Description and purpose of madder dye
Madder is a perennial plant, unpretentious to growing conditions and undemanding to care.
Other names that have become entrenched in popular usage are crapp, marina, petiole madder or Georgian madder. Procurement of raw materials for medical purposes involves the selection of the root part of the plant in the autumn, when the above-ground part has already died, or in the spring, when the first shoots have not yet appeared. The process is quite painstaking.
The dug up roots are thoroughly cleaned from the ground using cold water and then dried. You can dry it either in the open air, but not in the sun, or in a room with a low level of humidity and constant ventilation.
When drying in special drying chambers, the temperature should not exceed 50 degrees Celsius.
Indications for use are quite extensive. They are based on the numerous beneficial properties of this plant.
Preparations made on the basis of kappa are prescribed for the treatment of diseases of various body systems - digestive, respiratory, urinary, skin, etc. Thus, indications for use may include tuberculosis (intestinal or bone), osteomyelitis, rickets, ascites, gout, urolithiasis , dermatomycosis, ulcers on the skin and mucous membranes, acne, age spots, skin cancer and much more.
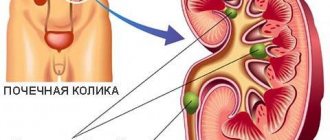
Madder plays an important role in the treatment of urolithiasis, which is a metabolic disease. The formation of stones in the urinary system is a fairly common ailment among the working population. Its share in the total number of urological diseases is large - from 32 to 40%, according to indicators in different countries.
Medicinal properties of madder
The roots and rhizomes of madder are used for medicinal purposes. Raw materials are harvested early in the spring, in March - the first half of April or at the end of the growing season - from the beginning of August until frost. Dig them out with a shovel, shake them off the ground, cut them off and remove the above-ground part of the plant. Then the unwashed roots and rhizomes are laid out for drying. Dry in the shade under a canopy or in a dryer at a temperature of 45 ° C. The shelf life of raw materials is 2 years. To avoid depletion of natural madder thickets, it is recommended to reuse them no more often than after 3 years.
Madder harvesting in orchards and vineyards should be carried out annually during the first plowing of the rows (in February - early April, as well as in November).
The need for madder raw materials is very great, since it is used not only in medicine, but also in light industry for the production of permanent dyes. However, after the synthesis of alizarin, madder has largely lost its industrial significance.
What kind of plant is this?
Madder is a herb from the Madder family. It is a perennial plant with a strong root system formed by small creeping roots and a central rhizome. The plant has a thin, straight stem with a wide surface.
The flowers of the plant are small, yellowish-green. They gather in inflorescences and are located at the ends of the branches. The plant blooms from June to September. After madder fades, fruits appear in the form of black drupes.
Under natural conditions, madder grows in Crimea, Azerbaijan, Dagestan, Asia Minor, and North Africa. She loves light areas, meadows, forests, and hedges. In ancient times, the plant was used to create a bright red dye. To make it more resistant, more and more new varieties were developed over time.
Today, this plant is not used so actively for industrial purposes, but its medicinal properties allow it to be actively used in medicine. A distinctive feature of the plant is that it is used both in conventional and traditional medicine.
Contraindications
As a result of clinical trials, it was revealed that madder roots are very effective against kidney stones.
Preparations from the roots also have diaphoretic, diuretic, antispasmodic and astringent properties. In traditional medicine, the dry extract of the plant is used as an antispasmodic and diuretic. Various medicinal forms of the plant are used for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, jaundice, constipation, enuresis (bedwetting), gout and polyarthritis.
In folk medicine, an infusion of rhizomes treats inflammation of the spleen; it is prescribed for menstrual irregularities. In addition, the plant is used as an adjuvant in the complex treatment of bone tuberculosis; it is effective as a laxative and diuretic.
For memory loss and jaundice, it is recommended to take rhizome powder mixed with honey. Externally, medicines based on the plant are used to lighten age spots, treat ulcers, and dermatomycosis. A decoction of rhizomes is used externally to treat skin cancer.
Infusion: 200 ml of purified water must be heated, but not brought to a boil (80–85 degrees), pour 20 g of dry roots into it, leave for 2–3 hours and strain. It is recommended to drink 75 ml of infusion after each meal. The drug is indispensable for urinary tract diseases.
Decoction for compresses: 10 g of crushed roots should be poured into 100 ml of water and boiled in a water bath for 10–15 minutes, after which the composition should be cooled and strained. It normalizes the metabolic processes of the epidermis.
It is strictly forbidden to take madder preparations for gastric ulcers, hyperacid gastritis and renal failure, for acute or chronic glomerulonephritis. It is not recommended to take madder during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Also, a contraindication for this plant is individual intolerance. An overdose of madder preparations can cause pain and exacerbation of chronic diseases. Before treatment, you should consult your doctor.
An infusion using the root is a well-known medicinal remedy for the fair half of humanity. This remedy based on madder helps fight inflammation in the spleen.
Also, with the help of this infusion, you can normalize the menstrual cycle. Preparations from this plant are used for pulmonary tuberculosis, but together with other medications prescribed by specialists. The infusion is a high quality laxative and diuretic.
