How does it manifest?
When a person has a history of internal diseases, signs of nocturia will occur in conjunction with other symptoms.
If we consider nocturia as a separate condition, then the following symptoms will be present:
- Night trips to the toilet more than 1 - 2 times.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Anxious dream.
- Increased fatigue.
- Absent-mindedness.
- Irritability.
All of the above symptoms mainly appear against the background of regular disruption of night sleep, which disrupts nocturnal diuresis. Signs of nocturia in women, less often in men, are swelling of the face, upper and lower extremities. Patients complain of surges in blood pressure and heart rhythm disturbances.
Before treating frequent nocturnal diuresis, it is important to determine the causes of this condition, since the prognosis for further recovery will depend on the quality of therapy. Symptoms of nocturia are a complex of disorders of the kidneys and urinary system, so it is important to listen to your body and do not hesitate to visit a doctor at the first signs of illness.
Folk remedies
For excessive urination or frequent urination in women at night, folk remedies containing natural ingredients can provide relief.
Here are a few examples of such recipes that will help in the treatment of nocturia.
If you suffer from frequent urges to urinate at night, just before going to bed, take 4-5 roasted coffee beans and chew them.
Women suffering from frequent urine discharge after childbirth are recommended to use small carrot tops. You need to take 3 tablespoons of raw material, add a liter of cool water and boil on the stove for 30 minutes.
After straining and cooling to room temperature, you can drink 1 glass 2 times a day.
In order to destroy pathogenic microflora and create a protective barrier, you can prepare decoctions based on oak bark. Pre-boil 1 liter of water, which is then used to brew 2 teaspoons of dry raw materials.
The container is left to infuse for an hour and filtered. Frequency of use: twice a day, 30 minutes before (or after) meals.
Teas from plant materials. You can purchase ready-made mixtures in pharmacies, which contain several herbs at once, or, if desired, prepare them yourself.
Thus, tea made from mint leaves and St. John's wort allows you to quickly remove toxins and help fight inflammatory processes.
If a person does not have diseases for which heating is contraindicated, then one of the options for alleviating the condition is taking a half-hour bath with the addition of herbal decoctions. Senna leaves and pine branches give a good effect in the treatment of nocturia in women.
An infusion of chamomile and horsetail is suitable as a soothing and disinfectant. They are taken in equal proportions and brewed like tea. Take 3 glasses a day in slow sips.
It is recommended to eat walnuts, pine nuts and dried fruits before bed, as they require a large amount of liquid for digestion.
Another recipe for herbal tea from the collection of folk remedies: combine twigs and leaves of St. John's wort and centaury and grind into a “leaf tea”. Pour boiling water over and leave for a little while. Drink for 2 weeks, morning and afternoon.
General information
Domestic urologists have traditionally used the terms “nocturia” and “nocturia” to refer to urination at night, putting into them completely different concepts.
Nocturia was diagnosed when the patient was forced to get up to urinate at night due to increased nocturnal urine output. Increased nocturnal diuresis was considered a consequence of cardiac or renal failure. Nocturia has been associated with nighttime urination, which is caused by irritative symptoms (storage symptoms).
In general, most urologists still associate night urination with BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia), and nocturia in women is not considered at all in most urology textbooks.
The symptom of night urination began to be actively studied in the late 90s of the 20th century, since the accumulated research by this time revealed the clinical heterogeneity of patients suffering from this symptom. These findings have prompted the need to reconsider and standardize the terms used.
In 2002, the ICS (International Continence Society Committee) proposed the term nocturia, which refers to the patient's need to get up one to several times at night to empty the bladder.
E.L. Wisniewski et al believe that the term “nocturia” should be more appropriately used to refer to nocturnal urination, and the term “nocturia” should be used to refer to increased urine output at night.
This symptom is observed more often in men.
Nocturia is considered a common symptom in elderly patients - nocturia in children from 7 to 15 years of age was detected in only 4% of cases, in men from 50 to 60 years of age - in 66% of cases, and in men over 80 years of age - in 91% of cases .
According to studies conducted in 1999, GL Robertson found that nighttime urine production in people from 21 to 35 years old is 14% ± 4% of the daily volume, and in older people - 34% ± 15%.
How to recognize the disease?
If you experience frequent urination at night, you should not hesitate to visit a urologist or nephrologist, since such a symptom may be the first signal of the development of any disease. The initial consultation with a doctor will include taking a medical history, prescribing laboratory tests and instrumental diagnostics.
- general urine analysis;
- bacteriological urine culture;
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and pelvic organs.
