So, your doctor has diagnosed you with radicular syndrome (sometimes slightly incorrectly called “radicular nerve syndrome”). No doubt you have some questions about this:
- What kind of disease is this? Why did it arise?
- How scary is this?
- How to treat it? Is it possible to get rid of this diagnosis, or is all that medicine can do only to relieve symptoms during exacerbations?
You will find answers to these questions in this article. And if you want to ask them directly to a specialist and get help, sign up for a consultation with me in Rostov-on-Don:
What is radicular syndrome
Radicular syndrome is one of the signs of many diseases associated with the spine. Most often, these are pathologies associated with the aging process of the body and occur in people over 40 years of age.
Radicular syndrome occurs when compression of the nerve roots extending from the spinal cord occurs. Spinal nerve roots pass from the spinal cord through a narrow opening in the vertebrae. In the presence of various factors, compression and inflammation of the spinal roots may occur here.
Pressure on the nerve root can be caused by a herniated disc, osteophytes - degenerative growths of bone tissue of the vertebrae, changes in vertebral height, displacement of the vertebrae and tumors. Currently, several definitions of radicular syndrome are used.
It is called myeloradiculopathy, radiculopathy or osteochondrosis. Most often, this disease develops in the lower back, less often in the cervical region, and even less often in the thoracic region. In order to understand how to treat radicular syndrome in osteochondrosis and what it is, let’s consider the importance of nerve pathways.
Find out how to take Neuromultivit.
Nerve fibers connect the anterior and posterior roots of the spinal cord. The anterior roots of the spinal cord are formed by the axons of neurons. The posterior ones consist of axons of afferent neurons. They contain a node that contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons. The posterior roots provide sensitivity, and the anterior roots provide motor reactions.
When spinal nerve fibers are damaged, movement disorders occur. The anterior and posterior roots are woven into a mixed nerve.
Each root is responsible for the work of a specific muscle. Based on this knowledge and the principles of the nervous system, the diagnosis of neurological diseases is based. Carrying out an examination, the neurologist determines which part of the spinal roots is affected.
The most important
Osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome is a consequence of long-term degenerative-dystrophic processes in the spine. This pathology is manifested by pain, numbness in the area that serves the damaged nerve, and limited mobility. When different segments of the spinal column are affected, the symptoms differ. If signs of the disease appear, you should visit a neurologist. It is important to carry out comprehensive treatment: medications, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, massage, etc. In the presence of intervertebral hernias, long-term pain that is not relieved by medications, and spinal deformities, surgery is prescribed. To avoid radicular osteochondrosis, you need to control your weight, eat right, include moderate physical activity, and wear comfortable shoes.
source
Causes
The reasons for the development of radicular syndrome include many factors . Let's look at their totality.
- Spinal osteochondrosis, associated with a decrease in the height of the vertebrae, can cause compression of the spinal nerve roots passing through them.
- Intervertebral hernia leads to compression of adjacent tissues, blood vessels and nerve fibers.
- Pinched nerves can occur as a result of the growth of osteophytes - bone growths on the vertebrae. This process accompanies diseases such as osteoarthritis and spondylosis.
- Injuries caused by various pathologies (spondylolisthesis, spinal subluxation) lead to nerve damage.
- Syphilis, tuberculosis, meningitis, osteomyelitis and other inflammatory diseases lead to damage to the root.
- Tumors of various origins.
- Large loads on the spine.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Incorrect posture.
- Excess weight.
- Metabolic and hormonal disorders.
- Spinal instability.
- Hypothermia.
- Congenital malformations.
Causes
Radicular osteochondrosis is a consequence of damage to the nerve roots that exit the spinal cord. These branches innervate the skin, skeletal muscles, diaphragm, and internal organs.
When nerve bundles are damaged, a sharp shooting pain appears that spreads to different parts of the body. In addition, the sensitivity of the area for which the inflamed nerve is responsible is impaired, and tendon reflexes are impaired.
