What is pyelonephritis?
Kidneys are vital for our body, and even more so for the baby’s body, since they are a kind of “filter” that removes all unnecessary and harmful substances. It is important to know that the kidneys produce vitamin D, which affects the formation and strengthening of bones.
Pyelonephritis is an infectious inflammation that occurs in the pyelocaliceal system of the kidneys , accompanied by difficulty urinating, change in the color of urine, and pain in the lumbar region.
This is a fairly common disease that can appear in a child at almost any age. According to statistics, the most common cases of the disease are recorded in preschool children.
Due to anatomical differences, acute pyelonephritis in children most often occurs among girls, since their urethra (urethra) is shorter and wider than that of boys.
Causes of childhood pyelonephritis
Children often have problems with the urinary system, and this is easier to notice in an infant, because the mother carefully monitors his every action. But in any case, it is necessary to know the limits of the normal state of the baby: when everything is in order, and when you need to urgently consult a doctor.
Kidney pyelonephritis in children does not occur out of nowhere, so there are always prerequisites for it
Most often, the child experiences a disturbance in the outflow of urine, which is called a failure in urodynamics. As a result, discomfort begins to be felt, due to which a complete imbalance of the body occurs, and the child often begins to be capricious.
Pyelonephritis in children can occur for the following reasons:
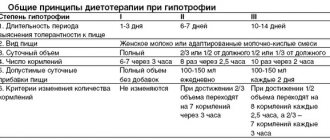
Diet for chronic pyelonephritis in adults
- Presence of urolithiasis. Some of them can be inherited, so mothers should be carefully examined during pregnancy, or better before it begins. The baby's health begins with the health of his mother.
- Excessive amount of vitamin D in the body. The fact is that it is a fat-soluble substance that is not excreted in the urine. Thus, it accumulates, which has a detrimental effect on the child’s kidneys.
- Ureteral reflux. Backflow of urine occurs because the baby has impaired or underdeveloped urinary tract muscles. As a result, there is a disruption in the normal movement of the contents of the hollow organs.
- Hypotrophy. It occurs mainly only in children and manifests itself in the form of impaired digestion. Initially, this creates a large load on the intestines, and then moves on to the excretory system.
- Prematurity entails poor development of the entire body of newborns, which is why the urinary organs, in particular the kidneys and the collecting system, suffer the most.
Remember! If your child does not tell you anything, but you notice something wrong in his behavior regarding urination, then it is better to have him tested at the clinic to find out the cause of the ailments in the child’s body.
An ultrasound may reveal a congenital anomaly of the kidney structure in a child.
These reasons do not always depend on the child’s parents, so it is practically impossible to protect him. But the main thing is that it is necessary to regularly examine the baby in order to prevent the development of any diseases in the early stages. The pathogenesis of childhood pyelonephritis also lies in the fact that the child may have congenital anomalies in the structure of the organs of the urinary system. This may be a congenital expansion or narrowing of the pyelocaliceal system. It is worth noting that the penetration of infections requires careful treatment, since it is because of them that most children’s pyelonephritis occurs.
Classification of pyelonephritis in children
In modern medicine there is no specific clear classification of the disease , however, it can be divided according to various criteria:
- Depending on the form of the process, pyelonephritis in children is divided into primary and secondary.
- Acute and chronic types are determined by the nature of the disease.
Primary pyelonephritis develops in initially healthy kidneys . However, the examination does not show factors favorable to the development of microorganisms in tissues.
Secondary pyelonephritis can be obstructive and non-obstructive . In the first case, inflammation is caused by congenital or functional disorders of urodynamics. In the second case, the disease is caused by dysmetabolic disorders, immunodeficiency states, and endocrine disorders.
Reasons for the development of pathology in children
Pyelonephritis in children, like any inflammatory disease, is caused by microorganisms that enter the kidneys in various ways and begin to actively multiply. According to pathogenesis, in the vast majority of situations, this disease is caused by E. coli, which enters the kidneys through the bloodstream from foci of chronic infection. Such a source of infection can be carious teeth along with chronic tonsillitis and otitis media. In rare cases, the infection can also come from the bladder or genital area. This is precisely the reason why girls usually suffer from cystitis and pyelonephritis three times more often than boys because of their short urethra.
Prevention of chronic pyelonephritis in children is very important.
