Calcitonin is
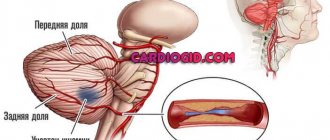
a hormone produced by the C cells of the thyroid gland that reduces the level of calcium in the blood, an antagonist of parathyroid hormone. Calcitonin is a tumor marker in the diagnosis of medullary thyroid cancer.
A tumor marker is a substance that is produced by malignant cells or the body in response to the presence of a tumor. Read more about various tumor markers here. Learn how to prepare for a blood test for tumor markers here.
Calcitonin consists of 32 amino acids, molecular weight - 3500 Da. Formed in parafollicular C-cells of the thyroid gland (1% of all cells). It is detached from a large protein, procalcitonin, before entering the blood. Receptors for calcitonin are found in bones, kidneys, brain (hypothalamus, pituitary gland), testicles, and lymphocytes.
Calcitonin secretion stimulator - decreased calcium levels in the blood - hypocalcemia. Excreted from the body by the liver and kidneys. The half-life is about 10 minutes.
Function of calcitonin in the human body:
- reduces calcium absorption in the intestine
- stimulates the release of sodium, calcium, uric acid, increases daily diuresis
- reduces osteoclast activity - prevents bone resorption (i.e. destruction)
- vitamin D synthesis stimulator
- reduces the secretion of gastric juice
- weak anti-inflammatory effect
The level of calcitonin in the blood depends on the concentration of free calcium and parathyroid hormone.
↓ calcium → release of parathyroid hormone → release of calcium from bone → increase in blood calcium levels → release of calcitonin →…
With medullary thyroid cancer, a mutation occurs in the C-cells of the thyroid gland, they begin to actively divide and produce calcitonin. That is why calcitonin increases significantly in this type of tumor. In other cancers, the tumor tissue may contain C-cells, which will lead to an increase in the level of calcitonin in the blood.
Blood test for calcitonin
The concentration of calcitonin can now be determined in many laboratories, which use various equipment for this purpose. The most reliable information about the content of this hormone can be obtained using 3rd generation analyzers based on the immunochemiluminescent method. More common 2nd generation analyzers using enzyme immunoassay methods are cheaper, but have a serious drawback - a significant error in the result. Their use may lead to inaccuracies in the diagnosis and subsequent treatment of patients.
If in a blood test calcitonin is the main indicator you are interested in, ask the laboratory what method is used to perform the analysis.
A very dangerous malignant tumor, C-cell carcinoma, or medullary cancer, can develop from the C-cells of thyroid follicles. A feature of this tumor is its relatively slow but steady growth. Over time, medullary cancer metastasizes to the lymph nodes located in the neck and mediastinum; through the bloodstream, metastases can also reach the lungs, liver, bones and even the brain. Treatment of C-cell carcinoma presents significant difficulties, since the tumor does not respond to antitumor chemotherapy drugs and radiation therapy. Only antitumor agents based on kinase inhibitors can have a minor effect on C-cell carcinoma. The only effective treatment for this type of cancer is surgery in the early stages of the process. This is the only way that gives a chance for recovery if cancer is diagnosed early.
Since C-cell carcinoma grows from cells that secrete calcitonin, its content in the blood increases sharply already in the early stages of cancer. This is why the content of this hormone is of such interest to endocrinologists and surgeons. Calcitonin concentration testing is the most reliable and early method for determining medullary cancer, which allows saving more than one thousand human lives.
Every year, approximately 100-150 new cases of C-cell thyroid carcinoma are registered throughout Russia. Statistical studies have shown that in 16 densely populated regions of the European part of Russia, about 40 diagnoses of medullary cancer are made per year.
Among all cases of thyroid tumors, the most dangerous are the anaplastic and medullary forms. While effective treatment methods have not yet been developed for anaplastic cancer, C-cell carcinoma is completely curable if diagnosed early. And only a blood test for calcitonin can help with this.
In 2012, the European Thyroid Association added to its recommendations an indication of the need for a single determination of calcitonin in all patients with nodules in the thyroid gland. This analysis does not have to be performed every year; a repeat study in the case of the first normal result is prescribed only if new nodes have been registered.
According to the results of large studies conducted internationally, when calcitonin levels are determined in all patients with thyroid nodules, previously unsuspected medullary cancer is detected in 1 case out of 300.