Degenerative disorders of the spine develop over a long period of time. First, the vessels that nourish the cartilaginous lining of the vertebrae become empty, for this reason there is a lack of nutrients and a disruption of metabolic processes. The disc becomes denser, thinner, and its outer shell (annulus fibrosus) protrudes. Cracks may appear on its surface, then the nucleus pulposus protrudes through them, causing rupture of the outer shell. This is how a hernia is formed. Then an autoimmune process is launched, in which the immune system mistakenly begins to destroy its own tissues. Due to age-related changes, ossification of cartilage tissue occurs and osteophytes form on the vertebrae.
Radicular syndrome develops when nerve bundles are pinched by protrusions, hernias, osteophytes, or displaced vertebrae. Pathology develops with inflammation of the nerve root, damage to the myelin sheath of the nerve, and a decrease in its blood supply.
Radicular osteochondrosis can be caused by the following factors:
- Excessive load on the spinal column due to excess weight, pregnancy, frequent wearing of high-heeled shoes, heavy physical work, and playing strength sports.
- Curvature of the spinal column (scoliosis, kyphosis), drooping arches of the feet, deformation of the legs.
- Regular static loads during sedentary work.
- Frequent hypothermia of the back, infections.
- Spinal injuries.
- Poor nutrition, lack of nutrients in the diet, excess salt intake, etc.
- Systemic diseases, etc.
Radicular syndrome can be provoked by various factors that act individually or in combination.
Types of radicular syndrome
Depending on the area in which vertebra the nerve root was affected, the clinical manifestations will differ.
Cervical radicular syndrome is accompanied by pain and numbness in the crown and back of the head, as well as directly in the neck. Speech may be impaired.
When the lower vertebrae of the cervical spine are affected, the pain radiates to the collarbones, shoulders, arms and chest. This is sometimes confused with heart pain.
Damage to the cervical intervertebral disc with radiculopathy is associated with intervertebral hernia of the cervical vertebrae. Women are one and a half to two times more likely to suffer from pain syndromes of radiculopathy, and men are more likely to suffer from the disease itself.
Thoracic radicular syndrome is characterized by pain in the area of the shoulder blades and is transmitted to the inside of the arms. The development of pathology in the upper region of the thoracic spine is determined by pain in the lower ribs; pain spreads from the lower ribs to the abdomen and even the groin area.
What vitamins should I take for bone fractures?
Radiculopathy in the thoracic spine often has signs of a psychosomatic nature. For example, a sensation of a foreign body inside the pharynx, esophagus or stomach, pain in the heart or stomach.
Lumbar osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome is accompanied by sensory disturbances in the lower back, abdomen, groin and lower extremities. The patient may experience weakness in the legs, this is a symptom of muscle weakness, which leads to the loss of independent movement of the person.
Severe lesions can lead to complete loss of the ability to move , dysfunction of the pelvic organs, problems with urination and defecation. We will consider radicular syndrome of the lumbosacral region in more detail: its symptoms and treatment.
Symptoms of damage to individual roots
Spine C1.
The pain is localized in the back of the head, often accompanied by dizziness and possible nausea. The head is tilted to the affected side. Tension of the suboccipital muscles and their palpation pain are noted.
Spine C2.
Pain in the occipital and parietal region on the affected side. Head turns and tilts are limited. Hypoesthesia of the skin of the back of the head is observed.
Spine C3.
The pain covers the back of the head, the lateral surface of the neck, the mastoid region, and radiates to the tongue, orbit, and forehead. In these same areas, paresthesia is localized and hypoesthesia is observed. Radicular syndrome includes difficulty bending and straightening the head, pain in the paravertebral points and points above the spinous process of C3.
Spine C4.
Pain in the shoulder girdle extending to the front surface of the chest, reaching the 4th rib. Distributes along the posterolateral surface of the neck to its middle 1/3. Reflex transmission of pathological impulses to the phrenic nerve can lead to hiccups and phonation disorders.
Spine C5.