The use of powder from the rhizome of madder with honey is necessary to cure jaundice and memory problems. To cure external diseases, madder is used to heal ulcers, lighten pigment spots, and for dermatomycosis.
This plant should not be used if the patient suffers from gastrointestinal ulcers, kidney stones, in which the kidneys function poorly, as well as chronic and acute glomerulonephritis. Do not exceed recommended doses.
Recipes:
- Infusion: 1 tbsp. warm water, dry plant root. Leave for about three hours. Used after eating food.
- Decoction: 0.5 tbsp. water, 10 gr. madder root. Boil for fifteen minutes. Compresses are made from the decoction for gout, rheumatism, polyarthritis and to improve the skin.
Lucidin contained in the plant belongs to the anthraquinone series of substances and has carcinogenic properties. It is believed that the plant, if used in its pure form for a long time, can cause cancer of the stomach, intestines and liver. For this reason, official medicine uses madder extract along with other plants.
The root is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- glomerulonephritis;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- stomach ulcer;
- individual sensitivity to the plant.
When the herbal remedy is used internally, the patient's urine may turn pinkish or red-brown. In the latter case, the dose of the herb is adjusted or its use is stopped.
Exceeding the recommended dosages of madder preparations is dangerous. As a result, a sharp increase in peristalsis of the renal pelvis and the release of large stones from them is possible, which is accompanied by a severe attack of colic.
Madder is often prescribed by veterinarians for kidney stones or urinary problems in pets when the stones block the ureters. The plant quickly loosens deposits and removes them. The entire process is naturally pain-free.
To treat cats and dogs, veterinarians prescribe madder extract, sold in pharmacies. A quarter of the tablet is dissolved in 25 ml of water. The medicine is given to the pet at the rate of 1 ml of solution per 1 kg of weight.
Herbal raw materials are also used for cosmetic purposes.
- For smooth skin. To care for the skin of the body, take baths with madder. Two tablespoons of crushed root are poured into 2 liters of water. Bring the mixture to a boil and simmer for five minutes. After complete cooling, the mixture is filtered and poured into a bath of water.
- For acne. An ointment is prepared from madder. It is applied to problem areas of the skin twice a day. After 15 minutes, the residue is washed off with warm water. Madder root is ground into powder. Mix a tablespoon of powder with 20 g of Vaseline or baby cream.
- For hair. The plant is used to add red shades to red or chestnut hair. A tablespoon of crushed madder roots is poured into a glass of boiling water. Insist for ten minutes. Henna is poured with still hot infusion. Leave for some time to release natural pigments. The substance is applied to the hair for three hours, after which it is washed off with warm water without shampoo.
The medicinal use of madder requires mandatory consultation with a specialist and a hardware examination to assess the size of the stones. With complex therapy using madder, even large kidney stones are reduced in size and passed more easily.
Madder is rightfully considered an effective remedy for
. So, with the help of this plant, urates (stones that form in the kidneys due to a violation of water-salt metabolism) are loosened, which helps them exit through the urinary canal.
- loosening of urates;
- elimination of pain during urination;
- elimination of dull aching pain in the kidneys;
- improvement of water-salt metabolism;
- decreased tone and increased peristaltic contractions of the muscles of the renal pelvis, as well as the ureters, which contributes not only to the advancement of stones, but also to their release.
We invite you to read: About planting early cabbage: timing and instructions - January 14, 2019
An alcohol tincture of the roots and rhizomes of madder is one of the components of the drug Cystenal, which has an antispasmodic and also a diuretic effect, thereby promoting the passage of small stones.
Indications for use of the drug: 1. Kidney stone disease.2. Treatment and prevention of urolithiasis.
The undeniable advantage of this drug is that it can be taken simultaneously with antibiotics.
Regimen: Take Cystenal 3-4 drops (dropped onto sugar) half an hour before eating.
During an attack of colic, a single dose of 20 drops is indicated. Patients who often experience colic attacks are recommended to take the drug three times, 10 drops each.
For heartburn caused by taking Cystenal, the drug is taken either during or after meals.
Contraindications In general, madder preparations, including Cystenal, are well tolerated. But it should be noted that when taking the drug, the urine turns reddish. If the staining is intense, the doctor reduces the dose of the drug (the doctor may stop taking the drug altogether).
The use of Cystenal is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- glomerulonephritis;
- severe renal failure;
- stomach ulcer;
- duodenal ulcer;
- intolerance to the components of the drug.
It is not recommended to take the drug for persons under 18 years of age.
and breastfeeding women.
Important! The duration of the initial and repeated courses of treatment, the dosage and regimen of Cystenal are prescribed only by a doctor!
One glass of water is heated, but without bringing to a boil. Add 1.5 tbsp to slightly cooled water, about 80°C. dry madder raw materials (root powder). It is left to stand for three hours and then filtered. Take 1/3 cup three times a day, after meals.
3 tsp Brew dried madder roots and rhizomes in half a glass of water and cook in a water bath for a quarter of an hour. After this, the broth is filtered and cooled. Apply as compresses to sore spots and wounds.
Madder roots in the amount of 2 tbsp. arable plant root in the amount of 20 g, flaxseed - 40 g. Collection in the amount of 4 tbsp. pour one liter of boiling water. The broth is given time to cool, after which it should be consumed immediately.
