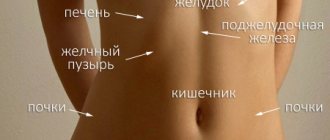
Classification by nature and severity
If a woman feels pain in the groin, this symptom is not always harmless. Usually, unpleasant sensations arise against the background of pathological conditions that pose a threat to the health or even life of a woman. According to statistics, in most cases, pain is caused by dysfunction of the organs of the reproductive system or infection in the urinary tract. When faced with this, first of all you need to pay attention to the nature of the pain and the degree of its severity. They can be:
- Spicy. A similar symptom is accompanied by cystitis in the acute stage, urolithiasis, arthrosis of the hip joint or lymphadenitis. Gynecological pathologies can also provoke severe groin pain. Severe pain can signal torsion of the cyst leg, ectopic pregnancy, rupture of the fallopian tube, exacerbation of adnexitis, and oncological lesions of the reproductive system. If the pain does not go away, this indicates the presence of a serious pathology.
- Dull and aching. They usually appear against the background of an inflammatory process that occurs in the pelvic organs. Chronic diseases of the reproductive system can also cause dull and aching pain. However, their appearance does not always indicate the presence of pathology. So, such a condition can be triggered by menstruation or excessive physical exertion.
- Pulsating. Typically, such pain is localized only on the right or left side of the groin area. The development of right-sided pain syndrome may indicate the presence of appendicitis. Sometimes this results from a rupture of a femoral artery aneurysm.
Pain in the left groin in women often occurs with kidney disease. In this case, it is the left organ that suffers. Pathology often manifests itself with additional symptoms. The most common of them are increased body temperature, difficulty or frequent urination, accompanied by a burning sensation.
Such pathologies should always be treated after consulting a specialist. Antibacterial drugs are most often prescribed. These include Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, Sumamed and so on. It is definitely recommended to take diuretics, such as Canephron, Cyston, renal collection, and so on.
Pain in the left groin in women may be due to infection. Most often these are diseases that are sexually transmitted. They are caused by microorganisms that gradually infect the vagina, uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes. This disease needs to be treated as soon as possible. Otherwise, the disease may become chronic.
Correction is always prescribed after the study. Most often, a smear test is performed and ultrasound diagnostics are performed. Drugs that can fight infection and inflammation include the following: Metronidazole, Terzhinan, Pimafucin, Vilprafen and many others. This or that type of medicine is prescribed only after bacteriological examination.
Pain in the inguinal lymph nodes
Enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes, their hardening, pain in the groin lymph nodes are a signal of trouble in nearby organs. In this case, pain in the inguinal lymph nodes can be very acute. Inguinal lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes) may indicate the presence of the following diseases:
- inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary organs (cystitis, urethritis, adnexitis, endometritis, orchitis, etc.);
- fungal diseases of the skin of the feet;
- benign or malignant tumors of the pelvic organs (in this case, the inguinal lymph nodes enlarge, remaining painless);
- syphilis (primary stage);
- sexually transmitted infections (AIDS, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, genital herpes, ureaplasmosis, etc.).
The pain is localized on the left
In most cases, this phenomenon indicates that something is going wrong in the human body. The following organs are located in the left groin of people: intestines, part of the bladder, ureters, kidneys. In women, this area also contains the ovary, fallopian tube and one side of the uterus.
If any unpleasant sensations occur, then the organs described above may be affected. Also, pain in the groin on the left often appears due to a pathological process in neighboring areas. It is almost impossible to make a diagnosis on your own. Let's look at the main reasons why pain occurs in the left groin in women, and also look at ways to treat them.
If you suddenly have severe pain in the abdominal cavity, you should not put off visiting a doctor. If your general health deteriorates at the same time, you should call an ambulance. Specialists will quickly assess the situation and make the correct diagnosis. If necessary, you may be offered hospitalization. Don't give up on it.
