The endocrine system of the body ensures the full functioning of human internal organs. If there is a suspicion of disruption of the endocrine system and if the thyroid gland is enlarged, endocrinologists advise donating blood for thyroid-stimulating hormone. Analysis of the hormone TSH allows you to detect and begin treatment of diseases of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and thyroid gland.
If the test shows that TSH is elevated, this means that hyperthyroidism has begun. Its consequences:
- rapid weight gain;
- dry hair and skin;
- breaking nails;
- poor memory;
- low hemoglobin;
- chilliness;
- reproductive dysfunction;
- low pressure.
Determining the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone is especially important during pregnancy; timely initiation of therapy that reduces the level of TSH in case of elevated titers allows you to give birth to a healthy child and maintain your own health.
Reasons for upward deviation of TSH levels
If, after donating blood for analysis, thyroid-stimulating hormone levels are elevated, there is no need to panic. An endocrinologist will tell you what to do if TSH is elevated. The pituitary gland and thyroid gland are complex, but correctable, systems. There are several reasons for increased hormonal levels:
- taking high doses of iodine;
- pituitary tumors;
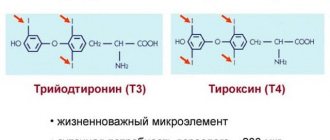
- decreased levels of hormones T3 and T4;
- thyroid diseases;
- problems after gallbladder removal;
- problems with the functioning of the adrenal glands;
- second trimester of pregnancy complicated by histosis;
- swelling of the thyroid gland;
- acute thyroiditis;
- diet;
- insomnia.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone reacts according to the feedback principle to the levels of T3 and T4 in the blood serum. Increasing the concentration of triiodothyronine and thyroxine can reduce the level of thyrotropin synthesis. The TSH level is determined simultaneously with T3 and T4.
Normal TSH in women
Women experience more hormonal changes in their blood than men, so it is important to monitor TSH levels on a regular basis. Doctors recommend monitoring this type of hormone from birth. That is why all tables with TSH norms indicate the acceptable limits of this indicator, starting with newborns.
Standards for different ages:
- newborns – 1.1-16.8 mIU/l,
- from 3 months to 5 years – 0.4-6.5 mIU/l,
- 5-14 years – 0.4-5 mIU/l,
- 14-25 years – 0.6-4.5 mIU/l,
- 30 years-50 – 0.4-4.0 mIU/l.
During pregnancy, this figure varies between 0.2-3.5 mIU/l. The TSH norm in women after 50 can decrease to a level of 0.27 -4.0 mIU/l.
The TSH level in women after 50 years of age needs to be monitored doubly carefully, since its excess or deficiency leads to the formation of a goiter. The same aggravation of the situation can occur at the age of 60, it all depends on the onset of menopause.
With increasing age, the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone decreases. It is worth separately monitoring the amount of TSH during periods of hormonal changes:
- during pregnancy,
- during lactation,
- at the stage of menopause,
- during the recovery period after thyroid treatment,
- in the presence of autoimmune diseases.
Advice! It is not worth comparing tests done in different clinics, since each laboratory may have its own characteristics of analysis, calculations and standards. It is better to donate blood for analysis in the same laboratory.
The drug Eutirox for increasing TSH levels in the blood
Taking Eutirox allows you to regulate the synthesis of thyroid hormones T3 and T4. When the normal level of thyroxine and triiodothyronine in the blood serum is reached, the symptoms of hyperthyroidism are relieved and full carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism is resumed. The renewed system of self-regulation of TSH, T3 and T4 functions if the tissues of the pituitary gland and thyroid gland are not damaged.
Why doesn't hormone replacement therapy always work? Men, women and children undergoing thyroxine therapy have individual physiological characteristics, medical history and symptoms. The endocrinologist prescribing treatment needs to take into account many factors:
- age;
- examination results;
- accompanying illnesses.
In some cases, the selection of dosage is unsuccessful and requires revision, so the treatment process is complicated and delayed for several months. If TSH is elevated, then with a successfully selected dosage of thyroxine it decreases after a few weeks.