An informative research method is urine analysis according to Zimnitsky, which allows you to determine the daily volume of urine. When conducting such an analysis, it is prohibited to consume diuretics, as well as foods that increase thirst. If other diseases are suspected, diagnosis includes consultation with a cardiologist, nephrologist, and additional diagnostic methods.
Diagnosis of nocturia
The problem can be identified in the early stages of pathology development. Diagnostics proceed as follows:
- Collection of relevant complaints from the patient (how many times he urinates during the day and at night).
- Finding out the process of development of nocturia, what it is associated with (taking medications, taking fluids before bed).
- Determination of the type of nocturia. Patients should keep a urination diary for 5 days to understand whether it is a pathology or not.
- Detecting the presence of chronic diseases of the kidneys, cardiovascular and other systems.
- General examination of the patient.
To confirm the pathology, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are required:
- General analysis of urine to identify its specific gravity, signs of inflammation, and bacteria. At night it should normally be higher. If you have diabetes, there will be sugar in your urine.
- Bacteriological culture of urine. To determine the flora that caused the inflammation. Sensitivity to antibiotics is also revealed in order to select a drug with a narrow spectrum of action.
- Zimnitsky's test. Examine 8 portions of urine every 3 hours. The ratio of daytime and nighttime diuresis is determined and the specific gravity of each portion is examined. Nocturia is characterized by a decrease in urine density and a predominance of nocturnal diuresis. Thanks to this study, one can suspect renal failure, diabetes insipidus, and inflammatory kidney diseases.
- Determination of level Its level is reduced in diabetes insipidus.
- Ultrasound of the bladder (allows you to determine the residual volume in the bladder), kidneys and abdominal organs.
- Examination of men - a digital examination of the prostate through the rectum is also carried out to identify an adenoma. The symptoms and treatment of nocturia in men are determined by a urologist.
- What is nocturia in women? This is a decrease in estrogen levels (determined by laboratory). In this case, there is a drop in the muscle tone of the bladder and a weakening of the pelvic floor muscles. Urinary disorders develop. The symptoms and treatment of nocturia in women are determined by a gynecologist.
Forms
Depending on the cause of development, nocturia is divided into:
- temporary, which develops during crisis conditions (diencephalic and hypertensive crisis) and tachycardia;
- constant, which develops in the presence of damage to internal organs and glands.
Based on the nature of daytime diuresis, nocturia is divided into:
- true, which is characterized by daytime oliguria (cessation of urination);
- unstable, in which a decrease in daily diuresis is not observed (accompanies thyroid disease, diabetes insipidus, liver cirrhosis, prostate adenoma and pernicious anemia).
Tips and tricks
If you experience frequent urination at night, doctors recommend keeping a diary where your drinking regime and the number of urinations will be recorded. Such indicators will help in making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment. In addition, you need to adhere to some preventive rules:
- It is recommended to refrain from drinking before bedtime.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Contact doctors in a timely manner.
- Correctly treat all associated diseases.
- Reduce intake of alcoholic beverages, coffee, strong tea.
- Healthy lifestyle.
- Moderate physical activity.
- Periodic laboratory tests of urine and blood.
Following simple rules will reduce the risk of developing nocturia and other diseases affecting internal organs and systems. Frequent nocturnal diuresis is considered by many doctors only as a symptom, so you need to look for the cause and not self-medicate.
Treatment of nocturia
First of all, you need to identify the cause. Only a doctor can diagnose and treat nocturia.
They are aimed at eliminating the provoking factors for the development of nocturia. To reduce discomfort from the disease, you need to:
- Avoid taking liquids and foods with a diuretic effect (watermelon, melon) 3 hours before bedtime. It is better to limit the water load on the body after 6 pm.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Do not take diuretics at night. Typically, such drugs are taken in the morning along with antihypertensives.
- Empty your bladder before bed.
Reasons for development
The causes of nocturia are various diseases, which include:
- Heart failure. The cause of the development of the symptom in this case is venous stagnation, as well as fluid retained in the tissues during the day.
- Kidney diseases (chronic glomerulonephritis, nephrosclerosis, chronic pyelonephritis, cystopyelitis, cystitis). The development of nocturia occurs due to the dilation of the vessels of the kidneys and an increase in their blood flow at night.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Cirrhosis of the liver. Nocturia in this case is caused by arterial hypertension developing with cirrhosis.
- Diabetes insipidus, in which nocturia is caused by hypertensive dehydration. Hypertensive dehydration occurs when it is impossible to replenish water deficiency and when there is a deficiency of the antidiuretic hormone vasopressin.
