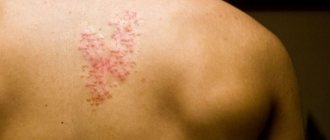
There are a huge number of viral infections in the world, among which herpes simplex is a common disease. Some people, when they hear the word “herpes,” think that it is a common “cold” on the lips, and nothing more. In reality, this disease is not so simple. The human herpes simplex virus can accompany you throughout your life, occurring without any particular symptoms. But if the functioning of the immune system in the body decreases and the immune system weakens, the virus will begin to appear not only on the lips, but also on other parts of the body. Therefore, the task is to determine the types of illness, their causes, and preventive measures.
Herpes - what is it?
Often, herpes g1 is understood only as a rash in the form of blisters on the lips, transmitted from person to person through tactile contact. Unfortunately, 90% of people have this virus in their bodies, which manifests itself at the most unexpected moments. For some, herpes simplex is a one-time occurrence, for others it is recurrent. It all depends on the body itself and the functioning of the immune system.
According to statistics, women are more often affected by the disease, but in men the infection manifests itself no less often. The herpes virus can affect the eyes and the skin around them, the mucous membrane of the face, genitals, and the central nervous system. The appearance of a recurrent virus can be noticed on the lips, nasal wings, cheeks, in the oral cavity, on the ears or forehead.
The herpes virus g1 has 5 types, the main ones being HSV 1 and 2 types. The remaining types have not yet been studied, but there is speculation that they manifest themselves only in the form of constant fatigue and unexpected skin rashes. Since HSV1 and HSV2 affect the human body most often, it is important to review their causes, main symptoms and treatments. But it is necessary to remember that at the initial signs of the disease, you should immediately seek help from a doctor, and not undergo treatment yourself.
Incorrect self-medication can lead to serious complications.
Transmission routes↑
All strains of the herpes virus are transmitted from person to person by contact, airborne droplets or sexual contact. They penetrate the mucous membranes and skin and are embedded in the cells of nerve endings. It is no longer possible to extract the herpes virus from there; it becomes our companion for the rest of our lives. Migrating along the nerve trunks and bloodstream, herpes simplex enters vulnerable areas of the body and causes a specific inflammatory process.
A healthy immune system successfully blocks the spread and replication of the virus. However, its failure allows the infection to affect the skin and mucous membranes, leading to characteristic vesicular rashes and general malaise. Itching and soreness are felt in the areas of the rash, and regional lymph nodes become enlarged. The rash lasts no longer than two weeks, unless there is a secondary infection. The vesicles heal without scarring.
In severe cases, herpes (especially type 1) manifests itself in the form of deadly cerebral infections (meningitis and encephalitis). Fortunately, CNS complications are rare, occurring in approximately 2 cases per million.
Herpes simplex type 1
Herpes simplex virus type 1 is common. However, it does not always manifest itself, since the human body has special antibodies g in the blood that suppress the action of herpes simplex. This virus, by its nature, can infect the upper limbs of a person and the face area.
Most often, the etiology of this disease is that a person comes into contact with an infected area or with secretions of an infected body, for example, with saliva or semen. In this case, virus g1 no longer disappears and remains in the body forever, migrating through its different parts. If the immune system begins to malfunction, the virus wakes up and actively manifests itself in rashes in the form of bubbles with liquid that appear on parts of the body.
When it enters cells, type 1 herpes quickly multiplies and uses all cellular resources for development. Before the rash appears, the patient experiences severe itching, which may be accompanied by a burning sensation. This form of hsv is most pronounced on the face, with the lips or nasal mucosa most often affected. It is even called “labial” herpes, because often the disease does not reach the oral cavity.
Herpes simplex type 1.
Most often, the infection enters the body in childhood, when the body is still weakened, has a less strong immune system and is capable of becoming infected at the slightest contact with a sick person. In this case, the first stages of infection begin on the 3rd day, and the symptomatic series is immediately noticeable: the patient feels unwell, his temperature rises, and severe rashes appear. Further times the disease will manifest itself at those moments when the patient’s body weakens, the immune system begins to work worse and antibodies are no longer able to fight the infection. In some situations, type 1 herpes can manifest itself completely unpredictably, appearing:
- on the genitals and their mucous membranes;
- in the oral cavity, which is more typical for childhood, and the small patient is diagnosed with herpetic stomatitis;
- in the neck, mucous membranes of the eyes, on the fingers.