TSH hormone: causes of decrease and increase in the blood
The reasons for increased TSH can be physiological and pathological. Physiological reasons for increased TSH concentrations include:
- psycho-emotional tension, stressful situations, as well as excessive joy, euphoria, emotionally charged events in life. Fear of blood sampling can also affect hormonal levels;
- physical activity, sports;
- late stages of pregnancy. TSH during pregnancy can fluctuate in both directions. Strictly speaking, already from the beginning of the third trimester a moderate increase in the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone can be observed. This situation is worth monitoring, however, large deviations in this indicator during pregnancy are quite acceptable;
- violations of the technique of preparing for the test.
Diseases leading to an increase in the blood hormone TSH:
- hypothyroidism of any etiology;
- hormone-producing tumors of the pituitary gland (especially often - adenoma or thyrotropinoma);
- autoimmune Hashimoto's thyroiditis (AIT);
- thyrotropin hypersecretion syndrome;
- hormone-producing lung tumors;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- severe gestosis and preeclampsia;
- high TSH can also be observed in severe mental disorders;
- lead intoxication.
Why can the concentration of thyrotropin be reduced? Low TSH, just like high TSH, is observed in a variety of conditions. There is only one physiological reason for this condition – pregnancy. But even in this case, the disease cannot be immediately ruled out. The doctor must always be on guard so as not to miss the early signs of the pathological process.
So, a decrease in the level of TSH in the blood is caused by:
- dtz or dutz (diffuse nodular toxic goiter);
- TSH is reduced in thyrotoxicosis of any etiology;
- thyrotoxic adenoma;
- gestational thyrotoxic condition;
- initial stage of ait with thyrotoxicosis;
- medicinal causes (taking medications such as levothyroxine sodium or iodine preparations);
- oncological diseases: this can be either cancer of the thyroid gland itself or oncopathology of other organs with manifestations of cachexia and intoxication.
It is worth noting that a change in the TSH level in any direction makes it clear to the specialist that the patient has dysregulation of the thyroid gland, but in order to establish a reliable diagnosis, additional tests will be required, at least to determine the concentration of the thyroid hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
How to take Eutirox correctly
TSH is elevated, the endocrinologist prescribed thyroxine, the dosage is correct, but there is no result? In order for the treatment to be effective, the medicine must be taken correctly, according to the instructions.
The concentration of thyroxine in the blood reaches its peak before 8 am, which means that taking the drug will be most effective in the morning. In addition, Eutirox has a tonic effect, so taking it in the evening can cause insomnia.
If levothyroxine is taken with or after food, half the recommended dose will not be absorbed. The drug is taken half an hour before meals.
The drug should not be skipped; one tablet is taken daily in the morning. Any omission lowers the hormone level, which means it does not allow you to adequately assess the result of treatment and correct it.
Hormone therapy with artificial hormone is not carried out in one course, the pills are taken for life. Hormone therapy replaces the functioning of the thyroid gland, which for some reason does not do its job of synthesizing substances necessary for the body.
Hormones of the endocrine gland are extremely necessary for humans. Synthetic analogues are able to replace hormones of the endocrine system in case of disruption of the gland, be responsible for normal cell growth, and regulate their renewal. The drug Eutirox is a medicinal analogue that has various pharmacological effects depending on the dosage.
The attending physician individually determines how to take Eutirox for hypothyroidism, taking into account the age, characteristics of the patient, in accordance with the duration and nature of the disease.
TTG: how to take it correctly
Preparing for a TSH test is simple, but to donate blood for TSH correctly, and the result has not been distorted, you need to follow several rules.
Blood tests do not have to be done on an empty stomach, but laboratory diagnostic specialists recommend refraining from eating for 3-4 hours. It is allowed to drink clean water without gas.
If the patient is taking hormonal medications, the medications are discontinued two days before the test. Of course, such actions must be agreed with the attending physician, and cancellation should only be with his permission.
