The lymph nodes in the neck are inflamed, what to do, how to treat. How to treat lymph nodes in the neck in an adult
Remember that only the attending physician can tell you in detail how to treat the lymph nodes in the neck!
Self-medication is fraught with consequences. The information below is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for medical advice. Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck is called lymphadenitis. Treatment of this disease should be aimed, first of all, at eliminating the cause of its occurrence, since lymphadenitis is not an independent disease, but only a symptom of some other ailment. Next, we will consider how to treat cervical lymph nodes depending on the cause of lymphadenitis.
Drug therapy
Most often, diseases of the lymph nodes are associated with the entry of infectious agents into the body that cause bacterial, viral or fungal diseases. Therefore, in order to eliminate the inflammatory process, drugs are prescribed that “kill” the infection:
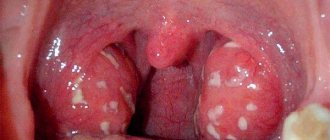
- Antibiotics. Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck in most cases are caused by bacterial infections (sore throat, tonsillitis), so antibiotic therapy is prescribed for treatment. If necessary, a swab is taken from the throat or nose to determine the type of pathogen, and depending on its type, tablets are selected. But more often, complex broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, to which most aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms are sensitive. These are penicillins and their derivatives, Ciproflaxacin, Summed, Amoxicillin, Flemoxin Solutab, Bicillin, etc.
- Antiviral drugs are effective when the cervical lymph nodes are enlarged due to a viral infection. This occurs mainly during seasonal epidemics in the cold season. In the case of ARVI, acute respiratory infections, influenza A and B viruses, the most effective drugs are Anaferon, Viferon, Kagocel, Ingavirin, Arbidol. Antibiotics are not prescribed in case of a viral infection, either at all, or only when a bacterial infection occurs.
- Antifungal agents are effective in cases of fungus in the mouth. This phenomenon is accompanied by a sore throat, white plaque on the tonsils and tongue, and inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes. The fungus can enter through common areas (for example, in a swimming pool), as well as after taking antibiotics. The most effective antifungal drugs are Nystatin, Flucostat, Fluconazole.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, which are used in the form of tablets for oral administration, lozenges, sprays, solutions for treating a sore throat. These products contain herbal anti-inflammatory components, antibiotics, antiviral components, as well as painkillers and anesthetics. Of the tablets for the treatment of neck lymph nodes, the most popular are Grammidin, Lizobakt, Immudon, Strepsils, Faringosept. Ingalipt, Kameton, Hexoral, Stopangin, etc. are prescribed in the form of sprays. A sore throat, which is the cause of lymphadenitis, can be treated with Lugol's solution, Chlorphyllipt.
Symptoms
Among the main symptoms that appear during the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes, the main one is the increase in size of this organ. It all depends on the cause of the inflammation. In this case, the occipital lymph node can increase to the size of a chicken egg, and such cases occur quite often.
In most cases, redness appears on the skin at the location of the lymph nodes. The inflammatory process can also cause a local or general increase in body temperature. Most often it does not exceed 37.5 degrees Celsius.
Headache and weakness can also be some of the symptoms of inflammation of the lymph nodes. In no case should you tolerate them for a long time, because irreversible processes in the body may begin. When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately seek help from a specialist. In this case, you can count on a speedy recovery.
Painful sensations from inflamed lymph nodes do not always occur. Many people may not notice any symptoms for a long time until the organ significantly increases in size. At the same time, in many cases the inflamed lymph node does not interfere with normal life activities.
Lymph nodes in a child's neck. Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck in a child, causes, treatment without fever
What to do if a child has enlarged lymph nodes in the neck: causes of inflammation and treatment at home
Have you noticed or felt round lumps on your child’s neck? It's probably swollen lymph nodes. This disease is called lymphadenitis. It is believed to be dangerous, but in childhood such inflammation occurs more often than in adults, and is not always a cause for concern. Let's look at why lymph nodes become enlarged in children, what you need to pay attention to, and how to properly treat this pathology.
