The ears, throat and nose have a close anatomical relationship, therefore the science of otolaryngology studies the pathologies of these three organs. ENT organs work as a single mechanism; an inflammatory process, for example, in the throat can provoke inflammation in the ear.
General information about ENT diseases
There are hundreds of types of ear, nose and throat diseases; they are diagnosed for all age categories of the population. ENT disease is a frequent companion of children attending kindergarten, adults who are forced to spend long periods of time among large crowds of people, and elderly people with weakened immune systems. Ear, nose and throat clinics treat the following pathologies:
- adenoiditis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis
- laryngitis, rhinitis, eustachitis, sinusitis
- external, internal, otitis media
- , frontal
- allergic rhinitis, Meniere's disease
A modern ear, nose and throat clinic has diagnostic and surgical equipment that allows you to remove foreign bodies from the throat, ears or nose, stop nosebleeds, remove polyps and other tumors.
An experienced otolaryngologist, based on the clinical picture, diagnoses the corresponding disease and prescribes treatment for ear, nose and throat diseases.
Symptoms of ENT diseases
The cause of most diseases of the organs of vision, hearing and breathing are respiratory infections. A decrease in local immunity in the autumn-winter period, sudden changes in temperature, hypothermia, contact with an infected patient - all these conditions contribute to the development of ENT diseases.
Symptoms of diseases are usually more pronounced in children, but they also bring a lot of discomfort to adults:
- sore throat, pain when swallowing, plaque on the tonsils
- loss of smell, hearing, nasal congestion
- sneezing, dry nose
- snoring in children and adults
- acute pain in the ear, tinnitus
In addition to the above signs, the need for treatment of diseases of the ear, nose and throat is indicated by any painful discomfort in the nasopharynx, the presence of symptoms of intoxication (weakness, aching joints, fever).
Treatment of ENT organs
To prevent the development of the inflammatory process, you must contact a qualified otolaryngologist.
Modern methods of treating the nose and throat, as well as ears, include:
- Drug therapy. Drugs aimed at eliminating swelling, relieving swelling, and painkillers are prescribed for each case of ENT disease. If a bacterial infection occurs, antibiotic therapy is used.
- Hardware procedures. Physiological procedures based on the use of electrophoresis, magnetic field, heat, ultraviolet radiation are used both as an independent method and in complex therapy.
- Inhalations. No treatment for the nose and throat is complete without inhalation therapy. Inhalation of drugs allows them to penetrate the mucous membranes faster and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Surgical intervention. It is used as a radical method in case of a threat to the patient’s life or irreparable health complications. Most often this is the removal of adenoids or tonsils in children, polyps in adults.
From this section Diseases of the ear, nose and throat you will learn:
- About what diseases of the ENT organs are
- About what symptoms indicate the development of ENT disease
- About what therapy is used for diseases of the ear, nose and throat
After all, a seemingly minor illness can lead to serious complications!
Ear, nose and throat diseases
Types and signs of otitis media in infants - what to do and what to do if your child gets sick
Ear, nose and throat diseases
A child has severe ear pain, what to do: step-by-step instructions
Ear, nose and throat diseases
Lethal sound levels: should you be afraid of noise?
Ear, nose and throat diseases
How does acute otitis media proceed, treatment of stages of pathology
A person receives information from the surrounding world through the organs of vision, hearing, smell, taste, and touch, which deliver all the important information to the brain.
Impaired functioning of the ENT organs is often considered to be the cause not only of general diseases, but is also a violation of the individual development of a person, which limits his abilities. Indeed, the ear, larynx and pharynx, nose, together with the paranasal sinuses, work as one whole: a disease of one organ can affect the condition of another, affecting certain systems of the body.
Let's see what ENT organs are:
- The pharynx
is a plexus of the oral, laryngeal and nasal parts. The tonsils are also located in the pharynx, which can become inflamed due to certain diseases of this organ. - The nasal cavity
is lined with mucous membrane and is connected through narrow openings to the frontal and maxillary sinuses; - The human ear
consists of three sections: inner, middle and outer. The inner part of the ear consists of a sound and vestibular analyzer. The middle section contains the tympanic cavity and auditory ossicles, as well as the Eustachian tube and mastoid process. The outer part of the ear consists of the pinna and the external auditory canal.
Otolaryngology is a branch of medicine dealing with the treatment of ENT organs
Otolaryngology is a special branch in clinical medicine that studies diseases of the ears, nose and throat, and also includes the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases of this group of organs. The diseases of these three organs are combined into one group for a reason; this is due to their functional dependence and anatomical proximity, as well as the fact that diseases that affect one of these organs have the ability to spread to another organ.
Otolaryngology is a combination of three disciplines: otology, laryngology and rhinology.
An otolaryngologist is a doctor who specializes in the prevention and treatment of diseases of the ear, nose and throat. An otolaryngologist is a specialty that includes the skills of a surgeon and a physician. In certain cases, an otolaryngologist performs surgical operations. The scope of action of an otolaryngologist involves the treatment of diseases associated with the ear, nose and throat cavity.
ENT - what kind of doctor is this?
The longest occupation name is correct. Other names have been abbreviated for convenience. After all, it is very difficult to pronounce this name of a medical specialty correctly, and it is easier to call a doctor an otolaryngologist or simply an ENT specialist. “What kind of doctor should he be and what should he do to be called that?” - many people ask this question.
Translation from Latin
In fact, an ENT is a specialist who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of 3 organs. According to Latin, the words in the title indicate the doctor's field of activity. Explanation of the word ENT:
- oto – ear;
- rhino – nose;
- laryng - throat.
