Renal colic occurs when there is an acute disruption of the outflow of urine from the kidney. The most common cause of renal colic is urolithiasis. When the stone is localized in the kidney, colic is observed in 50% of patients, in the ureter - in 95–98%.
Acute difficulty in the outflow of urine from the upper urinary tract leads to increased pressure in the renal pelvis and impaired blood circulation in the kidney. Thus, renal colic can lead to severe complications that pose a threat to the patient’s life, such as shock, acute purulent pyelonephritis, perinephric phlegmon, and acute renal failure.
Renal colic appears most often after physical exertion: fast walking, running, bumpy driving, sports games. The attack occurs suddenly, in the midst of complete health. The duration of the attack ranges from several minutes to a day or more. The pain is so intense and sharp that the patient rushes about and, unable to find a place for himself, takes a wide variety of forced positions to calm the pain. More often he tries to bend over, placing his hand on the lumbar region, in which he feels unbearable pain. The pain can spread to the abdomen, thigh, and genitals. Colic is often accompanied by increased urination and vomiting, which occurs due to pain and does not improve the condition. When urinating after an attack, stones may pass.
Renal colic requires emergency medical care and urgent hospitalization of the patient.
Self-diagnosis is fraught with dangerous consequences. Renal colic is easily confused with acute appendicitis and such equally serious diseases as perforated gastric ulcer, inflammation of the appendages, intestinal obstruction, intestinal infarction, and acute cholecystitis.
In the hospital, an examination is carried out, which consists of urine and blood tests, ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder. If necessary, an X-ray examination is performed. After this, treatment is prescribed.
First aid for renal colic may be necessary because the pain is very severe.
Necessary:
- Call an ambulance.
- Place the patient in a warm bath to relieve pain. If a bath is contraindicated or is not tolerated by the patient, you can apply a heating pad to the lumbar area. When you feel the urge to urinate, immediately empty your bladder.
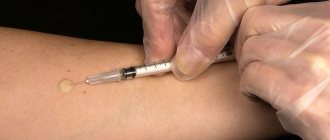
- Take antispasmodics: No-Shpu (Drotaverine, Papaverine).
- If there is colic on the left (important!), then you can take a painkiller, for example, baralgin, ketanov. If pain occurs on the right side (right-sided renal colic), then painkillers do not need to be taken, since the cause of pain may not necessarily be a kidney stone, but also appendicitis and other acute surgical diseases. In this case, taking an anesthetic drug will make it difficult to diagnose these diseases.
When is hospitalization required for a patient with renal colic:
- if after taking medications the pain does not go away;
- in the absence of urine, incessant vomiting, high temperature, etc.;
- if the pain bothers you on both sides;
- if the patient has only one kidney.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, in any case, the prognosis will be favorable, and you will soon forget about the terrible pain. Good health to you!
Vasily ERMAKOVICH, urologist of the surgical department of Central Medical Unit No. 91.
First aid for renal colic: algorithm
Naturally, emergency care for renal colic should be aimed primarily at relieving pain, but its strategy depends both on the person’s condition and on the presence of other ailments (hypertension, heart failure). First of all, you need to call specialists, waiting for them you can alleviate the condition a little. A hot sitz bath helps a lot (if the person does not have hypertension or a stroke), as well as painkillers, which are always administered as part of emergency care for renal colic. They can be taken either in tablet form or by injection.
Treatment
Treatment Goals
- Reducing pain;
- normalization of urination;
- stopping bleeding;
- normalization of body temperature.
After stopping an acute attack of renal colic, the doctor will give recommendations to prevent repeated episodes.
Lifestyle and aids
- Bed rest;
- drink at least 2 liters of water;
- a heating pad on the lumbar region or a hot bath;
- urinate in the potty to track the passage of stones.
Medicines
- Painkillers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antispasmodics. For a mild attack of renal colic, tablets or rectal suppositories are sufficient. Severe renal colic requires intravenous medications. If the pain does not go away after an hour or returns after the administration of medications, hospitalization is required.
