What is osteochondrosis?
Osteochondrosis is a disease of the spine, a characteristic feature of which is degenerative-dystrophic damage to the intervertebral discs, and then to the vertebral tissues themselves.
Dystrophic changes in the disc lead to weakening of its outer fibrous ring. Therefore, patients with osteochondrosis often experience such serious complications as protrusion (bulging of part of the disc) and vertebral hernia (dangling of the nucleus pulposus of the disc into the spinal canal).
According to the results of medical research, every second person experiences problems with the spine after 30 years. In 70% of cases, the cause of pain in the spine is considered to be osteochondrosis, which is a neurological disease affecting the ligaments of the spinal column.
Like any other disease, osteochondrosis cannot occur on its own, out of the blue, striking the back with acute pain. The first signs of spinal osteochondrosis do not appear immediately, but gradually.
Depending on the location of pain, there are three types of osteochondrosis:
- Cervical region;
- Thoracic department;
- Lumbar region.
Important! The main complications of osteochondrosis include protrusion of intervertebral discs, Schmorl's hernia, ankylosis of the spine, pinching of the roots of spinal nerves and blood vessels.
Treatment with a cervical collar
The Shants collar provides complete rest for the cervical region.
It securely fixes the neck, so that the head and neck are strictly in the same position. The Shants collar is used in the acute stage of the disease. There are several types of Shants collars, so you should choose the type prescribed by your doctor. For the treatment of neck osteochondrosis, there are also inflatable collars. They are an inflatable layer. Using a bulb, air is pumped into the layer, and then the layer is inflated. This collar is also effective in the treatment of osteochondrosis. But unlike the Shants collar, it allows the patient to move his head and neck. It is used mainly during the recovery period after illness.
Collars are worn on average 2 – 3 hours a day. Usually the duration is set by the doctor depending on the degree of development of the disease and symptoms. Treatment with a collar lasts about a month.
Causes
According to many experts who have studied this disease, the main cause of osteochondrosis is an incorrectly distributed load on the spinal column. As a result, in patients, directly in places where excessive physical pressure is applied, a change in the structure of cartilaginous tissue occurs.
Causes of spinal osteochondrosis:
- Hereditary predisposition to the disease.
- The presence of diseases of the endocrine system is a metabolic disorder.
- The development of orthopedic diseases, for example, flat feet, curvature of posture, diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
- Various injuries, bruises of the spine.
- Lifestyle: lack of activity, poor diet with a predominance of fast food and unhealthy foods.
- Having excess weight.
- Bad habits – smoking, alcoholism.
- Stress, fatigue.
- Pregnancy.
In most cases, the causes of osteochondrosis are associated with a person’s professional activity. The risk group includes the following professional categories:
- accountant;
- cashiers;
- IT workers;
- office employees;
- professional athletes;
- vehicle drivers.
However, it has been noted that signs of osteochondrosis appear much more often in women than in representatives of the stronger sex.
What is the treatment?
Traditional therapeutic methods
Osteochondrosis of the back can be cured using complex treatment, which is based on modern medications. The disease can be treated with the following medications:
- Painkillers that are used to make blockades are Lidocaine, Novocaine.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These drugs are taken in courses with breaks.
- Chondroprotectors.
- Warming ointments and topical gels.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment, which includes the following procedures, effectively helps with osteochondrosis of the spine:
Kinesitherapy gives good results for this disease.
- Reflexology. During the manipulation, a targeted effect occurs on the damaged area, as a result of which the patient’s pain and spasms are reduced, and blood flow improves.
- Kinesitherapy. During the procedures, a person moves a lot, performs therapeutic exercises, exercises on exercise machines, and stretches the spine.
- Electrophysiotherapy. This subtype of physiotherapy includes UHF, pulsed current treatment, transcutaneous electrical neurostimulation, and more.
- Swimming. Thanks to this method, it is possible to normalize the condition even in patients who have been diagnosed with severe osteochondrosis and find it difficult to perform gymnastics in the air.