It is impossible not to notice that at the end of both words there is “olog”. Translated, it means “science” or “doctor”. Among themselves, people often call such a doctor “ear, throat, nose.”
Types of ENT doctors
These doctors may have a narrower specialization. Specializations of otolaryngologists are divided into:
- Audiologist. Examines hearing impairments, conducts rehabilitation, and identifies the cause of hearing problems.
- Pediatric ENT. Engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of ENT organs in children.
- Foniatra. His competence is speech disorders, ligament damage due to trauma and other shocks.
- Oncologist. Specializes in the treatment of oncological diseases of the ENT organs.
- Surgeon. The specialist performs operations on diseases of the nose, ear, and throat.
The above describes which organs are diagnosed and treated by an ENT (otolaryngologist) or an ear, nose and throat doctor. But the list of diseases that a doctor specializes in includes specific names.
This is what an otorhinolaryngologist treats or diseases of the ENT organs:
- frontal sinusitis, tympanitis, hearing loss;
- tubootitis;
- ear noise;
- sulfur plugs;
- snore;
- laryngeal stenosis;
- boils in the ear canal;
- sinusitis;
- vocal cord disorders;
- sinusitis;
- laryngitis;
- nasal polyps;
- ear injuries;
- partial or absolute hearing loss;
- tracheitis;
- bronchitis;
- adenoids in the nasopharynx or throat;
- sinusitis;
- rhinitis.
People turn to an ENT specialist for treatment of pharyngitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx), otitis media, internal and external (ear pathology), chronic tonsillitis or acute (tonsillitis).
Treatment of ENT diseases
The specialists of the ENT-Asthma clinic have extensive experience in the effective and painless treatment of ENT diseases in both children and adults. Experienced otolaryngologists use a unique non-surgical method for treating diseases in their work.
ENT diseases are quite common. From time to time they can bother almost everyone. An otolaryngologist treats pathologies of the pharynx, larynx, ear and nose. A therapist and a general practitioner can also provide some assistance for diseases of this localization.
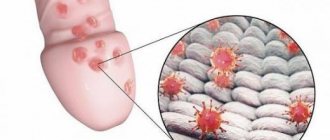
Angina
Sore throat is a disease of the tonsils. It is most often caused by a staphylococcal infection. With this disease, plaque is found on the palatine tonsils. It may be whitish or purulent, depending on the form of the pathology. This ENT disease is manifested by severe pain in the throat, aggravated by swallowing, increased body temperature and general weakness.
Diagnosis of tonsillitis is based on the detection of plaque on the tonsils during a general examination, as well as the results of a study of biological material taken using a smear from the affected area.
Treatment of sore throat is based on the use of antibiotics, antipyretics, antihistamines and painkillers (usually in the form of a spray). Also, for this pathology, it is recommended to gargle 5-6 times a day with a saline-soda solution.
How to make a diagnosis, features of the development of the disease
When making a diagnosis, a visual examination, including laryngoscopy or pharyngoscopy, is important. Standard clinical tests, a swab from the throat and nasal passages are also prescribed. The middle ear is examined and, if necessary, an x-ray is taken - for example, of the sinuses. The doctor decides what to do in each specific case. What is a doctor who treats the ear, throat or nose called in medical terminology? The name of his specialization is ENT or otolaryngologist, in common parlance - earworm.
Does your throat hurt and radiate to the right or left? Perhaps tonsillitis or another inflammatory disease of the larynx begins. If there are problems with the nose, rhinitis or sinusitis is highly likely to develop. Since the organs are interconnected, pathogenic microflora moves through the Eustachian tube into the middle ear. Sometimes the infection attack is limited - then the throat and ear hurt on one side.
With rapidly developing tonsillitis, especially purulent variants, the pain in the throat radiates to the ear. Similar symptoms are possible with the development of pharyngitis or laryngitis. The disease is accompanied by soreness and burning of the laryngeal mucosa. If the palate is inflamed, pain occurs when swallowing, and the throat is dry, then this is the reason for the possible onset of otitis media on the right or left side.
Cough during tracheitis or bronchitis (such ailments can be caused by progressive pharyngitis or laryngitis, mucus that irritates the epithelium enters the upper respiratory tract) needs to be mitigated and for this, taking mucolytics is indicated. Experts note that with otitis media, pain can radiate to the neck around the clock and the patient subjectively feels pain in the throat, which intensifies with swallowing and muscle tension.
Pharyngitis
It is an inflammation of the back of the throat. It is one of the most common diseases. Most often, pharyngitis occurs after hypothermia, which leads to a decrease in the level of local immunity. As a result, opportunistic microflora begins to multiply and damage the mucous membrane of the throat.
The main symptoms of pharyngitis are redness of the back of the throat, pain and soreness in the affected area, and increased body temperature. Diagnosis of the disease includes a general examination, as well as general blood and urine tests.
Treatment of this pathology is based on the use of antihistamines, antipyretics, and local anesthetics in the form of a spray. In case of a protracted course of this disease, the patient is prescribed antibiotics. In addition, doctors recommend drinking large amounts of warm liquid and gargling with a saline-soda solution.
Tonsillitis
This pathology is an inflammation of the tonsils. Most often, it develops after hypothermia or after contact with an already sick person.
The clinical picture of tonsillitis is characterized by swelling and redness of the tonsils, sore throat, which worsens when swallowing, as well as increased body temperature. This disease may be accompanied by difficulty eating.