10 g licorice root 12 g dandelion root 28 g madder root. 25 g of the collection is brewed in a thermos with a volume of boiled hot water of 500 g. The decoction must be infused for about 8 hours. Take according to the following regimen: morning, evening, 200 ml. The infusion should be taken in the morning and evening, 250 ml each.
12 g mint leaves 12 g wormwood 23 g sandy immortelle flowers 12 g buckthorn bark 12 g dandelion 45 g madder dried roots. Brew 25 g of herbal mixture with boiling water in a volume of 250 ml. After 60 minutes, filter the infusion and drink a glass twice a day.
3 g of dry powder of madder roots is poured into 375 ml of just boiled water, after which it is boiled for ten minutes. After filtering and cooling, the decoction can be consumed. Dosage: 0.5 cup three times a day after meals, an hour later.
3 g of powdered raw material is poured into one glass of cool water. You need to insist for at least eight hours. After filtering, the resulting infusion is diluted with a glass of boiling water. After a quarter of an hour, the infusion is filtered again and drunk over the course of a day in two doses.
- Kidney diseases
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Individual intolerance
- Gastritis with high acidity
- With caution during the lactation period, as well as pregnant women
- Children and adolescents under 18 years of age should stop taking madder preparations
Useful properties of the perennial madder
Madder has a variety of beneficial properties. In the treatment of urolithiasis, it has the following beneficial effects:
- Antispasmodic effect. Reduces the tone of smooth muscles and enhances their peristalsis.
- Diuretic action. Madder increases the rate of urine formation by reducing the level of fluid in body tissues. Prevents the reabsorption of various substances (water, salts, etc.) into the body from already formed primary urine. At the same time, the rate of elimination also increases.
- Analgesic effect. Madder in any dosage form can reduce the pain syndrome accompanying patients with urolithiasis.
- Antibacterial property. The beneficial substances of the plant eliminate microbes belonging to the coccus group.
- Anti-inflammatory effect. Actively suppresses inflammatory processes occurring in the body.
- Destructive effect on stones. Under the influence of substances contained in the described plant, the stones are loosened, which contributes to their faster and less painful removal. Madder has the greatest destructive activity on stones consisting of calcium phosphate and magnesium.
- Wound healing property. Promotes stopping bleeding and rapid healing of wounds in case of damage to the urinary tract during the passage of a calculus.
The consequence of this effect is the painless removal of sand and small stones, and a decrease in the acidity level of urine.
In general, in addition to the described properties, other properties are also attributed to madder:
- Anticancer activity. It manifests itself in the destructive effect of coumarins contained in the plant in relation to the genetic apparatus of the tumor.
- Antipyretic property. Anti-inflammatory activity helps lower high body temperature.
- Tonic effect. Gives energy, increasing performance.
- Hypotensive effect. Removing excess fluid and salts from the body, i.e. normalization of water-salt balance leads to normalization of blood pressure.
- Other. Antiallergic, anticonvulsant, antitoxic, antitussive, diaphoretic, astringent effect.
Madder contains coumarin, carbohydrates, and flavonoids. The root of the plant contains sugars, pectins, anthraquinones, citric, tartaric, malic acid and a number of other substances. It is the rich composition that can explain the numerous beneficial properties of the plant. The following beneficial properties of madder are known:
- One of the important abilities of the plant is the destruction of kidney and bladder stones. It is especially effective if the stones include calcium, magnesium and phosphoric acid salts.
- This herb helps with various diseases of the kidneys, bladder, and cholelithiasis.
- Women are often recommended to use madder for painful periods.
- The plant is used for cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis, hyperthyroidism, and the already mentioned stones in the urinary system.
In official medicine, the dry extract of the plant is used as an antispasmodic, diuretic, and helps to loosen urinary stones containing phosphates, magnesium and calcium oxalates. Plant-based products help reduce spasms and promote the passage of small stones.
In addition to decoctions and infusions, an ointment is made from madder, which is used externally for various injuries.
Madder dyeing - instructions, composition, dosage, side effects of use
Name of medicinal plant:
Madder tinting - madder tinting
Madder (Rubia tinctorum); homeland of Madder (Rubiaceae); madder
Russian names: tinting madder, Georgian madder, petiole madder, crapp, marzana, marina. Ukrainian: madder krasilnaya, drik krasilny.
Madder is a perennial herbaceous plant of the madder family (Rubiceae), up to 2 m high. The main root is powerful. Roots with thick creeping rhizomes extend from it. The roots and rhizomes are covered with reddish-brown exfoliating bark. The stem is thin, climbing, highly branched, tetrahedral, spiny and rough. The leaves are light green, obovate, dense, woolly-spinous below, opposite, collected in whorls of 4-6 pieces, up to 9 cm long and up to 3 cm wide. The flowers are small, yellowish-green, up to 1.5 cm in diameter , collected in few-flowered semi-umbrellas at the ends of stems and branches. The fruit is a juicy black drupe up to 5 mm long; their juice leaves almost indelible dark wine-red stains. It blooms in June - September, the fruits ripen in August - November in the first year of life. Propagated by seeds and vegetatively. Madder is widespread in the wild in Dagestan, Azerbaijan and other regions of the Caucasus, Crimea, and Central Asia. Grows in riverine tree and shrub thickets, on pebbles, steppe meadows, forest edges, in light pine forests, gardens, vineyards and along fences. Madder is undemanding to the mechanical composition of soils: it grows on sand, loams and continuous soils of solonetzes.