Features of manual therapy
The general principles of treatment for spinal osteochondrosis include procedures with a manuologist who performs massage, affecting all vertebrae. For a positive result, a minimum of 20 sessions are required. Before starting this treatment, you should consult your doctor, as there are a number of contraindications:
- diseases of internal organs;
- carrying a baby;
- cancer tumor;
- high blood pressure;
- recent injuries to the spine or legs.
When is surgery required?
Compression of the spinal cord is an indication for surgical intervention.
If chronic osteochondrosis of the spine has developed in adults and conservative therapy does not help, then radical therapeutic measures are resorted to. Surgical intervention is also necessary in the following cases:
- vertebral subluxation;
- hernia;
- acute compression of the spinal cord;
- spinal deformity.
After surgery, the patient recovers for a long time, taking medications and undergoing physical therapy.
Diet and gymnastics
Treatment of spinal osteochondrosis is impossible without special nutrition and gymnastic exercises. The diet involves split meals in small portions - at least 6 times a day. The daily fluid intake is 1.5 liters. It is recommended to cook all products using a double boiler so that the maximum amount of vitamins enters the body. With osteochondrosis of the spine, limit grapes, beans, flour, spicy, sweet, salty and other harmful foods. Allowed to use:
- fresh seasonal fruits and vegetables;
- dairy products;
- lean meat and fish;
- aspic;
- nuts and sunflower seeds;
- mushrooms;
- various cereals.
Exercise therapy will help strengthen weakened back muscles.
Thanks to gymnastics and exercise therapy, it is possible to strengthen the muscular and joint apparatus, as well as correct posture that has been affected by osteochondrosis. You should not be treated with a general set of exercises, since it will not suit everyone. You should consult a doctor who will draw up an individual training plan, taking into account the complexity of the pathology and the condition of the spine.
Stages of development
The development of osteochondrosis occurs in 4 distinct stages (degrees):
Osteochondrosis stage 1
It is characterized by the onset of a pathological process in the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc - its dehydration (dehydration) occurs, and subsequently the height of the disc decreases. At the same time, cracks begin to appear in the fibrous ring. At this stage, the patient usually does not feel any changes. Discomfort may occur when sitting in a sitting position that is unusual for a person, or when actively exercising.
Stage 2
At the second stage of osteochondrosis, continuation of degenerative changes leads to disc protrusion. The gaps between the vertebrae are reduced, and the fibrous capsule is destroyed. As a result, the roots of the spinal nerves are pinched, which provokes the appearance of point pain, the intensity of which increases with bending, turning, and other movements. Possible weakness and decreased performance.
Stage 3 osteochondrosis of the spine
It is characterized by the abrasion of the cartilage lining between the discs; the thinning of the tissue is clearly visible if you take an x-ray. The symptoms of spinal osteochondrosis are pronounced, intense, and the pain does not go away, and only strong painkillers can relieve it.
Stage 4
The fourth stage is the most complex neurological disorders in the spinal system, expressed in partial or complete limitation of joint mobility. With this diagnostic condition, bone growths (osteophytes) form at the site of the vertebral joints, which cause microtrauma to the nerve branches and adjacent segments of the spine.
In most cases, the symptoms of grade 4 osteochondrosis do not cause pain or discomfort, as the joints take on a fossilized appearance.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis in adults
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic change (destruction) of the bone tissue of the spine, articular cartilage, ligaments and intervertebral discs. As the disease progresses, pathological mobility of the spinal column develops, in which soft tissues, nerve fibers and blood vessels located near the lesion are infringed - this is how pain occurs.
The main symptoms of osteochondrosis:
- pain in the back, cervical region, lower back, shoulders and even ribs;
- discomfort, stiffness of the back during certain movements, lifting something;
- numbness of the extremities (arms and/or legs);
- aching sensation in the arms and legs, chills;
- muscle spasms;
- disturbances in the functioning of the genital organs;
- headaches, dizziness;
- pain in the heart area;
- sensory disturbance;
- muscle hypotension;
- increased fatigue, sometimes even in the eyes.
Excessive physical activity, overwork, hypothermia, injuries, body concussions and exposure to vibration can contribute to the occurrence of acute symptoms.
| Osteochondrosis | Symptoms and signs |
| Cervical |
|
| Chest |
|
| Lumbar | The main signs of the disease are:
|
What are the types of osteochondrosis by localization?
