Main symptoms:
- Lower back pain
- Lower abdominal pain
- Burning sensation when urinating
- Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder
- Frequent urination
Salt diathesis is a pathological process that results in the formation of excess amounts of substances such as oxalates, phosphates and urates in the kidneys. As a rule, this disease can develop as a result of an acute lack of fluid in the body. There are no restrictions regarding age and gender. However, the disease most often occurs in people aged 40–65 years.
Online consultation on the disease “Salt diathesis”. Ask a question to the specialists for free: Urologist.
- Etiology
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Folk remedies
- Prevention
Etiology
Salt diathesis, or urolithiasis as it is often called, can develop due to the following etiological factors:
- insufficient amount of fluid in the body;
- slow urine flow or prolonged stagnation;
- alcohol abuse;
- poor nutrition;
- changes in the chemical composition of urine due to long-term medication treatment;
- disruption of the metabolic process in the body;
- increased salt content in the body.
It should also be noted that salt diathesis can also develop if a person consumes an excessive amount of purified water.
In addition to the above factors, salt diathesis of the kidneys can form as a result of other underlying diseases of the kidneys or genitourinary system. In some cases, salt diathesis of the kidneys occurs during pregnancy.
Probable causes
There is a misconception that salt diathesis occurs as a result of eating allergenic foods (chocolate, citrus fruits). Salt diathesis is a manifestation of impaired functioning of the kidneys and other organs, so its causes are of a different nature.
Learn about the general rules of nutrition and diet for cystitis in women.
Read about what oliguria is in women and how to treat the problem at this address.
Salt diathesis is caused by:
- Violation of proper nutrition. A diet with an excessive amount of spicy, fatty foods and poor in nutrients leads to metabolic disorders. This, in turn, affects the work of the excretory organs, which are unable to cope with the load. Increases stress and consumption of incompatible foods.
- Hereditary predisposition - if from birth the state of the excretory system has pathologies, then their natural consequence can be salt diathesis. The genetic factor plays a decisive role in the development of pathology in childhood.
- Violation of the drinking regime. Normally, an adult should consume at least 1.5 liters of fluid per day. This is necessary for normal metabolism. Water is the basis for most processes that occur in the body. If it is in short supply, metabolic processes slow down. Toxins begin to accumulate in the renal pelvis, as a result of which salt diathesis quickly progresses. The kidneys cannot cope with their excretory function, harmful substances accumulate, which leads to serious intoxication.
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals. Even drinking enough water should not be considered a panacea. Sometimes the cause of salt diathesis may be the desire to drink purified water, which is purified not only of bad impurities, but also of vitamins and microelements necessary for the body. If you drink it regularly, a deficiency of nutrients occurs. Uncontrolled consumption of mineral water also becomes a trigger for metabolic disorders and the development of salt diathesis.
How to protect yourself and your loved ones from the development of such pathology
Diseases of the urinary system lead to serious complications that negatively affect a person’s health. That is why most doctors believe that it will be much easier to prevent the development of salt diathesis of the kidneys in the early stages than to treat it. To this end, a regular program of preventive medical examinations is carried out, in which patients undergo urine and blood tests. This makes it possible to detect the slightest changes and begin treatment immediately.
Rules for individual disease prevention:
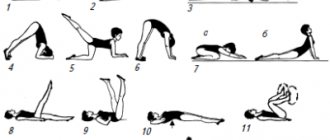
- Exercise regularly. Physical activity allows you not only to build and strengthen the muscle frame, but also contributes to the overall health of the body. That is why it is recommended to choose the optimal activity for yourself: dancing, wrestling, yoga, Pilates, swimming or any other games. If you don’t have time to visit the gym, you can train and perform therapeutic exercises at home.
- Give up bad habits. Alcoholic drinks contribute to the deposition of excess salts and toxic substances in the body, which negatively affect the blood vessels of the kidneys. Alcohol abuse also increases the risk of premature cardiovascular death and the development of other pathologies. For the same reason, you should stop smoking: nicotine affects the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the lumen of arteries and veins, which disrupt normal blood circulation.
