Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is an inherited heterogeneous disease characterized by hyperelasticity of the skin, which is associated with a deficiency in collagen formation. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome has various types of inheritance and non-ideal desmogenesis. This pathology depends on individual mutations and can manifest itself as a moderate course of the disease or unsafe for life.
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is considered the most common connective tissue disease and occurs in a ratio of 1: 100,000 newborns. There are no special methods of healing, only therapy in the form of care that can mitigate the effects of pathology.
General information
The main reason for the development of the syndrome is poor heredity, which leads to improper development and functioning of connective tissue structures.
According to statistics, pathology is relatively rare. On average, 1 person per 15–100 thousand is sick, however, this information may vary, because the disorder often remains undetected.
Diagnosis is difficult:
- the incompetence of doctors who have not encountered a congenital disorder;
- a variety of symptomatic signs that manifest themselves from different systems;
- the lack of genetic centers that could confirm the presence of the syndrome;
- the patient’s reluctance to see a doctor or undergo expensive screenings in laboratories.
A genetic mutation provokes a number of disorders that pose a serious danger to the body, affect life expectancy and often lead to disability. The first signs of the disease appear at different ages, often before 30 years. Some manifestations are noticeable in children 1-2 years of age.
There are no effective treatment methods, however, early diagnosis helps to partially avoid dangerous consequences and significantly improve the quality of life.
Lifespan
With this syndrome, life expectancy is clearly reduced. This is due to the possible development of disability. In addition, patients arrive in constant fear.
Hemorrhages, ruptures and pain lead to death. Fatal outcome - decreased life expectancy. Death occurs with a severe type of lesion.
Treatment should be gentle and comprehensive. If treatment measures are followed, the prognosis and further life expectancy increases. But you should definitely consult a doctor!
Classification
According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), the disorder is coded Q79.6.
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is divided into the following types:
- First. It accounts for 43% of patients. This option assumes a classic severe course, with a pronounced clinical picture. Patients with this type of disease experience increased mobility in the joints, abnormal skin extensibility, and vascular disorders. Women with this diagnosis often experience premature birth.
- Second. This type is similar to the previous one, only the damage to organs and systems is less pronounced. The course of the disease is classic, but milder. Cartilage tissue is affected mainly on the feet and hands, and the elasticity of the skin exceeds the norm by 30%. The risk of bleeding and the tendency to scarring is minimal.
- Third. A disorder with a relatively favorable prognosis. Increased joint mobility and deformation in various parts of the musculoskeletal system come to the fore. Hemorrhages, hyperelasticity of the skin and a tendency to form scars are absent or weakly expressed. The disease is transmitted from parents in an autosomal dominant manner.
- Fourth. A rare variety with a high degree of lethality. Increased skin elasticity is weak or absent, and hypermobility is detected mainly on the fingers. Vascular pathologies come to the fore, leading to the spontaneous formation of bruises under the skin and hematomas, including internal ones. Death is caused by internal bleeding caused by rupture of large vessels or organs.
- Fifth. It is transmitted to children in whose families one or both parents are sick. The type of inheritance is X-linked recessive. Accompanied by classic symptoms. The extensibility of the skin is significantly expressed. Joint hypermobility, bleeding and other signs are moderate.
- Sixth. Inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, affected children are born to clinically healthy or sick parents. If both spouses have a genetic defect, then all offspring will be born with pathologies. The peculiarity of this variety is eye syndrome, combined with hypermobility of the joints and hyperextensibility of the skin. There is muscle weakness, deformation of the spine, ankle and other signs.
- Seventh. Inherited differently. The disease can be suspected by small stature, combined with movable joints of the arms, legs and spine. Throughout their lives, patients often encounter dislocations that arise “out of the blue.” For example, when reaching out for a fallen object or lifting a heavy object.
- Eighth. This type is transmitted from sick parents. The leading symptom is dental problems that begin against the background of periodontal inflammation. This is the name given to the connective tissue structure that surrounds the tooth root. Pathology leads to early loosening and loss of teeth.