Physical activity, emotional stress, stress - all these factors affect the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood. For the most adequate assessment of the condition, it is necessary to exclude such provoking situations and a day before the blood test.
Smoking is prohibited for three hours before blood collection.
The day from the start of menstruation does not matter for TSH analysis, which makes it even more convenient for assessing the causes of infertility or cycle disorders.
If you suffer from acute respiratory viral infections, influenza and other acute infectious diseases, it would be advisable to reschedule the test to another day, since in this case the hormone level may change unpredictably.
Fluctuations in the concentration of thyrotropin in the blood can fluctuate cyclically throughout the day, so when you repeat the test, you should donate blood at the same time of day as the first time.
It should be noted that the data from the TSH hormone test reflect the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid system in the several weeks preceding blood donation. Therefore, if it is necessary to monitor adjusted hormonal therapy, the analysis is prescribed no earlier than two months after changing the dosage of the medications.
In addition to hormones, many other drugs can affect TSH levels. Their list is quite large: some of them can be canceled in advance of the study, and some must be applied continuously. In any case, you need to warn your doctor and laboratory technician about what medications you are taking on a regular basis. This will help you correctly evaluate the results obtained.
- Increase the concentration of TSH in the blood, for example, atenolol, many antiarrhythmics and beta blockers (metoprolol, propranolol and amiodarone), hormones (calcitonin, prednisolone), morphine and even motilium.
Thyroid gland and its hormones
The thyroid gland, called the thyroid gland in the 17th century, is located in the anterior part of the neck, next to it are the parathyroid glands. This small organ is a vulnerable place from the point of view of causing any injury or infection. The two lobes are connected by an isthmus, shaped like a shield. The gland, with its main endocrine function, is a participant in various processes of the body. Without the work of an organ, it is impossible to imagine the growth and development of any organism.
The main role of the thyroid gland, as it is popularly called, is the production of hormones:
- thyroxine;
- tyrosine;
- Iodine tyranine.
Thyroxine stimulates the growth of the body as a whole, increasing resistance to high temperatures. It is produced from the intrauterine stage of human development. Without it, growth in height, development of mental abilities, and stabilization of the immune system do not occur. Under the influence of hormones, protection is enhanced - cells are more easily freed from foreign elements.
The production of hormones is regulated by higher glands - the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. The pituitary gland produces thyroid-stimulating hormone, which causes the thyroid gland to increase not only the production of iodothyranine and thyroxine, but also activates the growth of the gland itself. The hypothalamus is the control center where nerve impulses arrive. It produces hormones that regulate the activity of the pituitary gland.
Thus, under the guidance of the hypothalamus, throughout the day, the thyroid gland produces up to 300 micrograms of thyroid hormones, which ensure the development and construction of the nervous system. When the amount of hormones is excessive or insufficient, the nervous system responds with excitability or depression.
Antibodies to TSH receptors
Another test related to thyroid-stimulating hormone is the determination of antibodies to TSH receptors. These are immunoglobulins belonging to class G, which act on thyroid cell receptors that bind to TSH. It is these receptors that regulate the production of thyroid hormones: by connecting with thyrotropin, they facilitate its penetration into the cell to stop the excessive production of hormones.
If antibodies attach to the receptors, they block the entry of thyrotropin into the cell, and thyroid hormones are produced in large quantities. There are three groups of antibodies:
- Blocking the functioning of TSH receptors, which leads to an increase in T4 and T3.
- Binds to receptors and causes a long-term increase in TSH.
- Reducing the activity of thyrotropin, as a result of which thyroid cells lose sensitivity to it.
Eutirox for hypothyroidism
Characterized by a decrease in the concentration of the hormone in the blood. Often, hormonal deficiency is not detected for a long time, since the symptoms develop slowly and do not affect the general health, but occur under the masks of other diseases. With chronic deficiency, a person's metabolic processes slow down, resulting in a decrease in the production of energy and heat. The initial or obvious symptoms of hypothyroidism include:
- chilliness;
- loss of appetite with weight gain;
- drowsiness;
- dryness of the epidermis;
- poor concentration, lethargy;
- dizziness;
- depression;
- constipation;
- cardiovascular disorders.