Radicular syndrome of this localization is manifested by pain in the shoulder girdle and along the lateral surface of the shoulder, where sensory disturbances are also observed. Shoulder abduction is impaired, deltoid muscle hypotrophy is noted, and the biceps reflex is reduced.
Spine C6.
Pain from the neck spreads through the biceps area to the outer surface of the forearm and reaches the thumb. Hypoesthesia of the last and outer surface of the lower 1/3 of the forearm is detected. Paresis of the biceps, brachialis, supinators and pronators of the forearm is observed. Reduced wrist reflex.
Spine C7.
The pain goes from the neck along the back of the shoulder and forearm, reaching the middle finger of the hand. Due to the fact that the C7 root innervates the periosteum, this radicular syndrome is distinguished by the deep nature of the pain. Decreased muscle strength is noted in the triceps, pectoralis major and latissimus muscles, flexors and extensors of the wrist. Decreased triceps reflex.
Spine C8.
Radicular syndrome at this level is quite rare. Pain, hypoesthesia and paresthesia spread to the inner surface of the forearm, ring finger and little finger. Characterized by weakness of the flexors and extensors of the wrist, and the finger extensor muscles.
Roots T1-T2.
The pain is limited to the shoulder joint and armpit area, and can spread under the collarbone and to the medial surface of the shoulder. Accompanied by weakness and hypotrophy of the hand muscles and numbness. Horner's syndrome is typical, homolateral to the affected root. Dysphagia and peristaltic dysfunction of the esophagus are possible.
Roots T3-T6.
The pain has a girdling character and goes along the corresponding intercostal space. It may cause pain in the mammary gland, and if localized on the left, it can simulate an angina attack.
Spines T7-T8.
The pain starts from the spine below the scapula and along the intercostal space reaches the epigastrium. Radicular syndrome can cause dyspepsia, gastralgia, and pancreatic enzyme deficiency. The upper abdominal reflex may be reduced.
Spines T9-T10.
Pain from the intercostal space spreads to the upper abdomen. Sometimes radicular syndrome has to be differentiated from an acute abdomen. There is a weakening of the mid-abdominal reflex.
Spines T11-T12.
Pain may radiate to the suprapubic and inguinal areas. The inferior abdominal reflex is reduced. Radicular syndrome at this level can cause intestinal dyskinesia.
Spine L1.
Pain and hypoesthesia in the groin area. The pain spreads to the upper outer quadrant of the buttock.
Spine L2.
The pain affects the front and inner thighs. There is weakness in hip flexion.
Spine L3.
The pain goes through the iliac spine and greater trochanter to the anterior surface of the thigh and reaches the lower 1/3 of the medial part of the thigh. Hypesthesia is limited to the area of the inner thigh located above the knee. The paresis that accompanies this radicular syndrome is localized in the quadriceps muscle and adductors of the thigh.
Spine L4.
The pain spreads along the front of the thigh, knee joint, medial surface of the leg to the medial ankle. Hypotrophy of the quadriceps muscle. Paresis of the tibial muscles leads to external rotation of the foot and its “slapping” when walking. Decreased knee reflex.
Spine L5.
The pain radiates from the lower back through the buttock along the lateral surface of the thigh and lower leg to the first 2 toes. The pain zone coincides with the area of sensory disorders. Tibialis muscle hypotrophy. Paresis of the extensors of the big toe, and sometimes the entire foot.
Spine S1.
Pain in the lower back and sacrum, radiating along the posterolateral thigh and lower leg to the foot and 3rd-5th toes. Hypo- and paresthesia are localized in the area of the lateral edge of the foot. Radicular syndrome is accompanied by hypotension and hypotrophy of the gastrocnemius muscle. Rotation and plantar flexion of the foot are weakened. Decreased Achilles reflex.
Spine S2.
Pain and paresthesia begin in the sacrum, covering the back of the thigh and lower leg, sole and big toe. Cramps in the hip adductors are often observed. The Achilles reflex is usually unchanged.
Roots S3-S5.