- Visit a therapist at least once every six months and undergo a general examination. Simple tests of urine and blood will help assess the condition of the body and detect various ailments in time. If you have a confirmed diagnosis of any disease, you need to visit a doctor every 3-4 months to monitor the dynamics of the most important indicators.
- Try to buy the most natural products without harmful chemical additives and preservatives. It is the food and liquid consumed by a person that have the greatest impact on the condition of the urinary system. Therefore, you need to make sure that the purchased products are fresh, and also install special filters that purify the water from salts and toxic impurities.
Salt diathesis of the kidneys is a pathology that requires immediate treatment, since there is a high probability of complications developing and the disease becoming more dangerous. That is why it is necessary, even after the onset of remission and removal of residual salts and sand from the kidneys, to adhere to a special diet and regularly undergo urine and blood tests. Such vigilance will help avoid the development of relapse of the disease and protect the body from undesirable consequences. If your close relatives have a predisposition to developing salt diathesis, you need to take care of their health from a very early age, instilling in children and parents the basics of proper nutrition.
Symptoms
Salt diathesis of the kidneys is characterized by an asymptomatic course of the pathology at the initial stage. As mineral compounds accumulate, the acidity of the urine increases, which begins to irritate the mucous membranes of the urinary system. Even in the absence of crystallization processes, complications develop:
- Women are diagnosed with cystitis, including hemorrhagic;
- In men, urethritis is detected.
The severity of signs of salt diathesis of the kidneys depends on the stage of inflammation and the person’s resistance to viral and bacterial infections. The acute course of the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower back and lower abdomen between urinations;
- temperature rise up to 40 °C, cold sweat, chills, fever;
- arterial hypertension, followed by a drop in pressure to low values;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, bloating;
- decrease in the volume of urine excreted.
Carrying out treatment at the acute stage allows you to avoid negative consequences and prevent the development of urolithiasis. Long-term accumulation of salts in the pelvis and tubules is characterized by the appearance of symptoms during relapses:
- temperature rise to subfebrile levels (37-38 °C);
- detection of dark blood clots and pus in the urine;
- pain and burning when urinating;
- nagging pain in the lower back, radiating to the sides and anus.
With chronic pathology, relapses of colds become more frequent against the background of a sharp decrease in immunity. A person constantly feels tired and drowsy. He becomes emotionally unstable, neurological disorders and depression develop.
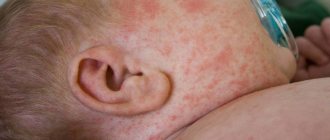
Symptoms and signs of salt diathesis
Signs of salt diathesis are similar in adults and children. The most common signs of the disease are:
- deep yellow color of urine due to large quantities of oxalates;
- reddish tint of urine with urate nephropathy;
- fever and lower back pain when infection enters the kidney;
- intense pain in the lower back and groin when stones move and blockage of the urinary tract with stones (renal colic);
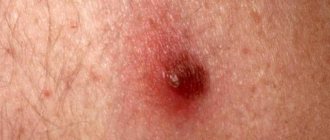
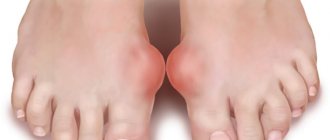
The cause of renal colic is blockage of the ureter with a stone. - joint pain due to the deposition of uric acid salts;
- redness and swelling of the joints;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
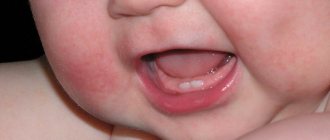
- bitter taste of bile in the mouth;
- curvature of bones (rickets) with phosphate nephropathy.