- Antiemetic drugs - if vomiting.
- Hemostatic drugs - if blood is detected in the urine.
- Alpha adrenergic blockers. They promote muscle relaxation and stone passage.
- Antibacterial therapy is prescribed both as a treatment for a diagnosed infection and for the prevention of infectious complications.
Procedures
- Remote shock wave lithotripsy - the essence of this method is to influence the stone using a shock wave generated by special devices. The stones break down and turn into “sand”, after which they pass out on their own in the urine. Can be used if the stone size is from 5 to 20 mm. Contraindicated in case of infection, bleeding and poor blood clotting, obesity, kidney tumors.
- Contact lithotripsy is the destruction of stones using ultrasound or laser, but this procedure requires an endoscope to be inserted through the urethra. The procedure is highly effective, but has a number of contraindications and complications, such as infection, bleeding and the formation of structures that narrow the ureters.
Surgical operations
If renal colic is complicated by acute urinary retention, acute pyelonephritis, sepsis, then emergency drainage of the upper urinary tract is performed. To do this, access is made through a small incision in the back or a stent is installed using an endoscope through the ureter.
Restoring and improving quality of life
After an attack of renal colic, it is better to limit physical activity, exclude sports, replacing them with quiet walks.
It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids, limit the consumption of salt and spicy foods.
Medicines to facilitate the passage of kidney stones
To speed up and facilitate the removal of stones, painkillers and antispasmodics are recommended. They relieve pain during stone removal:
- antispasmodics (No-shpa);
- painkillers (Baralgin, Analgin);
- Phytolit is a herbal preparation that has an analgesic and antispasmodic effect, as well as activating the breakdown of stones.
It is forbidden to independently select a medicine for urolithiasis.
This may make the condition worse. To prevent relapse of urolithiasis, nephrologists recommend:
- drink 2 to 2.5 liters of still (preferably alkaline) water per day;
- exercise moderately;
- eat a balanced diet.
When prescribing a treatment regimen, the nephrologist takes into account a history of chronic diseases, the presence of allergies, the age characteristics of the person, the chemical composition and size of the stones. In most cases, small formations are detected, which can be eliminated with medication.
Typically, the breakdown of stones takes about two weeks from the moment you take the first tablet. Diet and drinking plenty of fluids speed up excretion. Under no circumstances should you stop taking medications, otherwise the disease will worsen. If stones do not dissolve well, lithotripsy is indicated - remote crushing of formations with ultrasound or a shock wave. Large stones require surgery.
Nephrolithiasis is a common disease. Stones of different sizes appear in the kidneys due to metabolic disorders and infections. Men suffer from this more often than women. The main risk group is people aged 20–40 years. If you suspect stones, you should consult a doctor: in the early stages of the disease there is a chance to treat quickly.
Possible complications
- Acute urinary retention requires immediate hospitalization and can lead to renal failure.
- Acute pyelonephritis is an infectious and inflammatory process in the kidneys.
- Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response in response to infection. It develops when bacteria leave the site of primary localization into the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. This is a life-threatening condition that requires emergency treatment in a hospital.
- Bleeding is typical for calcium oxalate dense stones with processes.
Forecast
Approximately 80-85% of stones pass spontaneously. Approximately 20% of patients require hospitalization due to persistent pain and deterioration in general health.
The most painful and potentially dangerous aspect of urolithiasis and renal colic is the combination of urinary tract blockage and upper urinary tract infection.
According to statistics, the frequency of repeated attacks of renal colic due to urolithiasis is 50% within 5 years, 70% and higher within 10 years.
Types of medications for urolithiasis
Kidney stones are formed due to changes in the acidity of urine, but more often salt crystals and toxins accumulate inside the organ. They gather in dense formations. Medicines for dissolution are selected according to the chemical composition of kidney stones. There are 4 types of stones:
- Urates – occur in people who abuse protein foods. They are observed in only 10% of patients with nephrolithiasis. Often appear in middle-aged people. The formations are easily treatable with medication.