Sacral caudopathy. As a rule, polyradicular syndrome is observed with damage to 3 roots at once. Pain and anesthesia in the sacrum and perineum. Radicular syndrome occurs with dysfunction of the sphincters of the pelvic organs.
Symptoms
Signs of the development of radiculopathy are:
- radicular pain syndrome, pain is of the nature of burning, shooting, baking, they are localized at the site of the lesion, pain spreads in the direction from the spine to the internal organs or limbs, pain increases with sudden movement, sneezing, laughter and from exertion,
- curvature of the spine, due to pain the patient tries to take a position that minimizes it, the range of movements decreases, this causes certain parts of the back to “distort”,
- radicular vascular syndrome, impaired blood supply in the area of nerve fiber damage,
- decreased sensitivity of soft tissues and skin in the affected area, numbness leads to muscular dystrophy, poor wound healing, thinning of the skin and high injury rate,
- decreased ability to make voluntary movements (paresis),
- changes in neurological reflexes.
Depending on the area of damage to the spine, individual symptoms of the disease are distinguished.
In the cervical region, the pain is cutting in nature, it radiates to the shoulders, arms, sternum, and lower jaw. The pain intensifies when lying on the back, if the patient is asked to move his head. The pain intensifies when laughing or exhaling forcefully.
Pain in the thoracic spine appears after sudden movement, staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time, or during a coughing attack.
When the pathology is located in the lumbar region, the pain can be acute and shooting. As a result, movements become constrained and mobility decreases. Spasms are transmitted to the thigh, groin, lower back or abdomen. There are disturbances in urination and defecation.
Find out what injections are used for radiculitis.
Effective treatments
The main goal of treatment is to eliminate the root cause of compression of the nerve roots in the cervical spine. Initially, the pain syndrome is relieved, then the main problem is solved. The following treatments for radicular syndrome are used: drugs, gymnastics, physiotherapy, and folk remedies.
Medications
Medicines for the treatment of cervical radicular syndrome:
- NSAIDs (Movalis, Ibuprofen). They quickly cope with pain and influence the inflammatory process. Medicines should not be taken in long courses to avoid the occurrence of sharply negative side effects;
- painkillers (No-Shpa, Ketanov). The remedies help get rid of discomfort, but during this period, visit a doctor and start the necessary therapy. If you don’t do this and load the cervical spine, you will aggravate the situation, which will lead to serious complications;
- muscle relaxants. Relieve muscle spasms and cope with discomfort;
- B vitamins. Have a beneficial effect on the nervous system, which allows you to quickly restore the functioning of the nerve roots;
- chondroprotectors. They trigger metabolic processes, restore cartilage tissue, and prevent its further destruction.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
After relieving acute attacks of pain, the patient is prescribed procedures that influence the cause of compression of the nerve roots, which allows to slow down pathological processes and restore motor function to the damaged areas of the arms and shoulders.
Effective treatment procedures:
- massage. It is the most effective method of combating cervical radiculitis. Manipulations cope with pinched nerve roots, inflammation, discomfort, and symptoms of radicular syndrome;
- acupuncture. The introduction of special needles into pain points has a beneficial effect on metabolic processes, muscle spasms are stopped, which helps restore the normal functioning of the nerve roots and the conduction of impulses;
- exercise therapy sessions. Helps strengthen the muscle corset and restore motor function. An important aspect of the manipulations is an experienced instructor and regularity of exercise therapy.
Useful tips for patients
Recommendations:
- Cervical radiculitis often develops in patients who abuse salty, spicy, and smoked foods. By eliminating these foods, alcoholic drinks, sweets, you will help the body overcome the disease and cope with its symptoms;
- bed rest. Avoid physical activity during and after therapy. Although my health has improved significantly, putting stress on the cervical spine during this period is dangerous. Take care of your health, be vigilant, pathological processes cannot be completely cured, they are only slowed down;
- wearing a special bandage. The product helps relieve pain and helps maintain the cervical vertebrae in the correct position. You cannot wear a bandage for a long time; neglecting this rule can lead to muscle atrophy and worsen the situation.