- Ninth. Inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Clinical signs are manifested by excessive elasticity of the skin and too mobile joints. In parallel, there are problems with blood clotting and band-like muscle atrophy. The pathology can be complicated by massive bleeding, heart attacks and strokes.
- Tenth. In the patient's family, one of the parents is always sick. The main signs of this type are dislocations and subluxations of large joints of the shoulder, hip, and patella. Often injuries are recurrent in nature. Sometimes they appear during the newborn period, after passing through the birth canal.
If one of the spouses in the family has Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, then after conception it is recommended to undergo several genetic screenings to check whether the child has received the defective gene.
Causes of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Ehlers Danlos syndrome has various variations, which differ in the type of inheritance, in primary defects at the molecular and biochemical level. Gene mutation underlies each type of disease, which causes collagen pathology: there is a quantitative factor or a structural one.
The pathomorphological picture for any type of syndrome consists of very thin skin, a defect in the orientation of collagen fibers, an increase in the number of elastic fibers, proliferation and increase in the lumen of blood vessels.
Etiology
Collagen is an important protein element of every connective tissue structure, which provides it with elasticity and strength.
To date, scientists have identified 19 types of collagen proteins. In Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, substances of types 1, 3 and 5 are affected. As a result of gene mutation, there is a decrease or complete cessation of their production, which necessarily entails negative consequences:
- lack of amino acids that make up collagen;
- proliferation of elastic fibers;
- thinning of the skin;
- growth of additional vessels, expansion of their lumen;
- violation of the properties of organs and tissues;
- the occurrence of mucoid edema, indicating the first degree of connective tissue disorganization.
As it progresses, fibrinoid changes, inflammatory processes and sclerosis develop in the affected area - replacement of healthy areas with scar tissue.
The etiology and pathogenesis of the disease have been poorly studied, which is explained by the complexity of the mechanisms of collagen production and its functioning. For this reason, the classification of the syndrome often changed several years in a row. A relatively stable list has now been established.
What is Ehlers Danlos syndrome
Ehlers Danlos syndrome is an inherited connective tissue disorder. Associated with the destruction of the gene that is responsible for coding collagen. Because of this, the collagen structures of various body systems change their behavior patterns and develop insufficiently, which provokes pathologies of the skin, musculoskeletal system, eyes and cardiovascular system.
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome according to the ICD-10 scale is assigned code Q79.6. The disease occurs from 1 time per 5000 population to 1 time per 100 thousand population, as it has various forms and degrees of severity.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease primarily depends on its type.
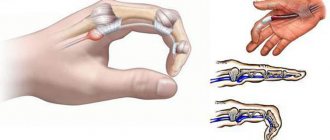
With hypermobility syndrome it is noted:
- excessive mobility of joints, frequent dislocations, subluxations, sprains and ruptures of ligaments;
- softening of the bones, often occurring before age 30;
- longitudinal or transverse flatfoot;
- acquired heart defects of varying severity;
- wandering muscle or joint pain;
- palate, the height of which does not correspond to normal parameters;
- easily stretchable, smooth and tender skin, poor wound healing.
Vascular pathology manifests itself:
- fragility of blood vessels, the appearance of bruises and hematomas for no apparent reason;
- tendency to cracks on the lips, anus and other parts of the body;
- pallor and thinness of the skin, clearly visible blood vessels in the chest area, slight damage due to minor contact;
- dizziness, frequent headaches, weather dependence.
With kyphoscoliosis it is noted:
- decreased muscle tone after birth;
- hypermobility of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine, as well as other joints;
- eye problems;
- fragility of the vascular walls with all the ensuing consequences - varicose veins, hematomas;
- early progressive curvature of the spine (scoliosis, kyphosis), which by the time of adulthood often deprives a person of the ability to walk and leads to disability.
What movable joints are can be seen in the photo on the Internet.
In the classic course of the disease the patient:
- very delicate, smooth and elastic skin, which is easily injured;
- the site of injury does not regenerate properly, so scars remain on the face and body;
- pronounced joint mobility, leading to frequent dislocations;
- there is a tendency to displacement of internal organs and the formation of hernias.
