Analogues of the drug according to ATC codes:
LORNIZOL ORNIDAZOL ORNIDAZOL ORNISIDE
Before using DAZOLIK you should consult your doctor. These instructions for use are for informational purposes only. For more complete information, please refer to the manufacturer's instructions.
Reviews about "Dazolik"
Dazolic allows you to deal with malicious agents in the shortest possible time, and therefore users often respond positively to it. The undeniable advantage of the drug is that its use rarely (compared to other antibiotics) produces undesirable effects.
The drug, due to its antiprotozoal properties, is often used in pediatric departments and in the treatment of adult patients.
However, it should be remembered that Dazolic is an antibiotic, and therefore its use should always be approved by a specialist. Self-medication in such cases can cause complications and the development of drug resistance in bacterial agents.
Release form, composition and packaging
White or almost white, film-coated tablets, round, biconvex, scored on one side.
| 1 tab. | |
| ornidazole | 500 mg |
Excipients: sodium starch glycolate (type A), starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate, polyvinylpyrrolidone K90 (povidone), purified talc, microcrystalline cellulose.
Shell composition: Eudragit E-100, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol 6000, isopropyl alcohol, acetone, purified water.
10 pieces. — strips (1) — cardboard packs.
Analogs
Dazolic is not always available in pharmacies, since it is an imported medicine. Instead, you can purchase medications with a similar composition, manufactured under other trade names.
The most affordable substitute for Dazolic, containing the same active ingredient in the same dosage, is the domestic Ornidazole. It treats the same diseases as Dazolic, but is cheaper and is sold in every pharmacy.
In gynecology, vaginal suppositories with ornidazole containing 500 mg of the active substance are used.
Ornidazole tablets:
- Gairo;
- Ornisid;
- Tiberal;
- Avrasor.
Full characteristics of Ornidazole - the drug and active substance:
It is a mistake to believe that there is no better drug than Dazolic. Any of the listed analogues is not inferior to it in bioavailability and effectiveness.
pharmachologic effect
Antiprotozoal drug, a derivative of 5-nitroimidazole. The mechanism of action is the biochemical reduction of the 5-nitro group of ornidazole by intracellular transport proteins of anaerobic bacteria and protozoa. The reduced 5-nitro group of ornidazole interacts with DNA in microbial cells, inhibiting the synthesis of their nucleic acids, which leads to the death of bacteria.
Active against Trichomonas vaginalis, Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica, as well as against anaerobic bacteria (Bacteroides spp. /including Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides distasonis, Bacteroides ovatus, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides vulgatus/, Fusobacterium spp., Clostridium spp .). Aerobic microorganisms are not sensitive to ornidazole.
What is Dazolic
The drug Dazolic is an antiprotozoal drug that has antibacterial activity. The main substance ornidazole, which is part of the drug, can act on the simplest anaerobic microorganisms. This modern drug causes the death of bacteria. Dazolic is often recommended for the prevention of infectious diseases. The medicine is also indispensable during gynecological operations. The medicine can be used to treat adults and young children.
Composition and release form
The drug Dazolik is produced in the form of round, biconvex tablets, coated with an almost white film coating; on the break you can find a core of the same color. Each tablet for oral use contains 500 mg of the active substance - ornidazole. The drug is packaged in blisters of 10 pieces in a cardboard box. The auxiliary components of the medicine are:
- titanium dioxide;
- starch;
- purified talc;
- povidone;
- microcrystalline cellulose;
- colloidal silicon dioxide;
- macrogol;
- Magnesium stearate.
Pharmacological properties
The antiprotozoal and antibacterial drug is a derivative of 5-nitroimidazole. The mechanism of action of the drug is the biochemical reduction of the nitro group of ornidazole by transport intracellular proteins of anaerobic bacteria. The active substance of the drug interacts with DNA in protozoan cells, inhibiting the synthesis of their nucleic acids, which leads to the death of microorganisms.
Absorption of the substance from the gastrointestinal tract is high. When ornidazole enters the body, it is quickly absorbed from the digestive tract; in plasma its maximum concentration can be observed 2 hours after administration. Next, the active substance penetrates into other tissues, passes through the placental and blood-brain barriers, and after 14 hours is completely excreted in feces and urine. Bioavailability – 90%. Plasma protein binding is less than 15%. The drug is metabolized in the liver by glucuronidation. Excreted by the kidneys.
