Antiarrhythmic drugs
Antiarrhythmic medications
help restore the normal rhythm of the heartbeat.
This effect is due to the blocking of adrenergic receptors, which respond to the activity of adrenaline. Before use, visit a doctor - he will always be able to answer you what it is, tachycardia, and how to treat this condition. Antiarrhythmic drugs are most effective in the treatment of sinus and supraventricular tachycardia. Among these tablets, the most popular are:
- anaprilin;
- adenosine;
- atenolol;
- verapimine;
- ivabradine;
- concor;
- cordanum;
- propranoprol;
- flecainide;
- egilok;
- etacizin.
Drugs that belong to the group of glycosides are best taken for tachycardia caused by heart failure. For atrial fibrillation, tablets are needed that contain substances that block potassium channels - for example, Cordarone
. In the absence of drug therapy for a long time, a person’s blood pressure may rise, which will only worsen the situation.
- anaprilin;
- adenosine;
- atenolol;
- verapimine;
- ivabradine;
- concor;
- cordanum;
- propranoprol;
- flecainide;
- egilok;
- etacizin.
Calming (sedative) drugs
Sedatives are pharmacological drugs whose action is aimed at reducing psycho-emotional stress. They are the main drugs for the treatment of psychosomatic pathology, which can cause the development of tachycardia. Medicines in this series can be divided into three groups:
- Plant origin.
- Synthetic products.
- Combined drugs.
Herbal preparations that are effective in the treatment of attacks of tachycardia include:
- Valerian extract
This medicine has long been well established as a folk remedy for acute and prolonged stress, neuroses and sleep disorders. The drug is able to slow down the heart rate, while dilating blood vessels and improving microcirculation and blood perfusion.
Available in tablet form and also in drop form. Use 1-2 tablets 20 minutes after meals or 30 drops dissolved in plain boiled water 3-4 times a day. The drug is not addictive, the recommended course of treatment is 2–3 weeks.
A product based on an extract from the herb St. John's wort. It is a natural antidepressant, has a pronounced sedative effect on the body, normalizes mood and sleep.
Allowed for children from the age of six. Available in capsules and tablets. It is recommended to take no more than three tablets per day, divided into doses of 1 tablet at equal intervals; for children under 12 years of age, no more than 1 tablet daily. Take before meals with plain water. The effect is observed two weeks after the start of treatment; therapy must be stopped gradually to prevent withdrawal syndrome.
Synthetic drugs are a group of tranquilizers. Most often, the following medicinal substances from this group are used to treat tachycardia:
Non-benzodiazepine tranquilizer. The main property of the drug is to relieve anxiety and relieve nervous tension, restlessness, and normalize sleep. These conditions lead to the development of attacks of sinus tachycardia. It is recommended to use 30 mg per day, divided into three doses at equal intervals, for a course of up to 1–1.5 months. It is recommended to begin treatment during an exacerbation of a psychosomatic illness. The medicine should not be addictive; it should be discontinued gradually, gradually reducing the daily dose over 7–10 days.
The drug is also a tranquilizer, has a pronounced sedative effect and is applicable for the treatment of neuroses accompanied by the development of tachycardia symptoms. The drug must be used in monthly courses with a break of 3–6 months. Use 1-2 tablets twice a day. Although the drug does not cause addiction, withdrawal is carried out gradually over a week.
The combined substances in the composition combine plant components and synthetic derivatives. These include:
Just like valerian, it is close to folk remedies, since it contains extracts of medicinal plants that have sedative properties. Due to its calming effect on the nervous system, it gently relieves neuroses and depressive states, reduces the body’s physiological reaction to a stress factor and reduces the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle.
Available in tablet form and in the form of an oral solution. The frequency of preventive treatment is 2–3 times a year, in courses of two to four weeks. It is recommended to take 5 ml or 2 tablets twice a day, respectively.