- Phosphates – formed from calcium salts when urine pH indicates alkalization. They require acidification of urine and dissolve well under the influence of drugs. A common cause of stones is infectious diseases. The formations have a smooth surface, so they rarely injure the kidneys.
- Oxalates - consist of salts of oxalic acid, occur when there is an excess of vitamin C in the body, consumption of vegetables and fruits, coffee, chocolate in large quantities. Often appear in the kidneys with diabetes and magnesium deficiency. They do not dissolve well under the influence of drugs.
- Cystines are rare formations (5% of cases), often appear against the background of genetic pathologies. They are difficult to remove and cause severe pain that cannot be treated with pills and injections. Often they can only be eliminated surgically.
Drugs for urates
Such stones are formed when the body's metabolism of uric acid is impaired. They appear not only in the kidneys, but also in the gallbladder. Urates are easier to eliminate than other stones. They are well treated with diet and pharmaceutical drugs. It is important to accurately select the correct dosage. The main goal of therapy is to reduce the acidity of urine. For this purpose, the following means are used:
Article on the topic: Treatment of hormonal imbalance in women with drugs and folk remedies
| Allopurinol | Potassium citrate | |
| Compound | allopurinol | potassium (99 mg per 1 capsule) |
| Action | normalizes uric acid metabolism, reduces its concentration, dissolves urate deposits | replenishes potassium deficiency, improves urine filtration and fluid removal from the body |
| Mode of application | 1–3 tablets (100 mg each) are taken once a day after meals with water | 1 capsule 1–5 times a day with food. The exact dose is prescribed by the doctor |
| Contraindications |
|
|
| Side effects |
|
|
| average price | 80 rub. for 50 tablets (per 100 mg) | 1185 rub. for 80 capsules |
From oxalates
This type of stone is more difficult to treat with pharmaceutical drugs than others. Medicines have little effect even on small formations, so treatment will take a long time. Oxalates often have to be broken down surgically. You can increase your chances of recovery by removing foods with oxalic acid from your diet and increasing the amount of fluid you drink. Effective means for dissolving and crushing oxalates:
| Cyston | Asparkam | |
| Compound | extracts:
The product is processed over steam from the extract from the mixture:
| potassium and magnesium aspartate |
| Action | Relieves inflammation, has a diuretic and antibacterial effect | Replenishes magnesium and potassium deficiency in the body, regulates metabolic processes |
| Mode of application |
|
The duration of treatment for urolithiasis of the kidneys is determined by the doctor. It is advisable to take vitamin B6 at the same time for better absorption of magnesium. |
| Contraindications | children up to 6 years old |
|
| Side effects | allergic reactions |
|
| average price | 310 rub. for 100 tablets | 80 rub. for 56 tablets |
From phosphates
These stones can be broken down and passed out of the kidneys by increasing the acidity of the urine. To do this, you need to increase the amount of citrus fruits and lean meat in your diet. You can take vitamin C. Treatment should be started as early as possible - the stones increase in size very quickly.
It will not be possible to completely dissolve the stones; all medications only crush phosphates.
