Definition
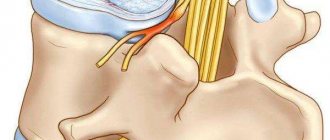
The thalamus is a part of the midbrain that acts as a relay for sensations such as touch, pain and temperature carried by different parts of the spinal cord. The thalamus, having received these sensations, integrates them and transmits them to the corresponding part of the cerebral cortex. Bleeding or a blood clot in the blood vessels can lead to stroke, which is the main cause of thalamic syndrome. People with irregular heart rhythms, high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels are at risk of developing this condition.
Story
In 1906, Joseph Jules Dejerine and Gustave Roussy presented a description of central post-stroke pain (CPP) in their article entitled "Thalamic Syndrome". The name Dejerine-Roussy syndrome was coined after their deaths. It included “severe, persistent, paroxysmal, often intolerable pain on the hemiplegic side, unresponsive to any analgesic treatment.”
In 1911, it was found that patients often developed pain and hypersensitivity to stimuli during recovery of function. The pain associated with stroke was thought to be part of it. It is now accepted that thalamic syndrome is a condition that develops due to damage that interferes with sensory processing. This prompted the start of pharmaceutical and stimulation research. The last 50 years have been filled with fireproof surveys. As of the early 2000s, longer procedures lasting months to years were being explored in the ongoing quest to remove abnormal pain.
Characteristic symptoms
A specific sign of obesity, against the background of which the largest reserves of fat deposits appear in the abdomen, arms and legs. In the absence of correction of the condition, against the background of HSPP, BMI will rapidly increase, morbid obesity develops, and clearly visible stretch marks appear on the body. It is no coincidence that the popular name for the pathology is pink striae disease.
Characteristic signs of hypothalamic syndrome:
- in boys. Plump white face, wide pelvis, development of gynecomastia. Early sexual desire appears, the size of the genitals is normal,
- in girls. Active formation of acne, hirsutism and increased hair growth on the body and in the face, nipples darken, menstruation becomes irregular.
Adolescents of both sexes exhibit one or two or more signs of the symptom complex:
- active growth of tumors on the body (lipomas, warts, vitiligo),
- drowsiness, slow reaction,
- thinning and brittleness of nail plates,
- pink stretch marks or stretch marks appear on the hips, abdomen, buttocks,
- in the morning the temperature rises for no reason, by the evening the indicators return to normal,
- allergies to various irritants often develop,
- Hands often sweat, the condition of the palms changes: cyanosis appears, cold extremities appear,
- blood pressure is unstable, arterial hypertension often develops,
- the teenager constantly wants to eat, the strongest appetite appears at night,
- thirsty
- bothered by headaches,
- in the area of absence of sweat glands, the dryness of the epidermis increases,
- the psycho-emotional state worsens, the teenager becomes aggressive, rude or withdrawn,
- the child suffers from panic attacks.
Against the background of hypothalamic syndrome, the following develops:
- sympathoadrenaline crisis with increased blood pressure, headache, tachycardia, tingling in the heart, panic attacks,
- vagoinsular crisis. Characteristic signs: upset stool, slow heartbeat, lack of air, increased volume of urine. Patients complain of increased sweating, feeling hot, weakness, and nausea.
Signs
Signs and symptoms of thalamic syndrome can range from numbness and tingling to loss of sensation or hypersensitivity to external stimuli, involuntary movements and paralysis. Severe and prolonged pain may also occur. Stroke victims who report pain or abnormal sensations are evaluated to confirm the diagnosis. The cause of pain is determined through a process of elimination. To rule out the presence of tumors or blockages of blood vessels, additional CT scans of the brain may be required.
The prognosis of thalamic pain syndrome depends on the severity of cerebral stroke. Lifelong pain management through medications may often be necessary.
Treatment of hypothalamic syndrome
Treatment of the disease takes quite a long time, most often lifelong. The choice of treatment for each person is specific and directly depends on the symptoms. This is done by an endocrinologist, and in the case of hypothalamic syndrome of puberty in girls, also by a gynecologist. Therapy is carried out in several stages:
- The factor that caused the disease is eliminated . Infectious processes, injuries are eliminated and tumors are excised. If there are a large number of pesticides, heavy metals, and drugs in the body, thorough detoxification is carried out. Intravenous injections of sodium thiosulfate and glucose , as well as salt solutions .
- Neuroendocrine syndrome is eradicated . Hormonal drugs are prescribed to replace missing substances, or speed up/slow down the synthesis of existing ones. Diets, vitamins and anorexants are prescribed ; if there is post-traumatic syndrome, a puncture needle is inserted into the subarachnoid space of the spinal pons. At this stage, all treatment is prescribed for up to six months.
- Drugs are prescribed to improve blood flow in all parts of the brain . The daily routine is adjusted, physiotherapy and special gymnastics are prescribed. Mass equalization also plays an important role. This stage goes together with the first two and is in no way the final one. Hypothalamic syndrome of puberty in girls with proper therapy is almost always cured by the age of thirty.
Development risk
The following are some risk factors for thalamic pain syndrome:
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
- Increased blood cholesterol levels (hypercholesterolemia).
- Elderly age.
- Blood clotting disorders.
- Irregular heart rhythm.
It is important to note that a risk factor increases the chances of developing the condition. Some are more important than others. The absence of a risk factor does not mean that a person will not acquire the syndrome.
