft-boiled eggs and light tea;
- the use of medications from the group of sulfonamides and their derivatives (“Argedin” and “Bactrim”);
- the use of special probiotics that effectively normalize the intestinal microflora.
The main danger of chronic colitis is a significant deterioration in the quality of life. The symptoms of this disease are similar to disorders associated with pancreatitis and colon tumors, so self-medication is fraught with serious complications, because only a visit to a qualified specialist will clearly establish the degree of development of the disease.
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional pathology that has a chronic manifestation. The main signs of the disorder are pain in the abdominal area, frequent visits to the toilet, prolonged constipation and diarrhea. Factors that influence the course of the disorder are:
- genetic predisposition;
- psychological disorders;
- dysfunction of the rectum;
- visceral hyperalgesia;
- traumatic effects on the gastrointestinal tract;
- hormonal activity.
Today, medicine has several areas of therapy to eliminate intestinal diseases; folk remedies, diet and drug treatment are especially popular. Regardless of the technique, the doctor must achieve the following goals: restore the intestinal microflora, normalize digestion, stabilize the psychological situation and establish the process of defecation.
Intestinal dyskinesias
Intestinal dyskinesia is a violation of the motor function of the intestines in the direction of spasms. This is preceded by individual characteristics of the human psyche, negative emotions and regular stress. The disease manifests itself in the form of pain in the lower abdomen of varying degrees of intensity, lasting from several minutes to an hour. This is especially evident after excessive overeating and wearing a tight belt. Dyskinesia is characterized by flatulence, bloating and rumbling of the abdomen.
Functional constipation
Functional constipation refers to stool retention that lasts more than 48 hours. A sick person feels incomplete defecation and a constant urge to stool of a false nature. This is due to disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, as a result of which feces and decay products simply do not move through the absorption organ of the gastrointestinal tract.
The development of the disorder is facilitated by psychogenic causes: the habit of artificially delaying bowel movements, anxiety, etc. Functional stool retention may be based on the background of intestinal dyskinesia, in which the patient experiences not only constipation, but also a change in skin color, the appearance of boils and rashes. Flatulence becomes a common occurrence for the patient. Treatment for the disorder should be immediate.
Dysbacteriosis
Imbalance in the intestinal microflora is quite common. This applies to both the qualitative and quantitative significance of microorganisms. Also, the likelihood of developing the disease increases sharply if the human body undergoes surgical interventions, since anesthesia, the use of antibiotics, hormones, and immunosuppressants increase the risks of developing the disease. The disorder in most cases is observed in young children, because their fragile bodies are prone to diseases.
To identify the causes of the disease, you need to visit a qualified doctor who will conduct certain studies and clearly establish a diagnosis.
Do not hesitate to talk with a gastroenterologist about stool pigmentation, since even the description of the stool can form a diagnosis. Excrement is taken for analysis to detect the degree of development of bacteria in the intestines, which is quite important, because the course of treatment will depend on the results of the test.
Often a person encounters hemorrhoids; it is typical for those people who lead a sedentary lifestyle or systematically lift heavy weights. Psychogenic anal itching is less common. But any of the ailments requires effective diagnosis and treatment. Do not neglect the recommendations of doctors, visit them on time and always be healthy!
Symptoms of the disease
The success of treating intestinal inflammation depends on timely detection. This is an important organ that reacts sharply to any violations. Often people may perceive the signs as simple poisoning from poor-quality food or water and limit themselves to a tablet, medicine, or strong tea. Meanwhile, the pathology progresses, and it is impossible to get rid of it in this way.
It is important not to miss the first symptoms so as not to lead the disease to a chronic form.
Symptoms for all types of the disease, regardless of its form, may be the same. This:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- pain;
- constipation;
- diarrhea;
- bloating;
- heartburn.
Moreover, pain is not always present. For this reason, the disease can progress for a long time, reaching a chronic form. Heartburn appeared - a common case. Everyone has their own method of dealing with such discomfort. Often drinking soda only complicates the healing process.
