5 Health • Children's health 09.12.2017
Dear readers, you have probably heard something about Giardia more than once. Even this word sounds somehow very unpleasant, right? Many parents are frightened if such a diagnosis is given to their child. Today, together with pediatrician Oksana Elhissi, we will talk about the symptoms, treatment of Giardia in children and the prevention of this disease. I give the floor to Oksana.
Hello, dear readers of Irina’s blog. Giardiasis is a common parasitic disease, and children are more often than adults at risk, especially if they attend large groups of children, for example, go to kindergarten or school. I propose today to talk about what every wise parent needs to know about this disease.
How does giardiasis become infected?
The cause of giardiasis is the simplest microorganism Giardia. Giardia primarily parasitizes the small intestine of humans, but is also found in some mammals and birds.
In its life cycle, lamblia goes through two stages:
- trophozoite - a unicellular microorganism in the vegetative stage, pear-shaped with flagella, through which it can move quickly;
- cyst - under unfavorable living conditions, the trophozoid turns into an oval cyst, incapable of independent movement. The cyst remains viable in a humid environment for three months. Even in the presence of small concentrations of chlorine, the cyst retains its viability.
When it enters the human body in the duodenum, two trophozoites are formed from one cyst. Parasites are firmly embedded in the walls of the duodenum or small intestine and, due to the favorable alkaline environment in these parts of the intestine, quickly multiply and grow.
The disease giardiasis is widespread throughout the world. The traditional leaders among regions with a high percentage of cases of infection are considered to be the tropical regions of Africa, Mexico and South America, the southern and south-eastern regions of Asia, where the level of sanitary and hygienic provision is catastrophically low. However, cases of giardiasis infection are also recorded in developed countries.
Both adults and children are susceptible to the disease, but children under five years of age account for the largest percentage of cases.
Let's see what Giardia looks like in the photo.
Why is lamblia dangerous?
Many parents not only do not know how to treat Giardia in children, but do not even think about how relevant medical intervention is in this situation. It is important to understand the essence of the pathogenic effect of Giardia on the body.
Here are the main influencing factors.
- Disturbance of enzymatic processes in the body. It is in the small intestine that the vast majority of macroelements, minerals, vitamins, and other nutrients are absorbed. Giardia, with its constant movements, disrupts all enzymatic processes and changes the concentration of enzymes in the intestines. Because of this, a person does not receive the required amount of even the simplest substances, which leads to gradual exhaustion.
- Imbalance of microelements and macronutrients. Some elements are not absorbed, other substances are not produced in the required quantities. This situation directly leads to a slowdown in cognitive and physical development in children.
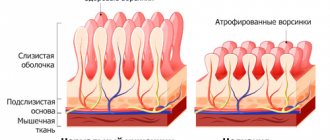
- Mechanical damage to the villi. Giardia moves around all the time, from time to time sticking to the intestinal walls. Because of this, delicate tissues become irritated, inflamed, and villi suffer. In some situations, the parasite can even invade the villi, completely destroying them. This leads to degeneration of intestinal structures. The absorption of nutrients is reduced to a minimum, and the symptoms of depletion intensify.
- Toxic influence. The parasite constantly synthesizes toxic substances, which it releases into the intestinal passages. Because of this, the nervous system suffers, and various allergic reactions often occur. The functional potential of the gallbladder, liver, and stomach suffers.
How the infection is transmitted
The mechanism of infection with giardiasis is fecal-oral through several routes of transmission:
- from a sick person or child to healthy ones through toys, utensils and household items, dirty hands;
- through contaminated water;
- through unwashed food.
Massive epidemics of giardiasis occur only through contaminated water. A small number of cysts (about 10 pieces) is enough to become infected with this serious disease. Animals, including domestic ones, can also be a source of infection.
Ways of infecting children with Giardia
Before treating a parasitic infection in a child, it is important to understand where Giardia comes from in his body. This will help avoid re-infection during the therapy stage. There will also be an excellent opportunity to eliminate the danger of infection in the future, when the therapy is completely completed.
Experts note that Giardia is characterized by a certain list of routes of transmission of parasites:
- Household contact is the most common route in which the disease is directly transmitted from a sick child to a healthy one, or from infected pets or objects. Most often, the contact-household route is used in preschool institutions. In them, children use shared toys, stationery, and towels, on which Giardia cysts remain.