The classification of spinal osteochondrosis has many forms and criteria. They differ in the location of the affected area and severity. All types of osteochondrosis are pathologies that are fraught with destructive changes in cartilage and connective tissue.
The most common and understandable classification for the common man, far from medicine, is based on the location of the lesion:
- Cervical osteochondrosis - it is characterized by occipital, cervical and interscapular pain syndromes. This disease has been increasingly diagnosed in young people over the past decade.
- Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is very rare, since it has more discs than the cervical and lumbar spine combined, the discs are smaller and thinner. Part of the load is taken by the ribs. Therefore, degenerative and dystrophic changes rarely occur in the intervertebral discs of the thoracic spine.
- Lumbar osteochondrosis most often occurs in people over forty years of age from a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle. It is characterized by severe pain in the lower back, pinching of the nerves and arteries of the abdominal organs, and many concomitant diagnoses of internal organs.
Complications
Degenerative processes that primarily affect intervertebral discs lead to a decrease in their density and loss of their shock-absorbing functions. The consequence of such changes is excessive mobility of the spine, facet joints, muscles and ligaments are affected.
The paravertebral structures involved in destructive processes cause compression (squeezing) of the spinal cord and its nerve endings. As a result, a patient with osteochondrosis feels pain, which is accompanied by the following symptoms and diseases:
- severe headache, migraine;
- decreased visual acuity;
- partial hearing loss;
- radiculopathy (radiculitis);
- autonomic dysfunctions (VSD);
- dysfunction of the genitourinary system;
- sciatica (compression of the sciatic nerve);
- intervertebral hernia;
- spondyloarthrosis;
- lumbago, lumbodynia;
- osteophytosis, spondylosis;
- spinal canal stenosis.
The worst thing is that along with osteochondrosis, other diseases begin to appear. The fact is that the neurovascular bundle is damaged, the blood supply deteriorates, and as a result, a disease of the entire organism as a whole.
Exacerbation of osteochondrosis
In spring, aggravation of the lower parts of the spine often occurs; in winter, the thoracic region becomes aggravated. Exacerbation may occur with changes in weather, stress, or physical exertion. When the disease worsens, painkillers, local ointments, and drugs that relieve swelling and muscle spasm are prescribed. Diuretics are used for severe edema, but sodium and potassium preparations must be used at the same time.
Symptoms and consequences of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
The most common type of osteochondrosis is the lumbar region. This is due to the fact that it is the lower back that experiences the greatest load in the process of daily life.
In the first stage, the main symptom is a slight stretching in the lower back. People rarely attach importance to such minor ailments. As the intervertebral discs wear out, negative symptoms also increase. In particular, the patient can no longer lie or sit in one position for a long time due to pain.
At the third or fourth stage of lumbar osteochondrosis, the following occur:
- lumbago - sharp and sudden pain, the result of which can be partial immobilization of the patient;
- sciatica - unilateral infringement of the sciatic nerve;
- radiculitis - compression of nerve endings in the lumbar spine;
- weakness of the lower extremities, muscle atrophy, venous congestion, dysfunction of sexual function and the functioning of the abdominal and pelvic organs are also often observed;
- radiculoischemia - failure of blood circulation as a result of compression of blood vessels.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis is based on the following methods:
- Taking an anamnesis involves studying the patient’s complaints and finding out the time of occurrence, causes, duration, and features of the manifestation of the disease.
- Physiological examination:
- a diagnosis of the patient’s body position, gait, and range of motion is carried out;
- the skin is examined to detect areas of redness, peeling, and rash;
- painful areas are palpated to determine local temperature, the presence of edema, muscle spasms, and induration;
- to detect the area of irradiation of pain, percussion is performed with a finger or a special hammer;
- pricking with a needle helps determine pain sensitivity.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing osteochondrosis:
- X-ray diagnostics plays a key role in this disease. Conventional radiography can reveal signs of the disease, such as narrowing of the gap between the vertebrae.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a research method that allows for accurate diagnosis of processes occurring in the spinal region. With its help, in particular, it is possible to determine the presence of a herniated disc and its location.