- Prostate adenoma (this is the reason why nocturia develops in men in many cases). Nocturia is caused by obstructed outflow of urine due to enlargement of the prostate gland, as a result of which urine returns to the bladder.
- Pernicious anemia. This symptom is the result of anemia and low blood pressure.
- Atrophy of the pelvic floor muscles (for this reason, nocturia develops in women). Provoking factors include pregnancy and childbirth, chronic increase in intra-abdominal pressure, mechanical injuries of the muscular-fascial structures of the pelvis, varicose veins, hernias of various locations, etc.
- Calcium channel blockade, which occurs with orthostatic swelling of the ankles.
- Edema that occurs due to venous stagnation of blood.
- Obstructive apnea, in which dilatation of the heart occurs (an increase in its volume while maintaining the thickness of the heart wall). Dilation of the heart causes the production of atrial natriuretic peptide, a hormone that is involved in the regulation of water and electrolyte metabolism by reducing the volume of water and sodium concentration in the vascular bed.
In rare cases, nocturia can be caused by hypercalcemia.
Nocturia can also be caused by taking diuretics and certain other medications at night, or drinking coffee, tea or alcohol before bed.
Pathogenesis
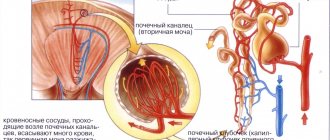
The amount of water in the body is regulated by the antidiuretic hormone vasopressin released by the hypothalamus. Under the influence of this hormone, the reabsorption of water in the kidney ducts increases (the concentration of urine increases and its volume decreases).
Normally, the level of antidiuretic hormone is higher at night, but with age, the secretion of antidiuretic hormone at night decreases.
In elderly people, there is also a decrease in the level of angiotensin II. This hormone affects the proximal tubules, increasing sodium retention, which causes an increase in urine volume.
The pathogenesis of nocturia is not fully understood. Most researchers believe that the most common and main factor in the development of nocturia is weakening of the heart.
According to the hypothesis, a weakened heart during the day is not able to cope with the load, so patients experience venous congestion in the kidneys and decreased diuresis. At night, during sleep, muscle tone drops, mental irritants and other factors active during the day are absent, so heart function improves, and blood circulation in general and in the kidneys in particular returns to normal. As a result of improved blood circulation, diuresis increases.
This hypothesis is theoretical in nature, since improvement in blood circulation during sleep has not yet been proven.
An important factor in the pathogenesis of nocturia of any origin is the weakening of pathologically increased tonic contraction of renal vessels during sleep, as well as a change in the conditions of tissue fluid absorption at this time. According to many researchers (Volhard, Klein, etc.), these factors are key in the pathogenesis of long-term nocturia in the absence of visible signs of cardiac weakness.
Because kidney disease associated with nocturia impairs the heart's function and can eventually lead to heart failure, it is often difficult to determine whether cardiac, renal, or vascular factors contribute to the development of nocturia.
According to some data, nocturia in older women can develop as a result of a deficiency of sex hormones that occurs with age. A deficiency of sex hormones causes dysfunction of the pelvic organs, which includes night urination.
Nocturia, which often occurs in the later stages of pregnancy, is associated with pressure on the bladder from the enlarged uterus.
Treatment of nocturia
A signal to see a doctor is frequent (two or more) trips to the toilet at night in the absence of a large amount of liquid drunk in the evening.
When the symptoms are confirmed by laboratory tests, treatment of nocturia begins. In essence, it represents the diagnosis and therapy of the underlying disease.
Various antimuscarinic drugs, for example, Solifenancin, have been successfully used to treat nocturia with overactive bladder.
Also, patients with nocturia, especially older women, are recommended to systematically train the pelvic floor muscles and avoid drinking heavily in the evening.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Nocturia is urination at night, which can indicate negative processes in the body. The condition is considered pathological if a person systematically gets up to go to the toilet at night more than 2 times over a long period of time (days, weeks, etc.). It is a type of urination disorder and is more common in the male population.
Symptoms
Normally, the ratio of daytime to nighttime diuresis is 2:1 (about 60 - 80% of the daily amount of urine is excreted during the daytime). With nocturia, nighttime diuresis exceeds daytime diuresis by 2 times.
Symptoms of nocturia include:
- increased urine production at night;
- small bladder capacity at night;
- insomnia, which develops due to the frequent need to visit the toilet at night;
- restless sleep;
- fatigue that is constantly present during the daytime.
Nocturia as a result of sleep disturbance is also accompanied by:
- decreased mental performance;
- decreased mental flexibility;
- memory impairment;
- depressed mood to the point of depression;
- increased irritability.