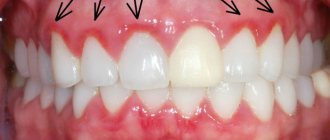
Acute herpetic stomatitis
According to statistics, it accounts for more than 80% of cases of all diseases of the oral mucosa in children.
Source of origin: The herpes virus is transmitted by airborne droplets and contact, and children just love to share sweets with each other, touchingly removing candy from their mouths to let a friend lick it, and playing with shared toys.
Features of the course: The disease can be severe, with an increase in temperature to high numbers, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Bubbles appear in the oral cavity, which quickly turn into small ulcers. After 3-4 days, the ulcers gradually heal and disappear without a trace. The illness usually lasts one to two weeks.
Symptoms
These include the formation of slight redness in the mucosal area. This is the very beginning stage. Then they increase in size and discomfort appears. Over time, the disease develops into an ulcerative form of development. The ulcers are covered with a film on top and are white or gray in color. They cause severe pain.
The course of the disease is accompanied by increased salivation, periodic increases in temperature, general malaise, and loss of appetite. Lymph nodes increase in size.
Aphthous stomatitis
It most often occurs in adults and is dangerous for its relapses, which occur mainly in spring and autumn, as well as a long course with periodic exacerbations.
Source of occurrence: The appearance of aphthous stomatitis is associated with a decrease in general and local immunity.
Features of the course: Aphthae are small formations of oval or round shape. They appear on the oral mucosa in both single and multiple quantities. Each such formation is surrounded by a thin bright red border and covered with a yellow-gray coating.
Causes
Everyone knows or has heard about what the body’s immune system is. It fights external irritants - molecules, germs and microorganisms, the appearance of which is undesirable in our body. Today, scientists have concluded that this common disease, in its various forms, may be caused by the human immune system reacting to external stimuli that it cannot recognize.
Other causative phenomena include:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- metabolic disorders;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- other reasons related to weakened immunity.
Allergic stomatitis
It is considered one of the most severe types of this disease.
Source: Allergy to medications (for example, antibiotics), to the materials from which dentures are made, to certain foods (oranges, strawberries...).
Article on the topic
Diagnosis and treatment of various types of stomatitis
Features of the course: The patient complains of burning, itching, and discomfort in the oral cavity. For a person suffering from allergic stomatitis, it is often painful not only to chew, but even... to swallow air.
Treatment recommendations
When the catarrhal form of the disease manifests itself, it can be cured quickly, at home. It is necessary to rinse your mouth several times with antiseptic agents every day, and also follow a diet that excludes the intake of spicy and salty foods.
In all other, more acute manifestations, they go to the Implantmaster clinic in Moscow. Qualified dentists will make the correct diagnosis and provide treatment. Photos of stomatitis, in different manifestations, are available on the company’s website, as well as on other resources on the World Wide Web.
To begin with, doctors prescribe medications that relieve pain and discomfort. Another goal is to avoid further development of the disease, which can develop into chronic stomatitis. Tablets and powders such as anesthesin, lidocainecept, hexoraltabs, decoctions of chamomile, calendula, and sage will help the patient stop the development of the disease and return to their normal lifestyle.
If there is a fungal origin of stomatitis, antifungal agents are used. Vitamin therapy, Cycloferon, Immunal are also useful for increasing immunity.
Article Expert:
Fungal stomatitis
Most often, this type of stomatitis affects children, from the first days of life, but also among adults, usually elderly and weakened, candidomycosis is not uncommon, and it is more common in women.
Source of occurrence: There are two ways of occurrence of fungal candidiasis - infection from a sick person with candidomycosis through direct contact or through household items and the transition of one's own conditionally pathogenic fungi into pathogenic ones under the influence of factors favorable for the development of the fungus (hypothermia or weakening of the body). Newborns become infected with such stomatitis when passing through the birth canal of a mother suffering from vulvovaginal candidiasis.
Article on the topic
How to keep your teeth healthy: 5 main rules
Features of the course: This type of stomatitis can be identified by a white, “curdled” coating on the tongue, palate, and inner surface of the cheeks.
Classification
The classification of stomatitis includes several types of pathology:
- bacterial stomatitis;
- viral;
- fungal;
- ray;
- chemical;
- aphthous.
To detect the disease at the initial stage and quickly get rid of it, you need to know the signs and characteristics of each form of the disease.
Features of the bacterial form
With the bacterial type of disease, stomatitis in the mouth develops due to the penetration of streptococci or staphylococci. Less commonly, the disease occurs due to other bacteria.
Stomatitis on the tongue or gums of a bacterial nature provokes the formation of a purulent rash, which quickly breaks out and ulcers form in these places. The patient experiences pain, especially when eating and drinking.
Features of the viral form
With viral stomatitis, papules – fluid-filled blisters – also form on the gums or tongue. The causative agent of the disease is most often the Epstein-Barr virus. This type of herpes virus can live in the body in a latent form for many years and not cause any symptoms.
Herpetic stomatitis can turn into bacterial if a secondary infection occurs. Ulcers and papules form, and after they open, wounds form. In some patients, the nature of the rash resembles that which occurs with sexually transmitted diseases.
Important! To make a correct diagnosis, a doctor's examination and diagnostics are required.
Gingivostomatitis (herpes type) can occur in both acute and chronic forms.
What is enteroviral vesicular stomatitis?
