Phlegm in the throat without coughing causes
Sputum is a pathological substance secreted mainly by the bronchi and trachea.
Most often, the appearance of phlegm in the throat is accompanied by a cough, but in some cases, increased secretion of phlegm can occur without a cough. Normally, there is no mucus in the throat, and the tracheobronchial structures contain mucus, which has a bactericidal effect and contributes to the death of inhaled bacteria and dust particles.
The amount of such mucus does not exceed 0.1 liters and, if it enters the oral cavity, it is either swallowed or spat out by a person.
Sputum in the throat, bronchi without cough: characteristics by color and composition
When unnatural processes occur in the human body, the amount of phlegm in the throat can reach 1 liter. The components of liquid discharge directly affect the color of mucus, which characterizes possible illness.
- Clear sputum is considered natural secretion. If the mucus is too thick and looks like glass chips, then the bronchi may have a narrowed shape from birth. In such cases, a person often experiences shortness of breath. Colorless sputum during normal functioning of the body should have a viscous consistency.
- White, foamy sputum is often observed in older people. Phlegm in the throat of old people is assessed as an age-related change.
- Yellow sputum without a cough characterizes the increased work of the immune system in the fight against external irritants. Yellow-green sputum occurs when there is congestion in the bronchi.
- Yellow sputum with a bright tint occurs when a large amount of toxins is inhaled and an allergic reaction of the bronchi. Yellow sputum in the throat is constant in the presence of bronchial asthma.
- Bloody sputum indicates ruptured blood vessels in the lungs. Brown mucus indicates long-term blood loss.
Description
Types of phlegm in the throat
Before talking about phlegm in the throat in the absence of a cough, it is necessary to understand the types of this secretion. By the nature of sputum one can judge its composition.
- Regular sputum is a mucous discharge. Does not contain any impurities and resembles slightly viscous saliva. As a rule, there is no distinctive smell.
- Mucopurulent sputum - in addition to mucus, it contains accumulations of purulent elements. A distinctive point is that there is much more mucus in this sputum than pus.
- The purulent-mucous character is distinguished by a large amount of pus with a heavy type of mucus.
- Purulent sputum - discharge is characterized by the presence of “pure” pus without mucus. Most often it has an unpleasant odor and a whitish or yellowish-white tint.
- Muco-bloody sputum - its composition has a large amount of mucous component mixed with blood streaks.
- The mucous-bloody-purulent nature of sputum is distinguished by the content of mucous, purulent and blood components in equal volumes.
- Bloody sputum - practically does not contain mucus and contains “pure” blood (possibly in the form of veins, coagules).
- Serous-mucous sputum - consists mainly of blood plasma, which sweats into the cavity of the bronchial tree.
It should also be noted that sputum in the throat without coughing can be divided depending on the consistency: liquid, mucus-like, thick and viscous. All this depends on the amount of mucus and the presence of impurities (blood cells, purulent particles, ciliated epithelium or detritus).
Causes of phlegm in the throat
There are many reasons for the formation of sputum, its entry into the throat and constant discomfort in the mouth from its excess.
Let's look at the most common causes of mucous sputum:
- Acute bronchitis - in the initial stages of this disease, sputum may appear in the throat without a cough. The sputum is of a normal mucous nature, no impurities are detected. As the course of the disease worsens, the presence of sputum is undoubtedly accompanied by a cough, the mucous character can turn into mucopurulent, and general symptoms may also appear, such as weakness and an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels.
- Qatar URT (upper respiratory tract), or, more simply, a cold, is also characterized by the possible presence of mucous sputum. However, here the presence of sputum in the throat without cough and other signs of the disease can be as residual effects after the disease. This is due to the removal and elimination of detritus from the respiratory tract.
- Bronchial asthma is a hypersecretion of mucus that forms during an attack, is removed from the respiratory tract and enters the oral cavity and pharynx. Sometimes, in the initial stages of not yet established bronchial asthma, the constant presence of phlegm in the throat may be the only sign.
- Pharyngitis, or inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane of the pharynx - cough in the case of the initial symptoms of pharyngitis may be absent, but discomfort in the form of a sore throat is still observed.
- Acute sinusitis is a leading symptom of the presence of mucus in the throat without coughing. The appearance of phlegm-like mucus, which is often confused with “true” phlegm, is associated with the flow of mucus from the inflamed areas of the maxillary sinuses along the nasopharynx, as a result of which this mucus appears in the mouth and causes discomfort.
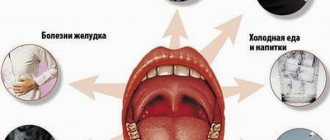
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a disease characterized by the reflux of gastric contents into the cavity of the esophagus, which provokes the development of inflammatory processes. With a long course of the disease, as a result of a violation of the evacuation of the contents of the stomach and its reflux into the esophagus, food passes into its upper sections. Compensatory mechanisms in the upper esophagus contribute to the formation of mucus, which can end up in the throat and resemble phlegm. In addition to mucus in the throat, there is sour belching, soreness, and pain along the esophagus.