Treatment of tonsillitis includes the use of antibacterial drugs, antihistamines, antipyretics and local anesthetic sprays. In the chronic course of this disease, accompanied by a significant increase in the palatine tonsils, the patient is recommended to undergo surgical treatment to remove them. This will relieve a person from tonsillitis and sore throat, but will also eliminate one of the immune barriers to pathogenic microorganisms.
"Ear, nose and throat" diseases in children
Particular care should be taken to identify ear, throat, and nose diseases in young children. Otolaryngology, as a separate field of medicine, has a whole branch that deals specifically with the manifestations of diseases in children. Every city or rural hospital must have a pediatric otolaryngologist, and examinations by him are a mandatory requirement for children at a certain age. Periodic examinations of children by a doctor will make it possible to detect possible disorders in the development of organs or signs of diseases, as well as eliminate them.
Otolaryngology uses a large number of methods and means to treat ear, throat, nose diseases, including: cauterization, electrophoresis, rinsing, and so on.
If you have been bothered by a constant runny nose, sore throat, or hearing loss for a long time, then you need to visit this section of the site! This section provides you with all the objective information that will help you understand the reasons why diseases of the ear, nose and throat develop, as well as study modern methods of treating them.
Abscess
This disease is quite dangerous. An abscess is a suppuration limited to connective tissue. If the abscess is opened not into the throat cavity, but into other tissues, the patient may develop severe complications that can lead to death. That is why it is important not to try to treat an abscess on your own, but to immediately contact an otolaryngologist.
This pathological process is most often accompanied by severe pain in the throat, which can radiate throughout the neck, swelling and swelling in the affected area, and an increase in body temperature up to 40 ° C or more.
Treatment of an abscess begins with antibacterial, antihistamine, and antipyretic drugs. If their use does not bring the expected results, surgery is performed to open and drain the abscess. The intervention can be performed in a hospital or in the treatment room of an otolaryngologist at an outpatient healthcare facility. After the operation, treatment with tablets continues until the patient recovers completely.
Ear diseases
Among this pathology, the most common diseases are the following:
- otitis;
- sensorineural hearing loss;
- deafness;
- abscess of the external auditory canal;
- damage to the eardrum;
- foreign body and cerumen plug in the external auditory canal.
If you have this pathology, it is important to promptly seek help from a specialist, since all these ENT diseases of the ears can lead to decreased and even hearing loss.
Otitis
Otitis is an inflammatory disease of the ear. According to the flow, acute and chronic forms of pathology are distinguished. Based on the nature of the damage, otitis is defined as catarrhal and purulent. According to localization, it can be external, middle or internal.
The clinical course of otitis media is accompanied by pain in the affected area and increased body temperature. In addition, with the purulent nature of the disease, the level of hearing may decrease. This disease requires immediate treatment, especially when it comes to otitis media or internal otitis. If you do not quickly relieve a person from such otitis, this will lead to deterioration or complete loss of hearing. Treatment of this type of ENT disease is based on the use of antibiotics in the form of ear drops or intramuscular/intravenous injections, antihistamines, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce the temperature and severity of the inflammatory process.
Common ear diseases: Otitis media
Otitis is an inflammation of the ear that can develop at different levels.
The external ear consists of the ear itself, which is called the auricle, the external auditory canal leading into the head, and the eardrum. The inner ear is a complex of the cochlea and special bones that transmit sound, which is located deep in the temporal bone and provides the functions of hearing and balance. The middle ear is the passage between the inner ear and the pharynx. Which is called the Eustachian tube. Otitis has several types, which are divided into groups:
Based on localization, otitis media is divided into external, middle and internal. According to the clinical picture, catarrhal and purulent. The causative agent is viral, bacterial and fungal. The course is acute and chronic.
Otitis occurs in both adults and children. The latter have their own characteristics and methods of treatment.
Sensorineural hearing loss
This disease is characterized by hearing loss. The reasons for its development may be the following:
- Constant exposure to noise on the auditory analyzer.
- Heredity (approximately 12.5% of people have a gene mutation that contributes to the development of sensorineural hearing loss).
- Damage to the auditory nerve.
- Acute infectious diseases (primarily influenza).
This chronic ENT disease most often progresses gradually, especially if the cause of its initial development is not eliminated. Therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the action of the provoking factor. Such patients are often offered ear prostheses for use.
Diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses
There are many different ENT diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses. The most common among them:
- rhinitis;
- deviated nasal septum;
- nose bleed;
- adenoiditis;
- sinusitis.
Rhinitis in its course can be acute and chronic. It occurs under the influence of one or another irritant, which can be pathogenic microorganisms, allergic pollutants, or active chemicals. In some cases, the cause of chronic rhinitis is the excessive use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops, which leads to atrophy of the mucous membrane. Treatment consists of eliminating the factor that provokes rhinitis, as well as using nasal drops, mostly salt-based.
A deviated nasal septum is a problem if this ENT disease leads to disruption of normal breathing patterns. Treatment in this case can only be surgical.
Nosebleeds can have a number of causes. Most often this occurs in cases where there is a blood vessel in the nasal mucosa that is located too superficially. Also, nosebleeds often develop against the background of elevated blood pressure. Treatment consists of cauterizing the bleeding vessel. This procedure should only be performed by an otolaryngologist.