Rickets is a common companion to phosphate nephropathy
Methods for diagnosing the disease
If suspicious symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a physician. A doctor in this specialty will give a referral for a consultation with a urologist if there are obvious problems with the kidneys. A preliminary diagnosis is made based on the patient’s complaints, medical history (propensity for poor diet, episodes of urolithiasis among close relatives, sedentary lifestyle) and general examination. If necessary, the urologist performs a tapping test: the palm of one hand is placed on the back surface of the back on the lower parts of the ribs, and the other hand strikes it. Increased pain indicates problems with the urinary system. It is necessary to differentiate uric acid kidney diathesis with the following pathologies:
- benign or malignant tumor;
- inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract;
- renal cysts.
Do not forget that before taking a general urine test, you must perform hygiene of the external genitalia with a cotton swab dipped in boiled water. One of my patients did not perform this procedure, as a result of which his biological sample was contaminated with bacteria from the skin and mucous membranes. This led to incorrect diagnosis and prescription of incorrect treatment. The man had to retake the tests in compliance with all the rules, after which the doctor was able to determine salt diathesis of the kidneys.
What methods are used to diagnose the disease:
- A general urine test provides information about the cellular composition and physiological characteristics of urine. Under normal conditions, it has a straw-yellow color and high transparency. Violation of these indicators, redness and turbidity of urine, the formation of sediment and sand at the bottom of the test tube indicate the development of salt renal diathesis.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys. Thanks to the ability of a sound wave to change length upon contact with tissues of different densities, it is possible to create a two-dimensional image of an organ. With salt diathesis, slight swelling of the pelvis is observed, and larger conglomerates can also be detected.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This technique is used for differential diagnosis between uric acid diathesis of the kidneys and malignant or benign neoplasms. The images can reveal minor changes in the structure of the organ.
Characteristics of the disease
Not everyone understands what salt kidney diathesis is and what the reasons for its occurrence are. This condition is an accumulation of various salts and sand in the kidney tissues. Salts may be urates, oxalates, phosphoric acid salts or carbonates. This diathesis is to some extent similar to urolithiasis.
In children, as well as adults, an increased content of the above salts can be detected during a urine test, and more often than not, several of their varieties are determined at once. Normally, in a healthy person, the kidneys participate in maintaining optimal water-salt metabolism in the body, removing excess salts. Signs of salt diathesis may occur when renal function is impaired.
The main etiological factors in the development of this disease are:
- hereditary predisposition;
- poor nutrition;
- drinking poor quality water;
- some gynecological diseases;
- chronic pyelonephritis.
As for heredity, diathesis is often detected in those individuals whose parents have a history of this pathology. Signs of diathesis appear when the kidneys are unable to cope with the load placed on them. It is important that this condition in some cases occurs in pregnant women. Salt diathesis of the kidneys very often develops against the background of chronic pyelonephritis associated with inflammation. The process of deposition and accumulation of salts occurs in the renal pelvis.
Application of traditional methods
Treatment with folk remedies should complement drug therapy. Traditional medicine can provide effective help, but its use should also be agreed with the attending physician.
One of the effective methods is the use of madder-based products. They are most effective in the presence of phosphate stones, which they successfully loosen. For treatment, you can use ready-made pharmaceutical drops - take 20 drops twice a day, simultaneously with meals, after diluting them in water. The course of treatment is 30–32 days. If the stones are large in size and pain occurs, it is recommended to purchase madder in powder form. The product is taken 2 times a day with water. If inflammatory reactions are detected, then it is better to prepare a tincture from the plant and consume 1 tsp. after eating (after 30 minutes).
Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs containing anthraglycosides are very useful for the treatment of renal diathesis. Among such plants, the following stand out: St. John's wort, senna, rhubarb. The composition is prepared as follows. The crushed plant (1 tablespoon) is poured with boiling water (250 ml) and infused for 25–35 minutes. This portion is drunk during the day, and the general course of treatment is 5 days.
Another direction of alternative medicine is the prescription of herbal products containing saponins. The most famous plants are horse chestnut, licorice root, and horsetail.
With the development of kidney stones, the following folk remedies will undoubtedly be beneficial:
- carrot seed powder;
- parsley infusion using leaves and roots of the plant;
- infusion from a mixture: sweet clover, juniper fruits, shepherd's purse, bearberry, rose hips, nettle;
- heather infusion;
- Birch juice;
- knotweed infusion.