- Zenker's diverticulum - a disease characterized by the presence of a pouch-like protrusion of one of the walls of the esophageal tube, which leads to food entering it and stagnation. As a result of the production of secretion by the mucous membrane of the esophagus, its accumulation in the Zenker diverticulum leads to entry into the oral cavity. This is one of the important and leading symptoms of pathology of the upper esophagus. When the process becomes chronic and becomes purulent, the mucus acquires a purulent-mucous character, and the clinical picture may change towards mediastinitis.
- Chronic or vasomotor rhinitis - a distinctive feature is the presence of a runny nose and nasal congestion. Mucus from the nasal cavity flows down the nasopharynx and into the throat, where it brings constant discomfort due to the lack of treatment for rhinitis.
- Allergic phenomena.
- Autoimmune diseases with pathological changes in glandular tissue (for example, Sjogren's syndrome). Constant dry mouth creates a false sensation of phlegm in the throat, but no cough is observed. Associated symptoms include dry eyes with a feeling of sand or dust, and dysphagic disorders.
The most common causes of mucopurulent sputum in the throat
- Chronic bronchitis is a constant discomfort that causes an accumulation of phlegm in the throat and is common among smokers who have already quit smoking. In this case, there may be no cough, but mucous sputum with streaks of pus as a result of inflammatory changes in the bronchi is present.
- Bronchopneumonia. Of course, it depends on the degree of activity of the infectious process, and in some cases the mucopurulent nature of the sputum is not accompanied by a cough, however, there are other symptoms: general weakness, malaise and constant drowsiness, fever up to febrility. Sputum examination, x-ray examination and laboratory manipulations (blood test, leukocytogram) help to confirm the diagnosis.
- Chronic sinusitis has the same symptoms as acute sinusitis (described above), but its course is long, and the accompanying symptoms are more pronounced (an admixture of pus appears in the mucus, the temperature rises to febrile levels, a “terrible” headache and pain in the sinuses, general malaise .
The main reasons for the appearance of purulent mucous sputum in the throat without coughing
- Bronchopneumonia. A feature of this disease is the presence of purulent-mucous sputum, less often with an admixture of blood, against the background of cough-free symptoms. A dry cough, of course, can appear over time, but already in the active phase of the disease. Along with sputum, signs of bronchopneumonia may include increased body temperature, dullness of percussion sound and bright auscultation data (small and large bubble rales, crepitus), as well as X-ray signs of focal pneumonia.
- Croupous pneumonia - a mild course of this disease is accompanied by the release of a fairly large amount of sputum, and auscultation data (in addition to wheezing, pleural friction noise is heard due to the addition of pleurisy) and a chest x-ray help to differentiate the diagnosis.
The main causes of the unpleasant symptom
The respiratory organs can clean themselves by removing dust and debris particles in the air. This occurs due to cilia, which move alternately up and down, and cells that produce mucus. They are located on the mucous membrane of the bronchi.
Even a healthy person produces a little mucus every day. But it does not cause discomfort, since its separation and swallowing occurs reflexively, the person does not even notice it.
But some people have constant phlegm in their throat. This is a pathology in which either an excessive amount of mucus is produced or the process of its removal is disrupted. The following reasons can lead to excessive sputum production:
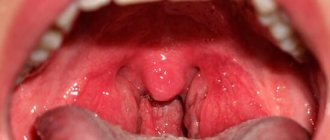
- Chronic sore throat. This is a very common disease that is a consequence of untreated acute tonsillitis. Accompanied by stench from the mouth, pain and sore throat, and white mucus. During periods of exacerbation, a purulent plaque forms on the tonsils, so the secreted sputum contains patches of pus.
- Bronchitis. To protect itself and fight inflammation, the bronchial mucosa produces excessive amounts of greenish mucus. Its appearance is wave-like - it appears and then disappears. Usually accompanied by a very pronounced cough reflex.
- Pharyngitis. The acute form of the disease is accompanied by discomfort in the throat, severe soreness and burning, the sensation of a foreign object in the throat, and the release of colorless mucus. With a chronic disease, such symptoms are constantly observed, but they are less pronounced.
- Rhinitis. An excessive amount of mucus forms in the nasal cavity, which can be difficult to blow out. Therefore, it flows down the throat and almost never leaves, causing discomfort.
- Chronic sinusitis. Accompanied by a constant feeling that mucus is flowing down the back wall of the throat. It is also characterized by nasal congestion, deterioration of the sense of smell, and a disturbance in general well-being. This condition is typical specifically for chronic sinusitis, while in an acute disease the nose is very clogged, the maxillary sinuses swell and hurt when pressed, and the patient cannot breathe normally.
- Esophageal diverticulum. A depression is formed in the organ, in which particles of consumed food accumulate. Over time, it begins to decompose, during which pathogenic microorganisms are released that irritate the mucous membrane. Accompanied by a strong odor from the mouth, belching with food particles, heartburn, epigastric pain and other symptoms.
- Reflux esophagitis. Due to the reflux of contents into the esophagus, its walls are irritated, which leads to the production of mucus. Sometimes acid can get into the throat, irritating it. The vocal cords also suffer, which is why many people complain of hoarseness. There is a constant desire to cough up mucus, as the person feels a lump in the throat, as if something is stuck. The pathology is also accompanied by heartburn and sour belching.
