The reasons for the appearance of ovarian cysts in women in most cases are trivial - a change in hormonal levels due to stress, improper rhythm of sleep and rest, nutrition, lack of sexual activity or, conversely, excessive passion for it. In each individual case, the follicular ovarian cyst develops unnoticed, its symptoms can be easily confused with premenstrual syndrome. However, women and girls of any age, including newborn female babies, are susceptible to this disease.
Follicular ovarian cyst is considered a fairly common disease that rarely develops into a serious pathology. However, you should not waste time and ignore alarming symptoms - in severe cases, surgical intervention and complete removal of the ovary may be required. And this can lead to infertility.
What is a “follicular ovarian cyst”?
An ovarian follicular cyst is a benign tumor. It can develop from a follicle that did not ovulate during the last menstrual cycle. The pathology usually occurs in women of reproductive age.
A woman's body undergoes hormonal changes every month. When the next menstrual cycle begins, the production of follicle-stimulating hormone begins. It is responsible for the maturation of the egg. The ovary always contains many primordial follicles that are ready to develop gradually. One of them, or in rare cases 2, ripen to form a graafian vesicle.
If LH is produced in a timely manner, the follicle opens, which is dominant. This causes the egg to enter the abdominal cavity. She is fully mature and ready for fertilization. However, if for some reason the opening of the Graafian vesicle does not occur, a follicular ovarian cyst occurs. It is a small benign formation in the organ. The size usually does not exceed 7-10 cm. About 80% of all types of ovarian tumors are cysts. The peculiarity of the follicular type of neoplasm is that it is not capable of developing into a malignant form.
The neoplasm has a single-chamber or two-chamber structure. Inside it there is an accumulation of fluid, which is saturated with estrogen. Diagnosis of such a tumor is quite simple. However, in practice, detection of neoplasms occurs infrequently. About 70% of patients do not even realize that they have a similar problem. The uniqueness of the pathology lies in the fact that a reverse transformation can be carried out. The tumor tends to disappear.
Depending on the location, a follicular cyst of the left or right ovary is isolated. In the first case, pathology occurs extremely rarely. The gland is supplied with blood through the renal artery. This leads to the fact that the maturation of the Graafian vesicle occurs much less frequently here. This reduces the likelihood of a tumor appearing. However, it must be borne in mind that the above statement is only a medical observation and does not guarantee that a tumor will not appear in the left ovary throughout the woman’s life.
The blood supply to the right side is different from the left. This gland is inextricably linked with the aorta. This fact helps to improve blood supply, which leads to increased maturation of the follicle. These patterns explain the fact that a follicular cyst of the right ovary is detected much more often. Another feature is the size of the tumor. The tumor in the right gland is usually larger than in the left.
Treatment
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor creates an individual program, according to which the treatment of follicular ovarian cyst will be carried out. For small formations (up to 60 mm), dynamic monitoring of the tumor is required for 1.5–2 months, because it usually disappears on its own within several menstrual cycles. In other cases, active intervention is required.
Conservative
For small ovarian cysts, treatment begins with conservative measures. The woman is recommended to take medications that promote regression of the tumor and restore the menstrual cycle. These include the following groups of drugs:
- Hormonal.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Vitamins.
Homeopathic remedies can also be used to gently normalize metabolic and regulatory processes. In addition to the above, physiotherapy (electric and phonophoresis, magnetic therapy) helps to accelerate the reverse development of the cyst.
Operational
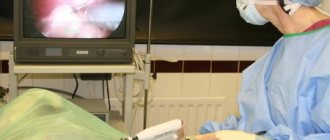
In cases where conservative methods do not help, as well as in large cysts, surgical correction has an absolute priority. Laparoscopic tumor removal is considered the safest and most reliable method. This technique involves using just a few small incisions in the lower abdomen, through which instruments with a miniature video camera are inserted.
The extent of the operation is determined by the size of the tumor and the condition of the surrounding tissues: only resection of the cyst or removal of the entire ovary (oophorectomy). A similar method is used to eliminate follicular cysts during pregnancy. After the operation, drains are left in the abdominal cavity for some time, and then the entrance holes are sutured so that they are completely invisible. The patient can be discharged from the hospital the next day.
If the cyst is complicated by apoplexy and internal bleeding, then a strip operation - laparotomy - will be required. It is necessary to suture the vessels, remove the remains of the cyst, conduct a thorough inspection of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis, remove all fluid from it, and rinse with antiseptics. After surgery, the woman is still under the supervision of doctors, and discharge is possible only after complete healing of the wound.
Treatment tactics for cysts depend on their size and clinical picture - measures can be limited to simple observation or expanded to abdominal surgery.
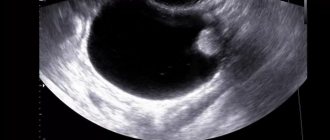
What does a follicular ovarian cyst look like with a photo
The appearance of an ovarian cyst depends on its type. Single-chamber or two-chamber neoplasms are distinguished. In the first case, the follicular cyst is visually similar to a round-shaped cavity. There are no internal partitions. The occurrence of this type of pathology is observed in 95% of cases. The remaining amount of the disease accounts for a two-chamber cyst. It represents two filled formations merged together. This is possible if, at the time of the onset of the pathology, the growth of 2 graafian vesicles was observed. To better understand what a follicular ovarian cyst looks like, it is recommended to study the photo.