Even in ancient times, artisans of the ancient Greeks, Romans, Egyptians and Persians highly valued madder root. Permanent red paint was obtained from it. In ancient times, madder was perhaps the only plant that was used to dye wool, silk and cotton fabrics. Madder root was well known in modern times. Textile workers were especially interested in it. The Free Economic Society of Russia established a high award - a gold medal and a cash prize for the development of resistant varieties of madder.
The medicinal properties of the plant have also been known since ancient times. Avicenna recommended preparing a drink from its roots in water sweetened with honey for the treatment of the sciatic nerve, paralysis, and loss of tissue sensitivity. The fruit was also used to make a drink with uxomed for an enlarged spleen. “It cleanses the liver and spleen and opens blockages in them,” wrote Avicenna.
Collection and drying of raw materials . The roots and rhizomes of madder are used for medicinal purposes. Raw materials are harvested early in the spring, in March - the first half of April or at the end of the growing season - from the beginning of August until frost. Dig them out with a shovel, shake them off the ground, cut them off and remove the above-ground part of the plant. Then the unwashed roots and rhizomes are laid out for drying. Dry in the shade under a canopy or in a dryer at a temperature of 45 ° C. The shelf life of raw materials is 2 years. To avoid depletion of natural madder thickets, it is recommended to reuse them no more often than after 3 years.
Noble navel, or Roman - Application, description and effect of a medicinal plant
Madder harvesting in orchards and vineyards should be carried out annually during the first plowing of the rows (in February - early April, as well as in November).
The need for madder raw materials is very great, since it is used not only in medicine, but also in light industry for the production of permanent dyes. However, after the synthesis of alizarin, madder has largely lost its industrial significance.
Chemical composition . The rhizomes of the plant contain organic acids (citric, malic, tartaric), triterpenoids, anthraquinones (ruberythric acid, haliosin, purpurin, purpuroxanthin, pseudopurpurin, rubiadin, ibericin and rubiadin, as well as alizarin in the free state) - 5-6%, iridoids, sugars, proteins, pectins and ascorbic acid. In the aerial part, carbohydrates, iridoids, phenolcarboxylic acids and their derivatives, coumarins, flavonoids (quercetin, kaempferol, apigenin, luteolin, etc.) were found; in the leaves - iridoids and flavonoids; in flowers - flavonoids rutin and hyperoside.
The rhizomes and roots of madder contain: ash - 11.30%; macroelements (mg/g): K - 28.80, Ca - 19.30, Mn - 1.90, Fe -2.50; microelements (CBN): Mg - 0.43, Cu - 1.71, Zn - 1.43, Co - 0.04, Cr - 0.65, Al - 0.50, Ba - 2.01, V - 0 .46, Se - 0.50, Ni - 0.63, Sr - 0.60, Pb - 0.13, I - 0.09. B - 43.60 µg/g. Mo, Cd, Li, Au, Ag, Br were not detected. Concentrates Fe, Cu, Zn, Cr, Ba.
Pharmacological properties . Madder roots in the form of an extract, as well as powder and other herbal preparations of the plant, loosen and destroy kidney and bladder stones, containing mainly phosphates and oxalates of calcium and magnesium. Galenic forms of madder also have an antispasmodic and diuretic effect. In addition, plant preparations reduce the tone and increase peristaltic contractions of the muscles of the renal pelvis and ureters, thereby promoting the movement of stones and their removal from the kidneys and urinary tract.
Application in medicine . Roots, rhizomes. In scientific medicine, dry extract is an antispasmodic, diuretic agent that helps loosen urinary stones containing phosphates and oxalates of calcium and magnesium, to reduce spasms and the passage of small stones in urolithiasis; is part of the complex drug "Cystenal". In homeopathy, powder, tincture - for anemia accompanied by amenorrhea, diseases of the spleen. In Tibetan medicine (as part of complex recipes) - for sore throat and diphtheria; in Indian - for amenorrhea and anuria; in Korean (as part of a multicomponent decoction) - for heart valve insufficiency. In folk medicine, powder, infusion, decoction, extract - for diseases of the kidneys, urinary tract, liver, spleen, respiratory organs, intestinal tuberculosis, bone tuberculosis, rickets, osteomyelitis, anemia with amenorrhea, ascites, dysentery, scrofulosis, gout, sciatica; externally - for ulcers, dermatomycosis, age spots. External decoction for skin cancer. In Turkmenistan - for memory impairment.
Sundew rotundifolia - Application, description and effect of a medicinal plant
Stems. In Turkmenistan, ointment (mixed with egg yolks and alum) is used externally for bruises, dislocations, and fractures.