- Allergy. The penetration of allergens into the bronchi also leads to excessive secretion formation. In this case, sputum is released until the effect of the irritant stops.
- Impaired metabolism and hormonal imbalances can also be accompanied by increased mucus secretion. Additional symptoms are also observed - night sweats, cough, sudden weight changes, insomnia and others. This condition may appear during pregnancy and disappear immediately after the birth of the child.
- Heart diseases. As a result, there is stagnation of fluid in the lungs. It is excreted very slowly and can stagnate in the bronchi and trachea. Therefore, there is a feeling that there is mucus in the throat, the person constantly wants to cough it up.
And with Sjögren's syndrome, sputum is not produced, but the person feels it. This is a disease in which the cells of the salivary glands are destroyed. As a result, the throat dries out, so the patient has a false sensation that there is phlegm stuck in the throat.
Also, discomfort may appear due to infection in the respiratory system, which leads to various respiratory diseases. For example, with tracheitis, a lot of phlegm forms in the throat, and other symptoms begin to manifest themselves after a while, when the infection has spread greatly. With pleurisy and asthma, the formation of sputum is almost always observed against the background of an increase in body temperature.
Excessive accumulation of mucus can also be caused by poor diet (eating spicy and salty foods, fast food), smoking, and frequent use of medications. Similar symptoms occur during prolonged stay in a room with dry air, as well as unfavorable environmental conditions.
Phlegm in the throat
Sputum is a secretion in the form of mucus formed in the cells of the epithelium (mucous membrane) of the bronchi. Fragments of bacteria, desquamated epithelial cells and other components may be mixed with this mucus. Mucus moves through the bronchi, mixes with saliva and nasal discharge. Normally, sputum should be transparent and released in small quantities, without causing any discomfort. Smokers and those who work in dusty environments may produce sputum in large quantities. Sputum usually forms in the lower parts of the respiratory tract (trachea, bronchi, bronchioles) and, accumulating, irritates the receptors, causes a cough reflex and comes out through the mouth.
Some patients call phlegm nasal discharge that flows down the back wall of the nasopharynx, as well as discharge from chronic pathologies of the oropharynx and larynx.
That is why sputum production can be associated with various pathological processes. In case of such complaints, it is necessary to conduct a full examination of the patient, find out the details of the medical history and conduct a series of tests.
Sputum with cough
A cough with sputum or a wet, productive cough may indicate various diseases of the respiratory system, from ARVI to allergies. There are a number of diseases and conditions that are characterized by coughing with sputum:
- Smoking. A larger amount of mucus forms in the lungs of a smoker, which the body tries to get rid of, causing a cough;
Infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract. Viral, fungal, or bacterial infections also cause coughing. Quite often, a common cold can cause complications in the form of tracheitis, bronchitis and other more severe diseases, accompanied by a wet cough;
Bronchial asthma. With this disease of an infectious-allergic nature, the secretory function of the lung mucosa also increases, as a result of which sputum is released;
Abscess (purulent focus) of the lung or bronchiectasis. If there is an abscess in the lung, it is possible to separate its purulent contents, requiring separation by coughing;
Tuberculosis. This disease is characterized by the presence of blood in the sputum;
- Entry of a foreign body into the respiratory tract. Foreign particles in the respiratory tract cause irritation and, as a result, cough.
Sputum with coronavirus
Coronavirus disease proceeds in much the same way as an ordinary acute respiratory viral infection or influenza. An infected person often experiences high fever (from 38 degrees), general weakness and a dry cough. Slightly less common are runny nose, sneezing, sore throat and muscle pain. Even less common are loss of appetite, shortness of breath, sputum production, headache, nausea and diarrhea.
Covid-19 is usually accompanied by a dry cough, which eventually develops into a cough with phlegm - thick mucus containing dead lung cells destroyed by the virus. These symptoms are treated with bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids and paracetamol. No special medical care is needed here. This stage lasts about a week - most recover because their immune system has defeated the virus.
According to the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Tajikistan, in 90% of cases, patients with coronavirus infection have an increase in body temperature, in 80% of cases, a cough with coronavirus appears - dry or with a small amount of sputum, in 55% of cases - shortness of breath (the most severe shortness of breath develops by 6-8 days from the moment of infection), 44% of patients develop muscle pain and fatigue, 20% feel chest congestion.
Green sputum indicates that the body is fighting acute infectious diseases, which include coronavirus
Green sputum due to coronavirus
Phlegm is a type of secretion consisting of mucus and saliva that is produced in our lungs and clears the throat of irritants. Green sputum indicates that the body is fighting acute infectious diseases, which include coronavirus. At first the mucus has a yellow tint, but gradually turns green. A similar shade of sputum is observed with bronchitis, sinusitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Green sputum with coronavirus is a sign of infection in the body.
Sputum with blood during coronavirus
Hemoptysis accompanies many infectious diseases of the respiratory system: bronchitis, pneumonia. Some bacteria have the ability to destroy lung tissue and increase the permeability of pulmonary vessels. Often the characteristic symptoms of such diseases are a significant deterioration in general condition, elevated body temperature, and severe weakness. The appearance of blood in coughed up sputum indicates the advanced stage of the disease.