- Computed tomography (CT) is similar in its diagnostic capabilities to MRI. The disadvantage of CT is the presence of radiation exposure during the study.
Polysegmental osteochondrosis
Manifestations of the disease are not in one, but in several parts of the body. For example, there is often a combination of damage to the third and twelfth vertebrae - in this case, osteochondrosis will be considered polysegmental.
Therapy in this case will be exactly the same as for standard signs of cervical or thoracic osteochondrosis. Magnetic therapy and other physical procedures have proven to be excellent for exacerbation of pain and discomfort due to polysegmental chondrosis. Now you know what types of spinal osteochondrosis exist.
How to treat spinal osteochondrosis?
There is no specific and only correct method of treating osteochondrosis - this process, under any circumstances, requires an integrated approach. If the doctor claims otherwise, you should think about his professional qualifications and consider looking for another specialist.
The comprehensive program traditionally includes the following components:
- physiotherapeutic methods of influence;
- special exercises and massages;
- manual therapy methods;
- drug treatment;
- reflexology, electrophoresis, etc.;
- traction.
Recommendations for treating osteochondrosis at home:
- Giving up bad habits and gradually transitioning to acquiring good habits. Smoking and alcohol lead to spasms of the already pinched vessels of the spinal artery.
- Dieting - avoiding fatty and cholesterol-containing foods: eggs, broths, poultry and pig skins.
- Limit the consumption of strong coffee and tea, gradually switch to herbal teas and fresh juices.
- Choose the right mattress and pillow for sleeping, preferably orthopedic.
- Restoring normal blood circulation in stiff muscles and discs through massage, self-massage, a complex of physical therapy, compresses, rubbing and taking herbal infusions and alcoholic tinctures of herbs.
Drugs for osteochondrosis
When treating this category of patients, specialists prescribe medications that have the following properties: relieve inflammation, restore the functions of the musculoskeletal system, stimulate the regeneration of intervertebral disc tissue and cartilage, and prevent the progression of osteochondrosis.
| NSAIDs |
The action is aimed at reducing the inflammatory process in the spine and relieving pain. |
| Antispasmodics | In case of osteochondrosis, they reduce pain and relieve muscle spasms:
|
| Antioxidants |
|
| For blood microcirculation |
|
| Chondroprotectors |
The action of such drugs is aimed at regulating metabolic processes in the body and rapid regeneration of spinal cartilage. |
| Injectable drugs |
|
| Gels and ointments |
|
Treatment of osteochondrosis follows the traditional path of treating many diseases of the musculoskeletal system: NSAIDs are prescribed to eliminate the inflammatory process in tissues, chondroprotectors to restore the level of synovial fluid and corticosteroids if the first two types of drugs are ineffective.
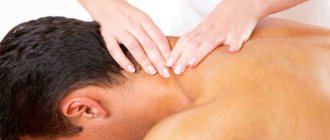
Massage
In order to get rid of osteochondrosis, various therapeutic procedures are used, including massage. It has many beneficial properties - muscle tone is relieved, blood flow in the spine is stimulated, intervertebral discs become stronger.
Manual therapy for osteochondrosis
Manual therapy relieves acute pain and helps restore posture. One of the most commonly used methods is visceral therapy. During its implementation, high-quality treatment of joints is carried out, blood circulation processes are improved, and the immune system is strengthened. Allows you to prevent exacerbation of various chronic ailments.
Exercise therapy - physical therapy
Physical therapy or exercise therapy for osteochondrosis is very important. Thus, special exercises to strengthen the back muscles contribute to the formation of a muscle corset, which in turn ensures an even distribution of the load on the spine. In addition, thanks to regular exercises, blood circulation and nutrition of tissues, including intervertebral discs, improve, the patient develops correct posture, and the range of movements in the spine increases.
In order for physical therapy and gymnastics to bring the expected effect, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Exercises for osteochondrosis should be performed regularly.
- All movements should be smooth and slow.
- Breathing should be smooth.
- Monitor your heart rate.