Good natural pills for kidney stones:
| Madder | Spilled | |
| Compound | madder rhizome extract | extracts:
|
| Action | It acidifies urine, loosens stones, relieves spasms and has a diuretic effect. | Relieves inflammation and spasms, stimulates the immune system, has a diuretic and antioxidant effect. |
| Mode of application |
|
|
| Contraindications |
|
|
| Side effects |
| allergic reactions |
| average price | 85 rub. for 20 tablets | 540 rub. for 100 capsules |
From cystine stones
The basis of stones is calcium and protein. During treatment, you need to eliminate sources of oxalic acid from the menu. Preparations containing magnesium salts can crush stones, but therapy will take a long time. For large formations, medications will prevent the stones from enlarging and improve the patient’s general condition. Doctors often prescribe the following drugs:
| Cuprenil | Kapoten | |
| Compound | penicillamine | captopril |
| Action | reduces the formation of cystine stones, inflammation, removes toxins | binds cystine in urine, gives low effectiveness in the treatment of nephrolithiasis (compared to penicillamine) |
| Mode of application |
|
|
| Contraindications |
|
|
| Side effects |
|
|
| average price | 1335 rub. for 100 tablets | 170 rub. for 28 tablets |
Universal action products
Some medications can be prescribed for all types of kidney stones. Most of these drugs change the chemical composition of urine. This helps to destroy the stones. The disadvantage of universal drugs is their low effectiveness, so they are prescribed only when it is impossible to choose a more effective drug. For nephrolithiasis the following are used:
| Blémarin | Uralit U | |
| Compound | citric acid, potassium bicarbonate, sodium citrate | potassium sodium hydrogen citrate |
| Action | alkalinizes urine, dissolves and prevents the formation of stones | |
| Mode of application |
|
|
| Contraindications |
| |
| Side effects |
| not identified |
| average price | 1090 rub. for 80 tablets | 920 rub. for 280 g (powder) |
Herbal medicines
Tablets, syrups and capsules based on natural raw materials are considered safe and are often prescribed to remove sand from the kidneys. These medications can be prescribed for nephrolithiasis in children and pregnant women. The disadvantage of herbal products is the high risk of allergic reactions. The degree of effectiveness in dissolving stones is low to medium. Deserved good reviews:
| Canephron | Urolesan | |
| Compound | extracts of centaury, lovage, rosemary | fir, mint, castor oils, oregano, hop, wild carrot extracts |
| Action | removes inflammation and spasms, has a diuretic, antimicrobial effect | removes excess salts from the kidneys, acidifies urine, relieves spasms, has diuretic and antiseptic effects |
| Mode of application | Take 2 tablets 3 times a day with water. | Take 1 tablet 3 times a day before meals. Treatment lasts from 5 days to a month. |
| Contraindications |
|
|
| Side effects |
| skin and digestive allergic reactions |
| average price | 500 rub. for 60 tablets | 415 rub. for 40 tablets |
Tablets to facilitate the process of removing stones
Antispasmodics relieve pain that occurs when stones move through the kidneys and out. No-Shpu and Papaverine are often used. If the patient suffers from low blood pressure, it is better to use Spazmalgon, Analgin. When treating nephrolithiasis, doctors may recommend the following groups of drugs:
- antibiotics (Ofloxacin, Amikacin) – for urolithiasis caused by infection, used orally and intravenously;
- anti-inflammatory (Furadonin, Furangin) - used together with antibiotics;
- diuretics (Hypothiazide) - relieve swelling, are selected according to the type of stones, help their active removal;
- alpha-blockers (Tamsulosin) - stimulate contraction of the bladder and reduce the tone of the ureters, which improves the passage of sand and stones.
Renal colic treatment
In some cases, an attack of pain due to renal colic can be controlled with medication. However, if an attack of renal colic is accompanied by complications, treatment of this pathology is carried out surgically in a urological hospital.
The method of performing surgery to remove stones from the urinary tract is selected individually. However, not all clinics are able to perform stone extraction minimally invasively (without incisions). That is why notify the ambulance operator in advance about hospitalization in a specific clinic, or organize a transfer there directly for the operation.
Only in our hospital, laser stone removal for renal colic is performed using the latest equipment - a laser generator from the German Richard Wolf Megapulse laser and a flexible urethroscope ("cobra"), which allows the necessary manipulations to be carried out with pinpoint precision. Our specialists completed internships in clinics in Munich (Germany) and Poland (at the largest endoscopy center in Europe, Karlstorz). Thus, the staff of our clinic guarantees the most progressive approach in the treatment of renal colic due to a stone in the ureter. The technologies we use have no analogues in Ukraine today.