A herbal medicine, the recipe of which uses the experience and knowledge of traditional healers in the treatment of neurosis-like conditions, insomnia, increased neuro-reflex excitability with a predominance of sympathetic regulation.
Available in tablets, approved for children from the age of twelve. Prescribe 2-3 tablets with a frequency of administration up to three times a day. A good effect is recorded with regular use for at least 2 months. Discontinuation of the drug is permitted abruptly, and no withdrawal syndrome is observed.
Non-benzodiazepine tranquilizer. The main property of the drug is to relieve anxiety and relieve nervous tension, restlessness, and normalize sleep. These conditions lead to the development of attacks of sinus tachycardia. It is recommended to use 30 mg per day, divided into three doses at equal intervals, for a course of up to 1–1.5 months. It is recommended to begin treatment during an exacerbation of a psychosomatic illness. The medicine should not be addictive; it should be discontinued gradually, gradually reducing the daily dose over 7–10 days.
Causes of tachycardia
To understand what tachycardia is, it is important to consider that cardiac tachycardia occurs due to many different reasons. Thus, such a condition can arise as a natural reaction of the human body to emotional stress and too much physical labor. Tachycardia can also be accompanied by increased body temperature, smoking, and drinking large doses of alcoholic beverages. The heartbeat becomes more frequent in the event of a sharp decrease in blood pressure , with anemia and, accordingly, a decrease in hemoglobin , as a consequence of the development of malignant tumors, purulent infections, and increased thyroid function. Tachycardia can also occur as a result of treatment with certain medications.
There are also tachycardias that occur due to the presence of pathology of the heart muscle or due to disturbances in the electrical conduction of the heart. Cardiac tachycardia is the first sign of cardiac decompensation.
Also, such a condition is a consequence of shock or collapse (this can be fainting, bleeding, etc.), as a result of a reflex to lower blood pressure.
A tendency to tachycardia is a characteristic symptom in people with vegetative-vascular dystonia . As a rule, in this case these are young patients. Rapid heartbeat is also observed in patients with neuroses .
A tendency to tachycardia is a characteristic symptom in people with vegetative-vascular dystonia . As a rule, in this case these are young patients. Rapid heartbeat is also observed in patients with neuroses .
Drugs for rapid heartbeat
Treatment of the pathological form includes the administration of local anesthetics and cardiac depressants (quinidine, lidocaine, procainomide). On the recommendation of a cardiologist, the patient is administered antiarrhythmic drugs (adenosine, verapamil, propranolol, flecainide).
All of these are measures of emergency assistance provided by doctors when calling at home .
While waiting for an ambulance, it is necessary to open the windows, providing the victim with free access to air, help him go out into the air, and put a cool compress on his face.
Further treatment should be carried out in a hospital setting .
Therapeutic measures consist of eliminating the underlying disease.
As part of therapy, patients are prescribed consultations with a neurologist and psychologist, taking tranquilizers and antipsychotics .
If the condition occurs due to problems with the thyroid gland, treatment is carried out with thyreostatic medications; in case of chronic heart failure, beta-blockers and cardiac glycosides are prescribed.
In some cases, surgical intervention is used , in which, for example, the area of the myocardium responsible for the arrhythmia is cauterized.
In some cases, surgical intervention is used , in which, for example, the area of the myocardium responsible for the arrhythmia is cauterized.
Physiological
Physiological tachycardia
It occurs as a normal reaction of the body to various external chemical or mental states of a person. Physiological tachycardia is provoked by nicotine, alcohol, caffeine, and other active compounds that overstimulate the nervous system. If you experience a rapid heartbeat after consuming these substances, you should completely eliminate them from your diet. Excessive physical activity also causes heart palpitations, especially for unprepared or physically weak people. In both cases, the use of special medications is not required; it is enough to change your lifestyle.
It is necessary to change your lifestyle and give up bad habits
The second reason for the appearance of physiological tachycardia is nervous stressful situations. A complex treatment is prescribed, which may have several regimens depending on the course of the disease.