Since coronavirus can cause serious complications, including breathing problems, severe pneumonia of an infectious nature. Symptoms of infectious pneumonia caused by coronavirus: elevated body temperature, pain in the chest and back, shortness of breath, cough with the release of “rusty” sputum and traces of fresh blood.
Coronavirus pneumonia is a dry cough without a runny nose
Sputum with blood is always a sign of serious problems in the functioning of internal organs. You need to see a doctor as soon as possible to simplify diagnosis, pay attention to your general health and accompanying symptoms.
Coronavirus without sputum
COVID-19 can cause serious complications, including breathing problems, severe pneumonia, and death. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately one in five people who become ill become severely ill—patients develop severe pneumonia, respiratory failure, and may require oxygen or mechanical ventilation. Coronavirus pneumonia is a dry cough without a runny nose.
After the virus enters the throat, a dry throat may appear, which occurs with a sore throat. Lasts approximately 3-4 days. But we are talking about dryness, not inflammation. A sore throat is an uncharacteristic symptom of coronavirus. And when we get the usual infections, mucus and phlegm most often begin to be released. A dry cough without sputum production is the second main symptom, which was recorded in 80% of all patients. It can be mild, but debilitating, making it difficult for a person to cough up.
Sputum without cough
Sometimes the accumulation of phlegm is not accompanied by a cough. The method of treatment will depend on the cause of the symptom.
The reasons for the accumulation of phlegm in the throat without a cough can be both physiological processes and diseases. In this case, patients complain of a feeling of a lump in the throat, which they want to cough up, but there is no cough. The accumulated mucus is difficult to excrete, and the person suffers from soreness and itching in the throat.
Additional symptoms accompanying this condition may include fever, severe runny nose, etc. Phlegm in the throat without a cough can be a manifestation of various diseases, so it is impossible to make a diagnosis based on this symptom alone. Additional diagnostics are required.
Diseases that may be accompanied by phlegm in the throat include:
Rhinosinusitis of various etiologies (allergic, viral, bacterial, fungal);
Latent forms of tuberculosis;
Smoking can also cause the formation of sputum that is difficult to cough up. Particles of tobacco smoke settle on the mucous membrane of the nose, throat, and nasopharynx and form thick, difficult-to-remove mucus.
Why does phlegm accumulate?
Accumulation of sputum is rarely the only manifestation of the disease. It is usually accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever, cough, runny nose, etc.
The main reasons for the accumulation of sputum include:
- A runny nose or rhinosusitis of any origin (viral, bacterial, fungal) can cause the appearance of sputum. Mucus and pus formed as a result of the inflammatory process in the nasal cavity and pharynx do not exit through the nose as a result of swelling and flow down the back wall of the larynx;
Acute viral diseases are the main cause of sputum formation. Usually, at the beginning, the patient’s temperature rises, the throat begins to hurt, when the inflammatory process spreads lower to the trachea and bronchi, a cough with thick sputum appears;
Gastro-esophageal reflux, gastritis and esophagitis. In these diseases, the contents of the stomach and esophagus are thrown back into the throat, irritating the mucous membrane, which causes chronic inflammation of the larynx and throat with mucus secretion.
Bronchial asthma is characterized by the reaction of the bronchi to various allergens. In addition to the formation of sputum, symptoms of this disease also include suffocation, wheezing in the chest, and coughing with difficult-to-clear sputum.
Pneumonia and pleurisy. Inflammation of the lung tissue and pleurisy is always accompanied by the formation of thick foamy sputum, high fever, and chest pain.
Constant phlegm in the throat without cough: causes and treatment
Sputum is a special secret produced by the cells of the bronchi.
As it moves through the respiratory tract, mucus from the nose and saliva are mixed into it. In a healthy person, it is transparent, mucous and is released exclusively in small quantities when coughing, and then only if he smokes or works in conditions of increased dust formation.
What is sputum
Sputum is a special secretion that is formed and secreted by the bronchi. Moving upward along the respiratory tract, it gradually mixes with nasal secretions and saliva.
The sputum of a healthy person is almost transparent. Mucus is usually released in small quantities during coughing, in fairly rare cases (in smokers or people whose professional activities involve contact with dust).
Copious amounts of sputum are usually observed with respiratory diseases. If over time the cough is eliminated and the sputum is completely eliminated from the patient’s body, such a process does not cause concern. The situation is different if the phlegm is firmly established in the respiratory tract and annoys the person for a long time and does not go away.
Causes of phlegm in the throat
The human respiratory organs are designed in such a way that they are capable of self-cleaning from the smallest particles of dust, microorganisms and other substances that enter the body along with the inhaled air. Special cilia that make oscillatory movements from bottom to top, and goblet cells that produce mucus are responsible for this.
They line the mucous membranes of the bronchi. Therefore, even in completely healthy people, sputum accumulates and is separated every day, but its volume is so small that a person does not even notice how regularly he swallows mucus removed into the pharynx from the respiratory system.