ENT diseases: human ear diseases, throat diseases and nose diseases
ENT diseases are pathologies of the ear, nose and throat. The doctor who treats these organs is called an otolaryngologist or simply ENT. Dysfunctions of the ENT organs lead not only to disorders in the affected organs, but also to a decline in overall well-being. Chronic diseases of the nose or diseases of the throat and tongue in childhood can lead to developmental delays.
general information
ENT diseases in medicine are combined into a common group for the reason that the ear, throat and sinuses work as a single physiological mechanism.
ENT diseases of the throat can cause diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses and vice versa. ENT ear diseases of an infectious and inflammatory nature can “go down” and cause signs of a throat disease.
Adenoids very often become the cause of tonsillitis (sore throat), otitis media and other ENT diseases of the ear.
Otolaryngology studies and treats ENT diseases of the throat, larynx, ear, sinuses, and also deals with the prevention of these ailments. A specialist in these pathologies must have the skills of a therapist and surgeon. In certain clinical situations, ENT diseases of the ear or nasal diseases require the otolaryngologist to perform surgical interventions.
Chronic diseases of the ENT organs are difficult to treat.
Types of diseases
There are a great variety of pathologies of the ear, throat and sinuses (see photo of ENT diseases). The complete list of ENT diseases includes hundreds of items.
Diseases associated with the nose, larynx and hearing organs are diagnosed in children and adult patients (what kinds of throat diseases there are - in the photo).
Children's ENT diseases are more common, which can be explained by the imperfection of the child's immune system.
Diseases of the nose
Let's consider what nasal diseases occur in patients of all age categories.
ENT diseases of the nose and other problems are:
- acute and chronic rhinitis (runny nose);
- sinusitis;
- frontal sinusitis;
- allergic rhinitis;
- sinusitis;
- nasal injuries;
- nosebleeds;
- foreign bodies in the nasal cavity.
By carefully examining images and photos of nasal diseases, you can be convinced that pathologies are localized mainly on the mucous membranes in the paranasal sinuses. Some nasal diseases (for example, sinusitis) are especially dangerous because they cause painful headaches and can cause decreased vision and meningitis.
ENT diseases of the nose must be treated at the initial stage of their development, since the transition of these ailments to a chronic form is fraught with protracted (sometimes many years) therapy.
Knowing the name of a nasal disease that occurs in a child is especially important for parents interested in the full growth and development of their children. For this reason, timely diagnosis and treatment of ENT ailments of the nasal cavity is so important. Chronic nasal diseases are best treated in specialized and specialized clinics.
Ear diseases
Ear diseases in people are also quite varied. Let us consider in detail what ear diseases are, what are the symptoms and treatment of ear diseases.
Acute and chronic ear diseases are:
- sulfur plug;
- external, middle and internal otitis;
- foreign bodies in the ear canal;
- ear disease tubootitis (eustachitis);
- injuries of the auricle, eardrum, inner ear;
- mastoiditis;
- Meniere's disease;
- labyrinthitis.
Symptoms of human ear disease are almost always associated with decreased hearing ability. Often, inflammatory processes in the ear are accompanied by fever and signs of general intoxication. Symptoms of ear disease in humans may also include fluid leaking from the opening of the ear and severe pain in the ear.
The symptoms and treatment of ear diseases can be studied more clearly if you look at images and photos of human ear diseases. More rare symptoms of ear diseases in humans are otogenic processes in the brain or cerebellum.
Symptoms of ear disease in adults may be more vague and subtle, making pathologies more difficult to identify. Signs of ear disease may be absent for a long time and sometimes appear only at the stage of manifestation of the disease.
Treatment of human ear disease includes drug therapy and physiological treatment. The most sustainable healing effect is achieved by hardware effects within the framework of physiotherapy. Treatment of ear diseases in humans also includes restoration or stimulation of the patient’s immune status.
Parents are interested in the question, what ear diseases occur in childhood? Answer: almost the same as in adults. However, in a child, pathologies are more acute, and therapy is longer.
How to cure laryngitis in a child? Recommendations in our article. Read about the treatment of pharyngitis in various ways, including traditional medicine methods, here.
Throat diseases
Let's look at what types of throat diseases there are, what the symptoms of throat and larynx diseases may be, and how to treat throat diseases. A detailed description and photo of throat diseases is provided.
For a more visual understanding of the topic, you can familiarize yourself with images and photos of diseases of the throat and larynx (throat diseases in pictures).
So, what are throat diseases? There are viral throat diseases, bacterial, allergic. The most pressing infectious disease of the throat is tonsillitis (see photo of infectious diseases of the throat). There are throat diseases without fever and with fever.
The main pathologies and diseases are:
- adenoids;
- tonsillitis;
- laryngitis;
- diphtheria;
- injuries;
- burns;
- foreign bodies;
- pharyngitis.
The most common throat diseases are catarrhal tonsillitis and acute tonsillitis. These are infectious and inflammatory diseases of the throat. They are also the most common childhood throat diseases.
Chronic throat diseases are quite common: recurrent tonsillitis (tonsillitis), chronic pharyngitis.
Chronic throat diseases are more difficult to treat and can lead to serious complications.
Diagnosis of throat diseases involves conducting a comprehensive examination in a clinic. For diagnosis, not only obvious signs of throat disease are indicative, but also the results of laboratory blood tests and other procedures.
Symptoms of diseases of the throat and larynx include: cough, discomfort, sore throat, sputum (sometimes mixed with blood), pain when swallowing. Signs of throat disease in adults may not be obvious. Children's throat diseases are more severe and can provoke concomitant illnesses.
Symptoms and treatment of throat diseases are interrelated: the otolaryngologist first takes an anamnesis, then decides how to treat the throat disease. Treatment includes inhalations, physiotherapy, herbal medicine, and medications.