Particularly noteworthy is medicinal tea with the following composition: birch leaf, bearberry, horsetail, dandelion root, juniper fruits, licorice root (all 10 g), lingonberry leaf, flaxseed (20 g each). This drink is taken 3-4 times a day, 150-180 ml.
Salt diathesis can be considered a rather insidious disease that can cause serious kidney problems. This disease cannot be neglected, and at the first manifestations you should consult a doctor, because at an early stage the pathology can be treated quite easily
For preventive purposes, special attention should be paid to proper nutrition and sufficient drinking regime
Diagnosis of diathesis
In most cases, based on patient complaints, the attending physician prescribes a general urine test to diagnose diathesis.
In most cases, based on patient complaints, the attending physician prescribes a number of laboratory and instrumental tests to diagnose diathesis:
- General urine analysis. Allows you to identify the concentration of leukocytes and erythrocytes in it, as well as determine the type of salts that will be fought in the future.
- General blood analysis. Determines the amount of creatine and urea in the body. Their increased concentration indicates a decrease in kidney function.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys. As a rule, it is ultrasound diagnostics that provides a complete picture of the condition of the kidneys. On the monitor, the presence of salts in the pelvis of the organ looks hyperechoic, that is, light.
MORE: Lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis in children: pathogenesis and treatment
Therapy for the disease is determined by the causes of its occurrence and the symptoms manifested. Treatment of urinary diathesis should be comprehensive.
The first place in the treatment of such a kidney condition is given to diet. Foods high in calcium and other substances that promote the formation of salts should be excluded from the diet. Such measures will lead to normalization of salt balance.
In order to speed up the process of removing salts, various diuretics are prescribed. It should be borne in mind that some of these products also remove potassium along with salts, so drugs based on this element are used at the same time.
If kidney stones are detected, they are crushed and eliminated. The procedure is performed using the laparoscopic method. Large stones are removed through surgery.
If the course of the pathology is accompanied by infection, sulfonamides and antibiotics are additionally prescribed. One of the most common and popular means for the treatment of urinary diathesis is Phytolysin, which is a natural preparation of plant origin, which includes extracts of birch leaves, parsley roots, horsetail, etc.
In addition, Phytolysin contains essential oils of orange, pine, sage and mint. They have a diuretic effect and help relieve spasms and inflammation. The action of such a drug is aimed at washing out stones and sand formed in the kidneys, as well as crushing larger stones.
Another fairly effective remedy used for the treatment of urinary diathesis is Canephron. The composition of the drug includes rosemary leaves, lovage root, rose hips, centaury.
The product has an antibacterial effect and helps to quickly eliminate the inflammatory process. Canephron is effective not only for kidney stones, but also in the treatment of glomerulonephritis or pyelonephritis.
The drug Cystenal will help dissolve stones in the kidneys. It has a diuretic effect and helps relax the ureters. Phytolit, which has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects, is often used to treat urinary diathesis.
In addition to medications, traditional medicine is widely used in the treatment of salt diathesis. Medicines based on madder have shown high effectiveness.
Madder extract. Used to loosen stones containing phosphates.
If the functionality of the kidneys is impaired and oxalates are detected in them, you should purchase a drug based on the same madder in the form of drops at the pharmacy. Take 20 drops 2 times a day with meals. The course of treatment is 30 days.
Madder in powder form is used for removing large stones to relieve pain. Take the product 2 times a day with a small amount of liquid.
For kidney inflammation, you should take madder tincture, 1 tsp. 30 minutes after eating.
In the treatment of urinary diathesis, medicinal decoctions containing anthraglycosides are also used. Such plants include rhubarb, senna leaves, St. John's wort, etc. You need to take any of the above herbs and chop them. One tbsp. l.
pour boiling water (300 ml) over the raw material and leave for half an hour. Take in small portions throughout the day. It should be remembered that the course of treatment should not exceed five days, since anthraglycosides provoke the destruction of kidney nephrons.