This fact has led the European endocrine community to believe that the financial costs of conducting 300 studies will be justified if at least one of them reveals the presence of medullary cancer. At the same time, the American Thyroid Association still believes that such a massive scale of calcitonin research is not economically justified. This concerns only the financial part of the issue; no one doubts the clinical value of this method.
Provocative tests
Provocative tests are several times more sensitive than independent testing of calcitonin in the blood. Prescribed when the test results of calcitonin concentration are normal, but in the presence of symptoms of medullary carcinoma.
The initial level of calcitonin is determined, then an intravenous injection of calcium gluconate or pentagastrin is given, which stimulate the release of calcitonin. After 5-10-15 minutes, blood is taken again for analysis and the increase in calcitonin is assessed. In healthy people, the increase is 30-90%, in patients with medullary carcinoma - 100-1000% and higher.
Role and functions in the body
A small number of C-cells produce a hormone, a violation of the concentration of which affects not only the musculoskeletal system, but also disrupts the course of physiological processes. Thyroid calcitonin reduces the absorption of Ca in the intestine, which prevents excessive accumulation of calcium in the blood.
Other important functions of the hormone:
- activates the process of vitamin D synthesis;
- suppresses inflammatory processes in the body;
- reduces the activity of osteoclast cells, which reduces the risk of bone tissue destruction;
- stimulates the release of uric acid, Na, Ca, increases the volume of urine excreted;
- reduces the secretion of gastric juice;
- stimulates the development of osteoblasts for rapid bone regeneration;
- interferes with the reabsorption of Ca by the kidneys, promotes the excretion of the trace element in the urine.
Facts about calcitonin
- calcitonin was discovered by scientists in 1961
- C cells (which produce calcitonin) were first described in 1976
- salmon calcitonin is more active than human or pig calcitonin
- Normally, the level of calcitonin in the blood depends on the amount of estrogens - the main female hormones
- with elevated calcitonin levels, other thyroid hormones - TSH, T4, T3 - remain within normal limits
- After total removal of the thyroid gland, you should not take calcitonin in tablet form; the body can exist without it
- increased hormone levels are not accompanied by changes in calcium and phosphorus metabolism
- stimulators of calcitonin release - alcohol, gastrin, glucagon
- Calcitonin preparations are used to treat Paget's disease, prevent acute bone loss in immobilized patients, and hypercalcemia in tumor diseases
Calcitonin hormone: general information
The concentration of a specific substance depends on the levels of parathyroid hormone (a regulator produced by the parathyroid gland) and free calcium. An important component affects the exchange of Ca and phosphate ions, which are responsible for the constancy of the membrane potential. For this reason, even small fluctuations in thioreocalcitonin are dangerous. The production of the hormone maintains optimal concentrations of potassium (K) and calcium (Ca). A long peptide of 32 amino acids provides counteraction to the influence of parathyroid hormone.
The main share of the thyroid hormone calcitonin is produced by parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland; thyrocalcitonin is also produced in small quantities by the structural elements of the lungs and gastrointestinal tract. To reduce Ca levels, the body uses several mechanisms.
In newborns, levels of an important regulator are increased in the first days of life. During pregnancy and in nursing mothers, the level of thyrocalcitonin is higher: it is important to protect the woman’s body from increased loss of Ca, to ensure optimal supply of the microelement to the fetus, for the formation of a complete musculoskeletal system.
Calcitonin is a specific indicator indicating a pathological process in the body. The hormone is a tumor marker for medullary thyroid cancer, but high values do not always indicate the development of a malignant process. If the levels are elevated, additional examination is required: ultrasound of the thyroid gland and tissue biopsy of the affected organ, a provocative test using pentagastrin or calcium gluconate. Excessive concentration of thyrocalcitonin may indicate active inflammation of the thyroid gland, lungs, and severe dysfunction of the excretory system.
Learn about nutritional features and rules for following the 5P diet for pancreatitis.
Instructions for using the drug Endorm to restore the functioning of the thyroid gland are described on this page.
Preparing for analysis
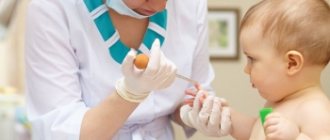
To determine the level of calcitonin in the blood, a blood test is taken from a vein.
Before collecting material, the following rules must be observed:
- do not eat food for 8 hours (you can only drink water), and about a day before the analysis, exclude fatty and fried foods, as this may negatively affect the result;
- a month before donating blood, stop taking medications, including oral contraceptives, as well as calcium supplements;
- the day before the analysis, avoid physical activity (they can lead to false results, namely a decrease in the concentration of calcitonin), and also do not drink alcohol;
- Before the study, it is not recommended to undergo ultrasound, radiography, fluorography and physiotherapeutic procedures;
- If possible, avoid stress or psycho-emotional overload, do not smoke three hours before the test.
