Viral eye infection: what is it?
Inflammation of the visual organs begins with a common cold or acute respiratory viral infection . Viruses spread very quickly from person to person and can cause entire epidemics.
For this reason, it is advisable for a patient with a pronounced ARVI to invite a doctor to his home .
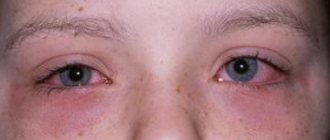
The most common disease in ophthalmology is adenoviral conjunctivitis , although a huge number of different viruses can cause similar symptoms. In addition to the general manifestations of ARVI, the patient experiences swelling of the eyelids, redness of the mucous membrane and clear discharge from the eye.
What are eye socket diseases called?
Inflammatory diseases of the orbit include orbital phlegmon and tenonitis.
Orbital phlegmon is a purulent inflammation of the eye tissue, accompanied by melting and tissue death ; its other name is orbital cellulite.
This disease poses a real danger to human life; it often occurs in children under the age of 5 years .
The main factor in the development of phlegmon is infection of the eye by bacteria through direct contact (during injuries or surgical procedures) or through the bloodstream. The disease's symptoms are similar to other ophthalmic inflammations, but it progresses much faster - from two hours to a day . In this case, the patient feels:
- sharp pain that intensifies with pressure;
- severe headache;
- inflammation of the eyelids;
- fever;
- loss of mobility of the eyeball;
- sudden drop in vision;
- exit to the outside of the mucous membrane.
Important! If orbital phlegmon is suspected, the patient should be immediately hospitalized , since further spread of the infection causes complete blindness, sepsis, brain abscess, and, as a consequence, death.
Tenonitis is an inflammation of the eyeball affecting Tenon's capsule of the eye.
Bacterial infection
You can distinguish a bacterial disease from a viral one by yellow or greenish discharge from the eye. Most often, bacterial inflammation occurs with the participation of streptococci and staphylococci.
up to 25% of the world's population are carriers of Staphylococcus aureus . It is not difficult to introduce an infection into the eye, and weak blood flow and the branching of the intraocular canals allow microorganisms to linger in the organs of vision.
Fungus
Eye diseases are difficult to treat, since fungi are organized into colonies, which, multiplying, are localized in various organs. The presence of good immunity allows you to restrain their activity for some time, but the slightest decrease in the body’s protective functions leads to an uncontrolled increase in the number of microorganisms .
Attention! Do not allow the fungal infection to spread throughout the body by delaying the start of treatment!
Healthy, undamaged eye organs are able to fight infection, and fungal diseases are less common than viral and bacterial ones.
Photo 1. Fungal infection of the skin around the eyes on the outside appears for various reasons.
This kind of inflammation is typical for people with immunodeficiency caused by chronic diseases, injuries, and taking potent medications.
Corneal infection
Corneal ophthalmia in most cases is caused by keratitis. Their development is considered a consequence of injury or pathogenic microflora. Sometimes a less dangerous, superficial form of the disease appears, resulting from meibomeitis, blepharitis, and dacryocystitis.
In the cornea of the eye, with the onset of keratitis, an accumulation of infiltrate occurs. Often an ulcer also develops in parallel. Even if it heals, this area of the stratum corneum will remain cloudy. The herpetic type of keratitis is more severe than other forms. Symptoms such as photophobia, pain, lacrimation are more pronounced and the risk of complications is higher.
Ophthalmoherpes is not just a cold located under the eye. Complications with this type of eye inflammation are considered the most dangerous, since even the slightest disruption of the stratum corneum leads to loss of vision.
It is important to select a suitable remedy for high-quality treatment of keratitis, so the nature of the pathology is first determined. The medicine for such inflammation is not selected alone, but a whole complex of medications is prescribed:
- Sulfonamides.
- An antiviral agent or antifungal if the causative agent is a fungus.
- Antibiotics.
- A solution of sulfonamides for irrigation of the mucous membrane - Furacilin, tetracycline, norsulfazole, penicillin, gentamicin.
- Eye ointments (erythromycin, tetracycline, etc.).
- Vitamin drops and remedies.
Intramuscular or intravenous drugs are administered only if there is no result of the therapy. In case of herpetic keratitis or the appearance of an ulcer, hospital treatment is required.
Exposure to allergens
In recent years, allergies have become a huge problem for humanity , affecting both adults and children. This is due to environmental problems, poor quality nutrition, and an abundance of chemicals used in everyday life.
The body daily encounters a whole range of substances that the immune system perceives as a threat . After contact with the allergen, the reaction follows immediately and includes the appearance of a rash, urticaria, shortness of breath, and copious discharge from the mucous membranes.