In the treatment of salt diathesis, it is recommended to use plants containing saponins. These include licorice, horsetail, horse chestnut, etc.
So, urinary salt diathesis is a condition in which there is deposition of sand and various salts in the renal pelvis. This pathology occurs in both children and adults.
Diagnosis is carried out through laboratory tests of urine, as well as ultrasound.
Treatment is mainly conservative. It is carried out only after consultation with a specialist and under his guidance. Self-medication is unacceptable! Therapy for urinary diathesis involves normalizing the drinking regime, following a diet, eliminating pain, treating concomitant diseases, and improving urine outflow by taking diuretics. If conservative treatment is ineffective, surgery is performed.
Treatment of salt diathesis
- elimination of pain (painkillers, antispasmodics);
- therapy for concomitant pathologies (anti-inflammatory drugs, uroseptics, and, if necessary, antibiotics).
Often, to treat salt diathesis, it is enough for the patient to change his lifestyle and follow a special diet. The main role in therapeutic nutrition is played by a salt-free diet and optimal water regime.
Diet for salts in the kidneys
Insufficient fluid intake leads to increased concentration of urine and accumulation of salts in it.
Patients are prescribed a diet for salt-induced kidney diathesis, namely, it is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of water per day.
During intense physical activity and in hot weather, the drinking rate should be increased. This helps “dilute” the urine and remove salt crystals from the kidneys.
The diet is prescribed by the doctor based on the chemical composition of the urine (which salts are contained in excess). If these are urates, you must adhere to a limited diet:
- meat and offal;
- coffee, chocolate;
- legumes
Detection of oxalates requires the elimination of products containing oxalic acid:
- tomatoes;
- sorrel;
- rhubarb;
- spinach;
- figs
A mandatory rule is a salt-free diet. It is not recommended to add salt to food during cooking. The patient can add salt to the food himself to taste, but not more than 2 grams. salt per day. It should be taken into account that industrially produced products contain excess amounts of sodium chloride. This applies to semi-finished products, sauces, smoked meats, canned food, sausages, sausages, and cheeses. You should buy special unleavened bread or bake it yourself.
With salt diathesis, you need to avoid foods rich in potassium, calcium and phosphorus. These are dried fruits, nuts, cottage cheese, bananas, etc.
Removing salts from the body
Proper nutrition prevents increased salt formation and helps prevent stones.
But if deposits have already formed in the kidneys, they are removed by increasing daily diuresis, in other words, by “flushing” the kidneys.
For this purpose, diuretics are used, both medicinal and folk (herbal medicine). To dissolve stones, special drugs are prescribed (Fitolizon, Cyston).
You cannot take medications on your own without a doctor’s prescription! If there are undetected large stones in the kidneys, diuretics are contraindicated due to the risk of urinary tract blockage.
Improper use of sand dissolving agents can cause the formation of stones.
Surgery
Progressive salt diathesis, which has developed into full-fledged urolithiasis, is treated surgically. Large stones are removed during surgery, small stones are crushed using remote lithotripsy (using electromagnetic waves), after which they are released naturally.
Radical treatment does not guarantee the absence of relapses. Once stones and sand are removed, the tendency for them to form does not go away. A patient with salt diathesis must adhere to a lifelong diet and undergo preventive treatment.
Urine formation during salt diathesis
The kidneys are not limited to just producing urine. These two small organs control many important aspects of the body:
- cleansing the blood of waste and toxins;
- blood pressure level;
- the amount of fluid contained inside the tissues and circulating through the vessels;
- the formation of red blood cells containing hemoglobin;
- quantitative content of the main components in the blood - sodium, potassium, calcium;
- exchange of vitamins and chemical signal substances - hormones.
The kidney is the body's main cleansing station.
Urine is formed in two stages in the nephrons. These small structures are found in large numbers in each kidney. Blood filtration occurs in the glomeruli. The filtrate from the glomeruli enters the tubules, which sort all the chemicals in it into useful and harmful. The first will go into the blood, the second will become the final urine.