Symptoms of intestinal diseases and their treatment
In a normal state, the intestines do not show any symptoms of disorders, so if discomfort, heaviness or pain occurs, then it is necessary to undergo examination by a specialist. Symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases vary. The most common symptoms that you should pay attention to first are:
- nausea and vomiting;
- spasms;
- flatulence and bloating;
- chronic constipation;
- lack of appetite;
- fatigue and apathy.
Symptoms of intestinal pathologies are divided into groups:
- Functional. Symptoms of functional diseases are represented by primary and secondary dyskinesia of the colon and are:
- hypomotor;
- hypermotor;
- mixed.
- Inflammatory and dystrophic. This group is characterized by the following diseases:
- Crohn's disease;
- chronic colitis;
- chronic enteritis;
- radiation enterocolitis;
- primary and secondary amyloidosis.
- Intestinal enzypomatia. These diseases have specific symptoms such as:
- digestive disorders;
- absorption disorders.
The first symptoms of intestinal problems are attacks of nausea with vomiting
Treatment of gastrointestinal diseases depends on the diagnosis.
Diseases must be treated comprehensively and at the same time following a diet. A gastroenterologist can prescribe precise and correct treatment after diagnosing the condition of the intestine.
There are diseases that do not show any symptoms for a long time, and the person does not have the slightest idea that he has problems with the intestines. Pathologies of the large and small intestines, which have different symptoms, are classified.
What happens in the intestines
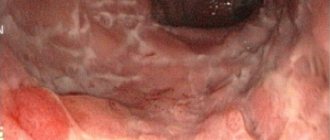
For intestinal inflammation, the symptoms and treatment are almost the same. This is colitis, in which the integrity of the mucous membrane is disrupted. Bacteria, getting on the mucous membrane, continue to damage it, capturing larger and larger areas. In damaged areas, an inflammatory process occurs, which is accompanied by swelling.
This leads to the fact that peristalsis (contractile functions) begins to act more and more slowly, and mucus secretion noticeably decreases. The disease progresses rapidly, which can lead to obstruction: the intestines simply stop performing their functions. With inflammation of the large intestine—the symptoms and treatment of which are the most severe—contaminated blood spreads throughout the body, putting other organs at risk.
The person feels pain, fever, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. The first thing you want to do in such a situation is to take anabolic steroids. Temporary help can be provided, but while the analgin components are in effect, the bacteria will affect large areas. This is unjustified help.
Important! Minor pain in the intestines accompanied by rumbling, diarrhea or constipation should prompt diagnosis and treatment.
You shouldn't risk your own health. The situation is serious and requires qualified medical assistance.
General symptoms of inflammatory changes in the intestines
In most cases, inflammation shows signs of itself that bother the patient and force them to go to a medical facility. Symptoms of intestinal inflammation:
- Abdominal pain. Often, patients cannot accurately indicate the location of the pain, but characterize it as squeezing or bursting, not suspecting that their intestines are inflamed. As a rule, pills relieve such pain only for a short period of time. The condition resembles irritable bowel syndrome.
- The appearance of nausea after eating (often this sign indicates inflammation of the small intestine or duodenum).
- Vomiting after eating, indicating inflammation in the upper parts.
- Bloating. This symptom indicates a deficiency of enzymes that are involved in the digestion process.
- Stool disorders (either prolonged constipation or frequent diarrhea).
- Weight loss, indicating insufficient absorption of vital substances by the intestinal walls.
- Anemia, which occurs due to the inability of the affected organ to “take” the required amount of iron from the food entering the body.
- Elevated temperature (from high to low-grade) is a classic sign of suppurative processes in the body.