Tachycardia from stress and nervous tension
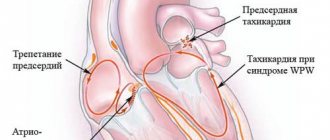
Class 2
The effect of these medications is associated with the effect on beta-adrenergic receptors located in the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes. This leads to inhibition of impulse generation centers in the heart and a decrease in myocardial excitation.
Beta blockers can be divided into non-selective and selective. In the first case, the drugs have the ability to influence beta receptors of the first and second types. This leads to a large number of side effects. Therefore, these funds are currently losing their relevance. To provide emergency assistance, the use of Propranolol is allowed. Selective agents have a blocking effect only on type 1 beta receptors located in the heart. They have undergone a large number of clinical trials, where they have proven their ability to reduce mortality from cardiovascular pathology. Therefore, these drugs for the treatment of cardiac tachycardia have won one of the dominant places. These include Bisoprolol, Carvedilol, Nebivolol. They are successfully used for the treatment of sinus, paroxysmal supraventricular tachyarrhythmia, and persistent ventricular tachycardia during exercise.
Tachycardia as an independent disease
Pathological tachycardia can cause premature death
The most complex tachycardia is treated over a long period of time and only with medications; traditional recipes are ineffective. In the most difficult cases, the problem is solved only after surgical intervention by surgeons. With this disease, an increase in heart rate is observed in a state of complete rest; depending on the underlying cause, it can be ventricular or supraventricular. The attacks are spontaneous, the pulse rate can reach 240 beats per minute. Delayed or incorrect treatment can cause death.
Class 3
By blocking potassium channels, these drugs increase the action potential and lengthen the refractory period in the cardiac conduction system. May have adrenergic and membrane-stabilizing properties.
This group of drugs for tachycardia is quite effective. In practical activities, we use Amiodarone, Sotalol. Amiodarone is recognized as one of the best antiarrhythmics. Its use is appropriate for life-threatening ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias. Sotalol has the same indications as the first representative. It is advisable to begin use in a hospital setting, since a proarrhythmic effect is highly likely.
Modern surgical methods of treatment
Surgical intervention is used only in emergency cases, when tachycardia directly threatens the patient’s life or after long-term unsuccessful treatment of the disease with medications.
Surgery
Before the operation, electrophysiological examinations are carried out in order to accurately determine the source of pathology and the sources of impulses. Modern medicine allows the use of radiofrequency ablation; during surgery, nerve fibers that conduct altered signals to the heart muscle are cauterized.
Electrophysiological study
If the pathology is ventricular in nature, then the installation of a special miniature cardioverter-defibrillator is indicated. The device is connected to the myocardium by microwires and provides rhythmic signals for contraction.
Implantation of cardioverter-defibrillators
Cauterization of the renal arteries shows a positive effect on restoring the physiological rhythm of the heart. It has been proven that thermal effects on the nerve endings of the intrarenal arteries have a very positive effect on stabilizing blood pressure and heart rate. To obtain a positive effect, just one procedure is enough; the nerves are cauterized using a medical laser. The new method also showed a positive effect during the treatment of gastric tachycardia.
Human renal artery
Catheter ablation (or radiofrequency ablation)
The method is the only possible one in cases where it is not possible to perform catheter ablation. Such severe cases occur when arrhythmogenic nerve areas are located not inside the heart, but outside. The cardiac defibrator works too often, which causes rapid wear and tear of the heart muscle - attacks of tachycardia can occur multiple times within one day. The method of ablation of the nerve plexuses of the renal arteries allows you to restore the physiological rhythm of the heart and eliminate the threat to life.
Medicines to combat the problem
Today, dozens of remedies are known to cope with tachycardia. However, we remind you once again: only a professional can make a decision about prescribing this or that medicine. Each case is individual, so do not ignore the problem and visit a specialist.