Kidney function - video
Salts are one of those substances that are completely controlled by the kidneys. They are formed in the body as a result of the transformations of oxalic, uric, phosphoric acid and cystine and have the appropriate names: oxalates, urates, phosphates, cystinates. These salts are present in any body and are found in urine in very small quantities. Under these conditions, salts transit through the kidneys and are excreted in the urine.
Salts in urine are a product of the activity of the renal tubules
Salt diathesis is a kidney disease in which the final urine contains too much oxalate, urate or phosphate. The changed composition of urine with a large amount of salts leads to stone formation - nephrolithiasis. The salts precipitate, bond with each other and form a hard calculus. Thus, each case of urolithiasis is preceded by salt diathesis.
Synonym of the disease: dysmetabolic nephropathy, tubulopathy.
Why does salt diathesis occur?
Doctors believe that this pathology has a hereditary etiology, so it can be detected even in young children. However, the disease may not manifest itself for many years and may occur in an adult.
Most often, sand begins to form when the urinary system ceases to cope with the loads placed on it by a person with a predisposition to the formation of salts. When the latter are in the urine, they irritate the mucous membrane of the bladder and urethra, causing inflammation - urethritis, cystitis, cystopyelitis, prostatitis.
If an ultrasound reveals individual crystals, then this does not at all indicate the presence of pathology, but if a urine analysis shows that it is quite concentrated over a long period, then grains of sand are eventually formed, and then stones of different shapes and sizes are formed. That is, hereditary urinary diathesis is a prerequisite for the development of urolithiasis.
Description of the pathology
Urinary salt diathesis is a disease in which the body has an increased content of calcium salts of uric acid, most often urates and oxalates. Otherwise, this pathology is called uricuria. There are two ways this disorder can develop:
- Salts are formed in increased quantities due to metabolic disorders. Such metabolic disorders can be congenital or acquired. As a result, excess salts settle in the kidneys and are then excreted in the urine.
- Calcium salts are formed in excessive quantities due to poor nutrition. Their appearance is promoted by foods high in organic acids. If a person abuses meat and fish food, this can cause an increased concentration of urates. If the diet is dominated by vegetable dishes, then the level of oxalates in the urine increases.
The development of pathology is promoted by dehydration. With a lack of fluid, salts are not washed out of the body. A urine test reveals a reddish sandy sediment. With urinary diathesis, echogenic inclusions are detected in the kidneys. They are determined during an ultrasound examination.
Uricuria is considered a borderline state between normal and pathological. Over time, the patient's urine density and acidity increases, which contributes to the crystallization of sand. The risk of urolithiasis increases, which manifests itself in severe attacks of renal colic.
Salt diathesis in children
In childhood, this disease is detected very rarely, unless it is a congenital pathology. Most often, treatment is required during adolescence. The reasons for the development of salt diathesis in children are poor diet, in particular the abuse of protein products. As a result, protein metabolism is disrupted and large amounts of uric acid accumulate in the urine and blood. The disease can be identified by such signs as moodiness, headache, aching back pain, loss of appetite, sudden weight loss, fatigue, memory loss and inability to concentrate. The first step when such symptoms appear is to reduce the amount of animal protein. It is impossible to completely exclude protein products, as this can harm the normal development of the child (amino acids contained in protein products are the main building material for a growing organism).
You also need to limit the consumption of sweets, offal, and mushrooms. You need to lean on vegetables, fruits, dairy products, and cereals. When treating a disease in children, the doctor usually prescribes vitamin therapy and drug support (metabolic drugs).
General symptoms
Clinicians note that at the early stage of development of salt diathesis, symptoms may be almost completely absent. Signs of salt diathesis of the kidneys can only be detected by clinical examination of the bladder.
As the pathological process develops, the following symptoms can be observed:
- burning when urinating;
- pain in the lower abdomen, which can sometimes radiate to the side;
- feeling of incomplete emptying after urination;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- frequent urge to urinate.