Inflammatory bowel diseases, according to the nature of their course, are divided into acute (the disease is severe, lasting up to one month) and chronic (the course of the disease can be sluggish with periods of exacerbation, this period lasts up to one year). Based on the localization of the suppurative process, the disease is divided into the following diseases:
- enteritis is an inflammatory process localized in the intestines, affecting both a separate part of it and the entire organ;
- duodenitis – inflammation of the duodenum; the disease in most cases begins from the first section, where the stomach passes into the intestines;
- mesadenitis - inflammation of the lymph nodes, which can provoke pathologies of the mucous membrane; in most cases, suppuration occurs due to the penetration of viruses and infections;
- colitis – inflammation of the mucous membrane of the large intestine; in most cases, inflammation affects the entire organ, but there is also suppuration in individual parts.
Diagnosis of the disease
With inflammation of the small intestine, the symptoms and treatment are no different from how inflammation occurs in other parts of the intestine. When you make an appointment with a gastroenterologist, you need to describe your condition in as much detail as possible. The gastroenterologist carefully listens to complaints and takes an anamnesis.
He may simultaneously palpate to determine the most affected area. At this time, the patient is on the couch, lying on his back with his knees bent. This initial examination helps the physician make assumptions:
- If the stomach is retracted, this may indicate spasms in the intestines.
- A swollen, enlarged, painful abdomen suggests that the patient has ascites or tumors.
- When a protrusion is detected, an assumption is made about the presence of a hernia or tumor.
Next, you need to undergo a series of instrumental and laboratory examinations. This:
- blood analysis;
- coprogram (stool analysis);
- bacteriological analysis of stool;
- FEGDS (fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy);
- colonoscopy;
- video capsule endoscopy;
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity.
Many clinics today use video capsule endoscopy to get a clearer picture. The method is expensive, but quite effective.
The patient is asked to swallow a special small capsule in which a microscopic video camera is mounted. During the day, this capsule passes through all parts of the intestine. Information about the state of each section is transmitted to the computer using radio waves. Based on the data obtained, a final diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have problems with the intestines, you need to consult a gastroenterologist. If a patient constantly feels discomfort and pain in the abdomen, then he should not look for a solution to this problem on his own, but would be better off visiting a doctor. At the appointment, the doctor will examine the patient and tell him the main points about the symptoms and treatment of this disease. Then he will refer the patient for additional examination, which will help establish the most accurate diagnosis. After this, the doctor will prescribe treatment with medications, herbal preparations and give dietary recommendations.
What can the appearance of stool tell you?
For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, stool is studied especially carefully in the laboratory. Even the first visual examination is sometimes enough to make the correct diagnosis. Here are some examples:
- dark, closer to black feces - the presence of bleeding in the upper intestines;
- obvious signs of blood - bleeding in the colon;
- gray or clayey color - jaundice, blockage of the bile ducts;
- green with a pungent odor – active inflammatory processes, pancreatitis;
- putrid odor – active process of rotting, fermentation;
- the presence of undigested food residues - lack of enzymes.
Intestinal diseases: how to recognize the disease
Although intestinal disorders have dozens of forms, most often the population experiences common forms of intestinal diseases without specific complications. In the table below you will find characteristic first symptoms and secondary signs indicating a possible disease. Attention: If you suspect a chronic illness, consult your doctor immediately. The sooner you start treatment, the lower the risk of encountering intestinal pathology.