- If discomfort and pain occurs in the muscles and spine, you need to reduce the amplitude and intensity of movements.
- Gymnastics and physical education can be done at any time of the day.
- For therapeutic exercises and physical education, choose comfortable clothes made from natural fabric.
- Before you start doing therapeutic exercises and physical education, you should consult your doctor.
Physiotherapy
Helps effectively combat painful manifestations in places where the pathological process is localized. There are many types of physiotherapeutic interventions. Most often they resort to the use of magnetic therapy, ultrasound therapy, and exposure to low-frequency currents.
The effects of physical procedures can be as follows:
- normalization of metabolism in affected areas;
- increasing the body's resistance;
- anesthesia;
- improvement of microcirculation in the spine and paravertebral tissues;
- removal of swelling;
- reduction of the inflammatory process;
- improving spinal mobility.
Rehabilitation treatment
It is possible to restore health after osteochondrosis, the main thing is to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and undergo rehabilitation treatment. This option is used only during remission of the disease, when there is no severe pain in the back. Not recommended for use during exacerbation. Treatment of osteochondrosis is carried out using several methods:
- Physiotherapy.
- Sauna, underwater hydromassage, classes in the pool.
- Working with a psychologist.
- Compliance with diet, nutrition correction.
- Laser treatment.
- Manual therapy.
- Use of healing mud.
- Magnetotherapy, electrophoresis.
- Massage.
Treatment
First of all, the doctor explains to the patient what osteochondrosis is and how to treat it. Describes a set of activities that must be carried out over a long period.
Treatment of the disease is carried out taking into account the stage. During the initial stage of the disease, massage, physiotherapy, and physical therapy are indicated. But as the degenerative process progresses, it is necessary to use various orthopedic devices to immobilize the spine. Drug treatment is also necessary.
Surgical intervention is indicated for complications and in case of ineffectiveness of conservative treatment.
Medications
The most important goals of treatment with pharmacological drugs are to relieve pain, eliminate inflammation of the nerve roots, restore the structure of cartilage, improve blood circulation and nutrition, and stop the development of pathology. There are several groups of medications that can be prescribed in this case.
In pharmacies they are presented in various forms and in a wide variety. The price of medicines may vary and you can always choose the most affordable one.
Table No. 2. Drugs used in the conservative treatment of osteochondrosis:
| Drug, composition, pharmacological group | Therapeutic effect | Instructions for use |
| Teraflex. Contains glucosamine and chondroitin. Refers to chondroprotectors. | Slows down the processes of degeneration of cartilage tissue, promotes its restoration. | Take 1 capsule for a month. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated. |
| Movalis. Contains meloxicam. Belongs to the group of NSAIDs. | It has an analgesic effect and reduces inflammation. | Take one tablet for pain. In case of severe pain, intramuscular injections of the drug are used. |
| Combilipen. B vitamins – pyridoxine, thiamine, cyanocobalamin. | Improves the conductivity of nerve impulses, restores microcirculation in the area of the affected cartilage. | A course of treatment is carried out with intramuscular injections. |
| Sirdalud. Contains tizanidine, which is a muscle relaxant. | Relaxes muscles, relieves tension, relieves pain. | Take one tablet 2 times a day. |
Medicines are prescribed according to doctor's indications. Self-medication may be ineffective, and in some cases even harmful.
Physiotherapy for osteochondrosis
What to do with osteochondrosis, besides taking medications, to speed up recovery? One of the most effective ways to treat this disease is physical therapy.
Its advantage is its selective effect on the site of the disease. Physiotherapy helps reduce pain, eliminate inflammation, and increase overall immunity. With their help, muscles relax, metabolic processes and blood circulation are normalized.
For osteochondrosis, the following are successfully used:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- shock wave therapy;
- quartz;
- electrophoresis;
- exposure to low frequency electric currents.
Physiotherapy is not performed if the patient is in serious condition, with an exacerbation of the disease, cancer, or mental disorders. In other cases, physical therapy has a beneficial effect on the recovery process, enhances the effect of medications, which allows them to be reduced in dosage.
You can see how some procedures are carried out in the video in this article.