Remember that if such a symptom appears, you should not take antispasmodics on your own. Such drugs can somewhat blur the clinical manifestations of the pathology. In this case, it will be very difficult for doctors to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
When you suddenly feel worse, you should immediately take a horizontal position. If you called a doctor, then while you wait, remember everything that could cause the pain in the groin. Any information will be useful to the doctor. It will help make a correct diagnosis faster.
Localization of pain on the left side indicates a pathological process in the ovary, kidney, ureter, fallopian tube located on the left side, as well as disturbances in the functioning of the sigmaid colon.
The inflammatory process in the sigmaid colon is accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and radiating pain to the left leg. The presence of stones in the left ureter provokes pain in the left region, reminiscent of renal colic.
The pain that occurs in the presence of ovarian cysts is dull, aching and is accompanied by menstrual irregularities.
On the left side of a person’s groin there are organs such as part of the bladder, part of the uterus, one of the fallopian tubes, the left ovary, intestines, and one of the kidneys. If pain occurs on this side, this may indicate the presence of pathological processes in any of the listed organs. The condition can be caused by:
- Kidney diseases. In addition to pain, a girl may experience fever, burning and other problems during urination.
- An ectopic pregnancy is observed. In this situation, the fertilized egg is not implanted in the uterine cavity, but in the ovary or in one of the fallopian tubes. This can lead to a nagging pain on the left.
- There is a problem with the functioning of the spleen. The organ is quite vulnerable due to the fact that it is very close to the surface of the body. Even a simple injury can cause a lot of problems. The presence of tumors can also provoke pain. A similar effect is observed when the patency of the urinary ducts is impaired.
- A woman has problems with the organs of the reproductive system. Pain can occur with endometriosis, which worsens during menstruation. In this case, unpleasant sensations are accompanied by brown discharge with clots.
- Observed during pathological processes in the stomach. Among them are constipation, bloating, which is caused by increased gas formation, as well as other disorders. In this situation, the localization of pain is located in the left lower abdomen. Tumors of the small intestine can cause the same symptoms.
- There are adhesions. They may appear after surgery.
- Ovarian apoplexy is observed. In this case, the woman may be bothered by throbbing pain, which is accompanied by general weakness, increased temperature and bleeding.
If the pain is of a pulling nature
Doctors classify the unpleasant, tedious sensations that courageous women endure for a long time as acute pain that threatens emergency medical intervention.
Abdominal pain - possible food poisoning or developing illness
These sensations may be harbingers of:
- gynecological pathologies;
- appendicitis;
- urolithiasis;
- rupture of a blood vessel, etc.
These characteristic nagging pains can signal that not all is well in the female genital area and warn of impending diseases, such as:
- inflammation of the appendages;
- menstrual pain;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- ovarian cysts.
One of the causes of pain in the groin is inflammation of the appendage
Carefully! If, in addition to nagging pain, disturbances appear during the act of defecation and urination, then the patient may be at risk of prolapse of the female genital organs, that is, genital prolapse.
This disease, in addition to the indicated symptoms, is also accompanied by a sensation of a foreign body or pain in the lumbar and sacral area.
But restlessness in the right groin is not always a sign of illness . Sometimes this pain is simply a reaction to unusual physical activity the day before or to intense workouts in the gym.
Why does pain appear in the groin on the right?
It is worth paying attention to the location of the pain. If it appears in the groin on the right, this may indicate the course of a number of diseases, the list of which includes:
- cystitis;
- myoma;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- chondrosis;
- arthritis;
- intestinal pathology;
- urolithiasis disease;
- appendicitis;
- endometriosis;
- adhesions;
- purulent processes.
Injury can also provoke pain.
However, the processes are not always pathological. The onset of menstruation, carrying a child, or the onset of preliminary contractions can lead to unpleasant sensations. Most often, pain in the groin on the right occurs due to enlarged lymph nodes and appendicitis.
In children
In girls, the cause of pain in the groin can be injury, an inguinal hernia (a rare pathology) and enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes, usually associated with a cold-like inflammation of the uterine appendages.
The number of reasons that cause groin pain in boys is much broader:
- Trauma (including trauma to the scrotum during childbirth).