For deficient thyroid function, so-called hypothyroidism, Eutirox, a synthetic analogue of thyroxine, is primarily indicated. This drug is used for replacement purposes. The drug belongs to the category of iodine regulators in the body.
Clinical experience and recommendations show that the use of Eutirox for long-term replacement therapy is safe. The severity of situations varies. Sometimes the depth of the patient's experiences does not correspond to the severity of the problem that befell him. An exception to the rule is old age and concomitant pathologies:
- adrenal insufficiency;
- inflammation of the heart muscle;
- acute myocardial infarction;
- acute inflammation of the membranes of the heart;
- atherosclerosis.
If you follow the recommendations in these cases, a dose adjustment of the drug is required. Eutirox is prescribed at 50 micrograms with further increases. Thyroxine is a hormone, and taking an artificial hormone, like taking any drug, is accompanied by side effects.
Effects of Eutirox
Eutirox is a hormonal tablet preparation that is chemically and molecularly identical to the human hormone. In case of hypothyroidism, which is accompanied by weight gain, the use of the drug leads to the fact that the function of the endocrine gland is normalized, and with good thyroxine levels, the weight is equalized. When taking a pharmaceutical product, allergic reactions are possible, which are detected in the initial stages of administration.
As for hair loss, when taking the drug, there is an improvement in hair quality, as opposed to the effects when hair loss is a symptom of insufficient function of the endocrine gland. When the condition passes, the hair will stop falling out, fragility and brittleness will disappear.
With an excess dose of the drug, signs of thyrotoxicosis appear - the opposite condition characterized by. The most common ones are:
- arrhythmia;
- high blood pressure;
- insomnia;
- irritability, short temper;
- weight loss;
- hyperhidrosis;
- menstrual irregularities in women.
When the drug substance accumulates in the tissues of the body, changes in the functioning of the digestive system and allergic reactions also occur.
When should you get tested for thyroid-stimulating hormone?
If there is any suspicion of a malfunction of the endocrine system, namely the thyroid gland, a specialist will prescribe an analysis to determine the concentration of thyrotropin. Typically such indications include:
- Delayed sexual development.
- The appearance of causeless weakness.
- Regular depression.
- Decreased sexual desire.
- Increase or decrease in blood pressure.
- Excessive sleepiness or, conversely, insomnia.
- Infertility and impotence.
- Puffiness of the eyes, neck, arms and legs.
- Excessive hair loss, including baldness.
All this may indicate a malfunction of the thyroid gland. And you can determine whether there is a problem only by blood. A TSH test is taken from a vein, in the morning on an empty stomach or at least three hours before breakfast. If you are already undergoing treatment, then it is not recommended to take the drug on this day, since the blood must be clean to make the result more reliable. Also, for two days you should not drink alcohol or eat fatty foods. Usually, when taking tests to determine pathologies of the endocrine system, they donate not only blood for TSH, but also for free T3, free T4 and antibodies to thyroglobulin.
Taking and stopping Eutirox
To avoid side effects, Eutirox must be taken correctly:
- early in the morning, usually half an hour before breakfast;
- with a small portion of plain water.
It is advisable not to skip taking the drug, but to take it constantly, at the same time, throughout the entire period indicated by the doctor. Fluctuations in hormone levels are undesirable for the thyroid gland if the drug is missed. This can lead to the growth of gland nodes. You should not take the drug in a double dose to replace the missed one - this will cause a sharp jump in function. It is advisable to take the missed dose in the morning on the same day, at lunch or in the evening.
After removal of the thyroid gland, the prescription depends on the amount of tissue removed. If part of the gland has been resected or 50% of the tissue has been removed, the need to prescribe Eutirox is determined by the tests performed. This category of patients needs to check the level of thyroxine in the blood and determine the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone. If they are within normal limits, then the use of the drug is not mandatory. If decreased gland function is diagnosed - low levels of thyroxine or, conversely, an increase in thyroid-stimulating hormone, then replacement therapy is necessary.