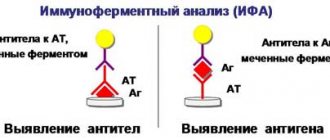
The level of calcitonin is determined using enzyme immunoassay or chemiluminescence immunoassay, with the ELISA method most often used. The results of the analysis usually have to wait for several days.
The test result can be affected by estrogens, adrenaline, glucagon, syncalide, so special attention should be paid to drugs containing these substances. If it is impossible to stop taking them before the study, you must inform your doctor about this fact.
How to prepare and donate blood
In the example, the endocrinologist explains why it is important to follow the rules of preparation for the study. Violation of recommendations leads to inflated or decreased indicators, which prevents timely identification of the pathological process or makes a person worry about a non-existent disease.
Elevated prolactin in men: what does it mean and what is the normal level? We have the answer!
Read about the normal levels of thyroid hormones TSH and T4 in women after 50 years, as well as the causes and symptoms of deviations at this address.
Follow the link https://vse-o-gormonah.com/hormones/testosteron/preparaty-dlya-povyshenija.html and learn about the causes of low testosterone in men, as well as how to increase the level of the hormone with the help of medications.
It is important to know 5 simple rules:
- Avoid alcoholic drinks, gym exercises, and nervous stress for one to two days before blood sampling.
- 8-9 hours should pass from the time of the last meal to the visit to the laboratory. Blood is donated only on an empty stomach; you cannot drink water, tea, coffee, milk, or other types of liquid. Antihypertensive drugs, diuretics, cardiac glycosides are allowed to be taken after donating the biomaterial.
- Avoid smoking 4–5 hours before the test.
- The analysis is carried out from the morning until 11 o'clock.
- There is no need to be nervous in a medical facility. You need to sit at the blood sampling room for 15–20 minutes to calm down.
READ ALSO: Peptide hormone calcitonin in women: norm, causes of deviations, preparation for the test and test results
What are the dangers of elevated calcitonin levels?
High hormone levels are established in the following pathologies:
- medullary cancer, hyperplasia or adenoma of the thyroid gland;
- melanoma;
- breast cancer;
- oncology of the liver and gastrointestinal tract;
- tumor metastases;
- thyroiditis;
- pneumonia, tuberculosis and other lung diseases;
- kidney failure;
- pernicious anemia;
- Graves' disease;
- Hashimoto's disease.
However, an elevated calcitonin value is not always dangerous. For example, in case of injury, its level rises to accelerate tissue regeneration.
Sometimes it happens that calcitonin is at the upper limit of normal, without exceeding it. In this case, you should start eating right, getting more rest, and avoiding injuries and strenuous physical activity. It is also advisable to conduct additional research to exclude the initial stages of dangerous diseases.
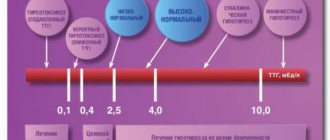
You should be wary if the hormone is elevated for a long time. Of particular danger is a blood level of more than 100 pg/ml calcitonin, which indicates a high probability of thyroid cancer and requires surgical intervention.
Reasons for deviations
Doctors record high levels of calcitonin in other types of pathologies:
- inflammatory process, active development of infection in the lungs: tuberculosis, bronchitis, pneumonia,
- renal failure (chronic form),
- Graves' disease, autoimmune pathology Hashimoto's thyroiditis,
- the period after surgery for partial or complete removal of the thyroid gland.
Thyroid calcitonin decreased reasons:
- against the background of a tumor process, C-cells do not yet produce an amount of tumor marker sufficient for the diagnosis of medullary carcinoma,
- positive dynamics of therapy,
- neoplasm tissue does not produce the hormone calcitonin,
- low rates are a sign of the absence of oncological pathologies and inflammatory processes in the body.
Blood testing using ELISA or LCL to determine calcitonin levels is an effective way to diagnose and monitor therapy for medullary cancer in the tissues of the thyroid gland and oncopathologies of other organs. The combination of the analysis with a provocative test gives an accurate answer about the presence or absence of medullary carcinoma.