- Inguinal (inguinal-scrotal) hernia. As in adults, a hernia appears as a swelling in the groin, on the right or left. When pressed, the swelling disappears, but when crying, laughing or coughing, it increases in size.
- Orchitis (inflammation of the testicle) - often occurs as a complication after mumps, infectious mononucleosis, chickenpox, etc.
- Testicular torsion is characterized by sudden, severe pain in the groin. The skin of the scrotum turns red or blue, and the twisted testicle is located in the groin above the other, healthy one. The cause of torsion in a child can be tension in the abdominal muscles or sudden movement.
- Hydrocele (hydrocele) is rarely accompanied by pain. Pain in the groin occurs only if the dropsy becomes infected. The scrotum of a boy with hydrocele is enlarged in size (entirely or only one half). The color of the skin of the scrotum does not change.
- Varicocele is varicose veins of the testicle. In young boys it is most often asymptomatic. Only in adolescence may a child begin to complain of discomfort or mild pain in the groin.
Spleen diseases
Pain in the left groin in women can occur with pathologies occurring in the spleen. It is worth noting that this organ is located very close to the surface of the body. That is why the cause of pain is often a banal injury. Various tumor processes in the spleen can lead to unpleasant sensations radiating to the groin. In this case, the nature of the neoplasm can be malignant or benign. Blockage of the ducts leads to the development of the same symptom.
Treatment of such pathologies is usually carried out within the walls of a hospital. In this case, a woman may be indicated for conservative or surgical therapy. Often, after correction, the patient is prescribed long-term medication, active supplements and enzymes.
Unpleasant sensations before menstruation
Painful sensations can also be caused by impending menstruation. Most often, unpleasant sensations occur in young or nulliparous women. This phenomenon is called oligomenorrhea. It has the character of an aching, cramping pain that can appear several days before menstruation and continue for the same period from the moment it begins.
Pain in the left groin in women sometimes becomes a symptom of pathology in the intestines. So, with constipation and diarrhea, similar sensations are observed. In addition, increased gas formation and bloating may occur. Various tumors of the small intestine lead to discomfort. Also, dysbiosis and inflammation can cause pain in the left groin.
Treatment in such situations is symptomatic. If the patient complains of constipation or diarrhea, then appropriate medications are prescribed. Among the laxatives one can highlight Duphalac, Gutasil, Senade. To strengthen stool, Immodium and an appropriate diet are often used. Treatment of intestinal diseases requires a long course of beneficial bacteria.
Soreness of the lymph nodes in the groin
In the groin area there are lymph nodes that protect the body from infection, which can provoke an inflammatory process. The pelvic organs are also protected. If the lymph nodes cannot cope with attacks from foreign agents, this can lead to swelling and tenderness.
They are caused by the onset of inflammation. If the lymph nodes have enlarged due to the progression of the underlying pathology, pain may be accompanied by symptoms of intoxication and an increase in general body temperature. Additionally, there may be a deterioration in the general condition, swelling of the skin in the affected area and redness. Pain in the groin area may intensify with physical activity.
There are primary and secondary lymphadenitis. In the first case, the lymph nodes are initially affected. In the second situation, the primary inflammatory process begins first, and then inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs. Most often, inguinal lymphadenitis results from:
- traumatic injuries;
- development of malignant neoplasms in the genital organs;
- the onset of infectious and inflammatory processes.
Additionally, a distinction is made between serous and purulent lymphadenitis. The first pathology is treated conservatively. To get rid of the second one, surgery will be required.
In men
The most common cause of groin pain in men is an inguinal hernia, described above in the section “Unilateral groin pain.”
Pain in the testicles and groin (aching, constant, not too intense) may be a sign of chronic prostatitis or prostate adenoma.
Vesiculitis (inflammation of the seminal vesicles) is also accompanied by pain in the groin area, testicles, perineum, and above the pubis.