However, it should be noted that such symptoms may indicate other pathological processes in the kidneys or genitourinary system. Therefore, with such a clinical picture, you should immediately seek competent medical help, and not engage in independent treatment.
Urolithiasis (salt) diathesis
Features of the clinical picture of salt diathesis of the kidneys
In most cases, the main symptoms of the disease develop gradually, as a result of which patients do not pay attention to them, attributing obvious signs to fatigue or a cold. That is why it is almost impossible to detect the disease at an early stage. Most pathological manifestations develop over several months and even years, which complicates the doctor’s work. The clinical picture of salt diathesis of the kidneys includes the following symptoms:
- increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees;
- unpleasant, pulling and cutting sensations when urinating;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- swelling, redness and microcracks on the surface of the urethra;
- release of a small amount of blood when blood vessels are damaged;
- detection of pathological foreign impurities and clots in the urine;
- headaches in the temples and back of the head;
- nausea and vomiting not associated with meals;
- weight loss up to 3%;
- dry skin, brittle hair and delamination of nail plates;
- formation of bruises under the eyes;
- weakness and decreased performance.
Diagnostics
First of all, the doctor clarifies the person’s medical history and lifestyle. After a personal examination, laboratory and instrumental tests are carried out. As a rule, the standard research program includes the following:
- clinical examination of urine;
- biochemical urine test;
- urine test for the amount of salt;
- blood test for ammonia;
- general blood analysis.
As for instrumental research methods, this includes the following:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- X-ray examination of the genitourinary system.
An accurate diagnosis can only be made based on the results of clinical studies. Treatment of salt diathesis without an accurate diagnosis can cause the development of more complex pathological processes.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the diagnosis, the following tests are done:
- general urine analysis. They check color, transparency and other external characteristics, as well as the chemical composition. At the initial stage, a high content of uric, oxalic and other organic acids in various combinations can be detected.
- general blood analysis. Thanks to it, the presence of an inflammatory process is confirmed, and thanks to biochemistry, an increased content of urea, creatinine, and nitrogen in the blood, which are considered indirect signs of uric acid diathesis.
- Ultrasound examination - salt in the kidneys is determined as echo-positive inclusions. If the disease has already reached the acute stage, sand and stones are visible on ultrasound.
Causes and pathogenesis
The tendency to develop urinary diathesis is of congenital origin, but quite numerous factors can provoke such a condition. Most often, the pathological syndrome develops in adolescence and childhood in the presence of kidney failure. In women and men, a similar problem arises for various reasons:
- Chronic inflammatory kidney lesions;
- Chronic dehydration;
- Unhealthy diet with abuse of salty and smoked, spicy or fatty, as well as incompatible dishes, which provokes a metabolic imbalance, negatively affecting the activity of the urinary structures;
- Prolonged refusal to eat;
- Chronic pathologies and inflammations, traumatic renal lesions;
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals, leading to immune instability;
- Intoxication;
- Congenital renal pathologies, hereditary renal failure;
- Long-term antibiotic therapy;
- Excessive physical overload, etc.
In fact, urinary salt diathesis is a borderline condition, which is characterized by a tendency to the appearance of various pathological processes. This organic feature provokes an increased content of salts in urine. The process of formation of salt diathesis is caused by metabolic disorders, as a result of which uric acid crystals settle in the kidney tissues. Against the background of metabolic failures, urate is formed, which can be seen by the characteristic reddish urinary sediment. In the kidneys, stones form and various pathological conditions develop. External factors such as diet, drinking regime, environmental climate, etc. are also of no small importance in the pathogenesis of salt diathesis.
Photo of salt in urine
Diagnosis of pathology
When identifying a disease, blood and urine tests will provide important information. They will allow you to assess the patient’s health status, determine the location of the source of inflammation, and the degree of progression of the pathology. In the chronic form of the disease, an increase in urea, leukocytes and proteins is observed in urine. When human immunity is not able to fully resist viruses and bacteria, tests show a decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells.