The tumor marker also indicates acute inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract and lungs. When comparing test data with the norm, it is important to take into account the type of study (CL or ELISA), units of measurement, gender and age of the patient. Calcitonin test shows level 2.0? This does not always mean the development of severe pathology: perhaps, when studying the blood, doctors used the ELISA method, and the indicators are normal.
What is calcitonin?
Calcitonin is the only thyroid hormone that is not associated with iodine metabolism in the body. It is formed in cells of the “C” type of gland, but in small quantities it can be synthesized by cells of other organs, for example, the lungs. The production of the hormone begins during the last weeks of embryonic development, but in the first months of a child’s life, due to the immaturity of both the gland and the mechanisms of biological molecules, its activity is low. The peak of calcitonin activity is 10-40 years, after which its level in the body decreases.
Mechanism of action of calcitonin
Bone tissue includes osteoclast cells, which are normally necessary for bone renewal, and osteoblasts, which are involved in the formation and ossification of the structural material of the body:
- Osteoclasts - expel calcium from bones into the bloodstream, which leads to the destruction of bone cells.
- Osteoblasts mobilize calcium back, causing less of it in the bloodstream.
Osteoclasts and osteoblasts are target cells for calcitonin. The hormone does not allow destructive cells to function, and vice versa, it activates the work of osteoblasts. The hormone calcitonin also regulates the level of phosphorus in the bloodstream, preventing it from being reabsorbed from the primary urine.
Patient preparation
2 weeks before the test, stop taking any medications. You can get tested without this if this is not possible. But then all data on taking medications must be noted on the analysis form so that an allowance can be made for this. To better prepare for the tests, you should completely eliminate alcohol and fatty foods from your diet the day before the test.
They also exclude severe physical strain and stress. Blood tests are never performed after X-rays and ultrasounds. Preparation also includes dinner no later than 8 hours before blood donation. You can't even drink tea and coffee.
The calcitonin test must be taken on an empty stomach; it is not even recommended to drink water 3 hours before the test. You also need to take the test in the complete absence of smoking 2 hours before the test. When you donate blood for analysis, your emotional state should be calm and even.
Indications for analysis
Venous blood to determine the level of an important hormone must be donated during the diagnosis of medullary cancer in the cells of the thyroid gland. An endocrinologist gives a referral for analysis.
Other indications for calcitonin testing:
- suspicion of C-cell hyperplasia in the thyroid tissue;
- for the diagnosis of a malignant process in the mammary glands, prostate, lungs with the development of a calcitonin-producing tumor. In a pathological process, the neoplasm is not located in the thyroid gland, but in other parts of the body;
- for early detection of the metastasis process;
- to monitor the results of therapy for thyroid cancer (medullary cancer);
- to identify a genetic predisposition to the development of cancer in relatives of patients who have been diagnosed with MEN II syndrome or medullary thyroid cancer.
Decoding the results
Interpretation of the results obtained is a job only for a specialist; you cannot engage in self-diagnosis based on the obtained conclusion without a medical education. The opinion that average hormone levels should be below zero is incorrect.
Calcitonin levels may deviate from the norm depending on various factors:
- age and gender of the patient: in men they are higher, and over the years the norm decreases;
- individual physiological characteristics of a person;
- analysis methods;
- pregnancy, during which there is more calcitonin in the blood.
Limits of calcitonin normal values
| Floor | Immunoenzyme method pg/ml (picograms per milliliter) | Immunochemiluminescent method pmol/l (picomoles per liter) |
| women | 0,07-12,97 | less than 1.46 |
| men | 0,68-32,26 | less than 2.46 |
| children | up to 70 |
A higher than normal level of calcitonin in a person may mean:
- medullary cancer or C-cell hyperplasia (an increase in the number of thyroid cells due to the acceleration of their neoplasm);
- some types of tumors localized in glandular organs;
- renal failure of various etiologies;
- cirrhosis due to alcohol dependence;
- inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis);
- the patient's use of medications containing estrogen or testosterone;
- presence of pregnancy (in the 3rd trimester);
- use of intravenous calcium supplements;
- inflammation of the thyroid gland of various etiologies (thyroiditis);
- bone osteodystrophy - Paget's disease (disturbance of the mechanism of bone tissue restoration);
- megaloblastic anemia;
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (tumor lesion of the pancreas with increased secretion of hydrochloric acid).
A decrease in the level of calcitonin in the blood can demonstrate:
- hypoparathyroidism or pseudohypoparathyroidism;
- primary osteoporosis (decreased bone volume);
- insufficient levels of calcitriol synthesized by the kidneys;
- thyroidectomy (removal of the thyroid gland).