Giardia can be transmitted to a child from a sick pet
- The food route is the second most common route among children. Kids do not always know that they can only eat cleanly washed fruits, herbs and vegetables. They may also contain parasite cysts. This path is relevant, first of all, for children living in rural areas. Meat products that have not undergone proper culinary processing can also be dangerous.
- The water route is no less common than the previous ones, a method of infection. The problem is that Giardia cysts can remain viable for a long time in water. Since it is not always possible to identify dangerous water, especially if it is taken from open water bodies, such infections are widespread. The waterway is relevant for both rural and urban children.
Protecting children from infection is a very important task, since getting rid of Giardia forever can be quite difficult.
Drinking low-quality water that has not been treated can cause the development of giardiasis
It is important to explain to your child from a young age why you need to wash your hands, drink only clean water, and not put toys in your mouth, especially strangers.
How to determine giardiasis in a child
After parasites attach to the intestinal walls, their integrity is disrupted, which leads to impaired absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, sugars and fats. There is a toxicological and immunological effect on the child’s body; the child may quickly begin to get tired and be capricious.
The incubation period can last from one week to two.
Afterwards comes the acute stage, which is manifested by increased body temperature, decreased appetite, abdominal discomfort, nausea, belching and frequent watery stools with a pungent odor.
However, according to statistics, in most patients the clinical picture of the disease is not so clear, which leads to a loss of time for diagnosis and transition to the chronic stage.
Symptoms and signs of Giardia in children
The main symptoms of giardiasis infection in children:
- intoxication of the body is manifested by weakness, mood swings, fatigue, complaints of body pain and headaches, fluctuations in body temperature;
- from the digestive tract - pain in the intestines, plaque on the tongue, gas formation and seething in the abdomen, loss of appetite and refusal to eat, nausea and vomiting, changes in stool character, weight loss. Sometimes there is an enlargement of the liver, the development of hepatitis, cholecystitis and pancreatitis;
- skin rashes - urticaria, dermatitis;
- exacerbation of bronchial asthma, increased coughing attacks;
- changes in blood counts;
- avitaminosis;
- in severe cases, signs of developmental delay are observed.
What is Giardia and why are they dangerous?
Giardia are parasites from the class of protozoa, very small in size, single-celled. Discovered in the mid-19th century, the pest has a primitive structure, but is equipped with both locomotion organs (flagella on the narrowed part of the body) and attachment organs (disc-shaped sucker on the wide part of the cell body). All this allows Giardia not only to live and remain in the child’s body, but also to move along his digestive tract.
Giardia is found in the intestines, mainly in the upper part of the small intestine. In addition, they can penetrate the bile ducts and liver.
The development of lamblia in a child and lack of treatment leads to various complications
During their life, many waste products are released into the host's body, which are toxic to humans. Giardia can also take away most of the nutrients, as they feed on the contents of the small intestine.
It is because of these two factors that a sick baby may experience numerous health problems:
- general intoxication of the body, in which the digestive tract, nervous and cardiovascular systems suffer;
- acute deficiency of vitamins, minerals and microelements, caused by depletion and death of the intestinal mucosa, as well as by the fact that nutrients are absorbed by a parasite and not a person;
- destructive processes in internal organs lead to changes in their functioning - not only the digestive tract, but also the lungs and heart suffer from lamblia.
Giardiasis disrupts the digestion process and impairs the absorption of nutrients by the body.
The connection between symptoms and treatment of Giardia in children is very clear. To finally get rid of the infection, babies need a long recovery. This is the only way to completely eliminate the negative consequences of the disease. It is not enough to simply remove Giardia from a child.
Diagnosis of giardiasis
A very common situation is completely asymptomatic giardiasis in children, which makes diagnosis difficult. To make an accurate diagnosis, clinical and laboratory examinations are performed.
Tests for Giardia in a child - how to take them?
Which doctor should I see? First you go to the pediatrician. All tests are prescribed by a pediatrician, infectious disease specialist or parasitologist. The doctor will tell you everything in detail.
To begin with, a parasitological study of the child’s feces is carried out - at least three studies with a break of several days.