By determining the composition of mineral salts, the cause of their accumulation can be determined. To do this, a three-glass sample and a daily urine test are carried out. To select the right antibacterial drug, doctors determine the pathogen through biochemical analysis.
When crystallization of salts has occurred in paired organs with the formation of stones, additional X-rays, CT and MRI are done, and ultrasound is prescribed. Hardware diagnostics makes it possible to determine the size of formations, their location, and also differentiate the disease from other pathologies.
Treatment
Treatment of salt diathesis includes not only drug therapy, but also a special diet and consumption of the optimal amount of fluid.
Drug therapy includes taking drugs with the following spectrum of action:
- anti-inflammatory;
- diuretics;
- vitamin B6;
- preparations containing magnesium;
- potassium and sodium complex;
- for general strengthening of the immune system.
Drug treatment of the bladder must be supplemented with diet. The diet includes the following nutritional recommendations:
- exclusion from the diet of fatty, spicy, salty foods;
- complete exclusion of alcohol;
- preference should be given to steamed food;
- limiting dairy and fermented milk products;
- exclusion of vegetables from the diet, except pumpkin and green peas.
Daily salt intake for adults as part of the diet should be no more than 12 grams.
Separately, fluid intake should be normalized. The daily norm for an adult is at least 1.5 liters. During the diet period, it is useful to drink mineral water, but without gas. A doctor can calculate the exact amount of water based on the person’s weight and age.
If you strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding treatment and diet, then salt diathesis will not cause significant complications.
Diet during treatment
Diet for salt diathesis of the kidneys is an obligatory element of complex therapy. Her diet should be agreed with her doctor. The most common diet involves setting table 7 (according to Pevzner). The menu is specified by the doctor, taking into account the type of salts predominant in the urine.
The following products are completely prohibited:
- when oxalates are detected: tomatoes, sorrel, figs;
- for urates: legumes, cocoa, coffee, chocolate;
- If there is a high concentration of uric acid, sorrel is strictly prohibited.
An important condition of the diet is limiting salt intake. Table salt can be added to dishes at a rate of no more than 2 g/day. It is advisable to consume bread only from salt-free dough. If it is not in the store, then it is better to bake it yourself. Regardless of the type of stone formation, it is recommended to exclude from the diet: semi-finished products, cheeses of all types, canned food, marinades, pickles, smoked foods, dried fruits, bananas, nuts of all types, cottage cheese, spicy dishes, seasonings, spices. Any type of alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited.
Desirable foods are: lean meat and fish, poultry, dairy products and whole milk, vegetables and fruits (not prohibited), and herbs. Watermelons, melons, and pumpkin have good diuretic properties. When signs of anemia appear, foods containing iron are useful: strawberries, pomegranate, apples.
Drinking regime during treatment should be controlled. During the day, a sick person should drink at least 1.8-2 liters of liquid, and with increased physical activity - at least 3-3.2 liters. It is most advisable to use compotes, rosehip decoction, diluted natural juices, and cranberry juice. In extreme cases, the daily requirement is covered with clean water. Carbonated drinks are prohibited.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is only possible if recommended by a doctor. It should also be noted that folk remedies are only appropriate simultaneously with traditional treatment. Otherwise, it is only possible to remove the symptoms for an indefinite period, but not the cause of the pathology itself.
Folk remedies for the treatment and prevention of salt diathesis involve taking herbal decoctions that are diuretic:
- corn silk;
- chamomile;
- black elderberry flowers.
However, it should be understood that it is better to use folk remedies after consulting a doctor.
Prevention
Prevention of this disease includes the following recommendations:
- proper, balanced nutrition;
- consume the optimal amount of fluid daily;
- annual examination by a urologist;
- excluding alcohol.
By adhering to such rules, you can avoid not only salt diathesis, but also many other ailments.
Is everything correct in the article from a medical point of view? Answer only if you have confirmed medical knowledge Share the article: Read us on Yandex.Zen Diseases with similar symptoms: Bacteriuria (matching symptoms: 4 out of 5) Urolithiasis (urolithiasis ) (matching symptoms: 4 out of 5)