Reasons for promotion and demotion
Even with minor deviations of the hormone content from the norm, we can talk about the development of certain diseases in the human body. The prerequisites for pathology are especially serious if a high level of calcitonin is diagnosed.
All predisposing factors that can provoke high values are conventionally divided into two groups.
Among the causes of tumors are:
- hyperplasia;
- melanoma;
- ganglioneuroma;
- metastasis to neighboring organs;
- small cell lung cancer;
- medullary type of tumor;
- thyroid C-cell adenoma;
- gastrinoma is a neoplasm of the gastrointestinal tract.
An increase in the level of the hormone in the blood can also be provoked by non-tumor pathological processes:
- chronic renal failure;
- thyroiditis;
- complete resection of the thyroid gland;
- an increase in the concentration of calcium in the blood fluid;
- pneumonia;
- tuberculosis;
- bronchitis;
- pernicious anemia;
- Graves' disease.
Some sources suggest that an increase in calcitonin can be triggered by injury, which is caused by the activation of hormone production for faster healing in fractures and severe bruises.
Such states are just a temporary phenomenon. After the body recovers, the level returns to normal. If there is a slight increase over a long period of time, then this is the first sign of a serious pathological process.
A decrease in the indicator can be caused by the following factors:
- consequence of surgery to remove part of the thyroid gland;
- negative effects from taking medications when the dosage is exceeded;
- the tumor marker did not reach the required level to determine the diagnostic indicator.
A decrease in the hormone is diagnosed extremely rarely compared to its increase.
Deviations from the norm
A significant increase in calcitonin in the blood is an alarming sign, as it often indicates the development of thyroid cancer.
In addition, such a phenomenon may be a sign of the following diseases and pathologies:
- renal failure;
- thyroid dysfunction (pancreatitis, neoplasms);
- cirrhosis due to alcohol consumption;
- pernicious anemia;
- some lung and breast tumors, benign or malignant.
In some cases, an increase in calcitonin in the blood is observed during pregnancy - during pregnancy, all systems of the female body, including the endocrine system, work in increased mode. A slight increase in the concentration of the hormone is normal, but if the numbers in the analysis are high, the expectant mother is advised to consult a doctor.
A decrease in calcitonin levels is typical for osteoporosis or after resection of the thyroid gland, when the production of all hormones decreases. In addition, this condition can be a consequence of severe physical exertion or severe stress.
The level of calcitonin in the blood is one of the most important diagnostic criteria, which allows timely detection of dangerous thyroid diseases, so even healthy people are recommended to undergo it about once a year.
Recommendations before analysis
Calcitonin is usually tested by ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). The test uses blood taken with an anticoagulant (EDTA, heparin).
In order to obtain the correct result, the patient must follow the recommendations regarding preparation for the analysis, which, in principle, are suitable for all biochemical tests:
- A month before the study, women part with oral contraceptives;
- Three days before taking blood samples, a person stops active physical exercise and excludes sports training;
- does not touch alcohol for 24 hours, even if there is a serious reason for this;
- 12 hours in advance, excludes all food in order to come to the laboratory on an empty stomach;
- An hour before the test, he no longer remembers cigarettes;
- Within half an hour, a person who comes to the laboratory calmly sits down, relaxes and rests.
The analysis can be done in one day, but the ELISA system is not designed for one person, so the patient must be warned about this. Perhaps the answer will be in a couple of days, or perhaps you will have to wait longer.
Norms of calcitonin in the blood
The results of the analysis depend on the method and types of antisera that the laboratory uses for diagnosis; this is due to the fact that calcitonin molecules are heterogeneous, and some methods cannot always determine the full amount of the hormone in the blood.
The table below shows hormone levels when using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method.
| Men | 0.7-8.4 pg/ml |
| Women | 0.7-5.0 pg/ml |
| Children under 15 years old | up to 45 pg/ml |
Currently, it is believed that the immunochemiluminescent method gives more accurate results than ELISA, but this test is more expensive and is usually used only in private practice. Below are the standards for the immunochemiluminescence method:
| Men | 0-1.95 mg/ml |
| Women | 0-1.46 mg/ml |
Briefly about medullary thyroid cancer
It is also called C-cell carcinoma because it mutates these cells. Although it is characterized by slow growth, it has high activity in terms of metastases; It almost never responds to conservative treatment, and only anectomy is required.