It is important to know that tachycardia is most often just one of the manifestations of more serious diseases. Therefore, treatment is carried out on the basis of detailed diagnostics of the body. It is necessary to fight not with the acceleration of the heartbeat itself, but with the cause that led to such phenomena. Medicines against tachycardia help quite well, but it often takes some time to find a suitable drug.
Today at the pharmacy you can find many types of medications designed to eliminate the symptoms of diseases of the cardiovascular or nervous system (one of which is tachycardia). Each of them works differently. The drug, dosage and duration of treatment are individual in each case. The decision about this is made by the attending physician.
Today, there are two main groups of drugs against tachycardia. These are antiarrhythmic drugs, as well as sedatives (better known to the average person as a sedative). Sedatives can be natural or synthetic. They are intended to normalize the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems, and are also aimed at reducing the number of attacks of tachycardia. Natural preparations include the following:
- Valerian.
- Hawthorn tincture.
- Persen.
- Motherwort.
- Peony.
As for medications of a synthetic nature, these include:
- Diazepam.
- Phenobarbital.
- Ritmilen.
- Ethacizin.
- Propranoprol (Anaprilin).
- Verapamin.
- Flecainide.
- Adenosine.
- Cordanum.
Traditional surgical methods for treating tachycardia
Surgeries are indicated in the treatment of the most severe forms of ventricular tachycardia; the pulse rate can increase to 240 beats; delay in intervention leads to inevitable death. To relieve an attack, defibrillation of the heart is performed, which allows for some time to stabilize its functioning in optimal parameters.
Electrical cardioversion/defibrillation device (defibrillator)
Before the operation, with the help of modern equipment, the specific location of the source of tachycardia (fibrous altered area on the heart) is determined. The final decision to perform surgery is made only after a thorough invasive examination of the heart and determination of the cause of aneurysm formation. To clarify the diagnosis, an additional electrophysiological examination may be performed.
Indications for surgery are:
- refractory to electrical pulse and drug therapy;
- the patient’s body does not tolerate effective antiarrhythmic drugs or they have shown their uselessness after prolonged use;
- programmed pacing may induce tachycardia;
- the patient has another cardiac disease requiring surgical intervention.
Surgical methods of treatment
During the operation, the aneurysm is identified and the anterior and posterior surfaces are examined. All zones of delayed nervous activity are localized along the edges of the aneurysm. Using programmed stimulation of the heart muscle, tachycardia is artificially induced and problem areas are re-identified. Detected anomalous locations are blocked. In the most difficult cases, the aneurysm is excised, and the identified arrhythmogenic focus is frozen. If indicated, coronary artery bypass grafting can be performed simultaneously.
In congenital tachycardia, the abnormal focus is most often located in the outflow tract of the right ventricle. Before the operation, the type of arrhythmia, the nature of the attacks and their frequency are determined. If the disease becomes extremely dangerous (the patient loses consciousness), then it is necessary to take a set of measures to intensively eliminate tachycardia as soon as possible. At the same time, no attention is paid to possible negative consequences; the patient’s life is saved by all available methods. Only after the crisis has been successfully localized is a further list of various measures to treat the disease developed.
Reliable drugs and vagal techniques
To relieve an attack of nodal arrhythmia, vagal tests can be used:
- Artificial induction of vomiting;
- Cough;
- Pressure on the eyeballs;
- Carotid sinus massage;
- Washing with cold water;
- Closure of the glottis during exhalation.
Most vagal tests are performed by doctors. The patient will not be able to treat tachycardia at home using these procedures.
If tachycardia is not controlled with medication, electrical pulse therapy is rational. The technique can save the life of a patient with respiratory depression. The procedure is performed against the background of resuscitation measures. The standard scheme includes pulse charges of 200-360 kJ. The manipulation is effective only for the first 30 seconds after the heart stops activity.