Dosage forms, route of administration and doses . Dry madder extract (Extractum Rubiae tinctoriae siccum) is available in tablets of 0.25 g. Take 2-3 tablets 3 times a day. Before taking the tablets, dissolve in 1/2 glass of warm water. The course of treatment is 20-30 days. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated after 4-6 weeks. Madder extract is contraindicated for glomerulonephritis, severe renal failure and gastric ulcer.
Cystenal is a complex preparation containing madder root tincture 0.01 g, magnesium salicylate 0.15 g, essential oils 6.15 g, ethyl alcohol 0.8 g, olive oil up to 10 g. Take 3-4 drops on sugar 30 minutes before meals; during an attack of colic, take 20 drops once. Patients with frequent attacks of colic are prescribed 10 drops per dose 3 times a day. For heartburn associated with taking the drug, it is taken during or after meals. Available in 10 ml bottles. Cystenal
Contraindicated in glomerulonephritis, severe renal failure and gastric ulcer.
Infusion of madder roots and rhizomes (Bulgarian recipe): 1 teaspoon of crushed raw material is poured into 200 ml of cold water, infused for 8 hours, then the extract is filtered and the raw material is poured again with 200 ml of boiling water and filtered again after 15 minutes. Both infusions are mixed and drunk in several doses throughout the day. * Powder of roots and rhizomes of madder: take 1 g 3 times a day with a small amount of water.
Contraindications and possible side effects : an overdose of plant preparations can cause pain and exacerbation of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Applications in other areas . In veterinary medicine, extract, dry extract - for urolithiasis. Madder has been used for dyeing wool and leather since ancient times. Currently it is used in carpet production. The color of the dyes obtained from it ranges from pink to purple. Feed (in hay) for cattle; When eaten in large quantities, cows' milk turns red. Honey plant. Cultivated in many countries of Western Europe and some Asian countries to obtain a dye. Madder grown in Dagestan, near Derbent, is especially valued for its high quality.
Pomegranate - Application, description and effect of a medicinal plant
Elements of agricultural cultivation technology . Madder seedlings suffer from spring frosts, so the sowing time should be selected in such a way that young plants are not exposed to frost. In winters with little snow, even at temperatures down to minus 15 ° C, madder can freeze, so it is placed in protected areas, and snow retention is carried out in winter.
In cultivation, madder grows well on light and medium loose soils with a deep arable layer. The area under madder is dug up to a depth of 30 cm, 2-3 kg of manure or compost, 4-5 g of nitrogen, 6 g of phosphorus and potassium per 1 m are added. The seeds are sown at a soil temperature of at least 6-8 ° C. The distance between the rows is 45-60 cm. The seeds are planted to a depth of 6-7 cm. They germinate at a temperature of 8-10 °C. Weight of 1000 seeds is 30-31 g.
When propagating by rhizomes, furrows are made with a depth of at least 8-10 cm. Rhizomes 6-8 cm long are laid at a distance of 10-15 cm from each other, quickly covered and rolled into the soil surface. During the growing season, 1-2 weedings are done. In the fall, the crops are hilled. In the 2nd year, early in the spring, dead parts of plants are removed and nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizers are applied at the rate of 3 g per 1 m2.
Commercial madder products are obtained in the 2-3rd year of plant life. Roots and rhizomes are removed late in the fall (after their regrowth stops) or early in the spring (before their regrowth begins). In this case, you can not remove the entire plant, but only part of it, leaving approximately one third of the rhizomes in the soil. This will make it possible to obtain another crop of raw materials from the same plot over the next 1-2 years. From just 1 m2. beds receive 0.3-0.4 kg of air-dried madder raw material in 2-3 years.
The cultivation of madder is possible on rain-fed lands, but when irrigated, its yield increases by 2-3 c/ha. For the industrial crop of madder, the most promising areas are the coastal regions of Central and Southern Dagestan; in Azerbaijan its yield reaches 12-13 c/ha.
Sources of information: rsml.med.by, mednet.by, drugs.com, webmd.com.
Contraindications to the use of madder
Considering the properties of kappa, contraindications for use can be described, i.e. those pathological conditions of the body that require the refusal of medicines containing this plant.
So, it is not recommended to use madder in the following cases:
- In the presence of a stomach ulcer, hyperacid gastritis;
- In case of renal failure;
- In chronic or acute glomerulonephritis;
- For galactose intolerance;
- If there is an individual intolerance by the body to any substance that is part of the plant;
- During pregnancy;
- During lactation.
There is also an age restriction—under 18 years of age is prohibited.
The use of madder should be agreed upon with a qualified medical specialist who will fully take into account all the pros and cons and describe the correct dosage and frequency of administration. Only a serious attitude will help protect yourself from side effects and get the maximum therapeutic effect.
Possible side effects are:
- The appearance or intensification of pain;
- Allergic reaction;
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases.
A clear sign of an overdose is the urine turning brownish-red.
There are a number of contraindications to the use of madder and drugs based on it. These are severe renal failure, gastric ulcer, chronic or acute glomerulonephritis, galactose intolerance, malabsorption, lactalose deficiency, hypersensitivity. There is also no data regarding the effect of the plant on pregnant and lactating women.
If the dosage is exceeded, the plant can provoke pain and exacerbation of chronic inflammation. There is also information that the products can provoke allergic reactions.