But sometimes situations arise when phlegm is constantly felt in the throat. Where does it come from in such cases? The main reason for this is either increased production of tracheobronchial secretions or a violation of its excretion. This is typical for:
Sticky phlegm in the throat: causes. How to get rid of
How to remove phlegm from the throat? This issue may bother the patient for a long time or arise suddenly. If this symptom is not accompanied by fever or pain...
Attention! Sinusitis and rhinitis are characterized by the production of yellowish sputum.
However, the accumulation of tracheobronchial secretions in the throat can also be observed against the background of complete health, for example, when consuming alcoholic beverages, spicy, cold or, conversely, hot foods, that is, foods that irritate the mucous membranes.
Diagnostic clue: sputum in the morning
If a person experiences the sensation of a lump of mucus in the throat exclusively in the morning, first of all he should suspect the presence of:
- reflux esophagitis;
- chronic sinusitis;
- cardiopathologies;
- adenoiditis.
Source: nasmorkam.net If viscous sputum is not yet coughed up, then the cause of its appearance should be sought in an unfavorable environment. Most often, this occurs among allergy sufferers and people working in chemical, paint, pharmaceutical and other industries associated with the release of dust, toxic substances and tiny solid particles into the air.
This can also be the result of banal dry air in a room where a person spends a lot of time, for example in an office or bedroom.
Important! Air conditioners greatly dry the air, so it is recommended to use them only simultaneously with household humidifiers.
Causes of mucus formation in the throat
1. Infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract. Most often, increased mucus production is a protective reaction of the body, as it tries to get rid of the infection. The mucus causes irritation and a cough occurs, which helps remove it. So cough is a very “useful” symptom. Also, the evacuation of sputum occurs due to the contraction of millions of cilia that cover the mucous membranes of the respiratory organs.
They move the viscous secretion closer to the oral cavity. However, with abundant mucus formation, a decrease in the cough reflex and poor function of the cilia of the mucous membrane, sputum accumulates and flows down into the bronchi and lungs. In this case, the condition worsens and the symptoms of the disease increase.
Rhinovirus infections initially cause damage to the nasal mucosa with increased production of nasal secretions. It can accumulate in the sinuses (maxillary, frontal), causing sinusitis. Then the infection descends into the nasopharynx, laryngitis and pharyngitis develop.
The next stage is tracheitis, bronchitis, in advanced cases, mucus collects in the lungs and pneumonia develops. The location of the primary lesion depends on the type of infectious agent, but often sequential involvement of all parts of the respiratory system occurs. Along with the appearance of mucus in the throat, the following occurs:
- cough;
- feeling of having a “lump”;
- runny nose;
- pain, sore throat;
- headache;
- chills;
- feeling of body aches;
- temperature increase.
2. A lot of mucus can also form in healthy people when:
- frequent consumption of too hot or cold food;
- smoking;
- drinking alcohol;
- frequent inhalation of heavily polluted air (work in hazardous conditions).
3. Allergic reactions are almost always accompanied by increased production of mucus, especially in the nasal cavity.
4. Diseases of the digestive tract:
- gastritis;
- stomach ulcer;
- esophagitis;
- diseases of the liver and pancreas.
5. Neurological diseases in which the pharyngeal reflex is lost or weakened:
- stroke;
- multiple sclerosis;
- severe traumatic brain injuries.
Most mucus accumulates in the respiratory tract in the second half of the night, closer to the morning. This is due to the fact that during sleep a person is in a horizontal position, which contributes to the stagnation of sputum, at night the mobility of the ciliary epithelium slows down and the cough reflex weakens. Often in the morning, immediately after waking up, a severe cough begins. After coughing up all the mucus that has accumulated overnight, the cough becomes weaker.
Phlegm in a child's throat
The most common cause of phlegm in the throat in children in the absence of other symptoms is adenoiditis. This insidious disease is not accompanied by fever, cough and other signs of acute respiratory infections. But it is typical for him:
- difficulty in nasal breathing;
- nasal voice;
- noisy breathing.
Although even these signs may be absent for a long time. Therefore, only an ENT specialist can make a correct diagnosis and determine the cause of the mucus.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
No special manipulations are required to diagnose the presence of sputum in the patient’s throat. He himself feels its presence in the form of a lump of mucus. This symptom is especially pronounced in the morning after waking up or immediately after eating.
Such accumulations in the throat make swallowing difficult. Expectoration of sputum does not always occur. Sometimes it seems to stick to the throat and causes nausea and vomiting. Provoked by a viral infection, sputum has a less dense consistency and is much easier to remove from the body.
Only a specialist should determine the most accurate reason for the presence of sputum in the patient’s mouth. He will also help you choose the most optimal treatment for such cases. To determine the cause of the presence of mucus in the nasopharynx, the doctor uses the following diagnostic methods:
- Visual inspection . An experienced doctor will quickly and accurately determine the causes of phlegm in the throat and indicate ways to eliminate this unpleasant phenomenon. To simplify this process, the specialist additionally listens to all the patient’s complaints.
- Laboratory diagnostics . It includes taking tests, based on the results of which the cause of the accumulation of discharge is determined.
The color of the sputum can also indicate the type of disease.