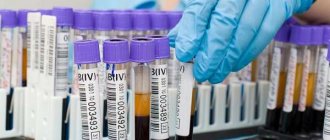
At the next stage, Giardia antigens are diagnosed in the patient’s stool and blood using the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method, and a search for specific immunoglobulins G and M is carried out using the ELISA method (immunofluorescence analysis). The detection of immunoglobulin M indicates the presence of Giardia in the body, immunoglobulin G is responsible for the “defense” of the body - its elevated levels can be detected for several months after treatment.
Blood for Giardia is taken from a vein. The analysis should be done on an empty stomach in the morning, before breakfast. A child of any age can donate blood for testing.
These diagnostic techniques are recognized as one of the most effective.
Giardia treatment, diagnosis and tests
In the case of an advanced form of the disease, treatment is more difficult. Treatment of Giardia in children involves removing them from the small intestine. The treatment regimen for giardiasis in children is carried out in the following stages:
- It is necessary to begin treating giardiasis in children with a strict diet. It is important to reduce intoxication, facilitate the functioning of the food system, and also increase immunity.
- Antiparasitic drugs are then prescribed. When they are administered, symptoms may worsen in a sick child: diarrhea, abdominal pain and skin rashes. But after three days, the treatment gives a positive result in children. If the attending physician determines an acute form of giardiasis, then the first stage is skipped and the treatment of giardiasis in children, namely the treatment regimen, changes: medications are immediately administered.
- The treatment ends with the restoration of the body. For this purpose, children use special medications to restore intestinal microflora, as well as to boost immunity.
Important! Only specialized doctors know how to treat Giardia in children and what medicine to use! They are the ones who diagnose the disease and determine which medicine for lamblia for children will be safe and effective.
But before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to make the appropriate diagnosis and pass the necessary tests, namely:
- Donate blood for Giardia. A blood test for Giardia in children is considered effective in the first four weeks of infection. If the disease is chronic, then such an analysis will not give any results. How to donate blood? This must be done on an empty stomach in the morning, the blood is collected from a vein.
- Donate feces This test allows you to detect Giardia cysts in a child’s stool. But since cysts may not be detected the first time, such an analysis is performed several times.
- Duodenal sounding. This test indicates the presence of cysts in the body, but is not used on children under 10 years of age.
If tests for Giardia confirm their presence, then a medicine for Giardia is prescribed, which will remove the parasites from the body. Treatment depends on the number of parasites in the body, as well as the degree of illness of the child.
Detection of parasites in the liver, symptoms and treatment
If Giardia was found in the liver, the symptoms may be slightly different. Giardia in the liver appears as a result of blood circulation in the body and the accidental movement of parasites to the corresponding organ. Symptoms that indicate the location of the parasite are the following:
- The presence of plaque on the tongue and in the oral cavity. Instead of plaque, ulcers or acne may appear.
- The child vomits frequently. Bile may also come out with vomiting.
- Pain in the right hypochondrium. This occurs because the liver increases significantly in size. The doctor detects organ enlargement by palpation.
Drugs for the treatment of giardiasis are prescribed after a child has been tested for giardia.
Treatment with folk remedies
But you can get rid of Giardia not only with medications. So, for giardiasis in children, many parents prefer to use traditional methods of treatment. Treatment of giardiasis in children with folk remedies is not considered the main method of treatment. This technique is recommended to be used as a supplement to the main treatment, which is determined and prescribed by a specialized doctor.
But if, nevertheless, the choice fell on folk remedies, then before starting treatment, it is necessary to consult a doctor and obtain his approval for certain procedures.
How to cure Giardia in a child using folk recipes?
In folk medicine, there are several popular and effective methods. These include:
- Fresh cucumber tincture.
The ideal choice would be a cucumber that has a lot of seeds. As a rule, a large overripe cucumber has a large number of seeds. 200 grams of cucumber are crushed and poured with boiling water (minimum 0.5 liters). The broth is allowed to brew for two hours, then it is filtered. The prepared decoction is given to the child throughout the day instead of regular water.
- Dandelion root tincture.
This root can be dried yourself or purchased at the pharmacy. Dandelion root is washed, dried and crushed. Then the crushed root is poured with one liter of boiling water (three tablespoons of the plant), placed on low heat and boiled for fifteen minutes.
Then the resulting decoction must be filtered and given to the baby before meals twice a day. The dose of the decoction is determined as follows: per 10 kilograms of weight - one teaspoon of decoction. The course of treatment is ten days.