| Disease | Description of the disease | First symptoms | Secondary symptoms | Causes | Risk factors |
| Enteritis | Inflammatory process in the mucous membranes of the small intestine. Inflammation can have an acute or sluggish chronic form. | Diarrhea (not morning, occurs after every meal). Nausea, sometimes to the point of vomiting. Abdominal pain around the navel. | In case of acute inflammation: high temperature; headaches; general weakness; increased sweating. With chronic inflammation: dull, aching pain of low intensity throughout the day; strong rumbling in the stomach after eating; with advanced enteritis - intense diarrhea (up to 10-20 visits to the toilet per day); rapid weight loss; vitamin deficiency. | Food poisoning. Acute infection in the intestines (salmonellosis, intestinal flu, typhoid fever, etc.) Rough, spicy, fatty or fried foods. Alcohol intoxication. | Taking strong medications. Inflammation in the human stomach – gastroenteritis. Other lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (chronic gastritis, enterocolitis, etc.) |
| Colitis | Inflammatory process in the mucous membranes that envelop the human colon. It can be acute or sluggish. | Intense pain in the lower abdomen. At night, a person suffers from gripping pains that disturb sleep. The stool is loose, frequent, and in the later stages mixed with blood or white mucus. Pain accompanies the desire to go to the toilet and the process of defecation. Diarrhea gives way to constipation, and vice versa. | In acute inflammation: fever; general weakness, lethargy; nausea with dizziness. With chronic inflammation: increased gas formation; unexpressed aching pain in the lower abdomen, in its left or right part; psycho-emotional disorders; depression; decreased appetite up to complete refusal to eat; general weakness; erectile dysfunction up to impotence; amenorrhea. | Food poisoning. Acute intestinal infection (dysentery, etc.) Dietary disorders. A “heavy” diet with an abundance of fatty or fried foods. Alcohol intoxication or other forms of systemic poisoning. | Chronic inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract (gastroenterocolitis, enterocolitis). Sluggish gastrointestinal diseases (pancreatitis, gastritis). |
| Ulcerative colitis | Inflammatory process in the rectum (located at the very end of the large intestine). | Pain in the lower left abdomen. Discharge of blood from the anus in the absence of visible injuries or noticeable scratches. Blood during bowel movements, blood particles in stool, including during remission. | With advanced ulcerative colitis, the inflammatory process spreads throughout the upper parts of the colon. The disease may be accompanied by morning diarrhea, followed by 7-10 days of constipation. | It has no diagnosable specificity. It is believed that the disease may be genetic in nature. | Hereditary predisposition. |
| Crohn's disease | Ulcerative lesions of all parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Mainly localized in the large intestine. If treatment is not completed, it eventually reaches the small intestine. | Blood and whitish mucus in the stool. Intense abdominal pain. Any localization of pain depends on the source of pain – the inflamed compartment. Bloating, feeling of tightness. Diarrhea followed by constipation. Acute phases alternate with short periods of remission. | If the disease is acute: sudden weight loss (bones and joints stand out); increased body temperature; pain in the anus; cracks in the anus with bleeding; aching pain in the joints; characteristic rashes on the face. In the chronic form: intestinal fistulas; abscesses in the intestines; development of partial or complete obstruction of individual intestinal compartments. | Presumably a genetic predisposition. | Age group: the disease is more common in young people aged 25-30 years, and in older people after 50 years and older. Heredity. |
All symptoms do not need to occur simultaneously to make a diagnosis. If a sluggish disease develops in a latent mode, the doctor will have to identify this disease by how the existing symptoms appear and what is the reason for their manifestation. Clarification of the diagnosis requires laboratory research. Tests show what caused the first symptoms and help select drugs for systemic treatment.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment begins with a cleansing enema. A strict diet is prescribed, sometimes this may involve fasting for several days. The course of treatment includes several methods:
- treatment with medications;
- pathogenetic therapy;
- symptomatic therapy;
- etiotropic therapy;
- diet or nutritional therapy;
- phototherapy.
The direction of treatment is determined by the attending physician. Sometimes a cleansing enema and taking sorbents are enough for the patient to count on discharge. But for the first day it is better to remain under the supervision of a doctor.
The disease is dangerous, threatening various complications. That is why such a thorough diagnosis is carried out. If the treatment is chosen incorrectly, the consequences can be in the form of liver abscesses, obstruction, and peritonitis.
Important! Self-medication is life-threatening, so drug therapy can only be prescribed by a doctor.
Etiology
The causes of the development of such gastroenterological diseases are conventionally divided into two groups - infectious or non-infectious. The first group includes the following etiological factors:
- exposure to enteroviruses, rotaviruses, adenoviruses;
- entry into the body of pathogenic organisms - salmonella, E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, dysentery;
- parasitic infection;
- exposure to fungal organisms.