Under normal conditions, a child’s body is quite capable of coping with pathogenic microorganisms. The main reason for the development of inflammation is considered to be a decrease in immunity, against the background of which the defenses are unable to cope with the infection. There are many reasons that lead to decreased immunity, for example:
- Complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
- Short breastfeeding along with early introduction of complementary foods.
- Vitamin deficiency in the body.
- The presence of chronic inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract.
- The presence of a hereditary predisposition.
Is it possible to become infected with pyelonephritis and what can trigger the disease?
Escherichia coli is the main causative agent of pyelonephritis infection.
It is impossible to become infected directly with pyelonephritis itself , since this disease is not transmitted by any means.
But there can be several reasons for inflammation.
The most common is Escherichia coli, but infection can also be caused by Proteus, Staphylococcus aureus, Mycoplasma, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Chlamydia, and Enterococcus.
All these bacteria are detected when urine is submitted for bacteriological culture.
Another cause of the disease may be a weakened immune system. If a child is susceptible to frequent colds, tonsillitis, if the baby suffers from dysbacteriosis, constipation or colitis, this is a reason to be more attentive to the symptoms of pyelonephritis. Even banal caries can serve as an impetus for inflammation.
Symptoms of the disease
One of the symptoms of pyelonephritis is pain when urinating.
There are various signs of pyelonephritis in children, if they occur, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- Fever. The baby's temperature rises to 38-39°C, while no symptoms of colds (redness and sore throat, cough, runny nose) are observed, the child feels unwell, headache and loss of appetite.
- Changing your urination pattern. For example, if a child drinks a lot of liquid but rarely goes to the toilet, or, conversely, drinks little but experiences frequent urges, this may also be an alarming symptom.
- The child may experience pain when urinating.
- Change in urine color (darkening or bright orange).
Somewhat different symptoms of pyelonephritis in an infant . As a rule, this is a violation of stool and regurgitation, as well as poor weight gain. These symptoms may also indicate other problems, so identifying pyelonephritis in an infant is very difficult.
In some cases, the disease may occur without any symptoms, so special attention should be paid to the health of the baby.
Regardless of the child’s age, incorrect diagnosis, and therefore incorrect treatment, triggering the disease can subsequently lead to the development of arterial hypertension, as well as the formation of phosphate stones in the kidneys.
How does pyelonephritis occur in different groups of children?
It is known that at any age, girls suffer from pyelonephritis more often than boys. This is easily explained by the physiological characteristics of the urethra. Girls have a shorter urethra, which makes it a favorable place for the proliferation and penetration of bacteria through the ascending route. The proximity of the vagina, in which a large number of opportunistic microorganisms are located, also plays a significant role.
It is traditionally believed that in boys, kidney inflammation goes away much easier, without causing visible complications.
The consequences of pyelonephritis for girls and boys vary significantly
Table: main consequences of pyelonephritis for children of different sexes
| Pathological process | Boys | Girls |
| Effect on the ability to conceive offspring | does not significantly affect | increases the risk of miscarriage or premature birth |
| Inflammatory diseases of other organs | urethritis and prostatitis in adulthood | high risk of developing cystitis during adolescence |
| Urolithiasis disease | the risk of occurrence increases several times | about thirty percent of girls who have suffered chronic pyelonephritis suffer from stone formation |
| Tendency to form narrowing of the ureters | significant | absent |
| Sexual dysfunction | expressed | weakly expressed or absent |
| Changes in immune system activity | the risk of contracting colds increases | increased susceptibility to pyogenic infections |
Features of the pathological process in newborns
Features of the disease in newborns:
- apathy, lethargy;
- loss of appetite;
- dry skin in cracks;
- the appearance of sticking in the corners of the mouth;
- decreased amount of urine and unpleasant odor from diapers;
- frequent regurgitation of food and vomiting;
- violation of the body's height and weight gain schedules.
Methods for diagnosing pyelonephritis
The diagnosis of pyelonephritis is made if a urine test shows an increased content of leukocytes (above 4000) and a high number of bacteria.
Diagnosis of pyelonephritis in children consists of conducting a general and biochemical urine test. It is very important to identify the disease at an early stage.
To do this, all children under one year old must undergo such an analysis every month, since it is at this age that the disease is most difficult to detect.
If the doctor suspects any inflammation, additional urine tests are performed according to Nechiporenko and Zimnitsky.
If a urine test shows an elevated white blood cell count (above 4000) and a high number of bacteria, then the doctor diagnoses pyelonephritis.