Diseases of the throat mucosa should be treated until symptoms disappear completely.
Causes
Common causes of ear, larynx, throat and sinus diseases are:
- general hypothermia (staying in cold air, swimming);
- sudden temperature change;
- local hypothermia (for example, drinking very cold drinks);
- injuries;
- weakened immunity;
- deficiency of vitamins and nutrients;
- stress.
Any systemic, infectious and inflammatory diseases can act as additional factors for the development of ENT pathologies.
General symptoms
General symptoms of ENT disease:
- temperature increase;
- painful sensations in the nasopharynx;
- signs of intoxication (weakness, fatigue, decreased performance);
- the presence of an inflammatory process;
- decreased immune status.
For a more visual study of the signs of ENT pathologies, you can familiarize yourself with images and photos: symptoms and treatment of ENT diseases.
Therapy
Treatment of ear diseases in humans, as well as therapy of other ENT diseases, is a comprehensive use of medicinal, physical, symptomatic and radical therapy.
In all clinical situations, a preliminary diagnosis and the appointment of the most adequate and effective treatment are required. In addition to treating the main illness, doctors generally strengthen the defenses and prevent relapses of ENT diseases.
Source: https://simptomed.ru/uho-gorlo-nos
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is an inflammatory disease of the paranasal sinuses. In the question of which ENT disease is the most dangerous, this particular pathology will be the correct answer. This is due to the fact that if it lasts for a long time, destruction of the bone wall of the paranasal sinus is possible. If its contents enter the brain, it can cause serious neurological disorders. It is for this reason that sinusitis should be treated immediately after the first symptoms occur.
The clinical picture of sinusitis is characterized by pain in the paranasal area, which changes in character when tilting the head, increased body temperature, and runny nose. Diagnosis of this pathology consists of general blood and urine tests, as well as radiography of the paranasal sinuses. Treatment will consist of the use of antibiotics, antihistamines, vasoconstrictor nasal drops, and antipyretics. In the case of chronic pathology, surgery can be performed to improve the outflow of purulent masses formed in the sinuses.
Diseases of the ENT organs
occupy first place among all diseases that are treated by doctors, both in children's and adult clinics. That is why they receive a lot of attention.
The ears, throat and nose are the “entry gates” of infection. That is why they have a protection system against bacteria and viruses. But when this system is in poor condition, the infection begins to spread and causes various diseases.
Diseases of the ENT organs can be acute or chronic. The reason for this is improper treatment and weak immune defense of the body.
Types of diseases
The list of ENT diseases is huge; it can include hundreds of clinical names. Diseases of the nose, throat and ear are often diagnosed in children and adults. Children are exposed to them more often due to imperfect immunity.
Nose diseases:
- runny nose or in acute and chronic stages;
- ( , );
- foreign body in the nasal cavity;
- nosebleeds, etc.
The pathological process affects the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Some chronic nasal diseases (for example, sinusitis and sinusitis) can cause serious complications in the form of painful migraines, blurred vision and the development of meningitis.
Ear diseases:
- internal, external and middle;
- eustachitis;
- sulfur plug;
- foreign body in the ear canal;
- injury to the inner ear and eardrum, etc.
The clinical picture of ear pathologies in almost all cases occurs against the background of hearing loss. Inflammatory processes are usually accompanied by an increase in body temperature, symptoms of intoxication of the body, discharge and acute sensations of pain in the ear.
In adult patients, signs of ear disease are often blurred and mild, so pathology is more difficult to detect and is delayed. Signs of a pathological process may not be felt for a long time.
Allergens
If the body is individually susceptible, they can cause sore throat and swelling of the nasopharynx. Allergens include dust, animal hair, pollen, etc.
Regardless of the cause of the allergy, you can get rid of it only if contact with the allergen is excluded or limited as much as possible. Also, therapy for allergic rhinitis consists of prescribing antihistamines.
Hypothermia
A cold can take you by surprise not only in the cold season, but also in hot weather. This is most often observed in individuals suffering from decreased immunity. In the cold season, low temperatures provoke spasm and constriction of blood vessels, disrupt tissue trophism, which, in turn, increases the likelihood of developing inflammatory processes and ENT diseases due to the penetration of infectious pathogens into the organs.
In the summer, the greatest danger to the throat is swimming in cold water, ice cream and chilled drinks.
Ears are more susceptible to cold gusts of wind and low temperatures, so they should definitely be protected by wearing a scarf or hat. A runny nose most often develops due to frozen feet, which is why you need to wear shoes appropriate for the weather and prevent them from getting hypothermic.
Any diseases of an inflammatory, infectious and systemic nature often become a provoking factor for the development of ENT diseases.
Diseases of the ENT organs
Impaired functioning of the ENT organs is often considered to be the cause not only of general diseases, but is also a violation of the individual development of a person, which limits his abilities. Indeed, the ear, larynx and pharynx, nose, together with the paranasal sinuses, work as one whole: a disease of one organ can affect the condition of another, affecting certain systems of the body.
ENT organs:
The diseases of these three organs are combined into one group for a reason; this is due to their functional dependence and anatomical proximity, as well as the fact that diseases that affect one of these organs have the ability to spread to another organ.
Descriptions of ENT diseases
What are the dangers of ENT infections?