The role of cervical lymph nodes in the body
Lymph node is an element of the lymphatic system, which is a pinkish-gray bean-shaped or round formation measuring from 0.5 mm to 2 cm. It transports lymph - a colorless liquid involved in metabolism, serving as a filter for cleaning tissues and cells and moving lymphocytes and phagocytes during infectious diseases. Lymph nodes permeate the entire body - from the popliteal areas to the head. The following groups are located in the neck area:
- submandibular, located on the right and left under the jaw;
- chin;
- anterior and posterior cervical;
- anterior and posterior ear;
- occipital;
- retropharyngeal;
- subclavian and supraclavicular.
The cervical lymph nodes are responsible for fighting diseases of the ENT organs (otitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, ARVI, influenza) and infections of the teeth and oral cavity (stomatitis, gingivitis, caries, pulpitis).
Causes of enlarged lymph nodes in a child’s neck
Lymph nodes are closely related to the human immune system. If they increase, this indicates the development of pathology in the body. When a signal is received that an infection has occurred, a large number of lymphocytes and phagocytes begin to be produced. They move to the lymph node, which causes it to enlarge. Causes of cervical lymphadenitis:
- Teething in infants. It’s not easy for the child’s body during this period; the nodules, together with the immune system, work hard. There is no reason to panic; over time they will return to normal.
- Previous occurrence of infected wounds, abscesses or boils. If located in the neck area, they can seriously affect the functioning of the lymphatic system. If the immune system is strong, the body will cope on its own, otherwise, without therapy, pus begins to accumulate in the nodes, spreading along with the lymph throughout the body. This complication requires urgent medical attention.
- Pathogenic microbes that live in the throat. In this case, the retropharyngeal nodes become inflamed. They are located at the junction of the edge of the auricle and the lower jaw.
- Infections of the face and mouth, atypical mycobacteria. Most often they cause inflammation of the nodes under the jaw on one side - left or right.
- Inflammation of the larynx, respiratory tract, skin infectious diseases. Their sign is enlarged nodules on the sides or back of the neck.
- Colds (adenovirus infection, influenza, ARVI) provoke an enlargement of the occipital nodes (we recommend reading: how to treat adenovirus infection in children at home?). This type of lymphadenitis is a sign of good immune function. As a rule, it goes away within 3 weeks, so it does not require treatment.
Diagnostics
Quite often, children and adults for a long time may not even realize that the lymph nodes are inflamed. Pain is not always present. If you notice an enlargement of the posterior cervical lymph nodes in yourself or your child, do not put off going to the doctor until tomorrow. It is better to immediately make an appointment with a doctor and determine the cause of the inflammation. Only after a competent diagnosis can a diagnosis be established and a suitable course of treatment be prescribed.
A visit to a specialist most often does not end with just an external examination. In the vast majority of cases, you will also have to undergo some tests, which will help determine the cause. It all depends on the situation and the doctor’s opinion. It is better to seek help from qualified doctors. In this case, you can be confident in the correctness of the diagnosis and the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
Ultrasound is one of the diagnostic procedures that every patient who comes with the problem of inflamed lymph nodes will have to undergo. However, even this cannot give a 100% guarantee when making a diagnosis. The accuracy in this case is no more than 70 percent. To answer what disease you have, the best way is to do a biopsy.
However, only a few can afford such a procedure. This diagnostic method makes it possible to establish a diagnosis with a 99 percent probability, after which the doctor only has to choose the right treatment to eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
A complete blood test is also one way to determine the cause of enlarged lymph nodes in the back of the neck. You can get results within a few hours.
Lymph nodes in the neck treatment. Causes
With inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes, the causes can be varied. In most cases, lymphadenitis is not an independent disease, but only a symptom indicating some problems in the body. These could be inflammations, infections or tumors. An experienced doctor can determine the location of the disease and its type based on the location of the affected node, its shape, size and degree of pain.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck may be associated with an increased concentration of pathogens in them, and an increase in their size may be associated with an increase in the production of lymphocytes.
Very often, inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck is caused by diseases of the upper respiratory tract - rhinitis, sinusitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, influenza, as well as inflammation of the middle ear - otitis media. Lymphadenitis can also be caused by oral infections - periodontitis, gingivitis, caries, stomatitis, inflammation of the gums and tongue.