In fact, a urine test for pyelonephritis in children is a fairly reliable indicator for making a diagnosis.
Read here how to avoid mistakes when collecting urine from infant boys, and in this article from infant girls.
A blood test is also ordered. The presence of the disease is indicated by low hemoglobin, high white blood cell count and increased ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). Modern laboratory tests make it possible to determine the diagnosis with high accuracy.
To exclude errors in diagnosis, urine culture and ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder are prescribed.
If any symptoms of the disease occur, do not postpone a visit to the doctor, because only qualified diagnostics can help make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Where and how does treatment take place?
The main means of combating pyelonephritis is an antibiotic . In addition to it, uroseptic and homeopathic drugs can also be prescribed. Their action helps to cope with inflammation, but in no case should you cancel the antibacterial agent.
Depending on the type of inflammatory pathogen, the doctor prescribes the type of antibiotic. Typically, the list includes the following drugs:
| Name | Operating principle | Side effects, contraindications | Dosage, method of application | approximate cost |
| AMOXYCYCLINE | Broad-spectrum antibiotic with bactericidal effect | Use with caution in patients with allergies and asthma, as well as premature infants and newborns | The daily dose is 25-50 mg/kg body weight, divided into several doses | 100 rub. |
| AMPICILLIN | Broad spectrum antibiotic | Contraindications: infectious mononucleosis, lymphocytic leukemia, hypersensitivity to ampicillin and other penicillins, liver dysfunction | A single dose is 25-50 mg/kg body weight. The daily dose is divided into 4 doses. Children weighing up to 20 kg are prescribed 12.5-25 mg/kg. | 30-60 rub. |
| CEFUROXIME | 2nd generation broad spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic. Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract | Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the drug and other cephalosporins, penicillins and carbapenems | The drug is administered intravenously and intramuscularly. Children up to 3 months – 30 mg/kg in 2-3 doses. Children over 3 months 30-100 mg/kg in 3-4 doses | 220 rub. |
| CEFTRIAXONE | 3rd generation broad spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic | Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, cephalosporins, penicillins, carbapenems | The drug is used intravenously and intramuscularly. The dosage for newborns (up to 2 weeks) is 20-50 mg/kg per day. Children under 12 years of age are prescribed 20-80 mg/kg. Dosages greater than 50 mg/kg are administered intravenously over 30 minutes. | 410 rub. |
| CEFOPERAZONE | Has an antibacterial effect against a wide range of bacteria | Contraindicated in renal failure, liver dysfunction | In the form of injections intramuscularly or intravenously. Small children are prescribed 50-100 mg/kg per day in 2 divided doses | 115-400 rub. |
Infants are treated with special care . For their treatment, special gentle drugs are used, such as Gentamicin or Keflex.
Treatment of acute pyelonephritis in children may require at least 3 weeks. After a course of antibiotics, a course of probiotics is required to restore the intestinal flora.
It is very important to complete the entire course of treatment and strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations , since untreated acute inflammation can develop into chronic pyelonephritis in children.
Treatment of inflammatory pathology
A variety of techniques are used to treat pyelonephritis in children. Traditionally, therapy consists of a course of antibiotics, various physical procedures and diet. As the inflammatory process subsides, other medicinal substances and herbal remedies are added. The effectiveness of therapy directly depends on the following factors:
- duration of the pathological process at the start of active therapy;
- the presence of concomitant pathologies of various organs and tissues;
- intensity of the inflammatory process and aggressiveness of the pathogen;
- quantity and nature of previous medications;
- preservation of the functional activity of the renal apparatus;
- activity of symptoms of internal poisoning of the body by decay products;
- life history;
- state of immunity.
Diet features
Proper nutrition for pyelonephritis is one of the important stages in the treatment of the disease. Fatty, fried, salty and very spicy foods not only negatively affect the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, but also have a bad effect on kidney function. Poor nutrition is one of the leading factors in the occurrence of a serious disease called urolithiasis.
Healthy food strengthens the overall immune system
To feed a child with pyelonephritis, it is recommended to use:
- not too hot or cold food;
- pure mineral waters;
- boiled, baked and stewed dishes;
- salt no more than five grams per day;
- food with sufficient energy value;
- fresh vegetables and fruits in large quantities;
- buckwheat, oatmeal, millet, pearl barley and rice porridge;
- black bread and crispbread;
- milk and dairy products (cheese, low-fat cottage cheese, sour cream, butter);
- poultry and fish;
- a large amount of liquid. The child should drink at least one and a half liters of plain water: this stimulates the kidneys.