During pregnancy
Many women are concerned about the question: are follicular ovarian cysts and pregnancy compatible? Considering that the pathology is accompanied by an anovulatory cycle, conception itself is called into question. But for some women, fertilization still occurs. The cyst should then be carefully monitored. Pregnancy management tactics will depend on the characteristics of the tumor: if it is small, wait until the end of the first trimester and remove it, and if a stalk is detected, this is done immediately. Otherwise, complications such as cyst torsion or spontaneous abortion are possible. Rarely, spontaneous tumor growth (regression) is possible.
The first signs of a follicular ovarian cyst
Often the pathology does not manifest itself at all. It can be completely asymptomatic. A cyst in this situation is detected by chance during a routine examination or diagnostics based on other complaints. Pathology can make itself known only if it has been present for a long period of time or has grown significantly. In this case, a woman may experience pain, menstrual irregularities, as well as facial hair growth and voice changes. A large cyst can cause abdominal asymmetry.
Symptoms of follicular ovarian cyst
First of all, the development of a cyst is indicated by the appearance of pain. However, they occur only if the neoplasm has reached a fairly impressive size. The pain is dull and localized in the lower abdomen. They may intensify during sexual intercourse or physical activity. In this situation, the pain syndrome is localized on the side on which the tumor is present. Sometimes a cyst is simply indicated by a feeling of heaviness and a feeling of compression in the pelvis.
If there is a rupture or torsion of the cyst, the pain becomes intense and radiates to the rectum. Additionally, the following symptoms occur:
- body temperature rises;
- nausea occurs;
- vomiting is present.
The symptoms of the pathology are in many ways reminiscent of the symptoms of the so-called acute abdomen. If a follicular cyst ruptures, the woman experiences short-term pain. The pathology does not pose a health hazard.
An enlarged tumor can affect other organs of the genitourinary system, in particular the bladder. With active growth, the neoplasm can also compress the lower parts of the intestine. This causes constipation and false urge to defecate. If there is compression of the vascular bundles, a woman may experience the appearance of varicose veins of the lower extremities.
If the pathology is hormonally active, this can lead to cycle disruption. A woman may develop irregular, infrequent menstruation. There may be delays. Additionally, uterine bleeding may occur, and menstrual flow becomes profuse. During menstruation, severe pain occurs.
Due to increased secretion of male sex hormones in the body, hirsutism is observed. With pathology, hair appears on a woman’s face and body, and her voice becomes rougher. Additionally, there is an increase in the size of the clitoris.
If a woman has a giant cyst, or there is an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, this can lead to abdominal asymmetry. Additionally, growth of its circumference is possible.
Conclusion
Remember that every ovarian cyst, regardless of its size and the reasons for its occurrence, is considered potentially dangerous. Any of the above complications may occur, each of which can lead to inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity, which will require urgent surgical intervention by a surgeon. When the first signs of complications appear (acute pain, nausea and vomiting), you should immediately call an ambulance and go to the hospital for examination.
In some cases, seemingly harmless cysts can transform into malignant tumors. To prevent such a turn of events and not to waste women’s health, do not forget about scheduled regular examinations with your gynecologist and rule out the reasons that may affect the appearance of cysts. Timely identification of the problem facilitates its rapid removal.
Causes and prevention of follicular ovarian cyst
The etiology of the appearance of cysts from follicular tissue has not yet been fully studied. However, it is assumed that malfunctions in the endocrine system can provoke pathology. This leads to increased production of estrogen by the ovaries. As a result, an anovulatory single-phase menstrual cycle develops.
Experts have identified a number of factors that can lead to disruption of menstruation or the ovulation process itself. They are divided into two groups - external adverse effects and internal factors of pathological influence. The first group includes:
- stress;
- overheat;
- physical exercise;
- nervous fatigue;
- hypothermia of the body.
The list of internal factors includes inflammation, functional disorders, various groups of diseases, infections, and STDs. All of the above conditions lead to hormonal imbalance. It helps delay ovulation and leads to further follicle growth.
To prevent the formation of pathology, it is necessary to carry out timely treatment of inflammatory diseases and other types of problems. Additionally, it is recommended to be regularly monitored by a gynecologist. If a woman has a recurrent course, first of all it is necessary to find out all the causes of the pathological condition. Then they are eliminated.
Reasons for the occurrence of education
For a long time, medical researchers could not find the cause of ovarian tumor disease. In modern medicine, the pathogenesis of development has become known. There are many reasons that can cause and provoke the disease . This:
- Inflammatory processes occurring in the ovaries and uterus.
- Congestion in the pelvic area.
- Abortion, forced and surgical interventions on the female body.
- Infectious diseases producing various pathologies.
The main reason may be hormonal imbalance.
The disorder itself occurs as a result of childbirth, which is a natural phenomenon and is restored over time with the use of supportive medications.
Hormonal imbalance occurs from the use of drugs containing hormones, if the wrong doses are used, or if the dose is increased without the consent of the doctor . This also applies to the use of untested contraceptives.
Thyroid disease affects hormonal levels like nothing else. Stress, frequent malnutrition, or vice versa, gluttony also play a role. Overwork at work, clothing that is not appropriate for the weather - all this can affect the disruption of the hormonal system . And this, in turn, can cause ovarian disease.
Often, adult women have a follicular cyst, which developed at birth or development inside the womb.
This could only happen because of the large amount of estrogens in the mother’s body, which caused a failure in the development of the ovaries in the fetus. And also with a strong hormonal surge at the time of childbirth. But such a cyst rarely develops and in most cases resolves on its own within a few months.