When treating, you need to take into account the fact that products based on this plant can cause the urine to acquire a pinkish tint. If it becomes too red, you should reduce the dose of the drug or discontinue it.
Analogs and cost of the drug
How much does madder (tablets) cost? The price of this herbal preparation is not very high and is about 70-90 Russian rubles (10 tablets).
How can you replace this medication if it does not suit you? The following medicines are analogues of Madder extract: “Urocholesan”, “Canephron”, “Urolesan”, “Blemaren” and others. These drugs have a similar effect on the human body, but have a completely different composition. In this regard, before taking them, you should definitely consult your doctor.
Contraindications and possible harm
Different forms of the plant can be prescribed for pathologies and diseases of the kidneys, diseases of the respiratory system, urinary system, spleen, rickets, gout, anemia and so on.
Externally, the product can be used for rosacea, ulcers, ringworm, and skin cancer. It helps lighten age spots. Madder is often prescribed for urolithiasis, as it has a strong nephrolytic effect, allowing stones to be removed from the kidneys and bladder more quickly.
Indications for use
Powder, decoction, infusion, extract of Madder are used to treat: diseases of the liver, kidneys, respiratory organs, urinary tract, spleen, intestinal and bone tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, rickets, ascites, scrofulosis, dysentery, anemia with amenorrhea, sciatica, gout.
Externally, Madder is used to lighten age spots, treat ringworm, skin ulcers, and rosacea.
There are good reviews about Madder, a decoction of which is used externally to treat skin cancer.
Selection of preparations with madder
Evdokia, 56 years old
I am very glad that my doctor prescribed madder for me, and not something else more expensive. Madder can be bought at any pharmacy.
I really liked the medicine itself. Already on the 2-3rd day of treatment I felt significant relief, the pain when urinating subsided. The examination showed that the stone began to disintegrate quite quickly, although initially its size scared me very much.
My course of treatment was 3 weeks. There were no side effects.
Kirill, 45 years old
After starting to take madder, my swelling went down quite quickly, and my joints became more mobile. From the very beginning, I visited the toilet quite often, but the process no longer caused as much pain. I can also note that the pressure has dropped a little, so my general condition is also pleasing.
Elena, 35 years old
A few months ago I was diagnosed with a stone in my kidney and sand in my urine. Then Urolesan and Canephron were prescribed.
The symptoms went away quite quickly and did not bother me for some time. But about a month ago they appeared again.
This time the doctor prescribed madder. Already in the second week of treatment, poor health was replaced by a feeling of health.
Madder was much cheaper for me than the previous treatment, and the effect was still just as excellent. So more expensive does not mean better.
Elvira. I bought tablets based on plant extract at the pharmacy. The doctor advised his son because he has kidney stones, and various herbal teas do not help. The tablet dissolves in water and is drunk like tea. The liquid is quite bitter, but it helps better than other plant-based products.
Natalia. Very good grass. I was recently diagnosed with small stones in my kidneys. The doctor said that we can do without medications. But I felt discomfort, so I decided to do something. A friend recommended madder. I brewed it like tea. The liquid turns out bright red. The taste is not so great, but the stones really went away, and quite quickly.
Oksana. One of the best herbs for removing everything that is not needed from the body. So, it helps remove sand from the kidneys. In addition to oxalates, it also helps remove dangerous salts that cause large stones. The latter are quite difficult to dissolve, but madder in combination with other herbs makes it possible to do this without resorting to surgical intervention.
Madder
Rhizomata et radix Rubiae - Madder rhizome and root
Madder - Rubia tinctorum L.
Georgian madder - Rubia iberica Fisch. Ex. DC. (Rubia tinctorum L. var iberica C. Koch)
Madder family - Rubiaceae
Other names:
- specks
— marzana
- dye root
Botanical characteristics. A perennial herbaceous, more or less pubescent plant with a powerful main root, from which second-order roots extend at depth;
creeping woody rhizomes extend from the upper part of the main root. The stem is branched, tetrahedral, prickly, rough on the edges, climbing, up to several meters long. Leaves are in whorls of 4-6, lanceolate-ovate, narrowed at the base into a distinct petiole, spiny at the edges. The flowers are small with a greenish-yellow five-toothed star-shaped corolla, in axillary semi-umbrellas, collected in leafy multi-flowered panicles. The fruit is double, drupe-shaped, fleshy, black, with coloring juice. It blooms in June-July, bears fruit in August-October. Georgian madder differs from madder in its larger size, ovate petiolate (rather than lanceolate sessile) leaves and the presence of drooping leaves.
Spreading. Madder is found quite rarely in Central Asia and in the south of the European part of the country. Introduced into cultivation for industrial purposes. Georgian madder grows in the Caspian regions, in the Eastern Caucasus, reaching the slopes of the mountains of Dagestan, Azerbaijan and Georgia.
The main procurement areas for Georgian madder are Dagestan, Azerbaijan, Ichkeria, and Ingushetia.