In addition, type 1 herpes virus can infect the upper surfaces of the myelin sheaths of nerve fibers. Hsv i 1 can cause headaches, a person begins to feel a loss of strength, and there is no talk of performance.
How is herpes simplex diagnosed?
This type of virus is usually diagnosed through a physical examination. Your doctor may examine your body for ulcers and ask you about some of your symptoms. Your doctor may also refer you for HSV testing. This is called a herpes viral culture test. He will confirm the diagnosis if you have ulcers on your genitals. During this test, your doctor will take a sample of fluid from the ulcer and then send it to a laboratory for testing.
Blood tests for antibodies to HSV-1 and HSV-2 can also help diagnose these infections. They can help especially when there are no ulcers on the body.
Herpes simplex type 2
Herpes of this type in most cases is perceived by the body as a foreign object, and g antibodies begin to be actively produced in the blood, which help reduce the risk of developing the disease in the future.
Herpes simplex by its nature affects the genitals, the area around the anus. Patients between 20 and 40 years of age who are sexually active are most often infected. Doctors diagnose herpes more often in women than in men.
Herpes simplex type 2 affects by its nature the genitals, the area around the anus.
The incubation period of the virus lasts from 1 to 10 days, after which the patient develops a feeling of weakness, reluctance to do anything, the temperature rises, and the lymph nodes in the genital area become enlarged. When the disease occurs, a person feels a strong burning and itching in the anal-genital area, and a rash appears in the form of blisters. This form of hsv 2 can take a long time to develop, and the wounds heal from 3 to 5 weeks.
Even if a patient has previously suffered from a previous type of herpes, this does not mean that he cannot catch type 2 herpes. A characteristic feature is that repeated rashes can appear frequently, which is not typical for the first type. Herpes simplex virus 2 is dangerous because it can cause cancer in the genital organs of people, in addition, inflammatory processes can terminate pregnancy. In severe cases, HSV type 2 can even lead to infertility. In addition, the level of sensitivity in the genitals and buttocks area decreases, and pain may be permanent.
Severe disease
Herpes types 1 and 2 are severe with generalization of the infectious process against the background of suppression of the immune system.
Risk factors:
- acquired and congenital immunodeficiencies, primarily HIV/AIDS;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- oncological diseases;
- immunosuppressive therapy (chemotherapy, glucocorticoids, cytostatics, radiation therapy);
- organ transplantation.
Herpesvirus can cause severe illness.
Against the background of suppressed immunity, the herpes virus causes serious illnesses:
- meningitis, encephalitis, meningoencephalitis;
- atypical pneumonia;
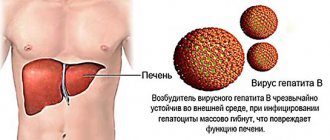
- viral hepatitis;
- keratitis, blepharitis, iridocyclitis.
Intrauterine infection of the fetus leads to spontaneous miscarriages, developmental defects, and slow mental development.
Therapeutic measures
The presence of hsv ii in the human body is not the most pleasant moment, because it is necessary to choose the right treatment that will help eradicate the disease. During treatment, it is advisable to give up bad habits so as not to aggravate the situation. The treatment complex may include both medications and traditional medicine. Moreover, they can be used externally or internally to not only remove external symptoms, but also get rid of internal ones. What medications should be used to treat a patient with herpes? The most well-known medicines include:
- "Acyclovir" - antiherpetic drugs that implement external
One of the most effective means in the fight against the virus
or internal use, because they are presented in the form of ointments or tablets that help in the fight against g1 disease. "Acyclovir" is a kind of standard in the treatment of herpes virus i. It has high performance both for external and internal use. - "Valacyclovir" is a powerful antiherpes drug that suppresses the effect of the virus in the body.
- Antiviral drops "Proteflazid".
- Flavoside syrup.