Dermatosparaxis (type 7C) is more characterized by problems with the skin, which acquires the consistency of dough and stretches greatly, and small and large hematomas form under it.
The surface of the face and torso is easily injured, but excessive scarring is uncommon with this disease. This is a very rare type of disease (only 10 cases), so the clinical picture is not well described. With arthrochalasia corresponding to type 7 (A and B), all the symptoms characteristic of the classical form occur, however, assessing them and making comparisons is problematic, because the total number of people who sought help is only 30 people.
Considering that collagen is part of all organs and tissues, the manifestations may be different. If a serious pathology is suspected, a consultation with a doctor is required, who will conduct an examination and, if necessary, tell you how to treat Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and what it is.
Symptoms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Symptoms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome vary depending on the type of disease.
The classic form is different:
- smooth, elastic skin, which is sensitive to wounds and bruises;
- joint hypermobility;
- joint dislocations;
- decreased muscle tone.
The hypermobile appearance has the following clinical manifestations:
- flat feet;
- fatigue;
- pain in the muscles and joints;
- the appearance of Raynaud's disease;
- termination of pregnancy due to premature rupture of the membranes;
- changes in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- very smooth skin, easily susceptible to wounds;
- presence of bruises;
- early progression of osteoporosis;
- mitral valve prolapse.
Skin elasticity in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Muscle hypotonia can be diagnosed in children. Signs of the vascular type of disease include:
- hypermobility;
- fragility of vascular walls, ruptures of blood vessels;
- the appearance of cracks and bruises.
Pregnancy for women with vascular type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is dangerous, as uterine rupture is possible.
The main symptoms of the kyphoscolic form include the following:
- joint hypermobility;
- congenital hypotonia in the muscles;
- delay in motor development;
- vulnerability of the skin;
- sudden retinal detachment;
- development of scoliosis.
The patient may have external signs of the marfanoid type.
In arthroclasia, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is characterized by:
- congenital dislocation of the femur;
- hypermobility of joints and recurrence of their dislocations;
- skin hyperelasticity;
- kyphoscoliosis;
- hypotension in the muscles.
Dermatosparaxis is different:
- excessive sensitivity of the skin;
- soft skin with the formation of additional folds;
- the appearance of hernias (in some situations).
There are situations where blistering rashes appear on the mucous membrane of the tongue and cheeks.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on the results of genetic analysis. It is carried out for children at risk, as well as for persons who have a characteristic clinical picture. First of all, the doctor is concerned about hypermobility of the joints, altered fundus, pathologies of the cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract.
To assess the general condition and identify complications, a thorough examination is carried out, including:
- laboratory tests (general, biochemistry, etc.);
- instrumental methods (MRI, CT, X-ray, ultrasound of affected organs);
- biopsy (taking a skin sample for subsequent cytological and histological examination, which will help identify the problem at the cellular level).
The diagnostic scheme is selected individually depending on complaints, genetic test results, age and gender. Often people first learn about the presence of complications, and after a while they receive a referral to a geneticist. Considering that not all doctors have encountered such patients, diagnosis is often delayed.
Treatment and prevention
There are no effective therapeutic methods that can eliminate the disease forever.
The treatment regimen is aimed at:
- replenishment of nutritional deficiencies;
- improvement of human condition;
- slowing down pathological processes;
- correction of defects.
Improvements can be achieved through complex treatment, including:
- physical therapy;
- physiotherapeutic methods;
- massages;
- taking medications;
- surgical intervention.
The list of medications includes:
- vitamins B, C, E, D;
- amino acid kartinin;
- mineral complexes with magnesium, potassium and calcium;
- chondroitin and glucosamine;
- drugs to normalize metabolism.
If indicated, serious defects of the spine, limbs, brain and other parts are eliminated promptly.
It is impossible to protect yourself from the occurrence of the disease. If suspicious symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor and insist on a genetic test, especially if there is such a diagnosis among your immediate family.