Laser contact lithotripsy for renal colic involves stone fragmentation by the energy of a laser beam. During such an operation, the instrument is inserted through the urethra (urethra), which avoids SURGICAL INCISIONS (as with the open method) and postoperative scars. The procedure is carried out with full visual control through a mini-video camera, which also eliminates damage to the walls of the ureter and kidney. After the operation, the patient is prescribed a special diet.
How to tell the difference?
When diagnosing, urate stones are clearly visible on ultrasound, but, unlike other types of stones, they are not visible on X-ray, which is due to their low density. You can accurately determine the composition of the stone by examining a stone that has previously passed or was removed during surgery. An analysis that confirms the presence of urate stones is pH testing, in which the acidity of the urine is below normal. Sometimes, to clarify the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a computed tomogram - with the help of this study, you can find out the exact density of the stone. But this study is not necessary: if there is a stone on an ultrasound, but not on an x-ray, and a shift in urine pH toward acidic is repeatedly detected, then you can try to dissolve it.
We diagnose nephrolithiasis (urolithiasis) only if the detected stone has a dense structure, is more than 0.5 cm in diameter and has an acoustic track (that is, ultrasound does not pass through it). If the “something” in the kidney does not fit this description, it is not stones. And there is no diagnosis of “sand in the kidneys”. Small “grains of sand” detected on ultrasound may turn out to be simply vessels, compacted fiber or encrusted renal papillae. If you were told about “sand” at the clinic, do not rush to take diuretics. Monitor the condition of your kidneys - do an ultrasound every six months. In this way, you can determine over time whether the stone is growing, or whether your kidney just always looks like that on an ultrasound.
Often, urate stones occur in patients with impaired purine metabolism, for example, with gout, so all patients with suspected urate nephrolithiasis must determine the level of uric acid in the blood.
Review of tablets that break up (dissolve) stones
Some medications contain a high concentration of active substances; uncontrolled use of potent drugs on the advice of neighbors, colleagues or relatives does not produce results or harms the body. The urologist selects medications based on data on the acidity level of urine, the chemical composition of kidney stones, and the general condition of the patient.
Oxalate dissolving tablets
Before starting therapy, the patient should know: stones formed from the accumulation of calcium and ammonium salts of oxalic acid dissolve worse than phosphates and urates; treatment is long-term. Proper drinking regimen is required to wash out dissolved stones. When crushing stones, it is important to follow a diet that limits oxalate-containing items and foods with a high concentration of oxalic acid.
Effective drugs:
- Cholestyramine. Synthetic product, copolymer of divinylbenzene and styrene. The active substance binds bile complexes, forms insoluble chelates, and actively removes harmful compounds from the body. Reducing the concentration of oxalates normalizes the functioning of the urinary system. The medicine lowers cholesterol levels; for a noticeable effect, it must be taken for a month. The average cost is 1,700 rubles.
- Cyston. The active ingredient is a complex of plant extracts. The drug dissolves stones, but does not affect the pH level of urine. A medicine with diuretic and anti-inflammatory effects. Reducing the concentration of hydroxyproline, oxalic acid and calcium reduces the stone-forming effect in the urinary system. A minimal list of contraindications; undesirable manifestations during therapy occur rarely. The herbal preparation is approved for children from two years of age. The average price is 460 rubles.
Drugs for the treatment of urate
Uric acid stones are the result of an addiction to red meat, legumes, cod, mackerel, offal, and the frequent inclusion of sorrel and spinach in the menu. Excessive consumption of coffee, strong tea and beer is another reason for the accumulation of stones.
When uric acid metabolism is disrupted, excess salts (urates) are deposited in the joints (gout, arthritis develops), kidneys and gall bladder. At the same time as taking tablets to dissolve uric acid stones, the urologist adjusts the diet to reduce the acidity of urine. If you follow the rules for using medications and diets, urates dissolve quite easily.
Effective tablets:
- Potassium citrate. The drug is suitable for patients with normal levels of calcium in the urine. The active component delicately dissolves stones. One of the advantages of the drug is the minimization of relapses of nephrolithiasis and urolithiasis. The medicine normalizes kidney function. The average price is 1380 rubles (180 capsules).