Acute inflammation of the testicles (orchitis) can be a complication of an infection, inflammatory disease of the genitourinary organs, or a consequence of injury. In this case, intense pain occurs in the groin and testicles, intensifying with movement. The pain is accompanied by swelling and redness of the scrotum. The patient's general condition worsens, body temperature rises, headache appears, and sometimes vomiting.
Acute epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis) is accompanied by similar symptoms
. Pain in the groin and testicles with chronic epididymitis is not so severe; it occurs periodically, but quite often, intensifying when walking.
A spermatic cord cyst causes aching pain in the groin of middle-aged and elderly men. Young men with this pathology usually do not experience pain, and accidentally discover a spherical formation on their scrotum.
Testicular torsion can occur with sudden movements during sports. In this case, the patient experiences severe pain in the groin and testicles. Half of the scrotum rapidly increases in size due to swelling. The skin of the scrotum turns blue. A twisted testicle is raised higher than a healthy one. Nausea and vomiting may occur. Body temperature rises.
Dilatation of the testicular veins (varicocele) is characterized by pressing, dull, intermittent pain in the groin that does not have a clear localization. Varicocele can be right- or left-sided, and pain is perceived by the patient on the opposite side, or spreads to the entire groin. Often the patient simply experiences a feeling of heaviness and discomfort in the groin.
Any pain in the groin in men requires contacting an andrologist, because... Many of these diseases, if left untreated, can cause a decrease in sexual activity, the development of impotence and even male infertility.
Groin pain during pregnancy
A nagging pain in the left groin in women can occur due to an ectopic pregnancy. In this case, the fertilized egg is not fixed in the cavity of the reproductive organ, but on the fallopian tubes or in the ovary. The embryo may also remain in the abdominal cavity, but such cases are quite rare.
This condition must be treated urgently. The sooner the correction is carried out, the greater the chances of a positive outcome. In some cases, it is necessary to completely remove the organ where the fertilized egg is attached.
A number of women are confident that the appearance of groin pain during pregnancy is normal for this condition. A number of experts also argue that the occurrence of unpleasant sensations can occur against the background of the child’s anticipation. However, the presence of diseases can also lead to the appearance of symptoms, the list of which includes:
- the presence of kidney stones;
- the course of the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes;
- groin injury;
- infections and inflammation of the genitourinary system;
- genital herpes.
Often, pain in the groin while expecting a baby is caused by tension in the ligaments of the pelvic joints. This is due to the physiology of pregnancy. The condition is not a pathology. However, in this case, the discomfort goes away during relaxation. If this does not happen, pain in the groin may indicate the possibility of a miscarriage.
Pain in the right groin in women
In almost 90% of cases, if pain is detected on the right side, urgent hospitalization is required.
Here are the cases in which it usually appears:
- Appendicitis. Everyone knows why it develops. Therapists and specialists always check this area during examination to rule out this cause. If the diagnosis is confirmed, an ambulance is urgently called for emergency surgery. A ruptured appendix can be fatal.
- Right ovarian cyst. Most often it occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance.
- Apoplexy of the right ovary. Sharp pain radiates to the right leg area. Urgent surgical intervention is required.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- The appearance of kidney stones.
- Inflammation of the appendages. A consultation with a gynecologist is necessary to prescribe medications. Sometimes drug treatment is accompanied by physical therapy.
During pregnancy, a pulling sensation in the groin and an increase in bleeding may indicate a threat of miscarriage. To avoid this problem, urgent hospitalization and protecting yourself from any stress is required.
What does inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes mean?
Lymphadenitis is the process of inflammation of the lymph nodes in any area of the body. Pain radiating to the groin in women, which is accompanied by lymphadenitis, appears as a result of sexually transmitted and fungal diseases of the reproductive system.
They require immediate treatment. If they are not affected, serious consequences may develop, which will become a catalyst for the development of cancer or infertility.
If it appears due to the presence of neoplasms in the form of polyps or papillomas, then blockage of the canals is likely. This is discovered during examination using a colposcope or x-ray.