Surgical intervention
The operation is indicated in cases where the radicular syndrome cannot be treated with conservative methods of therapy. The essence of surgery is to remove a hernia, a tumor that compresses the radicular nerve. Choose the most minimally invasive method.
The operation solves the problem, but the slightest mistake by the doctor can lead to impaired motor function or complete loss of sensitivity in certain areas. In addition, the operation costs a lot of money, so most patients are inclined to conservative methods of therapy, agreeing to surgical intervention only in emergency cases.
Folk remedies and recipes
Proven traditional medicine recipes:
- decoction of chamomile and calendula. Pour 200 grams of raw materials (1:1 calendula and chamomile) with a liter of boiling water. Strain the finished product and drink throughout the day. The decoction will help relieve inflammation and relieve pain;
- chestnut tincture. Pour 200 grams of finely chopped raw materials with a liter of alcohol or vodka. Insist for two weeks. Mix the finished product with sea buckthorn oil in a 1:2 ratio and rub into the damaged neck area overnight. To increase the effectiveness of the drug, wrap your neck with cellophane or a terry towel;
- honey + mumiyo. Mix the components in a 2:1 ratio, apply to the neck area, rub in a little, and you can massage the affected area for ten minutes. Then rinse with water and apply any moisturizer. The course of therapy is three weeks.
Please discuss all prescriptions with your doctor before use. If tumors are present, the above-described folk remedies cannot be used.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, it is very important to know the underlying cause. To do this, the patient is interviewed, a neurological examination is carried out, and reflexes are checked.
The diagnosis of discogenic radiculopathy is made based on the clinical picture, depending on where sensitivity and movement are impaired. This shows which vertebrae are included in the affected area. For example, pain in the lower back, spreading along the outer surface of the thigh and lower leg, indicates the presence of lumbar ischialgia. Lower back pain indicates lumbodynia.
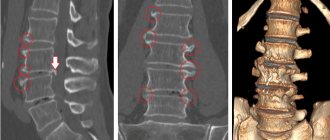
Diagnosis of radicular syndrome is carried out using x-rays in different projections, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography.
Diagnosis of the causes of sacrolumbar radicular syndrome
When contacting about the symptoms of radiculopathy, the first thing the doctor begins is to collect an anamnesis and clarify in the patient the time of onset of the disease, previous symptoms and concomitant disorders.
Most often, many causes can be excluded at this stage, but further instrumental examination is required according to the algorithm for diagnosing neurological diseases.
Neurological examination
It includes an assessment of neurological symptoms with further assumption of the topography of the lesion. Based on this stage, the patient is prescribed additional examinations.
X-ray of the spine
In 70% of cases, it allows diagnosing the cause and localization of the pathological process. In case of osteochondrosis, a hernial protrusion is visualized in the image; in case of injury, the boundaries of the fracture can be seen; in case of osteomyelitis and tuberculosis, bone cavities can be seen.
But diagnosis of tumors by X-ray examination is possible only when the process is localized in the vertebra itself. The study is carried out in direct and lateral projection.
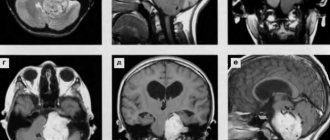
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging
They are the next stage of examination of a patient with radiculopathy and make it possible to more accurately diagnose the location and develop a treatment plan. At the same time, CT is the most informative in cases of damage to the articular and bone apparatus of the spine.
MRI allows you to diagnose the presence of tumors of the spinal cord and roots, in the absence of any pathologies on x-ray images.
General clinical examinations (blood tests, urine tests, ECG and others)
They are performed on all patients, regardless of the suspected cause of the disease. They help clarify the diagnosis in doubtful situations and adjust the treatment plan.
Treatment
Treatment of radicular syndrome is prescribed based on the causes of the disease.
The patient is prescribed bed rest and the use of a hard, even mattress for sleep.
Drug treatment includes the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are used in the form of tablets or ointments. They work to relieve pain, reduce inflammation in the area of damaged nerves and reduce swelling. Long-term use of these drugs has contraindications, so they are used during periods of exacerbation.