Indications for use
The main pharmaceutical effect of the drug is aimed at eliminating microorganisms related to protozoa. The active components of the antibiotic disrupt the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid, the main carrier of genetic information necessary for the normal functioning of living cells. Dazolic tablets can be taken only after examination and prescription by a doctor. The main indications for the use of the drug are the following conditions:
- giardiasis;
- dysentery, which is caused by the activity of amoebas (extraintestinal amebiasis);
- trichomoniasis;
- for prophylaxis before operations on the colon and gynecology.
Contraindications and side effects
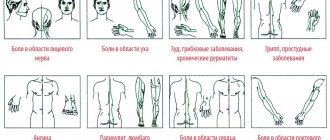
Before starting to use the tablets, the patient must undergo an examination (blood, stool, and urine tests). Only a doctor can prescribe medicine - self-medication can harm the human body. If all the doctor’s recommendations are strictly followed and the dosage is correctly calculated, the medication is well tolerated by patients. High individual sensitivity or an increase in the course of treatment in a patient can cause the following side effects:
- disturbance of consciousness;
- headache;
- rigidity;
- increased activity of liver enzymes;
- diarrhea;
- tremor;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- convulsions;
- incoordination of movements;
- peripheral mixed or sensory neuropathy;
- vomit;
- allergy.
Ornidazole has a depressant effect on the human brain, so you should not use the drug while driving or other work that requires precise coordination of movement. In order not to harm the baby, Dazolic should not be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
It is necessary to use the drug with caution in case of liver diseases. In addition, the main contraindications of the drug are:
- severe diseases of the central nervous system;
- epilepsy;
- children under 3 years of age;
- individual intolerance to the active substance or other components of the drug;
- chronic alcoholism.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction and distribution
Absorption from the gastrointestinal tract is high. Bioavailability - 90%. Time to reach Cmax is 1-2 hours.
Communication with plasma proteins is less than 15%. Penetrates into most tissues, passes through the blood-brain barrier and the placental barrier. Excreted in breast milk.
Metabolism and excretion
Metabolized in the liver by hydroxylation, oxidation and glucuronidation. T1/2 - 12-14 hours. Excreted in the form of metabolites by the kidneys (60-70%) and with feces (20-25%), about 5% of the dose is excreted unchanged.
Pharmacological group
The active ingredient of the drug - ornidazole - has an effect on Giardia, Trichomonas, dysenteric amoebas, some types of anaerobic microorganisms (anaerobic cocci, some strains of clostridia, fusobacteria, bacteroides). The death of harmful microorganisms occurs due to the interaction of the active substance with their deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) cells and the subsequent decrease in the synthesis of nucleic acids.
Side effects that the drug may cause include:
- perversion of taste sensations;
- diarrhea;
- nausea, vomiting;
- neuropathy (mixed peripheral, sensory);
- convulsions;
- muscle stiffness;
- tremor;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- dizziness, fatigue, drowsiness, headache;
- allergic reactions.
“Dazolik” itself and analogues of the drug rarely lead to the development of side effects. This is a relatively safe drug.
Headache, dizziness, impaired consciousness, tremor, rigidity, incoordination, convulsions, sensory or mixed peripheral neuropathy, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
Enhances the effect of coumarin anticoagulants and prolongs the muscle relaxant effect of vecuronium bromide. Compatible with alcohol (does not inhibit acetaldehyde dehydrogenase).
Dazolic is an antiprotozoal antibiotic, that is, the main pharmaceutical effect of the drug is aimed at destroying microorganisms that belong to protozoa. In particular, the active components of the drug disrupt the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid chains, the main carrier of genetic information necessary for normal life and reproduction in living cells. Antibiotic properties are effective against a wide range of microorganisms, which include:
- Giardia lamblia (intestinal lamblia);
- Trichomonas vaginalis (vaginal Trichomonas);
- Entamoeba histolytica (dysenteric amoeba);
- Clostridium perfringens (Clostridium perfringens);
- Bacteroides fragilis (bacteroides fragilis);
- Fusobacterium nucleatum (fusobacterium nucleoid or Plaut's bacillus).
It should be noted that the last three types of harmful microorganisms belong to anaerobic microflora, that is, such cells do not require oxygen for normal functioning. As a rule, these families cause particularly severe damage to the deep structures of the human body, which sometimes lead to gangrene, as an absolute therapeutic indication.