The best prevention of complications is following your doctor's recommendations and regular examinations. Such measures do not always protect against unpleasant consequences, but they help to endure them more easily.
Treatment methods
Elars-Danlos syndrome cannot be completely cured. However, competent therapy will help improve the patient’s quality of life, as well as prevent dangerous pathologies. There is no effective specific treatment for the pathology. Symptomatic therapy is carried out, which is aimed at reducing unpleasant symptoms and improving the general condition.
With Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, it is important to ensure that the child is not injured, takes special medications, attends physical therapy sessions, and performs therapeutic exercises
For children, you need to create a gentle regime, make sure that they do not injure their joints and skin. It is also important to limit physical activity and follow a special protein diet. The menu needs to be supplemented with bone broths, jellied dishes, and aspic.
Physiotherapy is also useful for EDS, for example, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, laser acupuncture. Treatment can be supplemented with acupuncture, massage, and therapeutic exercises.
The patient must take the following medications:
- Amino acids, for example, Carniton, Nutraminos.
- Chondroprotectors (Teraflex, Rumalon, Alflutop).
- Preparations based on B vitamins, ascorbic acid, tocopherol.
- Mineral-based products (Panangin, Asparkam, Pamaton, etc.).
- Metabolic agents (Riboxin, Coenzyme Q10).
- Nootropics (Piracetam, Semax, Cerebrolysin).
Surgery is prescribed only in severe cases. The patient can undergo chest reconstruction, removal of pseudotumors, correction of congenital heart defects, etc.
Forecast
How further events will develop after diagnosis will depend on the type of disease and the implementation of medical recommendations.
An unfavorable prognosis awaits patients with vascular type 4 pathology. Due to the fragility of the vessels, they are at high risk of developing an aortic aneurysm or rupture of internal organs, followed by bleeding. Most of these patients cannot be saved.
In the classic severe course, patients’ quality of life significantly decreases, and a number of limitations appear. The army is contraindicated for men with this diagnosis.
The second and third types also affect the quality of life, but in general they have the most favorable prognosis, which is confirmed by reviews on thematic forums.
Types and manifestations
There are 10 main varieties. Their differences lie in the gene defect, symptoms and inheritance patterns.
- It is called classic with a severe course. Occurs in more than 40% of cases. It is distinguished by autosomal dominant inheritance. In this case, the patient experiences increased skin extensibility. When compared with a healthy epidermis, with pathology it stretches twice as much. There is also curvature of the skeleton, an increased tendency to form scars and pseudotumors, and wounds often appear. Some patients may experience varicose veins in the legs. And a pregnant woman may experience premature birth.
- This is also a classic look, but with a soft flow. He has the same symptoms as in the first case. They are less pronounced. The skin does not stretch significantly, and the joints are especially mobile only in the feet and legs.
- This type has autosomal dominant inheritance. Increased mobility of all joints appears and there are pathological changes in the muscles and skeleton.
- This is a vascular species. You don't see him often. It is characterized by a severe course and a tendency to form spontaneous hematomas. Rupture of hollow organs and blood vessels may occur. The epidermis stretches a little, the fingers turn in the opposite direction.
- Has recessive inheritance. In this case, the skin is greatly stretched, and bruises and wounds often appear on it. Joint hypermobility is moderate.
- With this type of pathology, severe kyphoscoliosis and clubfoot are observed. There may be problems with vision. The formation of strabismus, glaucoma, and retinal detachment is possible.
- It can be inherited in an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive manner. The patient has hypermobility of the joints, which leads to frequent dislocations
- A distinctive feature is the fragility of the dermis. The patient develops severe periodontitis, which leads to tooth loss at an early age.
- It has autosomal recessive inheritance and is expressed by stripe-like skin atrophy and impaired platelet aggregation.
- Patients experience dislocations of the shoulder joints and patella. You can encounter congenital dislocation of the hip.
At the moment, type 11 has been excluded from the list. This is an X-woven version of flaccid skin.