Causes and pathophysiology
Although there are many factors and risks associated with strokes, very few are associated with thalamic Dejerine–Roussy syndrome. In general, strokes damage one hemisphere of the brain, which may include the thalamus. Sensory information from environmental stimuli enters it for processing. Then to the somatosensory cortex for interpretation. The end product of this is the ability to see, hear or feel. Thalamic syndrome after a stroke most often affects tactile sensations. Therefore, damage to the thalamus causes disruption of the interaction between the afferent pathway and the cerebral cortex, changing what or how a person feels. The change may be an incorrect sensation, an intensification or a dullness.
Classification of the disease
Due to the variety of causes that cause this syndrome and the very diverse symptoms, there is a very detailed classification of the disease.
Depending on the cause that caused the syndrome:
- primary nature (caused by injury or neuroinfection);
- secondary nature (caused due to constitutional obesity);
- mixed character.
Based on the clinical manifestations, hypothalamic syndrome occurs:
- vegetative-vascular form;
- neurotrophic form;
- neuromuscular form;
- pseudo-neurasthenic form;
- neuroendocrine form;
- psychopathological form.
This syndrome is also associated with:
- diencephalic epilepsy;
- violation of thermoregulation;
- disorder of motivation and desires;
- neuroendocrine metabolic disorders.
It is noteworthy that the syndrome, which is caused by damage to the hypothalamic area, manifests itself in the form of vegetative-vascular disorders in 32% of all cases.
Statistics also showed that in more than 27% of cases, this syndrome manifests itself in the form of a metabolic disorder. Even less often, namely in only 10% of cases of the disease, the syndrome manifests itself as a neuromuscular disorder.
And finally, in more than 20% of all cases, the syndrome manifests itself as a violation of thermoregulation.
The classification also includes options that characterize the severity of the disease. Based on this, we distinguish:
- light form;
- medium shape;
- severe form.
Article on the topic: When does menopause occur?
There is also a classification that is based on the nature of the development of the disease:
- recurrent;
- retrogressive;
- stable;
- progressive.
One characteristic feature should also be noted: during puberty of a boy or girl, the syndrome can either accelerate or, on the contrary, stop puberty.
The photo shows hypothalamic syndrome and its forms
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms associated with thalamic syndrome may include:
- Severe pain in the limbs (this may be constant).
- The reaction may be exaggerated: even a pinprick can cause severe pain.
- Superficial touch, emotional stress, and sudden changes in air temperature can cause severe pain.
- Weakness or paralysis of the affected limbs.
- Loss of position sense: inability to determine the position of a limb or the development of the illusion that it is not there when the eyes are closed.
- Abnormal involuntary movements.
How is it diagnosed?
Diagnosis of thalamic syndrome is carried out using the following methods:
- A thorough physical examination and assessment of the victim's symptoms.
- Assessment of medical history.
- Thorough neurological examination.
- Eliminating other causes of pain through the use of imaging techniques.
- Computed tomography of the head and neck.
- MRI of the brain.
- Angiogram of the brain.
How to treat
Treatment for thalamic syndrome is aimed at relieving pain. To achieve this, the following measures may be considered:
- Opioid use. Despite their effectiveness, relief lasts from 4 to 24 hours. In addition, they pose a high risk of developing addiction.
- Tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. They are effective for a short time.
- Use of anticonvulsants.
- Local anesthesia is relevant.
- Stimulation of the thalamus and spinal cord through implantation of electrodes.
Thalamic syndrome, as a rule, is not treated with commonly available pain medications. Pain medication is usually required for the remainder of life.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis is based on a set of measures that involve clinical and instrumental examination methods:
- collecting anamnesis, studying patient complaints and determining possible causes of pathology;
- checking superficial and deep skin sensitivity;
- establishing muscle strength of the limbs;
- visual field check;
- determination of reactions to auditory, visual and taste stimuli;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging;
- cerebral angiography.
Treatment of the pathology - symptomatic and pathogenetic - is based on the use of antipsychotics and antidepressants. A polypharmacotherapy regimen, a combination of drugs: an anticonvulsant, an antidepressant and an opioid, is considered effective. In cases where conservative methods do not bring results, surgical intervention is indicated, during which the doctor destroys the ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus. The operation is performed using a minimally invasive stereotactic method.
Along with traditional medicine, treatment of thalamic pain syndrome with folk remedies can be effective. Such therapy is aimed at relieving painful symptoms, but does not affect the causes and mechanisms of pathology.
Traditional medicine suggests treating the syndrome by pain relief or by trying to restore sensitivity to the skin, for which the following recipes can be used.
- Ginger infusion for bathing (to relieve pain): 50 grams of crushed dry root of the plant are placed in a thermos, poured with a liter of boiling water and infused for one hour. The contents are added to the bath. It is necessary to take water procedures for 15 minutes. Daily use of this infusion for bathing is contraindicated. Before taking a bath with ginger for the first time, you need to determine whether there are any allergic reactions to the plant. With a cotton swab moistened with the prepared solution, wipe a small area of skin on the wrist or elbow and wait 15-20 minutes.
- In case of loss of sensitivity, alcohol tincture of dandelions has a therapeutic effect. To prepare it, take 100 grams of the dry matter of the plant and pour half a liter of vodka. Infuse the medicine for a week, leaving the jar in a dark place and periodically shaking the contents. The tincture is used to rub the parts of the body that have lost sensitivity.
Thalamic syndrome is a complex of neurological symptoms caused by damage to the thalamus opticus. Diagnosis of pathology involves the use of clinical and instrumental methods. Treatment is symptomatic and pathogenetic.