Infectious processes on the skin - dermatitis, rashes, furunculosis, wounds and suppuration can also cause enlargement and inflammation of the nodes. These processes may be caused by exposure to the herpes virus, bacteria or fungi.
If the lymph node is very painful, this may be a symptom preceding the active phase of the disease. Microorganisms that can cause inflammation of nodes include pathogens of syphilis, gonorrhea, tuberculosis, streptococci and staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and pathogenic fungi.
Infection with tuberculosis, brucellosis and syphilis bacilli most often leads to a chronic form of lymphadenitis.
Also, enlargement and inflammation of the nodes can be caused by autoimmune diseases (rheumatism, gout, sarcoidosis, Sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus), and chronic alcoholism.
There are often cases when lymphadenitis is just evidence of a weakened immune system (as a result of stress, lack of vitamins and microelements in the body). The opposite situation may also occur - when the nodes become inflamed due to an allergic reaction, that is, an enhanced immune response to any irritant. In such cases, however, enlarged lymph nodes may be accompanied by other symptoms characteristic of allergic reactions - rash, hives, swelling, etc.
AIDS is a serious viral disease that affects the cells of the human immune system. Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck, as well as lymph nodes located in other parts of the body, may indicate the presence of HIV in the body.
Infectious mononucleosis can also lead to lymphadenitis. This is a disease in which pathological cells appear in the body, concentrating in certain organs, including the lymph nodes. Mononucleosis is characterized by a very strong enlargement of the lymph nodes, the size of which can reach 5 cm.
Tumors located in the upper part of the body can also cause enlarged lymph nodes in the neck. In some cases, we can talk about tumors of the tissues of the lymph nodes themselves - lymphomas.
Thus, there are a huge number of reasons that can cause enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, and it is impossible to list them all in a short article. In total, there are more than a hundred diseases that can lead to a similar phenomenon. Therefore, it is usually very difficult to draw a conclusion about what problem underlies lymphadenitis without thorough tests.
In some cases, the patient can also draw a conclusion about the nature of the disease associated with inflammation of the lymph node by its shape and other external signs.
The presence of many small inflamed nodes indicates a weakened immune system. The uneven contours of the node, its immobility and painlessness is a reason to contact an oncologist.
Enlarged lymph nodes without pain when pressing may indicate certain stages of tuberculosis.
An increase in pain when pressing, a rounded shape and mobility of the node most likely indicate inflammatory processes in the throat and neck. The location of the inflamed node may also indicate this - as a rule, during infectious processes of the throat, the submandibular lymph nodes become inflamed. If, for example, the lymph node on the left hurts, this means that, most likely, the source of infection is also on the left side.
It is also impossible to exclude lymphadenitis, which is not associated with any infectious disease, but arises due to mechanical damage to the tissue of the node.
Causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes
Many people rarely think about the fact that even a common viral infection can cause enlarged lymph nodes, which are the main barrier to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the human body.
Predisposing factors
- Exposure to bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa or parasites
- The effects of certain medications on the body
- Some diseases not associated with infection (for example, rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, sarcoidosis)
- Urogenital infection (specific nature of inflammation)
- Cancer
- Lipid metabolism disorder
- Graft rejection
- Psychological problems
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
Lymphadenitis is an inflammatory disease
Inflammation of the lymph nodes or lymphadenitis is inflammation caused by the appearance of pyogenic microorganisms (streptococci or staphylococci), toxins of these microorganisms or tissue breakdown products from the primary foci of purulent processes.
The primary focus should be understood as inflammation occurring in any organ or tissue. Microbes and toxins enter the lymph node with the outflow of blood or lymph, and sometimes inflammation occurs when microorganisms enter directly into the lymph node when it is damaged.
Read: Causes of stomatitis in children and adults: what are they associated with
There are cases when inflammation occurs not due to the fault of bacteria or fungi. Any disease with which a patient consults a doctor should be considered from the point of view of inflammation not only of a specific organ or tissue, but also of the lymph node.