During a course of drug therapy with Dazolic, the following undesirable consequences may be observed:
- From the gastrointestinal tract: dyspeptic indigestion, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- From the central and peripheral system: headache, dizziness, impaired consciousness, rigidity of individual muscles, intention tremor, convulsions that resemble epileptic seizures, impaired coordination of movement, especially fine motor skills, mixed or sensory-peripheral neuropathy.
Dazolic significantly enhances the therapeutic effects of coumarin anticoagulants, which can manifest itself in the form of pinpoint hemorrhages, hemorrhagic rash or purpura.
Ornidazole increases the duration of the muscle relaxant effect of Vecuronium Bromide.
| Category ICD-10 | Synonyms of diseases according to ICD-10 |
| A06.4 Amoebic liver abscess | Amebic liver abscess |
| Amebiasis of the liver | |
| Hepatic form of amoebiasis | |
| Hepatic amoebiasis | |
| A06.8 Amebic infection of another site | Amebiasis of extraintestinal localization |
| A07.1 Giardiasis [giardiasis] | Giardiasis |
| Giardiasis | |
| Intestinal giardiasis | |
| Giardiasis | |
| Hepatic giardiasis | |
| A59 Trichomoniasis | Acute trichomoniasis |
| Recurrent trichomoniasis in women | |
| Trichomonas infections | |
| Trichomoniasis | |
| Chronic complicated multifocal trichomoniasis | |
| Chronic trichomoniasis | |
| Z100* CLASS XXII Surgical practice | Abdominal surgery |
| Adenomectomy | |
| Amputation | |
| Angioplasty of coronary arteries | |
| Carotid angioplasty | |
| Antiseptic treatment of skin for wounds | |
| Antiseptic hand treatment | |
| Appendectomy | |
| Atherectomy | |
| Balloon coronary angioplasty | |
| Vaginal hysterectomy | |
| Corona bypass | |
| Interventions on the vagina and cervix | |
| Bladder interventions | |
| Intervention in the oral cavity | |
| Restorative and reconstructive operations | |
| Hand hygiene of medical personnel | |
| Gynecological surgery | |
| Gynecological interventions | |
| Gynecological surgeries | |
| Hypovolemic shock during surgery | |
| Disinfection of purulent wounds | |
| Disinfection of wound edges | |
| Diagnostic interventions | |
| Diagnostic procedures | |
| Diathermocoagulation of the cervix | |
| Long surgical operations | |
| Replacing fistula catheters | |
| Infection during orthopedic surgery | |
| Artificial heart valve | |
| Cystectomy | |
| Short-term outpatient surgery | |
| Short-term operations | |
| Short-term surgical procedures | |
| Cricothyroidotomy | |
| Blood loss during surgery | |
| Bleeding during surgery and in the postoperative period | |
| Culdocentesis | |
| Laser coagulation | |
| Laser coagulation | |
| Laser coagulation of the retina | |
| Laparoscopy | |
| Laparoscopy in gynecology | |
| CSF fistula | |
| Minor gynecological operations | |
| Minor surgical interventions | |
| Mastectomy and subsequent plastic surgery | |
| Mediastinotomy | |
| Microsurgical operations on the ear | |
| Mucogingival surgeries | |
| Stitching | |
| Minor surgeries | |
| Neurosurgical operation | |
| Immobilization of the eyeball in ophthalmic surgery | |
| Orchiectomy | |
| Complications after tooth extraction | |
| Pancreatectomy | |
| Pericardectomy | |
| Rehabilitation period after surgery | |
| The period of convalescence after surgical interventions | |
| Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty | |
| Pleural thoracentesis | |
| Pneumonia postoperative and post-traumatic | |
| Preparing for surgical procedures | |
| Preparing for surgery | |
| Preparing the surgeon's hands before surgery | |
| Preparing the colon for surgery | |
| Postoperative aspiration pneumonia during neurosurgical and thoracic operations | |
| Postoperative nausea | |
| Postoperative bleeding | |
| Postoperative granuloma | |
| Postoperative shock | |
| Early postoperative period | |
| Myocardial revascularization | |
| Resection of the apex of the tooth root | |
| Gastric resection | |
| Bowel resection | |
| Resection of the uterus | |
| Liver resection | |
| Small bowel resection | |
| Resection of part of the stomach | |
| Reocclusion of the operated vessel | |
| Bonding tissue during surgery | |
| Removing stitches | |
| Condition after eye surgery | |
| Condition after surgery | |
| Condition after surgical interventions in the nasal cavity | |
| Condition after gastrectomy | |