If a patient is diagnosed with herpes i virus, he can use traditional medicine. Most often, for herpes, they are used externally and do not require much effort to prepare:
- If an infection occurs, it is necessary to make compresses, for example, from celandine juice or from an apple or potato.
- Egg whites, which should be spread on infected areas, have a good effect against herpes.
- Do you want skin ulcers to disappear faster? Wet the area slightly and then rub with fine salt. The procedure should be repeated as often as possible, gently rubbing into areas of the skin.
Treatment of herpes↑
To date, science does not know a recipe for completely expelling the uninvited guest from the peripheral nerves. The goal of therapy is to slow down the multiplication of the virus in vulnerable cells of the skin and mucous membranes, if possible. The drug Acyclovir (trademark Zovirax) and new generation drugs developed on its basis (Valacyclovir, Famciclovir, Penciclovir) cope with this task. A dermatologist may also prescribe antiviral syrup Flavozid and Proteflazid drops.
Although drugs from the Acyclovir series can be used during pregnancy and lactation, this should be done with great caution. If the expectant mother knows that she is infected with the herpes simplex virus, she needs to think in advance about strengthening her immunity.
Herpes during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the virus can be dangerous to the life and health of the unborn baby
. Despite the skepticism of some patients about the disease, herpes g1 can cause serious complications not only in pregnant women, but also in the unborn baby. This is explained by the fact that when it enters the body, the strain settles there, populating at the cellular level, and the body of the mother and child are closely connected. If the disease is detected in the patient in the early stages, the pregnancy may end in miscarriage. If the fetus survives, the newborn is likely to develop:
- various rashes;
- damage to the eye areas;
- underdevelopment of the brain;
- delays in physical or mental development.
Complications
Since the herpes virus g1 develops quickly in the body, some microorganisms can get into the eye parts, which will lead to ophthalmoherpes, which in the future threatens not only a decrease in vision, but also its complete loss. In addition, herpes affects the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, which is fraught with the appearance of erosions and ulcers. The central and peripheral nervous systems are affected, which can result in paralysis. The disease affects the kidneys, adrenal glands, and genitourinary system.
What other types of virus exist: the causes of herpes on the body and how to treat it
If we talk about what types of herpes a person has, then we must not forget about its 5th serotype, which in medical practice is called cytomegalovirus (CMV). It, like other herpeviruses, is a chronic pathology.
Once in the human body, it remains in a latent state, and when certain conditions arise (decreased immunity, hypothermia, chronic illnesses) it develops into an acute course with characteristic symptoms, but this is not observed in every carrier of this herpes serotype.
Cytomegalovirus acts with severe symptoms of general intoxication of the body and pharyngitis. But the symptoms of rashes characteristic of types of herpes on the body are not determined, and accordingly, its treatment will be slightly different, aimed at reducing sore throat and eliminating the consequences of intoxication.
Acute development of the virus quickly turns into cytomegalovirus mononucleosis with the following symptoms:
- Temperature increase.
- Intoxication (weakness, muscle pain).
- Sore throat (not always observed).
When examining a patient, the doctor can detect all the signs of acute pharyngitis: hyperemic mucous membrane of the oropharynx, enlarged lymph nodes.
If during this period of development the virus cannot be stopped, then nearby organs (salivary glands, ears) are affected. It is also possible for CMV to spread to other body systems. For example, granulosa hepatitis may begin when the liver is damaged, pancreatitis when the virus enters the pancreas, pneumonia when it moves to the lungs, etc.
You have already discussed above what types of herpes exist and how to treat them. But for cytomegalovirus, slightly different types of therapy are used:
- Immunostimulating.
- Antiviral.
- Symptomatic.
- General strengthening.
Doctors pursue the same goals as for other herpes. Having found out the causes of the disease and the treatment, they select a comprehensive one to relieve symptoms and accelerate the transition of the virus into a latent state. To support and improve the functioning of organs that have been affected by the virus, appropriate medications are used:
- Glycosides for heart damage.
- Hepatoprotectors for liver disease.
- Antibiotics for damage to lung tissue.