Thus, allergic inflammation of the eyes usually occurs together with sinusitis , rhinitis, dermatitis and even bronchial asthma .
Wearing contact lenses
The main risk factors when wearing lenses are failure to comply with sanitary and hygienic standards during their storage and use, and an individual reaction to the components of the solution intended for lens care.
As well as the possibility of injury to the sclera when putting on and removing lenses.
The tear fluid released in the eye supplies the cornea with oxygen, but in the presence of a lens, the supply of oxygen is reduced, causing hypoxia of the cornea, blurred vision, and death of the upper layer of the epithelium. Subsequently, accumulations of necrotic tissue come to the surface and form microcysts , which reduce visual acuity.
Important! The appearance of the slightest discomfort in the eye when using contact lenses signals the possible development of an infection, in which case the lenses should be removed immediately . If discomfort does not disappear, consult a doctor!
Eye injury
Even minor damage to the eye that occurs in everyday life can have dire consequences .
The ingress of small fragments, grains of sand, metal shavings, and small insects injures the very delicate surface of the eye sclera .
Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the wound, which leads to complete inflammation of the organs of vision.
The only way to avoid this type of injury is to protect your eyes when performing dirty and dangerous work by wearing special glasses and masks.
Chemical exposure
A chemical burn to the eye is an emergency ; its consequences depend on the degree of danger of the chemical with which contact occurred, its concentration, time of exposure, and environmental factors.
Carefully! Contact with alkaline solutions is much more dangerous than with acidic ones !
Acids and their vapors destroy the protein of the eye tissue, causing it to clot . Dead cells form a film on the surface that prevents further penetration of the chemical. Alkalies easily enter the internal parts of the eye; the inflammation caused by them can affect several parts of the organ of vision at once.
Symptoms of eye diseases that occur under the influence of various factors are similar: local redness, swelling , increased lacrimation, blurred vision, itching, burning, photophobia . The place of localization can be the visual organ itself (its external or internal parts) and the peri-ocular area.
Diseases in ophthalmology are differentiated according to the location of inflammation.
Localization of inflammation in the eyes
The eye has a very complex structure. It consists of several parts and fabrics, each of which has its own functions. Inflammation of the organs of vision is understood as the totality of their various inflammatory pathologies. They affect one or another part of the organ of vision. When the eyeball is inflamed, a pronounced vascular pattern is observed. The reason is plethora. A chronic pathological process may affect the eyelids, lacrimal glands or corners of the eyes. In general, inflammation affects:
- conjunctiva;
- eye socket;
- cornea;
- iris;
- tear ducts;
- vessels.
It is worth distinguishing between inflammation itself and redness of the eye, which is caused by physical factors. These include dust, lenses, sand, bright light, wind, smoke and even headaches. Redness as a result of these factors is comparable to simple irritation, which most often goes away on its own. It can become a true inflammation only as a result of the addition of an infection caused by viruses, bacteria or fungi.
Diagnosis of eyelid inflammation in children and adults
There are a number of eye diseases associated with inflammation of the eyelid . They occur equally often in both children and adults.
Barley
An acute, transient disease of a bacterial nature. Barley is usually divided into internal and external.
External - a disease that develops as a result of infection in the hair follicle of the eyelash of the upper or lower eyelid, where a small abscess with a white head forms.
If you follow the rules of hygiene, the abscess opens on its own within three to five days , leaving no traces.
Meibomeitis and chalazion
The scientific name for internal styes, which is an inflammation of the meibomian (sebaceous glands), the secretion of which protects the eyes from dryness . Meibomeitis is more dangerous than regular stye, since the inflammatory process occurs on the inside of the eyelid.
Treatment of inflammation of the eyelids
Among the most common diseases of the eyelids, in which inflammation of the eye occurs:
- stye - the causative agent is a staphylococcal infection, in which pus collects on the edge of the eyelid and comes out on its own;
- meibomitis - pus accumulates deeper, so the lesion is subjected to surgical opening;
- the boil looks like a purulent compaction in the eye area, accompanied by swelling, and after the pus spontaneously comes out, a scar may form at the site of the compaction;
- blepharitis is accompanied by inflammation of the lower eyelids in the area of the eyelashes;
- phlegmon and abscess often appear as complications of all previous diseases;
- molluscum contagiosum.
For inflammation of the eyelids, therapy is carried out systemically. Antiseptics are used for topical use, and antibiotics are also prescribed internally. Abscesses can open in a hospital setting. Antibacterial ointments and other pharmacological drugs can also be used for treatment.
Diseases of the conjunctiva
Conjunctivitis is the most common ophthalmological disease, which is caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and allergens. All conjunctivitis is contagious and transmitted by airborne droplets , so those who are sick should be isolated if possible.