- Decoction of celandine.
To make this tincture, you need to take the plant, wash it, dry it and chop it. Then take one tablespoon of the crushed plant and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Let the broth brew for two hours, strain it and give the child one tablespoon before meals.
- Horseradish tincture.
Take horseradish root (2-3 pieces), chop it and pour one liter of cold boiled water. Then close the resulting mixture with a tight lid. Let the broth brew for three days, strain it and mix with honey. Let the tincture brew for another three days at room temperature.
Treatment with folk remedies can be dangerous for children, as some plants can cause allergies. In case of suspicious rashes, the use of tinctures should be stopped immediately.
How to treat Giardia in children. Modern treatment
Treatment of giardiasis begins immediately after diagnosis, even in the absence of clinical manifestations of the disease. The drugs and duration of treatment are selected taking into account the course of the disease, the characteristics of the child and include:
- drug therapy aimed at destroying Giardia and accompanying parasites;
- replacement therapy for complications such as hepatitis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis;
- enterosorbents – to reduce the toxic effect of parasites on the child’s body;
- medications to restore intestinal motility and microflora;
- necessary complexes of vitamins and microelements.
Treatment of giardiasis using traditional methods
Treatment of giardiasis in children should be comprehensive and step-by-step. During the therapeutic effect on the patient, signs of cholestasis and toxic damage to organs and tissues are gradually eliminated. The essence of antiparasitic treatment is to eliminate trophozoites and cyst forms of parasites.
Diet
The patient is prescribed an optimal diet. The goal is to create the most unfavorable conditions in the digestive tract, preventing the activity of Giardia. The basis of the diet is porridge, bran, fresh vegetables, fruits, berries, vegetable oil. You should avoid foods rich in carbohydrates. At least for the duration of active treatment.
It is recommended to arrange so-called fasting days. At this time, drink only water, xylitol, sorbitol, choleretic and antihistamines.
This “format” of influence on the body is possible only in the case of interaction with adult patients or older children.
Medication phase
The medicinal stage of therapy involves active influence on the parasite through specific medications. We are talking about such antiprotozoal medications as:
- Metronidazole;
- Ornidazole;
- Albendazole;
- Furazolidone.
Treatment usually consists of two courses. At the final stage, where the patient’s body must begin to actively recover, drugs of choice are prescribed from categories such as multivitamin complexes, enterosorbents, enzymes, plant-derived adaptogens, immunostimulants, and phytotherapeutic agents.
Preparations for the destruction of parasites
The basis for the treatment of giardiasis in children is the use of special antiparasitic drugs. What tablets and drugs do doctors usually prescribe for the treatment of lamblia?
"Nifuratel"
Currently, in general practice the drug Nifuratel (Macmiron) is prescribed for a period of 7 days. The effectiveness of this drug reaches 96%. "Nifuratel" has a wide spectrum of action and is approved for use in children from two months.
Side effects include, in rare cases, urticaria and itchy skin. "Nifuratel" is approved for use with concomitant liver diseases, as it is excreted from the body through the kidneys.
"McMirror"
When treating giardiasis with the drug "Makmiror" in patients with atopic dermatitis, there is an 80% reduction in skin manifestations. In children with bronchial asthma, attacks disappeared or decreased in 85% of cases. Allergic reactions are observed in all children taking this drug.
"Albendazole"
Another drug in the treatment of giardiasis is Albendazole. Its spectrum of action covers, in addition to Giardia, also helmites, so this drug is prescribed to children with combined infestations. The standard dosage is 15 mg per kg of the child’s body weight, 2 times a day for one week. The effectiveness of the drug ranges from 30-90%.
"Metronidazole"
The widely known drug “Metronidazole” is increasingly rarely prescribed for drug therapy in children due to the high risk of side effects and low efficiency compared to analogues of 20-70%.
Signs of Giardia in children
Over 20 percent of all acute intestinal infections in children are caused by giardiasis. With an intensive increase in the number of parasites in the intestines, the released toxins can cause symptoms of intoxication, allergic manifestations, and nervous system disorders in the child.