Relapses of herpes serotype 5 are possible and most often develop against the background of reduced immunity, stress, chronic diseases, etc. The causes of the constant manifestation of herpes can also be diseases such as HIV, tuberculosis, and oncological pathologies.
Preventive measures
Despite the fact that not everyone exhibits signs of herpes simplex, everyone needs to know the standard measures and prevention regimens:
- The first and main rule is that you need to follow the rules of personal hygiene, because the virus is transmitted through household objects and touch. This includes: eating only from your own dishes;
- using your own cosmetics;
- using condoms during sexual intercourse, refusing oral sex when the partner has a rash.
Causes
Most often, the virus appears in the body unnoticed by a person. Infection occurs in several ways:
- The pathogen enters the child’s body from an infected mother as it passes through the birth canal. Clinically, this may not manifest itself in any way, because the virus is in a latent state. If the child has a strong immune system, then herpes may continue to occur in a latent form. For obvious signs of infection to occur, an exacerbation of the pathology as a result of a weakened immune system is necessary;
- contact is the most common way pathology occurs in the body of an adult. You can become infected with herpes by sharing towels, bed linen, dishes with an infected person, by swimming in an enclosed body of water, by hugging, kissing;
- The herpes simplex virus often enters the body as a result of sexual contact between an infected person and a healthy person. In this case, type 2 genital virus can settle in the oral area; the etiology of the appearance of oral pathology in the genital area is similar. This occurs in those couples who practice oral sex;
- You can become infected with herpes through blood as a result of medical procedures or through cuts, wounds, or microtraumas.
Primary infection with strong immunity is asymptomatic, so a person may not suspect that he has become a carrier of the herpes virus (read more here).
Conclusion
Herpes simplex is not a simple disease that does not require treatment. The main types include 2 forms: herpes type 2 and type 1. When herpes simplex microorganisms enter the bloodstream, they begin to actively multiply, affecting the cells of the body. They may not manifest themselves, but they can transfer to a partner.
At the initial signs, you should immediately consult a doctor who will help cure the body by choosing the right medicine. The doctor prescribes special antiherpetic drugs that will help overcome the disease. If the patient has herpes simplex virus 2, the doctor may prescribe pain medications.
Among the folk remedies, the use of celandine juice is considered effective.
There are many medications available these days for herpes simplex. Most often the disease is treated with Acyclovir or Valacyclovir. Not only pharmaceutical drugs, but also traditional medicine help against herpes simplex. For example, a compress made from celandine juice or rubbed with egg white is an excellent treatment.
At the same time, there are no uniform standards for carrying out a treatment complex against herpes simplex. But there is one important scheme: the disease must be treated not only from the outside, but also from the inside in order to eradicate the infection.
The virus is dangerous, so you should not self-medicate. Since the virus has external manifestations, in the absence of therapeutic measures, scars may remain after the disease. The patient must remember the rules of prevention so that later he does not have to fight the disease.
Treatment of herpes virus serotype 3 with characteristic symptoms in children and adults
As in the case of herpevirus serotypes 1 and 2, therapy for the Zoster virus is aimed at reducing the clinical manifestations of the disease and the duration of its course. There are currently no drugs that completely eliminate infection in the body.
The herpes virus in children with characteristic symptoms and treatment requires drugs that will reduce itching, accelerate tissue regeneration, dry out the sores, and inhibit the virus. Antiviral agents are used for this:
- "Acyclovir".
- "Valacyclovir."
- Famciclovir.
For the first few days, it is recommended to lubricate the affected areas with ointments with the same effect, and then treat them with antiseptic preparations such as brilliant green.
Treatment of herpes (smallpox) in children occurs at home, while the child is additionally prescribed bed rest, plenty of fluids, and contact with peers is not allowed.
If we talk about the treatment of herpes zoster, then non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( Diclofenac, Ibuprofen ) are added to the above antiviral drugs. They help reduce pain during the disease.
If herpes is observed on the body with signs of an associated secondary bacterial infection (bullous type of rash), then the ulcers are treated with ointments or antiseptic solutions ( Levomekol ).
In complex forms of the disease or frequent relapses, drugs are used to boost immunity ( Genferon, Cycloferon ).