Conjunctivitis occurs with equal frequency in adults and children; their symptoms vary slightly depending on the nature of the disease.
Reference! Only an ophthalmologist can make an accurate diagnosis after an examination and laboratory tests!
Viral conjunctivitis develops quickly, like all viral diseases, and is manifested by redness and swelling of the mucous membrane, itching, burning, lacrimation, photophobia, and sometimes fever.
Bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria that, when multiplying in the eye, release toxins that lead to local inflammation . In the absence of the necessary treatment, the infection spreads, invades new organs, and causes complications in the form of otitis media, sinusitis, etc.
Names of corneal diseases
Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea, or the clear membrane of the eye.
This disease is characterized by lacrimation, pain and pain in the eye, foreign body sensation, clouding of the cornea and decreased vision.
In most cases, the development of keratitis is preceded by damage to the cornea , making it more susceptible to infections of various types.
In the future, any viruses and bacteria can cause inflammation.
Carefully! This disease poses the greatest danger to people wearing contact lenses . Constant mechanical impact on the cornea can eventually lead to partial or complete loss of vision.
What to do for eye inflammation
Any inflammation of the eye must be accompanied by a visit to an ophthalmologist. In addition to the cases discussed, more serious diseases associated with inflammatory processes of the cornea, retina, choroid and optic nerve may also be observed.
Untimely and incorrect treatment can lead to serious consequences, including complete loss of vision.
It is often impossible to distinguish between one or another disease on your own. But the main thing when an illness occurs is the timely initiation of therapy. Therefore, when the first alarming signs of inflammatory processes in the eye appear, it is necessary to exclude any irritants in the form of cosmetics or chemicals and consult a doctor.
Vascular diseases
A common disease that is a red vascular network on the eyeball.
There can be many reasons for this type of inflammation:
- eye strain;
- improper wearing of contact lenses;
- increased blood pressure;
- allergic reaction;
- bacterial infection.
The vessels often become inflamed as an addition to the underlying infectious eye disease, especially if the patient experiences pain and burning. In the case of a one-time inflammation, you need to give your vision organs a rest; if the redness is constant, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
Prolonged stress leads to vascular damage and local hemorrhage (looks like a solid red spot on the eyeball), and ultimately to blindness.
There is a viral type of inflammation of the choroid, called uveitis , caused by the herpes , and occasionally by cytomegalovirus . A characteristic symptom of this disease is floating circles before the eyes, blurred vision and severe lacrimation.
Causes of sore eyes
Inflammation of the eyeball can be caused by an infection, virus or fungus. Wind, dust, heat, cold, bright light and chemicals have a negative impact. In modern conditions of technological development, another factor dangerous to the eyes is a computer. Working for a long time behind it due to the high load on the eyesight can also lead to complications. In general, the reasons can be divided into several main groups:
- infectious factors;
- allergic reaction;
- influence of aggressive factors and irritants;
- injuries to individual parts or the entire eye.
Iris
In ophthalmology, there are inflammatory eye diseases such as uveitis and iridocyclitis. They are inflammation of the anterior part of the choroid of the ciliary body and the iris. Common causes of illness include influenza, tuberculosis, gonorrhea, herpes, bacterial infection and chlamydia. Iridocyclitis can develop as a result of gout, allergies, rheumatism or eye injury. Most often, only one eye is affected. Iritis - isolated lesion of the iris is diagnosed less frequently. When sick, its color may change. The disease can develop as a result of:
- tuberculosis;
- flu;
- syphilis;
- brucellosis;
- diseases of the sinuses or tonsils;
- leptospirosis;
- chronic caries;
- lesions of the cornea with a purulent abscess;
- penetration of infection.
Century
Inflammation of the eyelid is manifested by swelling and redness, as shown in the photo. The process can take over it completely. Sometimes the lower or upper eyelid becomes inflamed. Some diseases lead to this condition:
- Herpes . There are many types, but almost all are characterized by burning, redness of the eyelids, itching, pain and swelling around the eye. Eye pathology is characterized by the appearance of fluid-filled blisters.
- Chalazion . This is a slowly developing disease that occurs due to blockage of the sebaceous gland or a cold, gastritis. Colitis or blepharitis. In appearance, the disease is similar to barley.
- Blepharitis . Represents multiple chronic inflammations of the eyelid margins. Difficult to treat.
- Barley . The disease develops due to blockage of the hair follicle near the eyelash or sebaceous gland on the upper or lower eyelid due to blockage of the duct or the action of Staphylococcus aureus. Barley often appears in children due to weakened immunity, poor hygiene, exposure to dirt and acute respiratory diseases.