The formations are removed with a laser, liquid nitrogen or a scalpel. The specialist takes into account the woman’s age and whether she has children, since the use of a laser is not recommended if the girl has not yet given birth.
Particular attention is paid to pregnant women who experience heaviness in the groin.
Many drugs are contraindicated for them, so the following treatment methods have to be used:
- acupuncture, which helps relieve muscle tension;
- use of bandages;
- using exercises for pregnant women to reduce the load on the pelvic muscles;
- homeopathy and anaerobic gymnastics.
Doctors try to play it safe if pregnant women come to them, since they are responsible for each patient and her child.
To prevent miscarriage, they will insist on hospitalization. This measure allows you to shift responsibility to the hospital medical staff.
Which doctor will help with pain in the lower abdomen in the groin in women
If you don’t know who exactly you need to make an appointment with, it is recommended that you go to a therapist. He will conduct an initial examination and give a ticket to a specialist.
Usually this is a gynecologist or surgeon. If urolithiasis is detected, a consultation with a urologist is required, and if the problem arose due to injury, then you will be referred to a traumatologist or neurologist.
Diagnosis comes down to a survey, during which the doctor receives the information he needs and an examination. If this is not enough, you will need to undergo tests and do an x-ray or ultrasound.
Treatment is carried out only after identifying the cause of pain in the groin area. Specialists try to use medications and physical therapy, but if they are ineffective, then planned or emergency surgery is prescribed.
Conclusion
For prevention, it is recommended to lead an active lifestyle, eat right, spend more time in the fresh air and undergo periodic medical examinations. These measures will prevent the development of a number of serious problems and ensure a happy and healthy life.
Adhesive process in the pelvic area
Aching pain in the left groin in women, intensifying during menstruation, may indicate endometriosis. In this case, a woman often complains of chocolate-colored discharge with clots. Also, a representative of the fairer sex suffering from this disease may be infertile for a long time.
Endometriosis must be treated. The surgical correction method is most often chosen. After this, the patient is prescribed long-term hormonal therapy, which can temporarily lead to artificial menopause.
Often pain in the left groin occurs due to the formation of adhesions. These are so-called thin films that glue organs together and thereby cause discomfort. In most cases, adhesions appear due to previous surgical interventions. This process is also caused by untreated inflammation. The thing is that during infection, the abdominal cavity secretes a small amount of mucus. It is this that subsequently thickens and forms adhesions.
Treatment of the adhesive process can be carried out surgically and conservatively. Often these methods are combined for greater efficiency. Anti-adhesion drugs include Lidaza and Longidaza. Doctors also recommend that you undergo a course of physical therapy. Surgical treatment consists of using the laparoscopic method. Laparotomy in such cases can only worsen the situation.
Muscles hurt
Sometimes groin pain can be caused by significant physical activity. This phenomenon often occurs in athletes after competitions or intense training. The greatest load on the category of muscles located in the groin comes from:
- basketball players;
- volleyball players;
- tennis players.
The pain is nagging or aching in nature. If there is a muscle strain, or they were injured during physical activity, the pain becomes acute. Treatment can be prescribed by a traumatologist or sports doctor.
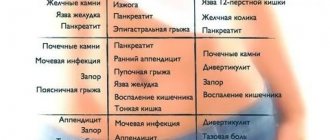
The nature of groin pain in various diseases
Acute
Such pain can occur when:
- urolithiasis;
- acute cystitis;
- arthrosis of the hip joint;
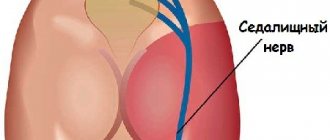
- pinched pudendal nerve;
- inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes.
Strong
Severe pain in the groin area is typical for the following pathologies:
- algomenorrhea (painful menstruation);
- acute adnexitis;
- ovarian abscess;
- orchitis;
- testicular torsion;
- malignant tumors.
Dumb
Dull, intermittent pain in the groin occurs with varicocele - varicose veins of the testicle.