It is no coincidence that such a powerful structure of the immune system is located in the ENT organs. It is here that the body most often comes into contact with various pathogens, and it is here that the “first line of defense” is located, for which local immunity is responsible, from the invasion of the body by various infectious agents - the culprits of acute respiratory infections. But if for some reason the local immunity was unable to cope with the infectious pathogen and the person nevertheless fell ill with an acute respiratory infection, then the ENT organs suffer first of all.
Inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs can be acute or chronic. Acute inflammation is caused by viruses, bacteria and fungi. Untreated infections and insufficient immune activity can lead to chronic inflammation. It should be noted that the ENT organs: the ear (both external and internal), nose and sinuses, as well as the larynx and pharynx are closely connected. For this reason, a disease of one organ often causes a malfunction in another.
The symptoms of an infectious lesion of the ENT organs are familiar to everyone. With rhinitis, difficult nasal breathing and various types of discharge (mucous, purulent) are noted. With the development of otitis, ear pain and hearing loss are observed; in the purulent form, pus may leak from the ear. If the inflammation process affects the tonsils, then this disease is called tonsillitis, and its main manifestations are an increase in the size of the tonsils themselves, hyperemia, and sometimes caseous or purulent deposits in the form of films or plugs. With pharyngitis, a person feels a sore throat when swallowing and notes redness and graininess of the back wall of the pharynx. Laryngitis and tracheitis are manifested by a dry cough and sore throat.
To prevent diseases of the ENT organs, drugs based on bacterial lysates Imudon®1 and IRS®192 are used. These drugs help activate local immunity due to interaction with the mucous membrane of the oropharynx and upper respiratory tract.
When treating inflammation of the ENT organs, antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, analgesic drugs and immunotropic drugs are used. Their use can be both local and systemic. In this case, bacterial lysates will also come to the rescue.
So what are the dangers of ENT diseases and why should they be avoided? First of all, diseases of the ENT organs are dangerous due to their numerous complications. These can be chronic inflammatory processes, generalization of infection, and decreased organ function. With advanced otitis media, hearing loss occurs, meningitis develops, and even disruption of the vestibular apparatus, which is located in the inner ear. Complications of acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) include chronic tonsillitis and damage to the heart, kidneys and joints.
Thus, by being attentive to the health of your ENT organs, you will not only maintain excellent hearing, breathe deeply, but also experience the aroma and taste of life to the fullest!
* Activates specific and nonspecific immunity 1 Instructions for medical use of the drug Imudon® lozenges dated 07/02/2018 2 Instructions for medical use of the drug IRS®19 dated 05/17/2016
Causes of ENT diseases
The causes of the development of diseases of the ENT organs are of an infectious nature in most cases. These include the following infections:
- streptococcal and staphylococcal;
- fungal infection;
- viral particles.
The causes of ear disease are bacterial flora. Development factors include local hypothermia and decreased immunity. Pathology of the ear canal often occurs as a complication of tonsillitis or acute tonsillitis.
The etiological factor in the formation of pathology of the nose and paranasal sinuses is bacterial and viral infection. With sharply reduced immunity, fungal flora becomes the cause. Inflammation of the nasal mucosa is called rhinitis. It can be acute and become chronic.
It is important that rhinitis rarely forms as an independent nosological entity; in most cases it is accompanied by acute respiratory viral infection or tonsillitis.
Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses occurs due to the blocking of the natural anastomosis between the sinus and the nose. Under normal conditions, accumulated mucus from the sinuses is removed through this opening.
When closed, anaerobic conditions are created in the cavity; this process leads to the development of anaerobic flora, which is pathogenic for the human body. A similar mechanism provokes the development of sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis and labyrinthitis. The causes are chronic rhinitis and deviated septum.
Throat diseases occur due to a decrease in local immunity; a violation is a condition for the development of sore throat or tonsillitis. Against the background of reduced immunity, pathogenic flora is activated, which becomes the cause of disease.
Risk factors
- weakened immune system;
- presence of adenoids;
- anomalies in the structure of ENT organs;
- deviated nasal septum;
- bad habits;
- dental problems;
- work in hazardous production.
List of ENT diseases
Each otorhinolaryngic disease is accompanied by different symptoms, but in some cases the symptoms of one disease may be similar to another. The following signs of ENT diseases are characterized:
- pain, discomfort in the throat area (larynx, pharynx);
- difficulty breathing;
- inflammation of the ENT organs;
- hearing impairment;
- weakness of the body;
- headache;
- deterioration of sense of smell;
- bleeding (blood discharge from the ear or nose);
- discharge from affected organs, etc.
Sinusitis
One of the common nasal diseases accompanied by inflammation of the paranasal sinuses is sinusitis. During the illness, one or possibly several paranasal sinuses are affected, as a result of which breathing becomes difficult, discharge appears, headaches occur, and body temperature rises. Sinusitis is classified according to the nature, shape, and anatomical location of the inflammatory process. Types of sinusitis by localization (depending on the sinus that is affected):
- Frontitis is a lesion of the frontal sinus. It is more severely tolerated than other types of disease. Accompanied by severe pain in the forehead, hyperthermia, nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, etc.
- Sinusitis is inflammation of the maxillary paranasal sinuses. The patient exhibits breathing problems, copious mucopurulent discharge, high fever, and pain in the bridge of the nose.
- Sphenoiditis is inflammation of the sphenoid sinus. The disease causes headache, discharge from the sphenoid sinus, deterioration of vision and smell. It is one of the most common childhood diseases, ranking first among acute respiratory viral infections.
- Ethmoiditis is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the ethmoid sinus. Accompanied by difficulty breathing, pain in the upper part of the nose, forehead, between the eyebrows, and severe nasal discharge.