There are no specific symptoms of giardiasis in children, and often the manifestation of invasion is very similar to other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, so parents need to know that giardiasis is widespread among children and perhaps the ailments listed below in a child are associated specifically with this type of human invasion:
Intestinal symptoms
These are the first symptoms of giardiasis in children; they are detected 7-20 days after infection:
- Frequent loose stools, with a fetid odor of hydrogen sulfide, but not containing any impurities of mucus or blood, which distinguishes giardiasis from acute intestinal infections.
- Cramping pain in the abdomen, they can be of varying intensity, depending on the severity of the disease, the pain can be mildly aching or severe cramping, the pain is most often localized in the upper abdomen and near the navel.
- Nausea, less often vomiting
- Bloating - this symptom is an integral part of diarrhea and pain with giardiasis. This occurs due to disturbances in the normal digestive process, dysbiosis and excessive formation of gases in the intestines.
- These symptoms may disappear on their own after 15-20 days, and giardiasis can either become chronic or disappear spontaneously after a few months, which depends on the degree of infection and the state of the child’s immune system.
Symptoms of general intoxication
With massive reproduction and the release of large amounts of toxins, an infected child begins to show signs of toxic damage to the body, and also due to a reduction in the absorption of essential nutrients, the following symptoms appear in children:
- Unmotivated weakness
- Increase in body temperature to 37.5 C
- Loss of appetite, weight loss
- Dehydration
- Increased fatigue
- Pale skin due to anemia, appearance of shadows under the eyes
- Children's tongues are often coated, and their mouth usually has an unpleasant odor.
Neuropsychiatric disorders
in children may manifest themselves with long-term chronic giardiasis, such as:
- Headache
- Decreased concentration, memory impairment
- Dizziness
- Nervous tics, twitching, grimacing, obsessive movements
Allergic manifestations
a frequent companion of chronic giardiasis in children. Allergic reactions may be as follows:
- Atopic dermatitis, urticaria (see neurodermatitis)
- Itchy nose
- Dry, flaky skin
- Allergic dry cough, up to the development of bronchial asthma
- Allergic conjunctivitis
Supportive treatments
Recommended Diet
During the treatment of giardiasis, it is recommended to eat a diet that reduces the amount of carbohydrates and increases the intake of fiber and protein. To do this, you need to ensure daily consumption of fruits, vegetables and greens. Whole grain bread and bran bread are excellent sources of fiber. In patients with signs of lactose intolerance, exclusion of all dairy products (milk, fermented baked milk, kefir, sour cream, yogurt, feta cheese) from the diet.
Before eating, you must thoroughly wash your hands and food - vegetables and fruits.
It is not recommended to use during treatment:
- strong meat broths and fatty meats;
- animal fats, margarine;
- legumes and dishes made from them;
- seasonings and smoked meats;
- sweets, refined sugar;
- sweet drinks and juices;
- mushrooms.
Enterosorbents and probiotics
If you have loose stools, it is recommended to take a course of enterosorbents (Smecta, Eneterosgel) for 10 days. Taking prebiotics and probiotics to restore intestinal microflora is also indicated. They enhance and complement the action of specific drugs, which has a detrimental effect on parasites.
For concomitant manifestations of pancreatitis, after the diarrhea has stopped, pancreatic enzymes and hepatoprotectors are prescribed. According to indications, symptomatic treatment is carried out by prescribing painkillers and antipyretics. After treatment, complexes of essential vitamins and microelements, as well as herbal medicine, are prescribed.
And now I suggest watching the video material. What does Dr. Komarovsky say about the treatment of giardiasis?
Prevention of giardiasis disease
If a child becomes ill, medications and tablets for Giardia are taken by all members of his family. The child is under the supervision of a doctor for another six months. If giardiasis is detected in the family, the first thing to do is isolate the child in order to minimize the risk of infecting other family members.
Then all family members need to be tested for the presence of Giardia in the body. And even if parasites were not detected, each family member should undergo a preventive course of treatment. Only in this case can you avoid infection with giardiasis.
And in order to reduce the risk of reappearance of Giardia to a minimum, it is necessary to follow certain preventive measures. The main ones are:
- Careful monitoring of the food supply of the whole family. Vegetables and fruits should be washed well to remove all dirt on them, as well as harmful parasitic microorganisms.
- Drink only filtered or boiled water. Drinking tap water is strictly prohibited! After all, this is how lamblia appears in the body.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules. It is important to teach your child to always wash their hands before eating, and also to wash them after walking and visiting public places.