Physiotherapy
Physical exercise is prohibited during the acute period of the disease. After eliminating this period, the doctor prescribes therapeutic exercises, which he develops together with the instructor individually for each patient.
With the help of exercises, the muscle corset is strengthened, which prevents curvature of the spine and allows you to correctly and evenly distribute the load on the vertebrae. With regular physical activity, medicinal substances penetrate the spine in higher concentrations than in their absence.
You must exercise under the guidance of an experienced instructor and carefully monitor your condition. If discomfort or severe pain occurs, the exercise should be stopped.
An approximate set of exercises for osteochondrosis
Prevention
Knowing what osteochondrosis is and its consequences, it would be useful to think about prevention.
Preventive measures are quite simple and easy to follow for anyone who cares about their health:
- injury prevention;
- regular physical training (swimming is very useful);
- maintain normal weight;
- do not load the spine;
- ensure correct posture;
- do not stay in one position for a long time;
- Avoid sudden movements when lifting weights.
If these rules are followed, the period of remission will be long.
Osteochondrosis is a rather serious disease. But with timely consultation with a doctor and adequate treatment, it is possible to stop its destructive effect.
Diet
The objectives of the diet for osteochondrosis include:
- normalization of metabolic processes;
- prevention of salt deposition in the spine;
- restoration of damaged cartilage structure;
- strengthening the ligaments of intervertebral discs;
- reducing excess weight and preventing obesity. It is known that excess weight increases the load on the spine and provokes the development of osteochondrosis, so patients with this disease are often diagnosed with obesity.
Dietary nutrition should be selected by the attending physician depending on the presence/absence of concomitant diseases. There is no single diet for osteochondrosis.
Diet No. 15 according to Pevzner, which contains all the necessary macronutrients, minerals and an increased amount of fat/water-soluble vitamins and carbohydrates, can be taken as the basis for therapeutic nutrition for cervical and lumbar osteochondrosis for patients with normal body weight. The energy value of the diet is 2600-2700 kcal (85-90 g protein, 90-95 g fat and 350-400 g carbohydrates).
The diet menu for osteochondrosis should be low-calorie, balanced, with an enriched vitamin and mineral composition. It is advisable to eat food cooked in a double boiler about 6 times a day and in small portions.
What products should be included in the menu:
- dairy products (whole milk and fermented milk products);
- vegetable dishes, greens. Particular emphasis should be placed on cabbage, cucumbers, radishes, celery, and beets;
- fruit and berry dishes, including jellies and compotes;
- vegetable oils;
- low-fat meat;
- jellied dishes, jellied meat;
- dark varieties of bread, dry cookies, muffins;
- eggs;
- nuts, seeds, sesame seeds;
- cereals;
- seafood (fish, shrimp, seaweed, mussels);
- still water.
In the diet for osteochondrosis of the spine, the following should be excluded:
- fatty concentrated broths,
- fatty red meat,
- refractory animal fats, poultry (duck goose),
- coffee and drinks containing caffeine (strong tea, chocolate).
The consumption of sweet foods and alcohol-containing drinks is limited.
Causes of pathology
Despite the fact that osteochondrosis is a fairly common disease, the reasons why the pathology develops have not been fully established.
The main factors are considered:
- excessive load on the spine;
- injuries;
- occupational hazards - heavy lifting or prolonged work in an uncomfortable, motionless position;
- excess body weight;
- heredity;
- poor posture.
Working in a static position is a common cause of the development of the disease
Osteochondrosis develops to one degree or another in almost all older people and is one of the processes of aging of the body.
Treatment of osteochondrosis with folk remedies
Before using folk remedies at home, be sure to consult with your doctor, because... There may be individual contraindications.
- Radish. Mix 300 ml of radish juice, 200 g of honey and 100 ml of vodka. Rub the resulting mixture onto your back. This folk remedy also helps with radiculitis and rheumatism.
- Finely crush the garlic and apply it in the evening before bed to the sore spot for 5-7 minutes, avoiding burns. After this, you need to rub sunflower oil into the sore spot and apply a warm bandage overnight.