Sinusitis is a common disease and many try to cure it on their own, using well-known treatment methods. Advice for those with a runny nose:
- It is advisable to stay at home during illness and avoid going outside.
- For elevated temperatures, use antipyretic medications.
- It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids (warm tea with lemon or honey)
- Do inhalations, take warm baths.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor. Possibly prescribing antibiotics.
Inflammation in the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity, which often occurs during infectious diseases, is called rhinitis. There is nasal congestion, excessive nasal discharge, a burning or tickling sensation in the nose, and difficulty identifying odors. Rhinitis is treated with drops, nasal sprays, runny nose tablets, rinses, and inhalations. Rhinitis comes in different forms:
- Acute rhinitis. Lasts from 7 to 10 days and is caused by viruses and bacteria.
- Chronic rhinitis. It differs in the duration of the disease. For chronic rhinitis, a more complex approach to treatment is required.
- Catarrhal rhinitis. The disease proceeds more moderately and accompanies various ENT diseases.
- Atrophic rhinitis. Symptoms: dry nose, constriction, possible nosebleeds.
- Drug-induced rhinitis. Occurs with long-term use of medications (drops, nasal sprays).
- Vasomotor rhinitis. The disease as a result of impaired blood vessel tone is accompanied by a severe runny nose.
Ear otitis
Ear inflammation is otitis media, in which the middle, inner and outer ear can become inflamed. There are left-sided, right-sided and bilateral otitis media. Research has shown that this is one of the most diagnosed ear pathologies today. Symptoms of otitis media:
- noise, congestion in the ear;
- poor hearing;
- ear pain of varying degrees;
- purulent discharge;
- elevated body temperature.
During the treatment of otitis, nasal drops are prescribed for local instillation to reduce swelling of the mucous membrane, antiseptic solutions for the ear canal, drops for instillation for severe ear pain, and antibiotics. With chronic otitis media, treatment is more complex, so self-medication and traditional methods should be avoided. In children and adults, otitis media is treated in the same way, but it is better to consult a doctor for recommendations.
Pharyngitis
The inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the pharynx is called pharyngitis. Mostly, the disease is considered infectious; it occurs when inhaling dirty air or under the influence of irritating factors (alcohol, cigarettes). Pharyngitis causes a sore throat, pain, discomfort, general weakness, etc. For treatment it is recommended:
- eliminate the factor that caused the illness;
- stop smoking;
- use medication prescribed by your doctor.
Symptoms of ENT diseases
Characteristic symptoms of diseases of the ENT organs:
- snore;
- gradual hearing loss;
- pain of various localization;
- feeling of nasal congestion and runny nose;
- cough;
- bleeding of the nose and ear;
- difficulty breathing, decreased sense of smell and nasal voice.
All these symptoms indicate pathological changes in organs of the ENT system. Therefore, it is necessary to understand where the manifestations come from and what diseases they refer to.
Diagnosis of ENT diseases
To determine the best treatment regimen, a correct diagnosis must be made. For this purpose, the otolaryngologist has such devices as:
During a simple examination with these devices, the ENT will be able to see the characteristic signs of a particular disease and make a diagnosis. He pays attention to the condition of the eardrum, nasal passages and conchas, the mucous membrane of the nose and throat, as well as the tonsils. Examination of the outer ear and nose can be performed without the use of special instruments. Also during the appointment, the doctor must palpate (feel) the adjacent lymph nodes.
Endoscopic examination is used to accurately diagnose the ear, nose and throat. An endoscope is a flexible tube with a video camera at the end, which is inserted into the cavity of the organ being examined. The image from the camera is displayed on the monitor and the doctor can examine everything up close.
Additionally, the ENT prescribes blood tests and a smear for bacterial culture. They will help determine the type of infection and its degree of pathogenicity. In some cases, a puncture is performed, that is, fluid is taken with a syringe for further study in the laboratory (for example, for sinusitis, fluid is taken from the paranasal sinuses).
What else does the otolaryngologist check? If you have ear disease, you should have your hearing checked. The easiest way to do this is by voice, when the patient is at a distance of 6 m, and the doctor whispers different words that the person must hear and repeat. More accurate hearing tests involve the use of special equipment, such as audiometry headphones.
Another method used to diagnose ENT organs is radiography. It can help rule out other conditions and look for abnormalities in the ears, nose and throat, such as pus collection, swelling, fractures, or foreign objects. X-rays are also necessary if intracranial or pulmonary complications are suspected.
More advanced technologies are used in magnetic resonance and computed tomography (MRI and CT). The first type is suitable for diagnosing brain lesions and detecting tumor formations. All bones are clearly visible on CT, so it is more often used to detect fractures and foreign bodies.