Treatment and symptoms of intestinal inflammation caused by this etiology are nonspecific, and the disease itself is contagious, that is, it can be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person through household objects or due to poor personal hygiene.
The second group of etiological factors includes:
- chronic gastroenterological diseases and non-compliance with diets prescribed by a doctor;
- poor nutrition;
- alcohol abuse;
- uncontrolled and unjustified by health conditions taking medications;
- poisoning by toxins, chemicals, heavy metals, poisons;
- circulatory disorders in the gastrointestinal tract;
- consequences after abdominal surgery;
- complications after gamma irradiation;
- food allergies;
- decreased intestinal tone;
- autoimmune diseases;
- inflammation of nearby organs and tissues;
- abdominal organ injuries;
- excessive physical activity, constant stress;
- diseases of the pelvic organs, including STDs.
In rare cases, inflammation of the large intestine or other localization is not etiologically established.
Diet for illness
In the first three days, complete fasting is recommended. You can only use mineral water without gas. Along with medications, the patient is given intravenous glucose.
When coming out of fasting, stale bread, vegetable broth without salt, and porridge with water are allowed. Products that can provoke fermentation are excluded from the diet. It is completely necessary to exclude dishes and products that can irritate the mucous membranes. This:
- vegetables;
- fruits;
- berries;
- chocolate;
- hot dishes;
- alcohol;
- beer;
- dairy products;
- salty, sour, fried, fatty foods.
This diet should be followed throughout the entire treatment. Food should be liquid, not hot, with minimal or no salt. It is advisable not to smoke during this period, and even after treatment, nicotine can irritate the mucous membranes.
After treatment is completed, it is advisable to adhere to the same rules and carefully introduce lean meats, skinless poultry, and sea fish into the diet. All dishes can be steamed, boiled, or baked only with the permission of a doctor.
Food is taken in small portions, warm, at the same time every day. Everything is thoroughly chewed. It is necessary to constantly monitor the condition of the stool, try not to react emotionally to certain events.
Colon
One of the most common diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is inflammation of the colon or colitis. The causes of colitis are considered to be infections, unhealthy diet, as well as the ingestion of poisons used in everyday life and industry.
This type of disease can occur as a separate disease, due to disturbances in the immune system, or be the result of certain dysfunctions of the stomach and small intestine.
Medicine distinguishes four types of inflammation of the large intestine:
- Spicy;
- Chronic;
- Ulcerative;
- Spastic.
If a diagnosis such as inflammation of the large intestine is made, the symptoms and treatment are different for its different types.
Acute colitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Periodic abdominal pain accompanied by unstable stools;
- The appearance of mucus and blood impurities in the stool;
- Lethargy and increased temperature against the background of the patient’s general malaise;
- Painful urge to defecate.
With insufficient therapy or its absence, acute colitis can become chronic, the symptoms of which are in many ways similar to acute colitis, however, treatment is much longer and more complex. The main signs of chronic colitis are:
- Cramping pain in the abdomen;
- Weakness and nausea;
- Lack of desire to eat;
- Increased abdominal volume and flatulence.
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammation of the colon mucosa with the appearance of ulcers. This inflammation can develop over a long period of time with periodic exacerbations. The most common symptom of this disease is pain in the lower abdomen, manifested by periodic attacks. After a short period of time, defecation involves blood, and the amount of blood released often reaches 300 ml at a time.
During exacerbations, blood can flow in a stream, which leads to a sharp drop in blood pressure. Distention of the colon with the formation of peritonitis is also possible.
With spastic colitis, the patient passes feces in the form of small dense lumps. With such a symptom, it is necessary to carry out the necessary tests and examination of the patient using special equipment.
Not a day without movement
You should not lie or sit for too long; this should be alternated with walking. Lack of movement often provokes congestion in the intestines even in a healthy person and causes constipation, poor blood supply, and negative peristalsis. Recommended:
- walking;
- knee lift;
- bends;
- body turns.
Simple exercises can be done without getting out of bed. Bicycle, swimming pool - only after the doctor’s permission.