- So, if white mucus comes out during expectoration, it is highly likely that fungi of the genus Candida can be found in it, the appearance of which is provoked by sluggish tonsillitis.
- A small amount of clear sputum (occasionally with the presence of white streaks) indicates chronic pharyngitis.
- In case of purulent sinusitis or pharyngitis, the sputum takes on a yellowish tint. Viscous greenish mucus is usually a companion to hypertrophic pharyngitis.
Phlegm in the throat during pregnancy
Almost all pregnant women suffer from heartburn. This is no secret to anyone. Most often it is caused by reflux esophagitis. Therefore, the fact that discharge collects in the pharynx can serve as a secondary sign of the development of a defect in one of the gastric sphincters. As a rule, after childbirth the problem goes away on its own, since the reason for its occurrence is compression of the abdominal organs by the pregnant uterus.[ads-pc-1][ads-mob-1] to contents ?
How to remove phlegm. What do we have to do?
The first thing to do when an unpleasant feeling appears in the throat is to make an appointment with an otolaryngologist, because only a doctor is able to establish the true cause of its occurrence and prescribe treatment appropriate to the circumstances. However, before visiting an ENT specialist, you can take several measures to improve your condition and remove accumulated mucus.
- Carry out inhalations with decoctions or infusions of herbs, mineral water or saline. This remedy will help soften the mucous membranes and facilitate the removal of discharge.
- Take homeopathic medicines. If the patient suspects the presence of sinusitis or rhinitis of any origin, you can start taking Sinupret or another similar medication. They will help remove swelling and improve nasal breathing, so that more mucus will be removed through the nose and flow down the nasopharynx in smaller quantities.
- Drink at least 2 liters of purified water per day, since the accumulation of discharge is often the result of a lack of water in the body.
- Stop smoking.
Medicines against phlegm
Drug treatment is prescribed only by a doctor after examining the patient and conducting a number of additional studies! Depending on the detected cause of sputum accumulation, the ENT recommends that the patient take one or another medicine, in particular:
- antihistamines (Eden, Loratadine, Suprastin, Diazolin, Erius, etc.), if discomfort is the result of an allergic reaction;
- antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs if the patient has green sputum and the presence of a bacterial infection in the sinuses or mouth is proven;
- antiseptic sprays and lozenges (Efizol, Strepsils, Orasept, Tantum Verde, Yox, etc.) are used in the presence of tonsillitis or pharyngitis;
- antacids (Almagel, Rennie, Maalox), prokinetics (Motilium, Motilak) and antisecretory (Omez, Lanza) drugs necessary for gastrointestinal diseases.
At the same time, expectorants and mucolytics, for example, ACC, Lazolvan, Ascoril, Ambroxol, Libexin, Bromhexine and others, are usually not used to eliminate discomfort in the throat , since their action is mainly aimed at eliminating discharge from the bronchi and lungs.
Traditional methods of getting rid of phlegm
Quite often, doctors themselves recommend that patients use folk remedies to eliminate discomfort in the throat. But if in some situations they can be used independently, in others only as an auxiliary therapy. Therefore, before starting to use any folk remedies, you still need to consult an otolaryngologist.
The most effective of them are:
Thus, phlegm in the throat can be either a sign of the development of a particular disease or a consequence of addictions or work in hazardous industries. Nevertheless, it is not difficult to get rid of discomfort; the main thing is to contact a specialist in time to find out the true cause of its occurrence and receive competent recommendations on how to eliminate it.
The use of folk remedies
Folk remedies will help remove phlegm from the throat - gargles, inhalations and internal remedies. There are a large number of recipes for their preparation.
Recipes for rinsing solutions
Let's look at the most effective recipes for preparing cleaning products:
- Saline solution. Salt has a disinfecting effect, destroys pathogenic microflora, and helps clear the throat of mucus. But the product can dry out the mucous membrane, so it is recommended to use it no more than once a day. To prepare the solution you need 1 tsp. add salt to a glass of warm water, stir well and use as intended.
It is impossible for undissolved salt crystals to remain. They can lead to irritation of the mucous membrane and injury to its surface.
- Soda + calendula. Add a few drops of calendula tincture to a glass of water, add half a teaspoon. soda, stir well. Baking soda is an excellent antiseptic and helps to quickly thin mucus. Calendula - moisturizes the mucous membrane and prevents it from drying out. Calendula tincture can be prepared at home. Pour 100 g of flowers with 100 ml of alcohol and leave to infuse for 15 days in a dark place. Then strain and use.
- Herbal decoction. Brew 1 tbsp. l. chamomile or calendula with a glass of boiling water. Then put on low heat and cook until the liquid turns dark brown. Remove from heat and strain. Use after cooling to body temperature. Repeat rinsing with this product every 3 hours. Helps quickly remove mucus from the nasopharynx if the procedure is repeated regularly.
- Soda + iodine. Take 1 tsp per glass of water. soda and 3 drops of iodine. This remedy has pronounced expectorant properties. It can also be used to prevent seasonal diseases by gargling every morning.
All of the above products are safe, do not cause an allergic reaction, and are very effective. But before using them, you need to consult a specialist.