If the thyroid gland is completely removed, the course of treatment covers the rest of your life. When prescribing Eutirox for the purpose of blocking the production of hormones by the thyroid gland itself, as a rule, the treatment course is determined for a specific period of 1–2 months.
When planning pregnancy, it is advisable to use the Eutirox hormone in the following cases:
- if a woman has had a thyroid disease;
- if you have undergone surgery on the gland and are prescribed replacement therapy.
With hypothyroidism, pregnancy is almost impossible. Carrying out adequate therapy with the prescription of hormonal drugs is the success of the development of pregnancy. During the period of gestation, taking a hormonal drug is mandatory for those for whom it is indicated. A woman who is pregnant and does not take replacement medications runs the risk of giving birth to a child with signs of thyroid insufficiency and mental retardation.
There are cases when it is necessary to increase the dose of Eutirox. Then the observation of such a pregnancy falls within the competence of not only the gynecologist, but also the endocrinologist. Children suffering from hormonal deficiency due to hypothyroidism also need to take this drug in the dosage and course as prescribed by a specialist. The portioned dose depends on the child’s body weight and age.
Self-discontinuation of the drug will lead to a new development of symptoms of hypothyroidism, when the production of thyroxine is impossible naturally. Cancellation of Eutirox while blocking hormonal production will not lead to pronounced changes.
Who should donate blood for TSH?
When a doctor prescribes a blood test for TSH to a patient, it most often means that he has a dysfunction of the thyroid gland. However, there are a number of other reasons to order such an analysis. What questions can thyroid-stimulating hormone answer?
- First of all, understand whether there are problems with the functioning of the thyroid gland, and also indirectly evaluate the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
- Is the therapy for thyroid diseases well chosen? Do you need to change the dosage or medication? It is not always possible to determine from the first time which medicine and in what dose the patient needs. It is very important to prevent sharp fluctuations in the level of thyroid hormones and TSH, since hormonal “swings” can unbalance the functioning of all organs and systems, causing serious health problems. In order to monitor treatment, the doctor must prescribe a TSH test.
- Are there problems in the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in a newborn? This is especially true for children whose mothers suffered from thyroid disease during pregnancy.
- What are the causes of infertility? Is the treatment chosen correctly? Thyroid hormones and pituitary hormones are produced in close conjunction with gonadotropic hormones, so disturbances in sexual function often go along with other endocrine problems.
What specific symptoms can prompt a doctor to prescribe a test for the TSH hormone and suspect pathology in this area?
- Clinical picture of hyperfunction of the thyroid gland
- tachycardia (increased heart rate);
- restlessness, anxiety, suspiciousness;
- sudden and rapid weight loss;
- insomnia, sleep disorders;
- tremor (uncontrollable shaking) in the limbs;
- fatigue, weakness;
- stool disorders, diarrhea;
- photophobia;
- blurred vision, myopia;
- exophthalmos (bulging of the eyeballs), dry eyes, feeling of “sand,” redness, swelling of the eyelids.
- Clinic for decreased thyroid function (hypothyroidism)
- dry skin, cracks;
- stool disorders such as constipation;
- so-called “cold allergy”;
- peripheral edema, water balance disorders;
- alopecia (baldness);
- fatigue, lethargy;
- menstrual irregularities, mental instability.
- An increase in the size of the thyroid gland (goiter) without other clinical manifestations.
- The patient is a newborn at risk for thyroid pathology.
Drug overdose
Taking Eutirox will bring hormone levels back to normal only in situations where it is justifiably prescribed. There is no need to be afraid of taking hormones. You need to be wary of a lack of hormones. The drug Eutirox is inexpensive, accessible and effective.