It is strictly forbidden to eat:
- chips and crackers with fillings;
- canned foods;
- vegetables fried in vegetable oil;
- hot spices;
- salty foods, which cause fluid retention in the body;
- red meat in large quantities;
- carbonated drinks and packaged juices.
What medications can be used
There are several guiding principles on which drug therapy for pyelonephritis is based. If they are followed, the disease progresses much more slowly.
- Prescribe antimicrobial therapy as early as possible.
- Intravenous administration of medication through a catheter in severe cases of the disease.
- Use of several medications at once if necessary.
Table: drugs used to treat pyelonephritis in children
| Name of the drug group | Effects | Medicines |
| Antibiotics | destroy the pathogen, preventing its reproduction in the cells and tissues of the kidney |
|
| Immunomodulators | stimulate the activity of the body's immune system, forcing it to independently fight infection |
|
| Herbal remedies | improve urine passage, providing a mild diuretic and regenerating effect |
|
Physiotherapy for pyelonephritis
Physiotherapeutic measures can be reasonably included in the course of treatment of kidney pathologies. Physical factors, acting on the kidney tissue, can completely eliminate residual inflammatory phenomena, prevent the spread of the pathogen and strengthen the immune system. A few days after the start of treatment, positive dynamics in urine passage are observed.
Contraindications for which physiotherapy is not recommended are:
- acute renal failure;
- acute pyelonephritis with purulent process;
- chronic liver failure;
- primary and secondary immunodeficiency;
- fever and hemorrhagic syndrome in the form of skin rashes;
- recently suffered a particularly dangerous infection.
If you are unsure whether your baby is at risk, be sure to consult with your child's doctor.
Laser therapy helps relieve pain and spasms
For the treatment of acute and chronic pyelonephritis in children, the following are most often used:
- mineral, mud, sulfur baths;
- hot and warm showers;
- laser therapy;
- treatment with magnetic fields;
- ultrasound therapy;
- ultra-high-frequency and ultra-high-frequency therapy;
- administration of drugs using electrophoresis;
- mud wraps and seaweed wraps;
- baths and saunas;
- mineral carbonated waters;
- treatment with currents of different frequencies.
Surgery
Surgical intervention for pyelonephritis is most often necessary in cases of obstructive pathology, when the renal pelvis is blocked by a large staghorn stone, as well as when a secondary purulent infection is attached. Operations are divided into several types:
- emergency, which is carried out in the first two hours after preparing the patient;
- urgent, which is carried out within 24 hours from the moment the child is admitted to the hospital;
- planned, the implementation of which surgeons plan in advance.
Most pediatric operations for acute pyelonephritis are emergency. After completing all the necessary measures, the patient goes to the operating table, where doctors begin to eliminate the pathology.
The procedure of surgical intervention for pyelonephritis is extremely rarely resorted to
The operation is quite simple:
- For minor injuries and small pustules, a laparoscope is used.
- If the kidney damage is larger, an oblique incision is used in the lumbar region.
- The skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue are sequentially dissected. Using a blunt retractor, the muscle bundles are pulled apart and the kidney is exposed.
- The kidney and its vessels are carefully examined, and the pelvis is checked for the possibility of phlegmon formation.
- The renal pedicle, which includes the ureter, renal arteries, veins and lymphatic vessels, is ligated.
- The renal capsule is incised, pustular lesions are removed or the stone is removed.
- The patency of the vessels is restored and a glove drain is placed to the renal bed.
- The wound is sutured, leaving room for removal of the contents.
The surgical intervention itself lasts no more than three hours. In the first few days after the procedure, the child will be in intensive care, where doctors monitor the condition of each patient. Recovery after surgery does not last more than two weeks.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine is widely used to treat inflammatory kidney diseases in young children. These products are quite easy to use, do not affect the liver and do not cause dysbiosis, unlike antibiotics. It is worth remembering that you cannot completely refuse medical prescriptions: with the help of antimicrobial drugs, the causative agent of the pathology itself is eliminated, which folk remedies cannot do. Be sure to keep in mind that in response to the use of an unfamiliar substance, the baby may experience an allergic reaction: this is why it is so important to consult your local pediatrician before starting to use any traditional medicine.