Inhalations
You can also do inhalations at home. The procedure is performed as follows: prepare a solution or decoction in a deep vessel. Then the person bends his head over it, covers himself with a towel and inhales the vapors. Session duration is up to 10 minutes.
To prepare solutions and decoctions, you can use the following recipes:
- Dilute 1 tsp in a liter of water. soda, add 2 drops of iodine.
- Take 1 tbsp per liter of liquid. l. sea salt, add a few drops of pine essential oils.
- Prepare a decoction of mint, chamomile, lemon balm or other herbs. To obtain the effect, they must be used for inhalation for a month.
- Potato inhalation is also very useful. Boil the potatoes in their skins and drain the water. Cut the potato in half and inhale the vapors emanating from it.
After the procedure, you should not go outside or into a cool room. It is best to lie under a blanket and put on warm socks.
Products for internal use
If the mucus in the throat does not go away, you can take folk remedies orally with an expectorant effect. An effective preparation is prepared on the basis of Borjomi mineral water with the addition of honey (1 tablespoon of honey per liter of water). It is also useful to drink milk with soda, raspberry tea. Such remedies boost immunity and help cough up accumulated mucus.
You can also apply compresses to the neck to remove mucus. You can use “Star” balm. It should be smeared on the neck, sternum, and wings of the nose. The drug warms perfectly and helps normalize breathing. But you should not allow the product to get into your eyes, as this can cause burning and itching.
A potato compress warms well. The vegetable must be boiled, peeled, and pureed. Wrap the still warm potatoes in cheesecloth and apply to your throat.
If you do not cough up sputum for a long period, you need to undergo an examination. Otherwise, the underlying disease may become chronic . And this will lead to various consequences.
Associated symptoms
Associated symptoms of sinusitis are usually:
- runny nose;
- swelling of the sinuses;
- the presence of mucus or pus in the paranasal sinuses;
- nasal congestion.
The sensation of a lump in the throat appears when mucus flows down the back wall of the throat. The intensity of the process depends on the disease and its form. Chronic rhinitis occurs in a more latent and sluggish form, acute rhinitis can be accompanied by fever, headache, weakness, loss of smell and other symptoms.
With pharyngitis and tonsillitis the following is observed:
- inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa;
- a sore throat;
- swelling, redness;
- pain when swallowing;
- dry cough.
Mucus accumulates in the throat and causes discomfort.
With diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, namely reflux esophagitis, the contents of the stomach can involuntarily enter the esophagus, irritate it and cause the production of additional sputum. Gastroesophageal reflux disease is accompanied by symptoms such as belching, heartburn, retching, and a feeling of a lump in the throat.
Another disease of the gastrointestinal tract, in which sputum appears, is a diverticulum of the esophagus (protrusion). Food remains are retained in the protruding pouch, and the process of their decay causes additional secretion of sputum.
Cardiac pathologies contribute to a slowdown in gas exchange in the lungs, stagnation of blood in the lungs, which in turn slows down the removal of natural secretions. It accumulates in the bronchial tree. In the morning after sleep, the accumulation of such sputum reaches its maximum. Cardiac problems are indicated by shortness of breath, unstable heart rhythm, swelling of the legs and other specific symptoms.
Hormonal imbalances in the body lead to an increase in the level of sputum secretion. Diagnosis of such disorders is impossible without additional laboratory tests, both sputum and blood.
Autoimmune pathologies accompanied by a false sensation of accumulation of a large amount of sputum include Sjogren's syndrome, in which the functioning of the salivary and lacrimal glands is disrupted, and the mucous membrane in the mouth dries out.
The latent form of tuberculosis can sometimes manifest itself only by increased secretion of sputum, night weakness and increased sweating. In this case, the cough is practically absent.
In case of cancer, the diagnosis can sometimes be made after examining the composition of sputum. It may be viscous, contain blood, and have an unpleasant odor.
Considering the variety of reasons why sputum forms without coughing, if you find discomfort and excessive secretion, you must seek qualified medical help and not self-medicate.
What treatment can the doctor prescribe?
If the diagnosis does not reveal serious disorders and pathologies (cardiological, oncological, tuberculosis, hormonal imbalances), then for the treatment of bacterial, allergic, viral and fungal diseases accompanied by sputum discharge, antibacterial, antihistamine, antiviral and other drugs are prescribed, depending on the established diagnosis.
Antihistamines normalize the amount of sputum produced during allergic reactions. These include:
For severe allergies, an allergist may recommend a course of treatment in a hospital.
If there is copious secretion in the presence of a bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed. Before prescribing, it is necessary to analyze the discharge and determine both the presence of the bacteria themselves in it and their sensitivity to pharmacological drugs.
- Amoxicillin;
- Cefuroxime axetil;
- Azithromycin;
- Cefotaxime;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Cefepime.
For the treatment of tonsillitis and their varieties, sore throats are used:
- Phenoxymethylpenicillin,
- Benzylpenicillin,
- Benzathine
If the infection is resistant to the above drugs or has an allergic reaction to them, the following is prescribed:
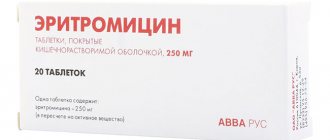
- Erythromycin,
- Azithromycin,
- Spiramycin,
- Clarithromycin,
- Lincomycin,
- Clindamycin
For lower respiratory tract infections it is recommended:
Antiviral drugs are recommended to be used only in the initial stages of the disease (Eogoferon, Ingaferin).