Harvesting, primary processing and drying. Raw materials from wild plants are harvested in early spring (March - first half of April) or at the end of the growing season (from early August until frost) by hand, digging up rhizomes and roots to a depth of 20-30 cm. In this case, rhizomes predominate in the raw materials. To preserve the thickets, harvesting on the same plantations is carried out once every 2-3 years. In orchards and vineyards where madder is a weed, it can be harvested annually while plowing the rows. On farms, the procurement of raw materials is carried out in the 3rd year of the crop, digging out the entire underground part of the plant. Roots usually predominate in such raw materials. The collected raw materials are shaken off the ground, freed from the above-ground part, large roots are cut into pieces transversely and, without washing, laid out for drying as quickly as possible. Dry the raw materials in a thin layer under canopies or in attics with good ventilation. Drying is possible in artificially heated dryers at a temperature of about 45°C. During drying, the raw materials are turned over to prevent them from molding.
Standardization. The quality of raw materials is regulated by the State Fund XI.
Microscopy. In microscopic examination of whole and crushed raw materials, calcium oxalate raphides located in the cells of the bark parenchyma are of great diagnostic importance. All wood elements are highly lignified. Thils are often found in the vascular cavity.
According to SP XI, the authenticity of raw materials is also confirmed using fluorescent microscopy.
Numerical indicators. Whole raw materials. Bound anthracene derivatives not less than 3% (photoelectrocolorimetric method); humidity no more than 13%; total ash no more than 10%; other parts of madder (stems, leaves, etc.) no more than 1.5%. No more than 1% organic and no more than 1% mineral impurities are allowed.
When quantitatively determined, the content of the sum of anthracene derivatives and free anthracene derivatives is found, and then the content of bound anthracene derivatives is calculated from the difference.
Crushed raw materials. Bound anthracene derivatives not less than 3%; humidity no more than 13%; total ash no more than 10%; particles that do not pass through a sieve with holes with a diameter of 7 mm, no more than 10%; particles passing through a sieve with holes measuring 0.25 mm, no more than 5%; organic impurity no more than 1%; mineral impurity no more than 1%.
External signs. Raw materials collected from wild plants consist mainly of rhizomes; collected from cultivated plants - from the roots. The raw materials are pieces of thin curved cylindrical rhizomes of various lengths, thickness from 3 to 18 mm. The surface is longitudinally wrinkled, red-brown in color, with a weak, peculiar odor and initially a sweetish and then bitterish-astringent taste. With water it gives a reddish-brown color (dyes). A cross section reveals red-brown bark and orange or brick-red wood. There is usually a cavity in the center of the rhizomes. When chewing, saliva turns brownish-red. Humidity no more than 13%.
Both types - Georgian madder and dyeing madder - are allowed for use.
Chemical composition. Rhizomes contain hydroxy- and hydroxymethylanthraquinones (5-6%). The main ones are rubirethric acid (alizarin aglycone), lucidin primeveroside (lucidin aglycone), haliosin (pseudopurpurin aglycone) and rubiadin glycoside. Free anthraquinones have also been isolated - alizarin, pseudopurpurin, xanthopurpurin, lucidin, munyistin, 1-methoxy-2-oxyanthraquinone and rubiadin. The grass and rhizomes of the plant contain the glycoside asperuloside and a number of organic acids. Flavonoids (rutin) were isolated from the aerial part of the plant.
Storage. In a dry, well-ventilated room, protected from light. The shelf life of raw materials is 2 years.
Pharmacological properties. Madder has the ability to gradually loosen and destroy urinary calculi. The mechanism of this action was previously associated with rubirethric acid, which acidifies the urine, as a result of which the urine becomes capable of loosening stones containing calcium and magnesium phosphates. Currently, the main importance is given to the chemical affinity of madder dyes that interact with calcium and magnesium phosphates. Indirect evidence of such a mechanism of chemical interaction of stones with madder preparations is considered to be their staining in vitro, loosening and heterogeneity, as well as the intravital coloring of bones in experimental animals, which is caused by madder dye. As a result of loosening, the stones crumble into smaller stones and sand.
Madder preparations have diuretic properties, are called bactericidal against coccal flora, reduce the tone of the circular muscles and increase peristaltic contractions of the longitudinal muscles of the renal pelvis and ureters, thereby promoting the movement of stones and their removal from the kidneys and urinary tract.
Of the madder preparations studied in the VILR pharmacology laboratory (dry extract, powder tablets, sum of glycosides and ruberythric acid), the galenic forms have the most active diuretic and antispasmodic properties: extract and powder from madder roots.
Medicines. Dry madder extract. "Cistenal".
Application. Madder preparations are used for urolithiasis to facilitate the passage of small stones, mainly magnesium and calcium phosphates, and to reduce spasms.
Dry madder extract (Extractum Rubiae tinctorum siccum) is produced in the form of tablets of 0.25 g, brown in color, with a bittersweet taste. Hygroscopic. Take 2-3 tablets 3 times a day, after dissolving them in 1/2 glass of warm water. The course of treatment is 20-30 days, a second course is carried out according to indications after a 4-6 week break.
Cystenal is produced in the Czech Republic. Available in 10 ml bottles. Consists of the following components: tincture of madder root 0.01 g, magnesium salicylate 0.15 g, essential oils 6.15 g, ethyl alcohol 0.8 g, olive oil up to 10 g. Prescribed orally 3-4 drops of sugar for 30 minutes before meals, in case of an acute attack of colic, take 20 drops in sugar or water.