| Condition after resection of the small intestine | |
| Condition after tonsillectomy | |
| Condition after removal of the duodenum | |
| Condition after phlebectomy | |
| Vascular surgery | |
| Splenectomy | |
| Sterilization of surgical instruments | |
| Sterilization of surgical instruments | |
| Sternotomy | |
| Dental operations | |
| Dental intervention on periodontal tissues | |
| Strumectomy | |
| Tonsillectomy | |
| Thoracic surgery | |
| Thoracic operations | |
| Total gastrectomy | |
| Transdermal intravascular coronary angioplasty | |
| Transurethral resection | |
| Turbinectomy | |
| Removal of a tooth | |
| Cataract removal | |
| Cyst removal | |
| Tonsil removal | |
| Removal of fibroids | |
| Removal of mobile baby teeth | |
| Removal of polyps | |
| Removing a broken tooth | |
| Removal of the uterine body | |
| Removing stitches | |
| Urethrotomy | |
| CSF duct fistula | |
| Frontoethmoidohaymorotomy | |
| Surgical infection | |
| Surgical treatment of chronic limb ulcers | |
| Surgery | |
| Surgery in the anal area | |
| Colon surgery | |
| Surgical practice | |
| Surgical procedure | |
| Surgical interventions | |
| Surgical interventions on the gastrointestinal tract | |
| Surgical interventions on the urinary tract | |
| Surgical interventions on the urinary system | |
| Surgical interventions on the genitourinary system | |
| Heart surgery | |
| Surgical procedures | |
| Surgical operations | |
| Vein surgery | |
| Surgical intervention | |
| Vascular surgery | |
| Surgical treatment of thrombosis | |
| Surgery | |
| Cholecystectomy | |
| Partial gastrectomy | |
| Transperitoneal hysterectomy | |
| Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty | |
| Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty | |
| Coronary artery bypass surgery | |
| Tooth extirpation | |
| Extirpation of baby teeth | |
| Pulp extirpation | |
| Extracorporeal circulation | |
| Tooth extraction | |
| Tooth extraction | |
| Cataract extraction | |
| Electrocoagulation | |
| Endourological interventions | |
| Episiotomy | |
| Ethmoidotomy |
We suggest you read What to do when a wasp bites your leg
DAZOLIK: DOSAGE
The tablets are taken orally after meals.
For trichomoniasis, adults are prescribed 1.5 g once or 1 g in combination with intravaginal administration of 500 mg (vaginal tablets) at night. Treatment can be carried out for 5 days, prescribing 500 mg orally 2 times a day (morning and evening), also prescribing 1 vaginal tablet of 500 mg at night. For children, the dose is set at the rate of 25 mg/kg body weight once.
For amoebic dysentery, adults and children with a body weight of more than 35 kg, 1.5 g 1 time / day, with a body weight of more than 60 kg - 2 g / day. For children over 3 years old and weighing less than 35 kg, the daily dose is set at the rate of 40 mg/kg body weight. The course of treatment is 3 days.
For other forms of amebiasis, adults and children over 12 years of age - 500 mg 2 times a day for 5-10 days. Children over 3 years old and weighing less than 35 kg - 25 mg/kg body weight once for 5-10 days.
For giardiasis, adults and children weighing more than 35 kg - 1.5 g 1 time / day, children over 3 years old and weighing less than 35 kg - 40 mg / kg / day. Duration of treatment is 1-2 days.
To prevent infections caused by anaerobic bacteria, prescribe 0.5-1 g before surgery and 0.5 g 2 times a day after surgery for 3-5 days.
Indications for use
You can use Dazolic only after consulting your doctor. This drug is highly effective against microorganisms such as gram-positive bacteria, anaerobic microorganisms, amoebas, Trichomonas, Giardia. Due to these organisms, a person may face the following diseases:
- Amebiasis is a disease accompanied by damage to the intestines (it causes an inflammatory process in the liver, which leads to extremely painful sensations);
- Trichomoniasis is a serious infection that spreads sexually (it affects the human urinary system and causes inflammation);
- Giardiasis is an infectious disease accompanied by an intestinal infection;
- Thrush is a bacterial vaginosis in which a person experiences severe itching and burning in the genital area;
- Anaerobic infections are pathogenic microorganisms that can occur due to operations on the peritoneum;
- Prevention of infectious diseases before and after surgical interventions.