Pulling, aching
Pain of this nature is typical for chronic gynecological diseases (chronic adnexitis, endometriosis, endometritis) and chronic prostatitis. Aching pain in the groin can be accompanied by acute cystitis, as well as physiological menstruation.
In addition, nagging pain occurs in the groin muscles after excessive overload during sports training.
Pulsating
Throbbing pain is usually concentrated in the right or left side of the groin. Right-sided throbbing pain causes the doctor to suspect, first of all, appendicitis.
Severe unilateral throbbing pain in the groin can also occur when a femoral artery aneurysm ruptures (an aneurysm is an enlargement of a vessel associated with stretching or thinning of its wall). The rupture leads to the accumulation of blood in the surrounding tissues; the pain radiates to the groin.
Adhesive process in the pelvic area
Dull pain in the left groin in women can be a symptom of ovulation. Every month, hormonal changes occur in the body of a representative of the fairer sex. So, a follicle grows in one of the ovaries. Having reached the desired size, the formation ruptures. After this, the egg is released into the peritoneal cavity.
In this case, treatment is not required. Only when the pain becomes regular and unbearable is a woman indicated for hormonal correction. For this, in most cases, drugs such as Duphaston, Logest, Diane and others are used.
Pulsating pain in the left groin in women, which is accompanied by fever, weakness and bleeding from the genital tract, may be a sign of organ rupture. Most often, apoplexy of the right ovary or its cyst occurs. However, there are also cases where the pathology occurred on the left.
Treatment in such cases is exclusively surgical. In most operations, the doctor tries to preserve healthy organ tissue. However, this is not always possible. Apoplexy without bleeding can be treated in a hospital using conservative means. The woman is prescribed bed rest, cold on the stomach and sedatives.
Pain near the groin (above, below)
Pain localized near the groin can be a sign of diseases such as urethritis, bladder stones, uterine prolapse, endometritis (inflammation of the uterus). An ectopic pregnancy can also cause pain near the groin.
The cause of unilateral (right or left) pain above the groin can be an inguinal hernia. Right-sided pain above the groin is characteristic of appendicitis. Bladder diseases may be accompanied by pain above the groin in the center of the lower abdomen.
Pain below the groin (lower groin) is most often a muscle pain. Pain of this localization is possible with prostatitis.
Joint pain
If a woman experiences pain in the groin on the right or left, it is necessary to pay attention to the moment it appears. If discomfort intensifies while walking, it is most likely caused by coxarthrosis, a chronic disease of the hip joint. Its appearance can be determined by the following symptoms:
- pain is localized only on one side;
- at rest the pain subsides;
- While walking, the woman initially feels severe pain. Then it decreases. However, if a woman walks for a long period of time, the unpleasant symptom will return;
- if there is aching pain in the lower back that radiates to the groin, the woman may have osteochondrosis. To get rid of the problem, you will have to undergo a course of anti-inflammatory treatment. Additionally, the doctor may refer the patient to a chiropractor or massage.
Prevention
To avoid pain in the groin, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle. At the same time, you need to carefully reconsider your drinking regime. It is necessary to promptly identify and treat foci of infections in the body. Always protect yourself with a condom during sexual intercourse.
Why does groin pain appear in women: on the right, on the left - tips and recommendations on News4Health.ru
Life in the modern world is replete with many factors that negatively affect human health. The main ones are poor ecology, questionable quality of food, contaminated drinking water, poor quality medical care, as well as stressful situations and bad habits. Therefore, it is so important to pay attention to regular healing of the body using various methods and means. Be sure to consult a specialist so as not to harm your health!
Which doctor should I contact?
It is recommended to begin identifying the root cause of pain and its subsequent treatment by visiting a therapist. The doctor will make an initial diagnosis, on the basis of which he will refer the patient for additional research or to a specialist. If there is a lump in the groin area that looks like an inflamed lymph node, you can immediately make an appointment with a surgeon. Women who have previously suffered from urolithiasis or have reason to think about its presence can additionally visit a urologist.