Patients with frequent attacks of colic are prescribed 10 drops of cystenal 3 times a day. If the drug causes heartburn or irritates the stomach, take it after meals.
28.06.2015
Instructions for use of madder
There are several main forms in which madder is used in folk and traditional medicine:
- Decoction. The decoction can be used to remove excess salts from the joints, which is especially important for arthritis, gout, polyarthritis, and osteochondrosis. It can also be useful for dropsy, jaundice, and diseases of the spleen. To prepare the plant, you need to grind the roots and rhizomes of the plant to a powder, take a teaspoon of this powder and pour 1.5 cups of boiling water over it. This product must be put on fire and boiled for 10 minutes, then strain and cool. Drink half a glass three times a day, approximately 40 minutes after eating.
- Infusion. It is an analgesic, antispasmodic, and diuretic. It helps well with cholecystitis and gallstone disease. To prepare, you need to pour a teaspoon of crushed raw materials with a glass of cold water and let it brew for eight hours. Then strain the extract and pour a glass of boiling water over the raw material again. After 15 minutes, strain the infusion. Mix these two remedies and use them throughout the day, dividing them into two doses.
- Tincture. A tincture of the plant is indicated for inflammatory processes in the kidneys and urinary tract. It kills bacteria, especially various water cocci. The tincture also helps with joint diseases. You need to consume it a teaspoon after meals, and it is important to drink at least one and a half liters of clean water per day.
- Herbal tea. Madder is a common component of restorative herbal teas. In particular, tea with its use helps remove stones from the kidneys, gall bladder, and urinary tract. If, in addition to madder root, you add chamomile flowers and birch leaves to tea, you can use it to improve heart contractions without affecting rhythm, pressure and breathing. Pour a glass of boiling water over the herbal tea package and let it brew for five minutes. Use once a day in the evening, preferably after meals. The course of treatment is 3-4 weeks. For prevention, it can be used once a year with a course of the same duration.
- Madder extract in tablet form. Madder extract in tablet form is popular in official medicine. Capsules should be taken orally, 2-3 pieces three times a day. Right before use, you need to dissolve the tablets in warm water. It is advisable to drink them at clearly defined times. The course of treatment is 20-30 days. If necessary, and only with the permission of the doctor, the course can be repeated in about a month.
- Drops. Madder is also used in the form of drops. They help dissolve calcium oxalates or remove them from the body. The product helps relieve swelling, which has a beneficial effect on kidney function. It is usually recommended to take 20 drops, after dissolving them in 150 ml of water. They should be taken twice a day, preferably while eating. The course of treatment is 30 days.
- Powder. Powder based on the roots of the plant is used to eliminate pain and spasms, and helps remove small stains. It is recommended to use the powder three times a day, one gram, diluting it in 100 ml of warm boiled water.
- The drug Cystenal with madder. Cystenal must be taken orally as drops. This is a tincture of madder root, to which ethanol, essential oils and magnesium salicylate are added. The remedy is indicated for cystitis and urolithiasis, which are accompanied by secondary inflammation and spasms. You need to take 3-5 drops three times a day. It is recommended to do this 15-30 minutes before meals, dissolving the product in water or placing it on a piece of sugar. If necessary, a single dose can be increased to ten. If you have increased stomach acidity, you should take the drug during or after meals. In case of decreased secretion of gastric juice, it is recommended to combine Cystenal with products containing pepsin and hydrochloric acid. The course of treatment is 3-4 weeks.
Medicinal recipes based on madder
The use of madder for medical and medicinal purposes is mainly in the form of extracts, powders, decoctions, infusions and alcohol tinctures.
- Decoction for urolithiasis: madder - a couple of teaspoons are poured with boiling water and infused for two to three hours, after which it is filtered. Be sure to take 1/3 cup of the decoction before meals. In addition, this decoction can be used for menstruation accompanied by pain. The same decoction will help with spleen disease; in this case, the dosage should be doubled and taken half an hour before meals.
- A decoction for external use for skin diseases and to eliminate age spots: Take a teaspoon of dry madder roots, previously crushed, into a glass of water and cook in a water bath for a quarter of an hour. After cooling, the broth is filtered and used for compresses and lotions.
- Madder powder for diseases of the kidneys, spleen, respiratory organs, liver: Making the powder: grind dry madder roots on a grater, the resulting material must be passed through a sieve. Take the resulting powder one gram up to three times a day.
- Madder tincture for kidney diseases of the urinary tract, accompanied by inflammation: The alcohol tincture of madder must be diluted with water in a ratio of one to ten. Take the diluted tincture half an hour after meals in the amount of one teaspoon. During the treatment period, you must drink at least one and a half liters of purified water daily. This tincture has a high bactericidal effect on microorganisms of the coccus group.
Madder is recognized as a traditional medicine and preparations based on madder are easy to find in pharmacies. The main form of release is madder extract in tablets (0.25 grams each). Up to three tablets diluted in half a glass of warm water are used per dose. Take three times a day, and the course of treatment may take a month. And if the need arises, it is repeated after a month and a half.