Instructions for use of the drug
Instructions for use of the drug
Before starting to use the drug, you must consult with your doctor. It is permissible to take it only after an extensive diagnostic examination. The patient himself should also study the annotation to minimize the risk of side effects. Remember that you can take Dazolic only after meals - otherwise you risk heartburn, nausea and vomiting. Remember that the dosage and duration of treatment is determined by the doctor depending on the disease. Most often, the medicine is used for no more than 2 weeks. Instructions for use read as follows:
- When treating children under 12 years of age, use 25 mg per 1 kg of child weight. The duration is selected individually; the drug can be used as a complex therapy.
- To treat giardiasis, take 2 Dazolic tablets 2 times a day. To do this, take capsules with 1.5 mg of active ingredient. For the treatment of the same disease in children, take 1 tablet of 40 mg. The duration of treatment is 2 weeks.
- To get rid of an amoebic infection, you need to take 1 tablet of 1.5 mg Dazolic once a day. If a person’s body weight exceeds 60 kg, then the dose of the active substance is increased to 2 mg.
- To cure extraintestinal amebiasis, you need to take half a Dazolic tablet 2 times a day. The average duration of therapy is 5-10 days. If it is necessary to treat children under 1 year old, take 0.125 g, from 1 to 6 years - 0.25, from 7 to 12 - 0.375.
- Dazolic is also used as a prophylaxis for infectious diseases after and before surgery. To do this, take 1 capsule of the drug for a week.
To preserve the beneficial properties of the drug, it must be stored in a dry, cool place. The shelf life of the medicine is 3 years. It is strictly forbidden to take it after the date indicated on the package. In this case, Dazolic can lead to serious complications.
special instructions
When treating trichomoniasis, both sexual partners should be treated simultaneously. Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery.
Ornidazole has a depressant effect on the central nervous system, so it should not be used while driving or other work that requires precise coordination of movements.
For liver dysfunction
The drug should be used with caution in case of liver diseases.
Use in childhood
Contraindication: children under 3 years of age (for this dosage form).
Side effects
There is not a single drug that does not have side effects.
Despite the fact that Dazolic is considered relatively safe, some side effects may occur, including:
- Possible allergic reactions to the components of the drug
- The occurrence of a headache
- Drowsiness, dizziness, and extreme fatigue
- Taste disturbance
- Fainting
- Muscle twitching, cramps.
The list of side effects is, of course, quite impressive, but its positive effect on many harmful bacteria makes it necessary to prescribe it to patients.
Analogues of Dazolic
Orgil
Tiberal
Gairo
Naxojin
Analogs of Dazolic are few in number; usually the therapeutic effect of a pharmaceutical drug, in case of any contraindications to its use, is replaced by the following antiprotozoal drugs: Ornisidom or Avrazor.
If you haven’t found Dazolic in pharmacies, its price doesn’t suit you, or there are contraindications, then the best solution here is an unquestioning and thoughtful selection of the best analogue of the product. Of course, it is better to do this with a doctor. Ornidazole Dazolic can be replaced with:
- Zanitro (Zanitro);
- Zolgine (Zolgin);
- Orzol (Orzol);
- Ornigil (Ornigil);
- Ornidazol (Ornidazole);
- Ornimac (Ornimac);
- Protozal (Protozal);
- Intezol (Intezol);
- Methressa (Metressa);
- Methride (Metrid);
- Metronidazole (Metronidazole);
- Trikasaid (Trikasayd);
- Efloran (Efloran);
- Tagera (Tagera);
- Fazigine (Fazigine).
Analogues are represented by the following drugs: “Tiberal”, “Ornisid Forte”, “Ornisid”, “Orniona”, “Ornidazole”, “Lornizol”, “Quinizol”, “Gayro”, “Avrazor”. Only a doctor can choose the right analogue of Dazolic. Analogues have an effect similar to that of the original drug. You can learn about the effectiveness of the original from customer reviews.
Many people report that they experienced nausea, vomiting, and extreme thirst while taking the drug. Sometimes there are disturbances such as dizziness, drowsiness, and difficulty concentrating. Despite the large number of possible side effects, the drug often helps patients get rid of infectious diseases, and quite quickly.
How much does Dazolic cost? The price at which this drug is sold in pharmacies is relatively low. The cost of the medicine is on average 280 rubles.
The drug is effective if the diagnosis is correct. Any problems specified in the instructions for the drug “Dazolik” are perfectly eliminated. Price, contraindications for use, possible adverse reactions of the body - information on the basis of which a decision is made on the implementation of treatment based on the use of a specific medicine. Before starting therapy, you should consult your doctor.