Secret area
There is only one point to pay attention to. A normal person without signs of hypothyroidism is able to work for 3 days in a row and then recover quietly for 2 days. A person who takes the artificial hormone levothyroxine has a hard time tolerating this condition. With an active lifestyle, with increased physical and emotional stress, a large dose of the hormone is required. In case of an overdose of Eutirox in case of hypothyroidism, problems with the functioning of the heart arise during the recovery period after workload:
- increased heart rate;
- tachycardia;
- arrhythmia;
- heartache.
The effect that a hormone similar in its chemical properties has in tablets to “native” thyroxine in a state of excitement remains unknown and is being studied by medicine, as well as pharmacology. Opinions tend to favor the effect of the body processing the artificial analogue. Nevertheless, the drug fully performs its function, and the most important tasks remain nuanced. People taking Eutirox work and rest safely, reproduce and raise healthy offspring.
Combination with other dosage forms
An overdose of thyroxine or an increase in the effect of the drug can occur with the use of certain products and dosage forms. If the dose was exceeded when taking Eutirox, the following symptoms appear:
- chest discomfort;
- dyspnea;
- convulsions;
- loss of appetite;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- sleep disturbance;
- fever and excessive sweating;
- diarrhea;
- vomit;
- rash;
- irritability.
Taking herbal decoctions and vitamin complexes is carried out after consultation with an endocrinologist.
The medicine becomes poison for the body when acute signs of overdose are observed, appearing within 24 hours:
- , in which an increase in all signs is obvious.
- Mental disorders - convulsive seizures, delirium and semi-fainting states, leading to the development of coma.
- A sharp decrease in urine output (anuria).
- Liver atrophy.
Despite the fact that Eutirox is a drug that regulates iodine in the body, you can take iodine-containing synthetic (Iodomarin) or natural (kelp) forms. contains inorganic iodine, which is not produced in the body, and therefore must come from outside. This is especially important for pregnant women and people suffering from insufficiency of the endocrine gland.
Structural analogues
Trade analogues of the drug are represented by the names Bagotirox, Tireot and Novotiral. Despite the fact that all these pharmacological products share one active ingredient - levothyraxine, there are differences in their action. Eutirox, when taken as prescribed, unlike other structural analogues, does not have (or in rare cases has) side effects. Indicated for the treatment of childhood deficiency conditions.
Combining with other drugs, prescribing or changing the dose on your own is strictly not recommended. Only a doctor, based on the physiological characteristics and individual health indicators of the patient, selects the drug, dosage and course of treatment.
First aid for overdose
When you feel the first signs of illness, you need to see a doctor or call a specialist to your home. You should not delay calling an ambulance if your condition worsens, or in the following cases:
- if an overdose occurs in a child, pregnant woman, or elderly person;
- serious heart rhythm disturbances and chest pain;
- diarrhea with bloody discharge;
- high blood pressure;
- pathologies of a neurological nature - seizures, paralysis, paresis;
- disturbances of consciousness.
Depending on the severity of intoxication, drug therapy is carried out using symptomatic drugs, blood purification procedures for unconscious patients.
Good day everyone!
I have grade 2 hypothyroidism, so I have been taking Eutirox daily for the fifth year now. I’ll tell you and show you clearly through the tests whether Eutirox is capable of reducing TSH, especially during pregnancy, and how I myself took this drug in various dosages - Eutirox 50 mcg, 75 and 100.
Eutirox was prescribed to me more than 4 years ago, when, after several miscarriages, I began to get to the bottom of the reasons and thoroughly examine my body. Among other things, it turned out that I have a high TSH hormone. Eutirox 50 (and later in other dosages) was prescribed by the endocrinologist precisely in order to reduce it.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
, or
TSH
,
thyrotropin
,
thyrotropin is
a tropic hormone of the anterior pituitary gland.
If TSH is elevated, then, as the doctor explained to me, the body literally oppresses the fetus and for this reason the pregnancy may be frozen or not developing.
But in addition to normalizing TSH, you need to monitor the level of prolactin, cortisol (and a number of other indicators), which also mean a lot for a good pregnancy and the correct formation of the baby.