- Melt two tablespoons of butter. Add two finely crushed teaspoons of propolis and one tablespoon of honey. Mix thoroughly and give the resulting gruel to your baby twice a day: you can add it to porridge or spread the mixture on a sandwich. This way you will reduce the inflammatory processes that occur in the genitourinary system. Use within two weeks.
- Add a glass of oatmeal to a liter of boiling milk and cook for ten minutes. Cool, add sugar or honey and offer the resulting mixture to the child at least three times a day for a month. This will help cleanse the body and remove all toxins that weakened kidneys cannot cope with.
- Use a herb called bird's buckwheat, which will help destroy the pathogen: it has an antiseptic effect. Dissolve two tablespoons of chopped herbs in a glass of boiling water and let it brew. You need to give your child water twice a day: in the morning and in the evening. The course of treatment consists of twenty procedures.
- Dissolve five grams of fresh dill seeds in a glass of water. Heat the resulting liquid over low heat and bring to a boil. After cooling, let the child drink the solution and wrap him tightly in a blanket. With the help of dill, high fever during pyelonephritis is well reduced.
- Dissolve ten grams of birch buds in a liter of water. Place the pan on the stove and bring to a boil. Dip a sprig of parsley into the resulting mixture and add a teaspoon of ginger. After the liquid has cooled, give it to your baby throughout the day. Birch buds in combination with ginger cope well with inflammatory phenomena of various etiologies.
Photo gallery: traditional medicine for pyelonephritis
Dill seeds are good for relieving pain from pyelonephritis
Milk combined with oatmeal helps cleanse the body
Birch buds reduce inflammation
Diet for pyelonephritis
When treating pyelonephritis in children, diet should not be neglected, since proper nutrition promotes a speedy recovery.
Doctors recommend excluding spicy, fatty, salty and fried foods from a sick child’s diet. Do not consume concentrated broths, onions and garlic, or coffee. In special cases, protein foods are also excluded. Conversely, increase your consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits , especially watermelons, cucumbers, zucchini and melons.
In the first week of the disease, strict bed rest and a dairy diet (cottage cheese, kefir, unflavored yogurt) are required. Reduce daily salt intake to 3 g. Give vegetables only fresh, boiled or stewed.
Treatment of pyelonephritis
Treatment of childhood pyelonephritis depends on the condition of the child, because the disease may be at an initial stage or at a more advanced stage. Thus, the attending physician determines whether the baby needs nursing care. If so, he will be admitted to a hospital and his condition will be constantly monitored. This is done in order to track the development of the disease: whether the child’s condition is improving or the disease, on the contrary, is rapidly progressing.
The child should be given complete rest and careful care
With such observation, the question of which method is best to treat the patient is still being decided: conservative or progressive. Despite the fact that surgical intervention is extremely rarely necessary, doctors do not deny its possibility.
Here are the principles that underlie the treatment of pyelonephritis in children:
- Maintain complete peace. The child is provided with bed rest, measures are established to eliminate intoxication of the body. At this stage, his general well-being is restored so that without any danger one can proceed directly to the treatment of pyelonephritis itself.
- Compliance with all hygiene rules. The baby should not be exposed to the penetration of third-party microbes and infections into his body, so his body, clothes and bed should always be clean.
- Symptomatic therapy. Simply put, taking the necessary medications that are aimed at improving the condition of the body. These are anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antipyretic agents and various vitamins.
- Measures aimed at ensuring that the child does not experience a relapse of the disease in the future. The fact is that if pyelonephritis takes a chronic form, then there is a high probability of developing complications.
To restore the child’s normal condition, it is necessary to prescribe a certain course of medication.
Thus, slowly but persistently, doctors achieve a high-quality cure for the child. If everything goes well, then you will soon forget that there were serious inflammatory processes in your child’s excretory system. And all this thanks to experienced specialists.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky on the treatment of pyelonephritis in children
In articles and videos, Oleg Evgenievich talks in detail about pyelonephritis in children, symptoms and treatment of the disease, as well as the actions of parents in the event of such a diagnosis.
Dr. Komarovsky never tires of repeating that the child’s health must be strengthened from a very early age : walk with the child in the fresh air more often, regularly ventilate the room and not overheat the baby. Such simple measures will strengthen the child’s local immunity and will significantly reduce the risk of inflammatory processes in the body, including pyelonephritis.