- If a child has bad habits such as thumb sucking or nail biting, then he needs to be weaned off this to reduce the risk of contracting giardiasis.
- You should not swim in bodies of water if they are dirty or have an unpleasant odor.
- Try to protect your child from contact with pets as much as possible. At least until he masters self-care skills. In addition, it is recommended to give antiparasitic drugs to pets.
If all family members, especially a small child, follow all these preventive methods, then the likelihood of contracting giardiasis can be reduced by 60%. And it is extremely important that if your baby develops any digestive disorder, with the manifestation of the above symptoms, it is necessary to urgently undergo an examination. After all, the earlier the diagnosis is made, the faster and more effective the treatment process will be.
It should also be remembered that when undergoing treatment for giardiasis, a re-examination of the body is necessary. This is done even if all signs and symptoms of the disease have passed successfully. Thanks to this series of preventive measures, the likelihood of re-infection with Giardia is reduced.
Treatment of giardiasis in children using traditional methods
Traditional medicine also has remedies against this disease.
Horseradish with honey
You need to take a few horseradish roots, wash them thoroughly and grate them on a fine grater. Place in a small jar and fill with boiled water. After 3 days, strain the mixture and add honey in a 1:1 ratio. After another 3 days, take half an hour before meals.
Dosage for children over 10 years old is 1 dessert spoon 3 times a day, and children under 2 years old can be given half a teaspoon. After a ten-day course, you need to take a break for a week and then repeat the course.
Mixture of pumpkin seeds and honey
Take 100 g of pumpkin seeds, grind in a blender with two tablespoons of honey. Add 20-30 ml of water. Give this mixture to the child to eat an hour on an empty stomach. After taking it, it is recommended to do an enema.
How to cure Giardia in a child using non-drug means?
Many parents are in no hurry to give their children synthetic medications, preferring natural ones. Of course, in folk medicine there are many ways to treat giardiasis, but it should be understood that herbal decoctions will act much more slowly, and the course of treatment will last for a whole month. At the same time, if the child continues to come into contact with objects and people infected with Giardia, then there can be no talk of a complete recovery. It should be remembered that herbal treatment is not recommended for children under 6 years of age - they may experience an acute allergic reaction.
Here are some recipes:
- Medicinal infusion of celandine. You will need one tablespoon of celandine, pour 500 ml of boiling water over it and place it in a thermos. The drink should steep for 2–3 hours, then it should be strained and given to the child 1 tbsp. l. before eating. You need to take the decoction for 5 days, then break for 2 days and repeat. It is recommended to take three such courses.
- A decoction of dandelion root is also considered an effective folk remedy for Giardia. Dry roots must be crushed and placed in an enamel pan, pour in 500 ml of water and boil over low heat for 15 minutes. After cooking, you need to cool and strain. Take the decoction in the morning and evening on an empty stomach. The dosage is calculated depending on the child’s body weight: per 10 kg – 1 tsp.
- Bergamot oil can be dripped onto a sugar cube and given to the child once a day, on an empty stomach.
- Ripe, seeded cucumbers can also help remove Giardia from a child's body. You need to chop 200 of these cucumbers and pour 1 liter of boiling water, leave for two hours, strain. The child should drink up to 500 ml of this decoction per day, and the course of treatment is one week, then a break of 2-5 days and repeat.
- Viburnum is an effective remedy not only against Giardia, but also for strengthening the immune system. A child can add viburnum fruits to tea (the berries must first be crushed).
Causes of giardiasis in children: when conditions are created for parasites to enter the body
Infection with protozoa occurs by the fecal-oral mechanism. Cysts released into the environment through feces can easily spread further. The transmission routes for small intestinal giardia are as follows:
- When drinking raw water. Microorganisms can also be present in tap water; regular chlorination does not kill them. In boiling water, inactive Giardia die after 10 minutes.
- Upon contact with contaminated everyday items: toys, dishes, etc.
- Along with earth and sand.
- From mother to baby during breastfeeding.
- In case of improper processing (or lack thereof) of greens, vegetables and fruits.
The risk of infection increases if the child’s habit of keeping their hands clean is poor. Often, while walking, children accidentally lick their hands or various objects, suck fingers, and bite their nails.
Infection with Giardia in newborns can occur when Giardia cysts enter the body through water (bathing, drinking unboiled water).