Analgesics (Ketorol, Baralgin) reduce pain.
Muscle relaxants relax cramped muscles and relieve pain.
Vitamin complexes and preparations containing B vitamins (Neuromultivit, Milgamma) are prescribed to nourish nerve tissue and strengthen the nervous system.
Chondroprotectors are useful for preventing the destruction of spinal tissue. They nourish cartilage tissue, preventing its destruction. One-time use of such drugs may not be effective. They should be used in courses over a month. The duration of such a course should be determined by the doctor depending on the patient’s condition.
Depending on the part of the spine, treatment may have its own characteristics.
For example, cervical osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome and its treatment will be associated with a decrease in the load on the vertebrae. For this purpose, a special orthopedic Shants collar is used. It fixes the neck in a normal position, relieves stress and relaxes spasming muscles.
Find out what magnetic therapy can do for your joints.
It is worn during exacerbations or when working for a long time in a sitting position. To sleep, you need to choose a pillow that will not cause neck curvature; the mattress must be firm. Such devices will help speed up the healing process.
Wearing orthopedic corsets is useful for the thoracic and lumbar spine.
Physiotherapeutic
Various methods of physiotherapy have a good effect.
These are ultrasound, magnetic therapy, spinal traction (traction therapy), electro- and iontophoresis with the use of drugs, acupuncture. They are characterized by painlessness and the ability to act directly on the lesion.
Nerve cells are very sensitive to ultrasound. Ultrasound therapy is very useful for the nervous system, it normalizes its condition, reduces the sensitivity of receptors, relieves pain, and produces a “micro-massage” at the cellular level.
Spinal traction can be done in different ways. In the treatment of radicular syndrome, dry traction of the spine is used - this is traction under a person’s own body. For example, when you are hanging on a horizontal bar. The doctor can do this manually or using vertical or horizontal tables.
Acupuncture affects reflex points. It triggers the processes of regeneration of nerve fibers, stimulates blood circulation in a given area and relieves pain.
Laser therapy is very effective in treatment. It acts directly on the affected area, activates tissue regeneration, improves microcirculation, relieves swelling and inflammation.
Almost all of the above methods of physiotherapy have the properties of pain relief, relieving swelling, relaxation, improving nutrition of damaged tissues in the affected area, restoring metabolism and improving blood circulation. These methods are prescribed sequentially one after another under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
Surgical
If conservative treatment does not bring adequate relief, surgical treatment is resorted to. It is prescribed in severe cases , in the presence of intervertebral hernias, bone growths on the vertebrae and other complications.
Prevention of CS
Preventive measures to prevent CS include a standard complex of strengthening the body:
- Following a diet with a minimum content of fatty, fried, salty foods. You need to exclude tobacco and alcohol. More fresh fruits, vegetables, dairy and grain products.
- Taking a complex of vitamins.
- Physical exercise. It is not necessary to go to the gym: it is enough to do gymnastics, including turns, bends, squats and the like, 2 times a day.
- Once every six months to a year it is necessary to undergo a massage course.
- You should see a doctor once a year, regardless of your condition.
Osteochondrosis of the spine with radicular syndrome is a dangerous pathology, expressed in acute pain. Since CS is the consequences of some disease, its symptoms can be different.
Effective treatment requires a visit to the doctor, because measures taken independently can aggravate the situation.
Prevention
As a preventative measure, it will be useful to follow a diet and maintain a balanced diet. Then you can avoid problems with excess weight, the development of metabolic disorders and lack of vitamins. You can take vitamin B complexes as prescribed by your doctor, which help improve the functioning of the nervous system.
Sports activities with moderate loads, aimed at developing and developing joints and muscles, and strengthening the back muscles, are very useful. It is always necessary to maintain correct posture; during long car trips, it is useful to place a cushion under the lower back to maintain the natural curve of the spine.