If discomfort is concentrated in the spine or caused by injury, it is worth visiting a neurologist and traumatologist. The first specialist can additionally refer the patient to:
- neurosurgeon;
- physiotherapist;
- osteopathologist;
- manual technician;
- physician for private household plots.
If pain develops against the background of symptoms that are characteristic of gynecological diseases, you can visit a gynecologist.
Diagnosis and treatment of groin pain
If you experience even minor pain, you should consult a doctor. Depending on the disease, a woman may need to consult a surgeon, therapist, urologist, gynecologist, or oncologist.
Diagnosis of the disease includes:
- examination and questioning of the patient’s complaints;
- carrying out laboratory tests (blood test, urine test, cytology smears, stool test for occult blood);
- instrumental studies (colposcopy, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, cytoscopy, colonoscopy).
Treatment is prescribed depending on the disease. In the presence of inflammatory processes, drug therapy (anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, painkillers and hormonal agents) and physiotherapy (UHF, magnetic therapy) are necessary.
Appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy, and cyst rupture require surgical intervention. Surgical treatment is also recommended in cases where drug therapy does not produce positive results.
Before making a diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a diagnostic test. If a woman experiences groin pain, the following tests are performed:
- Detailed patient interview. The specialist will ask you to describe the duration of the pain, the nature of the pain, the exact location of the pain, as well as its irradiation. Then a visual inspection and palpation of certain areas of the body will be performed.
- Laboratory research. The patient will have to undergo a general blood and urine test, stool test, and smears. Research can be carried out in a comprehensive manner.
- Additional methods. If the above diagnostics are not enough, instrumental studies will be carried out. For pain in the groin, a colonoscopy, ultrasound of the pelvic organs and a number of additional studies may be prescribed. Their list depends on the symptoms accompanying the pain syndrome.
Kinds
An unpleasant sensation in the suprapubic region is classified depending on the projection - it can be on the right, on the left, without a specific location. The pain can only worsen with physical activity, for example, while walking. In this case, the pain radiates to the leg or is concentrated exclusively in the suprapubic region. In all cases, the symptom relates to pathology, and the woman requires diagnosis. Also, pain in the groin is one of the warning signs during pregnancy.
It hurts on the left
This location of discomfort indicates the presence of a left-sided ectopic pregnancy, sigmoiditis, or urolithiasis. Possible inflammation, damage to the ovary, or the formation of cystic neoplasms inside it. The type of stone removal depends on its chemical composition and size. Damage to the sigmoid colon and ovary is eliminated conservatively. In case of ectopic pregnancy or damage to the ovary, surgery is indicated. Hormone-dependent cysts are removed with drugs of similar properties, but the option of surgical intervention cannot be ruled out.
Hurts on the right
This localization of an unpleasant sensation is characteristic of the development of appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy, adnexitis, constipation, colitis, and urolithiasis. Concomitant signs of the listed conditions may coincide (in all cases, nausea, abdominal wall tension, hyperthermia occur). Therefore, the doctor first of all carries out a differential diagnosis - establishes the cause of right-sided groin pain in a woman.
It hurts down there
Observed in cystitis, endometritis, endometriosis. Inflammation of the bladder, uterus, and proliferation of the internal uterine layer beyond the organ are listed. Pain in the lower abdomen is one of the manifestations of the pathological process in the large intestine.
During pregnancy
Regardless of the period, it indicates the gradual detachment of the fertilized egg, constipation, colitis. Also, pregnancy can be ectopic, and as the ovary or fallopian tube expands, the unpleasant sensation increases. If, in addition to pain, there is bleeding from the genital tract, this is a symptom of an incipient miscarriage or premature birth. This is possible after stress, physical activity, due to inflammatory damage to the urogenital tract.
When walking
The most common explanation for pain in this location is inflammation of the ovary (regardless of the cause of the development of this condition). Discomfort in the groin when walking appears due to ectopic pregnancy, damage to the nerve fibers of the suprapubic region, and appendicitis. Somewhat less often, the pain increases with physical activity due to the movement of the stone along the ureter.