- Ointment based on plantain and sage for osteochondrosis. To prepare this healing ointment, you need to mix 40 grams of Vaseline, 50 milliliters of vegetable oil and 2 tablespoons of crushed sage and plantain leaves. Apply the resulting mixture to the sore spot and rub in with light stroking movements. After rubbing, the back should be wrapped in warm woolen cloth.
- Sedative collection. You need to mix 2 tablespoons of calendula, licorice and mint with one tablespoon of yarrow, pour the mixture with a liter of boiling water and let it brew for 12 hours. Then the strained infusion is taken three times a day, one-third of a glass, throughout the course of treatment.
- Warm up your arms, neck and shoulders in a hot shower. After quickly wiping, we smear these areas with honey and glue the palm together, sharply tearing it away from the skin. We do this until the palm stops sticking. Then wrap yourself in a sheet, compress paper and a warm scarf. Go to bed. Wash off in the morning.
- Horseradish leaf. Take one horseradish leaf and steam it with boiling water. Turn the leaf over with the inside facing you and apply it to the sore area. Wrap it up well and go to bed. In the morning you will feel that the pain has subsided.
Prevention of osteochondrosis.
To prevent osteochondrosis and prevent its exacerbations, it is advisable to follow several rules that will reduce the load on the spine: - always keep your back straight. — try not to lift heavy objects. If necessary, lift them by crouching rather than bending over. — move more often, do not let your back muscles atrophy. — hang on the horizontal bar and swim as often as possible.
A set of therapeutic exercises for osteochondrosis . 1. Stand with your hands on your hips. Start tilting your head: forward, backward, right, left. You need to do 10 head tilts in each direction. 2. Stand with your hands on your hips. Move your pelvis: forward and backward. In each direction - 10 movements. 3. Hanging or half-hanging on a bar that can be adjusted above the door (7-10 s). 4. Get down on your knees. Place your arms straight on the floor and form a pocketknife position. Return to the starting position. 5. Standing on your knees again, place your straight arms on the floor. Arch your back as far as possible. Take the starting position (15-20 times). 6. Lie on your back. Place your hands on your bent knees and press your legs toward your stomach.
Exercises for lumbar flexibility - prevention of osteochondrosis These exercises can be included in a complex of morning exercises. They help keep the spine flexible and healthy. - Stand with your hands on your hips. Move your pelvis forward and backward. 10 times in each direction. - Get on your knees, stretch your arms forward, belly touching your thighs. Fold like a pocket knife. Repeat the exercise 15-20 times. - Lying on your back, press your knees bent to your chest.
Prevention of cervical osteochondrosis - Lie on your side, raise your head and keep it suspended, counting to 5. Breathing is voluntary. Repeat 4-6 times. - Lie on your stomach, put your hands on the back of your head. Slowly raise your head, offering resistance with your hands. Repeat 3-5 times with spontaneous breathing. - Lie on your back, head on a hard pillow. Rhythmically press your head on the pillow 5-6 times, for each pressure - 5 s.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis - Lie on your back, straighten your legs. Place one hand on your chest, the other on your stomach. Take a shallow breath and tense your muscles. Exhale and relax. Repeat this 5 times. - Lie on your back. Legs are straightened, arms are along the body. Bend your legs at the knees and clasp them with your hands. Then pull it towards your stomach. Raise your head and touch your forehead to your knees. Smoothly return them to their original position. Repeat 4-5 times. - Lying on your back, bend your knees, spread your arms to the sides. Turn your torso to the right and left. Turn in each direction 4-5 times. — Lying on your back with your knees bent, grab the edge of the sofa or the headboard with your hands. Slowly raise your torso, trying to reach your hands with your feet. Repeat the exercise 4-5 times. - Lie on your stomach with your legs straight. Hands lie along the body. Leaning on your legs, stomach and lower body, raise your head and shoulders. Repeat 4-5 times. — Lying on the floor, spread your arms to the sides. Turning your torso slightly to the left, reach your left palm with your right hand. Do the same in the other direction. Repeat 5-6 times. - Stand between 2 chairs. Feet together, hands on the backs of the chairs. Rise up on your toes and rotate your pelvis in one direction or the other. Repeat 4-5 times.