Ear, nose and throat diseases
The second edition of the textbook (the first was published in 1981) introduced new chapters on methods of general therapy, clinical presentation and treatment of fungal diseases of the ear, nose and throat. The order of presentation of the material has been changed. The textbook corresponds to the program approved by the USSR Ministry of Health and is intended for students of medical schools.- About the book
- Preface
- A Brief History of Otorhinolaryngology
- Diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses Clinical anatomy
- Clinical physiology
- Research methods
- General therapy and care methods
- Diseases of the nose Congenital anomalies (deformities)
- Diseases of the external nose
- Diseases of the nasal cavity
- Preparing patients for operations in the nasal cavity
- Diseases of the paranasal sinuses
- Inflammatory diseases
- Rhinogenic complications
- Fungal infections of the nose and paranasal sinuses
- Diseases of the pharynx and esophagus
- Clinical physiology of the pharynx
- Pharynx examination methods
- Clinical anatomy and physiology of the esophagus
- Methods for studying the esophagus
- General therapy and care methods Injuries and foreign bodies of the pharynx and esophagus
- Hypertrophy of lymphadenoid tissue of the pharynx
- Inflammation of the pharynx
- Inflammation of the tonsils of the pharynx. Sore throats
- Complications of tonsillitis
- Lesions of the pharynx in systemic blood diseases
- Chronic tonsillitis
- Prevention of sore throats and chronic tonsillitis
- Fungal infections of the pharynx
- Diseases of the larynx, trachea and bronchi
- Clinical physiology
- Research methods
- General therapy and care techniques Injuries and foreign bodies
- Laryngeal edema
- Acute inflammation of the larynx
- Fungal infections of the larynx
- Chronic inflammatory diseases of the larynx and trachea
- Chondroperichondritis of the larynx
- Laryngeal stenosis
- Diseases of the nervous system of the larynx
- Ear diseases
- Clinical physiology
- Research methods
- General therapy and care methods
- Diseases of the external ear Trauma and foreign bodies
- Developmental anomalies
- Inflammatory diseases
- Middle ear diseases
- Aerootite
- Acute otitis
- Mastoiditis
- Traumatic diseases
- Chronic purulent diseases
- Tympanoplasty
- Inner ear diseases
- Cochlear neuritis (auditory nerve)
- Meniere's disease
- Otosclerosis
- Otogenic intracranial complications
- Audiology and hearing care
- Task
- Tumors
- Malignant tumors
- Ear tumors
- Specific diseases
- Scleroma
- Syphilis
- Expertise
- Allergic diseases (allergic sinusopathy)
- Preparing patients for surgery on the paranasal sinuses and care in the postoperative period
- Clinical anatomy of the pharynx
- Clinical anatomy
- Clinical anatomy
- Catarrhal otitis media
- Labyrinthitis
- Control questions
- Tumors of the respiratory tract Benign tumors
- Tuberculosis
Source: Palchun V.T., Voznesensky N.L. 'Diseases of the ear, nose and throat' - Moscow: Medicine, 1986 - p.272
Treatment of ENT diseases
Various methods are used in the treatment of pathologies of the ENT organs.
Physiotherapy
Based on the use of ultrasound, electric current, heat, “blue lamp”, electrophoresis, magnetic field and other methods based on physical influence. These treatment methods are considered one of the safest, they are used either independently or in combination with drug therapy.
Drug therapy
As a rule, in the treatment of all ENT diseases, antibiotics are used, which relieve inflammation, swelling, fight infection, preventing the development of further deterioration. There is nothing wrong with these drugs; it is important to understand that the risk of complications from untreated inflammation of the ENT organ is much higher than the possible harm from the antibiotic. The only and main rule in this case: only a doctor can prescribe the drug, its dosage and duration of use.
Inhalations
They can be attributed to both physical and drug therapy. They are used for pathologies of the nose and throat; the medicinal substance with this method of treatment enters the body with inhaled air, i.e. through the upper respiratory tract.
Surgical methods
They are used in severe cases, when other treatment methods do not bring the desired effect, and there is a threat to the patient’s life. The most common example of operations on the ENT organs is the removal of adenoids, tonsils and polyps.
Disease therapy
What to do if diseases of the ENT organs are diagnosed? Follow the doctor's recommendations. Having clarified the nature of the infection, the doctor prescribes antibiotics or antiviral agents.
If the pathogen is one of the types of bacteria, then antibacterial agents are prescribed:
- Traditional penicillin series: Amoxicillin or its improved version Amoxiclav, their dispersible generics - Flemoxin or Flemoclav Salutab. Generics taste good and dissolve easily, turning into a suspension.
- Macrolides - Azitsin, Sumamed. They differ in a short course of administration. The blister contains 3 tablets. This antibiotic has a prolonged effect.
- Cephalosporins are more modern, powerful drugs. Sorcef, Cefixime are indicated if the disease is rapidly progressing or the patient cannot tolerate other groups of antibacterial agents.
Among antiviral drugs, the leaders are Arbidol and Amizon. And the protective properties of the body will be supported by Imudon or Immunal.
If your ear is blocked or there is inflammation, then ear drops will be required. These are Sofradex, Otinum, Anaurin. They all have a different mode of action, so you should not self-medicate.
How to treat a throat? Anesthetics and antiseptics are suitable - tablets or lozenges for resorption: Adjisept, Chlorophyllipt, Faringosept, Lizak, Farington, Anzibel, Isla. Spray treatment is also effective for children over 3 years of age and adults. Popular: Kameton, Ingalipt, Tantum Verde, Miramistin, Yox, Givalex. For rinsing, you can use Furacilin solution, specially prepared by Tantum Verde, Rotocan.
To treat the nose, use Rinofluimucil, vasoconstrictor drops, Protargol with silver ions and other agents that the doctor will name.
For coughs, an emollient, antitussive tablets, lozenges, and syrups are prescribed.
Prevention of ENT diseases
Diseases of the ENT organs, the symptoms and treatment methods of which are described above, can be prevented. In order to reduce the likelihood of developing diseases of the ENT organs to a minimum, the following recommendations must be followed:
- strengthen the body's immune defense;
- avoid physical and mental overstrain;
- lead an active lifestyle, walk more, play sports;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- do not overcool;
- harden your body;
- avoid stress if possible;
- observe the work and rest schedule.