To relieve local inflammation of the upper respiratory tract (throat, larynx) and thin sputum, sprays, tablets and lozenges are used:
- Strepsils;
- Faringosept;
- Hexoral;
- Septolete;
- Lugol;
- Cameton.
Possible complications
The lack of high-quality diagnosis and treatment aimed at eliminating the symptom in the form of constantly present phlegm in the throat can lead to the development of the following complications:
- allergic edema of the larynx;
- spread of the inflammatory process to the tonsils and upper respiratory tract;
- decrease in voice timbre;
- the addition of a bacterial infection with damage to the mucous membrane and soft tissues of the throat;
- significant decrease in local immunity;
- the appearance of an unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth.
The constant presence of phlegm in the throat is one of the symptoms that may indicate a painful condition of the nasopharynx, upper respiratory tract, digestive system of the body, paranasal sinuses, and a tendency to allergic reactions to external and internal irritants.
Elimination of the feeling of discomfort in the larynx is carried out through drug therapy for the underlying disease, which causes the accumulation of excess mucus. Folk remedies and physiotherapeutic methods can also be used, which increase local and general human immunity.
Traditional medicine to help
Along with pharmacological drugs, traditional medicine is also used to treat the respiratory system. They are time-tested, have a gentle effect, and, as a rule, do not cause allergic reactions.
Traditional methods are especially effective for treating diseases at the initial stage and for combating residual effects. Their effectiveness has been proven even in the presence of a bacterial infection.
Drinking medicinal teas, infusions, fruit drinks, vitamin drinks replenishes fluid loss in the body during illness and removes toxins. Drinking milk with honey and soda softens the mucous membrane.
Rinsing relieves irritation, inflammation and swelling, improves sputum production. Rinsing with decoctions of sage, chamomile, and oak bark gives good results. You can gargle with salt and soda solutions. The optimal number of rinses is 3-4 per day. After rinsing, it is not recommended to drink or eat.
Inhalations are recommended to be taken after the temperature has normalized. To prepare inhalations, use medicinal infusions brewed in a water bath (chamomile, calendula, sage, coltsfoot, birch buds and others). You can use essential oils (eucalyptus, lavender, fir, tea tree). Inhalations performed with alkaline mineral water also have a calming, softening effect.
After inhalation, active sputum production and significant relief of the condition are observed.
To combat phlegm, it is recommended to take radish juice mixed with honey, as well as a medicinal composition prepared from aloe leaves and honey.
How to get rid of phlegm at home
Since sputum is not an independent disease, but only a symptom, the underlying disease should be treated. To remove mucus from the throat, you should drink a lot of liquid or try to remove it by coughing and coughing. It is recommended to take standard pharmaceutical medications that can loosen mucus and use traditional methods. The latter, alas, bring results only after 2-3 weeks of use.
- Yoga lessons at home for beginners
- English elastic knitting
- How to cleanse the intestines of toxins
With the help of drugs
Depending on the cause of the sputum, the patient is prescribed certain medications. If you self-medicate, you may be able to eliminate the symptom, but not the underlying disease. After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes:
- antibacterial drugs (“Amokislav”, “Flemoxin”);
- antiviral tablets (Arbidol, Viferon);
- special sprays (“Inhalipt”);
- expectorants (“Mukaltin”, “Lazolvan”, “Sinupret”);
- inhalation with mucolytics (“Ambrobene”, “Lazolvan”).
Folk remedies
If the mucus in the throat does not clear up, it is recommended to use recipes from traditional healers along with medications. For phlegm caused by a cold, you should drink herbal decoctions. Chamomile, oregano, St. John's wort, coltsfoot, and oak bark have excellent expectorant properties. The decoction is prepared simply: 1 tbsp. spoon of any herb pour 1 tbsp. hot water, boil, judge and take several times a day. You can simply drink mineral water by heating it and adding honey.
Effective rinses:
- Saline solution. Dissolve 1 tbsp in 1 glass of water. spoon of salt.
- A mixture of salt, iodine, soda. Take 1 teaspoon each of soda and salt, pour a glass of water (warm), add a couple of drops of iodine.
Tips for treatment and prevention
The main advice for treatment, regardless of whether the diagnosis is established or only suspected, is not to self-medicate. The sooner you seek qualified medical help, the faster and more effective the treatment will be. Whatever medications are prescribed, the course of treatment must be completed, especially when it comes to antibiotics. Untreated acute conditions tend to become chronic. Any chronic respiratory disease is difficult and time-consuming to treat.
As for disease prevention, if it is carried out regularly and in a timely manner, most diseases can be avoided. And even if the disease does occur, it is easier and passes faster.
Prevention measures for both adults and children include: staying in the fresh air, active lifestyle, balanced diet, reasonable daily routine, stable positive psycho-emotional state. For adults, it is very important not to develop bad habits (smoking, excessive drinking).