- Allopurinol. The medicine suppresses the synthesis of uric acid and prevents the accumulation of urates. The active component of the urological drug is allopurinol (1 tablet contains 0.1 g of active substance). The drug is often prescribed to lower uric acid levels. Most patients note a positive effect from taking tablets that dissolve stones. The medicine rarely causes negative effects. In case of renal failure, the drug is not prescribed. You cannot take breaks longer than two to three days between taking pills: in the absence of regular use, increased (negative) uricosuria indicators return. The average price is 90 rubles (50 pieces).
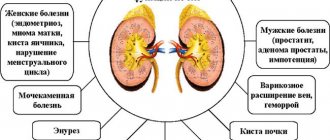
Causes
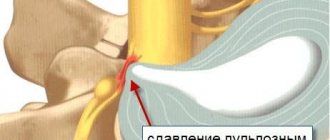
The most common cause of renal colic is a stone getting stuck in the urinary tract. This usually occurs in the ureter, where the stone stretches the walls, trying to pass down. Inflammation occurs at the site where the stone gets stuck, the flow of urine is disrupted, stones with sharp edges can injure the mucous membrane and cause bleeding.
Kidney stones are formed due to a violation of mineral metabolism, which leads to the deposition of salts of various minerals in the renal pelvis (this is the cavity in the kidney that passes into the ureter). Salts gradually accumulate and turn into rocky formations. Most often these are salts of calcium, uric acid and phosphate. The sizes of the stones vary from grains of sand to several centimeters.
In addition to stones, the causes of renal colic can be:
- upper urinary tract infections (due to swelling of the mucous membrane and blockage of the ureter with inflammatory products);
- kidney tumor;
- kidney tuberculosis;
- kidney injury (urine flow is disrupted by blood clots, or external compression of the upper urinary tract by a hematoma occurs);
- tumors of the retroperitoneal space and pelvis, causing compression of the urinary tract from the outside;
- gynecological diseases.
Symptoms of stone formation
At the initial stage of development of nephrolithiasis, symptoms of stone formation may not appear. The urinary system tends to self-cleanse, and even minor stones are eliminated from the kidneys naturally. When the stones reach a significant size, the first characteristic symptoms appear - pain in the lumbar region, radiating to the genitals. Thus, nephrolithiasis can be mistaken for diseases of the reproductive system and ignored. To confirm the diagnosis of urolithiasis, ultrasound or radiography is necessary. You can also get tested to check for the presence of protein in your urine.
Frequent urge to urinate is a symptom of kidney stones
Among the most common symptoms of nephrolithiasis:
- sharp pain in the lumbar region, which has a prolonged aching character;
- urinary disturbance;
- constant desire to urinate, with an empty bladder (false urge to urinate);
- blood in the urine;
- pain when urinating;
- frequent urge to urinate.
The presence of at least one of the above symptoms may indicate the development of urolithiasis, so it is very unwise to ignore or avoid visiting a urologist. Regular examination and testing will reveal the presence of stone formation and effectively eliminate the problem when it first appears. It is especially important to undergo examination for people who have a hereditary predisposition to the development of nephrolithiasis.
Read
About cranberries for pyelonephritis
Who's at risk
- Heredity.
- Dehydration. Working in conditions of increased air temperature or increased fluid loss due to increased sweating.
- Poor nutrition. First of all, this concerns the use of table salt. Too much salt in the diet increases the amount of calcium the kidneys have to filter and significantly increases the risk of kidney stones. An abundance of meat, cheese and wine promotes the formation of uric acid stones. Calcium stones often form with excessive consumption of coffee, tea and chocolate.
- Excess weight.
- Inflammatory bowel disease, malabsorption syndrome (poor absorption in the intestine) and intestinal surgery.
- Diseases of the parathyroid gland leading to disturbances in calcium metabolism.
- Chronic urinary tract infections.