Conjunctiva
The inner lining of the eyeball and the inside of the eyelids is the conjunctiva. Its inflammation is called conjunctivitis. It can be caused by chemical irritation, infection, allergies or injury. Inflammation of the conjunctiva has several types, each of which is characterized by its own causes:
- Bacterial . It is noted if the eye is swollen and red. Signs of inflammation also include photophobia, swelling of the conjunctiva and lacrimation. The cause is the ingress of bacteria.
- Hemorrhagic . Characterized by hemorrhage on the eyeball and eyelids. The cause is picornavirus, which is contagious.
- Adenoviral . Develops due to damage to the upper respiratory tract. The cause is an adenovirus.
- Allergic . Can be caused by various allergens, such as fungus.
Pustules in the eyes
Discharge of pus in the eye area is often a consequence of the development of infection in the conjunctival sac. This is how the body reacts to the rapid proliferation of bacteria. An abscess on the eye may be associated with:
- Keratitis . Purulent inflammation of the cornea, accompanied by suppuration. Symptoms include photophobia, pain in the eyeball, eyelid spasm, and corneal clouding. The causes may be burns, trauma, neurogenic factors.
- Barley . Disease of the sebaceous glands due to their blockage. The causative agent is staphylococcus or demodicosis.
- Allergies . Caused by prolonged exposure to an irritant on the body.
- Acute purulent conjunctivitis . May develop due to bacteria, viruses or allergies.
- Trachoma . Infection due to chlamydia. It is characterized by the formation of boils and the subsequent release of pus from them.
Blown out eye
Even ordinary wind can cold the eye and cause inflammation. The mucous membranes of the organ are not protected by the skin, so their condition is particularly affected by external factors. The risk of eye tissue pathologies increases with:
- prolonged exposure to an air conditioner operating at high power;
- walking in the wind after swimming;
- being in a vehicle near an open window;
- sticking your head out of a car traveling at high speed;
- windows and doors open wide, which leads to drafts.
Inflammation of the eyes in a child
Bacterial, hemorrhagic or allergic conjunctivitis is the most common disease not only among adults, but also among children. In a child, it also leads to inflammation of the eye tissues. Other causes of this symptom are the same as those listed for adults. These are diseases:
- barley;
- blepharitis;
- viral keratitis;
- allergy;
- herpes;
- chalazion.
Inflammation of the eye during pregnancy
In addition to the main causes, hormonal changes are a factor in the development of inflammation of the eye tissues in pregnant women. Due to a decrease in estrogen levels and a decrease in the amount of moisture, the normal functioning of the visual organs is disrupted. The eyes begin to itch, water and turn red. They are noted to be dry and tired. This hormonal change causes inflammation.
Problems with the lacrimal gland
In medicine, this disease is called dacryoadenitis . It begins with pain in the corner of the eye, then swelling and redness appear.
The gland increases in size so much that a person, looking at his nose, is able to see its edge.
Other symptoms of dacryoadenitis are similar to other inflammatory diseases: pain when opening the eye, fever, headache, enlarged cervical lymph nodes.
The cause of the disease can be a viral or bacterial infection , and dacryoadenitis usually manifests itself as a complication of other diseases . The disease occurs in the same way in adults and children, but the infection spreads faster in a child, therefore, in order to avoid serious consequences in the form of abscesses, this inflammation is treated in a hospital.
Inflammation of the eyes in children. Causes and treatment
If a child’s eye suddenly becomes inflamed, this may indicate the occurrence of diseases such as dacryocystitis, dacryoadenitis or canaliculitis. With dacryocystitis, inflammation occurs directly in the wall of the lacrimal sac, which is accompanied by severe swelling of the eyelid, lacrimation and almost complete closure of the eye. Dacryoadenitis usually develops after measles, flu, mumps or tonsillitis and manifests itself in inflammation of the lacrimal gland. The upper eyelid swells, the eye hurts, becomes very red and does not move. Canaliculitis occurs as a complication of dacryocystitis or conjunctivitis, characterized by inflammation of the lacrimal canals, accompanied by profuse lacrimation and purulent discharge.
In the treatment of dacryocystitis, its form is important. In case of acute illness, electrophoresis, quartz treatment, penicillin, intramuscular or tablet antibiotics are used. The chronic form is treated surgically with subsequent treatment. For dacryocystitis in newborns, massage or probing is prescribed.
Dacryoadenitis is eliminated with antibiotics and eye treatment with antiseptic solutions.
With canaliculitis, the purulent contents are squeezed out, and the site of inflammation is treated with an antiseptic, antibiotic or hormone-containing drops.