What to do if you suspect its appearance? It is urgent to do a blood test for calcitonin - the simplest and most reliable diagnostic method. A noticeable plus, unlike a biopsy, is that this analysis is never wrong.
When does calcitonin decrease?
Most often, calcitonin deficiency occurs:
- with primary osteoporosis;
- after resection of the thyroid gland due to disruption of the synthesis of all its hormones;
- also the reasons may be frequent overwork;
- heavy physical activity;
- hypoparathyroidism;
- elderly age;
- cretinism;
- insufficient synthesis of calcitriol in the kidneys.
What does this mean? It is an active metabolite of Vit. D3, formed in the skin during tanning. It has the property of increasing the absorption of Ca by the intestinal mucosa. The gland tissue is susceptible to swelling and cannot produce enough hormone. Reduces calcitonin and lack of sleep with frequent overwork, exceeding the dose of hormones during treatment if the tumor marker has not reached the required level for diagnosis.
Signs:
- if there is less calcitonin during pregnancy, this leads to fetal pathologies or miscarriages;
- low thyrocalcitonin in combination with high parathyroid hormone usually indicates secondary hyperparathyroidism;
- symptoms of cretinism develop;
- dementia appears;
- the skeletal system becomes fragile and fragile, fractures become more frequent;
- when treating fractures, a very weak level of reparation is observed.
If calcitonin is reduced, there is a deterioration in general well-being, decreased performance, and the development of renal failure, first slightly, and then noticeably increased fatigue.
Acceptable level for men, women and children
IHL method:
- boys, men - calcitonin level should not exceed 2.26 pmol/l;
- girls, women - the maximum concentration of thyrocalcitonin is 1.46 pmol/l.
READ ALSO: Peptide hormone calcitonin in women: norm, causes of deviations, preparation for the test and test results
ELISA method - acceptable level of calcitonin:
- for adult men – from 0.68 to 32.26 pg/ml;
- for adult women – from 0.07 to 12.97 pg/ml;
- for children – up to 79 pg/ml.
Calcitonin 2.0: normal or not
The question can be answered with an integrated approach to assessing test results. For representatives of different sexes, the values differ; the level of thyrocalcitonin in children also has different indicators.
It is important to know the units of measurement for different types of blood composition studies: the chemiluminescence immunoassay method - pmol/l, for studies using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) - pg/ml. Different laboratories use the second generation of analyzers (ELISA) or a more modern approach: the third generation of devices (ICL).
If the transcript indicates that the calcitonin value is 2.0, then you need to take into account the nuances:
- first pay attention to the units of measurement (pg/ml or pmol/l);
- for adult women, men and children using the ELISA method, this indicator will be within acceptable limits (pg/ml measurement);
- for men and boys (blood test using the ICL method) the value also does not exceed the upper limit of 2.46 pmol/l;
- the same test for women and girls (indicators in pmol/l, IHL method), level 2.0 - alarm signal: upper limit - 1.46 pmol/l. We need to figure out why the level of thyrocalcitonin exceeds the norm. It is important to conduct additional research and do a provocative test to exclude oncopathology.
General concepts
If you want an answer to your question about the amount of its production, you must say that the thyroid gland synthesizes it in a minuscule amount and healthy people do not have a lot of it in the blood. It is produced by parafollicular cells (C cells), they are located near the follicles, which is why they got their name and there are not so many of them in the parenchyma.
They are also surrounded by A and B cells of the thyroid gland. The functions of calcitonin are not fully understood today. The main physiological role of calcitonin (in foreign literature it is called thyrocalcitonin) is the regulation of calcium-phosphorus metabolism.
It has no effect on general metabolism. This hormone stimulates the work of osteoblasts (bone cells), responds and helps the entry of Ca ions into bone tissue. There is a direct connection between calcitonin and parathyroid hormone. Which? Thyrocalcitonin is a complete antagonist of parathyroid hormone, which, in contrast to calcitonin, drives calcium into the bloodstream, while washing it out of the bones.
Parathyroid hormone causes hypercalcemia for this reason. But the most important feature and importance of calcitonin is that it increases noticeably with the appearance of thyroid cancer. This feature is the basis for its use as a tumor marker long before the manifestation of the disease in the thyroid gland.
Studies have shown that its increase never raises doubt among doctors that the thyroid gland is affected by oncology, in particular, aggressive medullary cancer. In complete health, the content of calcitonin in the blood is very small and this is absolutely normal. It is also produced in the intestines, but production there is even less than in the thyroid gland, so the intestines are not considered as its source.