Komarovsky considers pyelonephritis in children to be a rather serious diagnosis, recommending to remain calm and not take rash actions.
If you observe symptoms of pyelonephritis in your baby, do not wait for the development of acute forms of the disease and do not treat the child with “folk remedies” , but immediately seek qualified help.
According to statistics, almost 30-40% of all children have suffered from cystitis at least once. Children who suffer from pyelonephritis are at risk.
Girls are most often prone to such infections. Find out how to properly care for the intimate hygiene of newborn girls in this material.
Read what a fever in a child without symptoms can tell you here.
Symptoms
For pyelonephritis in children, the protocol is quite extensive. This medical document presents many characteristics of the pathology, including obvious symptoms. Considering the patient’s age, predisposing factors, and the level of the body’s protective abilities, the signs will differ.
The main associated conditions are:
- High body temperature. Often this is the only symptom of the disease. When you have a fever, the thermometer stays at 38 degrees.
- Intoxication of the body. Due to the release of toxins, the child has a feeling of nausea, he suffers from vomiting, and his appetite is either minimal or completely absent. The younger the patient and the more advanced the degree of the disease, the more pronounced the symptoms.
- Feeling of pain in the abdomen and lower back. It is imperative to pay attention to the child’s complaints. Until the age of four, it is difficult for them to explain what exactly is bothering them. Subsequently, patients can describe the nature of the pain, which is often aching or pulling.
It is worth noting that, unlike adults, children rarely suffer from various disorders during urination due to pyelonephritis. More often they are concerned about urinary incontinence. Parents may also notice the appearance of swelling on the face, more pronounced after a night's sleep. The biological fluid (urine) becomes cloudy and dark and has an unpleasant odor.
If a child patient has chronic pyelonephritis, which recurs with a certain frequency, then the child will soon develop symptoms of infectious asthenia. He becomes irritable, gets tired quickly, and his performance at school decreases.
With the development of pathology at an early age, developmental delays, including psychomotor development, cannot be ruled out in the future. Therefore, it is very important to go to see a doctor every month, take urine and blood tests, and dynamically monitor their indicators. And if there are alarming changes, treat the pathology.
In infants
How to treat pyelonephritis in children should be determined by the leading specialist. Self-therapy can be quite dangerous and lead to complications. Particular attention should be paid to infants and newborns, since they still cannot really tell or even show what the problem is.
Often accompanying symptoms are:
- Temperature within 39-40 degrees;
- Periodic febrile convulsions are possible;
- Belching and vomiting;
- Baby's refusal to feed;
- Pallor of the skin;
- There is blue discoloration around the mouth and above the upper lip;
- Dry skin and sagging, indicating dehydration.
Parents should be wary even when the child begins to behave restlessly. Since infants often scream and cry during bowel movements, as well as defecation, it is worth paying attention to the indirect signs of pyelonephritis, which were described above. It is best to seek emergency medical help in this situation.
Disease prevention
It is important to maintain oral hygiene to prevent pyelonephritis.
As you know, it is better to prevent a disease than to treat it for a long time.
Since respiratory diseases become common causes of pyelonephritis , to prevent pyelonephritis in children, one should take more walks in the fresh air, ventilate the room, and do wet cleaning to reduce the content of pathogens of such diseases.
is very important to maintain oral hygiene . Everyone has long known that it is necessary to brush your teeth twice a day, and if caries occurs, immediately seek help from a dentist. You will learn how to choose an electric toothbrush for the whole family in a separate article.
Reviews from parents about the treatment of pyelonephritis in children
Evgeniya, 30 years old, Volgograd
My daughter (2 years old) was diagnosed with pyelonephritis. We ended up with her in the hospital just before the New Year, on the 20th of December, and on the 30th she was already discharged. Therefore, antibiotics were administered at home.
We went to the hospital after a bad urine culture. After antibiotics, we took a course of Urolesan, until there were no relapses.
Zhanna, 25 years old, Omsk
My daughter and I donated urine for bacterial culture at the hospital for free, but before that we had to donate urine several times at our own expense.
Along with antibiotics, we took a course of drugs for intestinal flora, because there were severe disorders. When an ultrasound of the kidneys was done at the clinic, there were no changes.
Natalya, 31 years old, Lipetsk
My son had pyelonephritis due to congenital narrowing of the ureters.
Elevated white blood cells were treated only with antibiotics, and we use Canephron and herbal preparations only for prevention.