I will not go into these questions, each organism is individual. In my case, TSH and prolactin were elevated
. Therefore, on the doctor’s recommendation, I lowered TSH with Eutirox and prolactin with Dostinex.
During planning
the doctor decided to play it safe as much as possible, so I alternated taking Eutirox at a dosage of 50 mcg. and 75 µg, so that TSH is in the region of 0.3 - 2.45 µIU/ml. These indicators are most favorable for the body preparing for pregnancy.
When I got pregnant
, two weeks later I took a TSH test to check how my body reacted to my new position. As a result, here is a photo of a plate with my analyzes:
TSH, naturally, began to rise. By the way, the 3rd generation TSH analysis is considered more informative. Sometimes during pregnancy I took both regular and 3rd generation TSH, following the doctor’s advice.
As a result, from the beginning of pregnancy until childbirth, in order to keep TSH normal, I took Eutirox at a dosage of 125 mcg.
Here are my results after three months of taking Eutirox at this dosage:
TSH is quite low, but for me this was the norm so that the hormone does not suppress the fetus.
Thus, I immediately told you how Eutirox worked in my case, really lowered TSH and helped me get pregnant, carry and give birth to a baby. Of course, in addition to the thyroid gland, I had problems that had to be solved before and during pregnancy. For example, at first I was given hCG injections, and from the middle of pregnancy - blood thinning injections. In addition, I was faced with gestational diabetes.
But that was all a long time ago, and now I’m a mother, and this is the most important thing!
Well, it’s time to talk about the drug itself.
Here is a photo of two packaging options for the drug Eutirox: 100 and 75 mcg:
After giving birth, I came to my usual dosage of Eutirox - 50 mcg. per day. Now, after consulting with a doctor, I slightly increased the dose - 75 mcg.
100 mcg. It is convenient to break it in half at risk if you need to drink 50 mcg. per day. And the dosage of Eutirox is 75 mcg. - in general, a convenient format when it’s prescribed for you to take it that way.
Active ingredient
drug:
Levothyroxine sodium.
Produces
: Germany.
The tablets are white, very small, and have no taste.
They should be taken daily, in the morning, on an empty stomach, preferably 30 minutes before meals.
I don't always follow this rule. Especially with the birth of a child, you constantly lack time for yourself. But I still try to stick to it.
By the way, if you are going to take the TSH hormone test, be sure to drink Eutirox in the morning
(if, of course, you are already taking it)
1 hour before the analysis
, so that the analysis is more informative! This was told to me by a very experienced endocrinologist, whom I trust 100% and who helped me throughout my pregnancy.
I’ve been taking this test for so many years, but I didn’t know about it. That's why I'm sharing with you!
I have also attached the most important fragments of the instructions. It is very large, so I didn’t take pictures of the whole thing.
It is important that during pregnancy and breastfeeding
They continue to take Eutirox! So it was with me. But, as I said, I have been drinking it constantly for several years now. Here again, everything is individual. Be sure to consult your doctor with all questions!
Directions for use and doses
:
(To enlarge the instructions, click the left mouse button, for a larger enlargement, click again)
Indications for taking Eutirox and contraindications:
Name: Olga, Moscow
Question: The endocrinologist prescribed me Eutirox 50 mcg. I’ve been taking it for the second month, yesterday I had it checked and received data that TSH is 0.012 mU/l, the norm is 0.4-4.00.
Free T4 24.15 Pmol/l norm 9.00-19.05.
Answer:
Eutirox is a synthetic hormone thyroxine (T4), produced by the thyroid gland.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone during pregnancy
While expecting a baby, it is important to monitor hormonal levels, especially in the first trimester, when the fetal thyroid gland is not yet functioning and its development depends on maternal hormones.
The TSH level during pregnancy is not constant and varies depending on the period. Thus, the lowest rates are recorded in the first trimester, although in some cases this trend continues until childbirth. It is especially pronounced during multiple pregnancies: in 100% of cases, women expecting twins or triplets have a reduced level of thyrotropin. If the laboratory uses tests with low sensitivity, the number “0” may well appear on the analysis form.