Massage courses allow you to relieve tension and tightness in the area of spasmed muscles, making them soft and elastic. It is useful to wear orthopedic shoes; they maintain correct posture and the physiological position of the spinal column. Special orthopedic devices are also used for posture: a neck collar, a corset, shoe insoles, pillows and mattresses for sleeping.
Diagnosis and treatment
To treat radicular syndrome correctly, it is necessary to clearly determine the location of the pinching. For these purposes, modern diagnostic methods are used to promptly identify a clinical abnormality. Informative diagnostic methods are:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the vertebral sections.
- CT (computed tomography) of the spine.
- Electroneuromyographic examination.
- X-ray scan.
It should be noted that thoracic radicular syndrome with somatic symptoms requires a more thorough examination to exclude possible pathology of the internal vital organs.
In case of a confirmed diagnosis of a neurological nature caused by degenerative-dystrophic disorders of the spinal column, conservative treatment methods are used. At the initial therapeutic stage, it is necessary to block pain attacks. Traditional pharmacological drugs are used as painkillers - analgesics (Baralgin, Analgin, etc.) and non-steroidal groups (Diclofenac, Movalis, Ibuprofen, Ketorol, etc.). If the diagnosis of lumbodynia with radicular syndrome is confirmed, then a local blockade based on the anesthetic drug novocaine, which has a strong anesthetic effect, is used to eliminate the pain syndrome. In addition, treatment of radicular syndrome involves the use of other pharmacological agents:
- Ointments and gels, for example, Fastum gel, Finalgon, Viprosal.
- Muscle relaxants – Sirladud, Baclofen, Midocadm, etc.
- Vitamin preparations – Combilipen, Neuromultivit, etc.
In special cases, when neurological pathology is accompanied by vegetative-vascular dystonia, angioprotectors, vasodilator dosage forms, psychotropic and/or sedative pharmacological groups are prescribed.
Physiotherapy and reflexology and physical therapy play an important role in the complex treatment of a neurological condition. Once pain is eliminated, the patient is offered a set of therapeutic and preventive procedures that help restore damaged neurotic areas of the spinal column.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/tqkQD57qpiU
In addition, an obligatory element of complex therapy is compliance with dietary nutrition standards. And you should not neglect traditional medicine treatments. Warming ointments and herbal compresses will help relieve pain before starting complex drug therapy. Impaired mobility can be restored with alcohol tinctures based on wild garlic, red pepper, garlic, radish, honey, and so on.
Clinical picture
Cervical radicular syndrome manifests itself in different ways, it all depends on the damage to a particular spinal root.
By the nature of the pain, you can determine the localization of the pathological process:
- C1. Compression of the upper spinal root provokes constant headaches that are not relieved even by strong analgesics. Discomfort extends to the area of the back of the head and crown;
- C2. Damage to this root is manifested by the symptoms described above; in addition, hypertrophy of the chin muscles is formed, which is why they begin to sag. This situation leads to the formation of a “double” chin;
- C3. Pain on one side of the neck (similar to the side of the injury). In the same area, a feeling of numbness appears, the skin/muscles under the chin sag. Many patients complain of a lack of sensation on one side of the tongue, although there is no numbness, and speech is impaired;
- C4. Discomfort is noted in the area of the collarbone, shoulders, and in some situations the pain reaches the heart and liver. The neck muscles are weakened, so there is frequent pain in this area;
- C5. Depending on the side of the lesion, numbness of the arms and shoulders appears in this area. When moving their arm, victims complain of weakness in the shoulder joint;
- C6. Discomfort covers large areas: pain spreads from the neck, felt throughout the arm, right down to the fingertips. The muscles lose their tone, it is difficult to move the arm;
- C7. Pain is noted in the neck, shoulder blade area, and the shoulder is affected on all sides. The tone of not only the biceps is reduced, the triceps are also affected;
- C8. Numbness spreads to the neck, the entire arm (all fingers are affected). The muscle weakness is severe, making it difficult to raise the arm.
Note! When turning or tilting the neck, the pain intensifies, sometimes patients lose sensitivity in certain areas for some time