Enteroviral vesicular stomatitis is a form of inflammation that most often affects children under 10 years of age. This type of stomatitis is very contagious, so it is important to isolate the child.
The peculiarity of this form of pathology is that irritation and rash occurs not only in the mouth, but also on the palms and heels. Patients experience nausea, vomiting and other dyspeptic symptoms. Possible loss of appetite and increased nervousness. Vesicles may or may not appear. Sometimes the skin simply becomes covered with white spots.
Features of the fungal form
Often, fungal catarrhal stomatitis develops after taking antibiotics. As a result of the drug's action, bacteria die, but the immune system weakens. This creates favorable conditions for the fungus to live.
Often, an inflammatory process in the mouth of a fungal nature develops after the activation of fungi of the genus Candida. Candidal stomatitis causes the formation of white sores. There are small wounds on the tonsils that are very painful. A dense white coating appears on the lips, tongue and gums. Thrush in the mouth is treated only after the causative agent of the disease has been accurately identified.
Features of radiation stomatitis
This form of pathology occurs exclusively after undergoing a course of treatment for cancer. Many drugs have a powerful effect on the body, and patients experience drug-induced stomatitis.
If irradiation was carried out, ulcerative stomatitis develops. Multiple erosions appear, which are very painful. On examination, you can see thickening of the mucous membrane.
Features of chemical stomatitis
This form of the disease develops in response to exposure to acids or alkalis. The mucous membrane is not able to neutralize this effect and inflammation begins. As a result, ulcerative areas and scar tissue form on the affected areas.
Features of aphthous stomatitis
With aphthous stomatitis, lesions can be single or multiple. The sizes of the ulcers vary. Some are small spots, while others reach the size of a large pimple. There is a red spot around the lesion, and a white coating in the center.
Aphthae in the mouth are often accompanied by extended symptoms:
- weakness;
- temperature;
- general malaise.
Note! This is one of the most frequently recurrent forms of chronic stomatitis - the disease pattern repeats up to 4 times a year.
After about the age of twenty, this form of the disease occurs less frequently. The soreness almost goes away, but ulcers may form. Some call this form of pathology childhood stomatitis, since it most often occurs in a child, and not in an adult.
Important
The choice of treatment tactics is dictated by the cause of stomatitis: for bacterial types, antibiotics are recommended, for viral types, antiviral agents are recommended, and for stomatitis caused by hypovitaminosis, taking vitamins.
At the appointment, the doctor will teach you how to properly treat the mucous membrane and aphthous elements using antiseptics and painkillers.
To prevent re-infection with bacteria, antibacterial drugs are prescribed, and to speed up the recovery of damaged mucous membranes, sea buckthorn oil, rose hips, and propolis ointment are prescribed.
Basic principles of therapeutic therapy in adults
Treatment of various forms of stomatitis involves, first of all, strict adherence to hygiene rules and doctor’s recommendations. Along with a diet that excludes hard, spicy, salty, hot and too cold foods, drug therapy is required.
Pain relief for inflamed areas
Most often, local anesthetics are used to eliminate pain in the form of the following drugs:
- Anestezin (tablets are ground into powder before use);
- Hexoral Tabs (active ingredients – chlorhexidine and benzocaine, which not only relieve pain, but also have an antimicrobial effect);
- Lidocaine Asept;
- Lidoxor (a local anesthetic and at the same time an antiseptic, available in the form of a gel).
You can also use folk remedies - decoctions of sage, calendula or chamomile, infusion of Kalanchoe.
Antiseptic and anti-inflammatory therapy
To effectively eliminate the manifestations of stomatitis, you need to regularly rinse, treat the oral cavity with sprays, and dissolve antimicrobial lozenges and tablets.
Most often, the disease is treated using:
- Inhalipt , Hexoral , triple-action gel Cholisal Kamistad gel (active ingredients - chamomile and lidocaine);
- For rinsing, you can choose traditional Chlorhexidine , Miramistin , Furacilin Equarom based on eucalyptus extract ;
- Stomatidin and Eucalyptus M have a good effect .
Antiviral treatment and elimination of intoxication
Drugs in this group are necessary to eliminate specific causes of stomatitis. For example, antiviral therapy using special ointments and tablets is mandatory in the case of herpetic stomatitis.
Antiallergic drugs should also not be ignored, since most types of stomatitis occur with characteristic symptoms of hypersensitization.
For this purpose, use:
- the most popular antiviral agents are Acyclovir , Famciclovir , Viferon ;
- Fluconazole , Levorin , Nystatin , Candide are used to combat fungus ;
- The most commonly prescribed antihistamines are Claritin , Loratadine , Suprastin , Fenistil , Tavegil .
Means for restoring epithelium
This group includes drugs that promote mucosal regeneration, improve trophism and rapid epithelization:
- Vinizol (Shostakovsky balm in the form of a spray) - helps clean wounds and speed up the process of tissue regeneration, acts as an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agent;
- and sea buckthorn oils - promote rapid healing and are indicated during the recovery phase;
- Solcoseryl - provides high-quality oral hygiene and restoration of the mucous membrane;
- Propolis in spray - promotes the healing of ulcers and other injuries, additionally anesthetizing inflamed areas.
Treatment of stomatitis can only be effective with an integrated approach to this problem.
Timely detection of symptoms and contacting a doctor will allow you to avoid negative consequences and quickly restore the inflamed areas, preventing the development of dangerous complications and constant relapses.