Causes of tuberculosis of the genitourinary organs
The causative agent of tuberculosis is mycobacterium, which was first identified by Robert Koch back in 1882. Today, more than seventy different types of Mycobacterium tuberculosis are known, although only bovine and human strains affect the genitourinary system.
As is known, almost the entire population of the globe is carriers of this pathogen, and only a small part of humanity suffers from the disease. First of all, it depends on the number of bacteria in the human body and the state of the immune system, which does not allow these bacteria to multiply. Those patients who have a history of chronic inflammatory diseases of these organs and are constantly in contact with patients with tuberculosis are most at risk of contracting tuberculosis of the genitourinary system.
Tuberculosis of the genitourinary system can occur due to direct penetration of the pathogen or when it is introduced from another diseased organ, most often the lungs. In most cases, this occurs through the bloodstream. This type of tuberculosis of the genitourinary system is called secondary.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Determining the etiology of tuberculosis of the genitourinary system plays an important role in choosing treatment tactics for the disease.
Among the main reasons for the development of pathology, experts identify:
- Protracted course of pulmonary tuberculosis. In most cases, the disease is detected against the background of chronic changes in the organs of the urinary system.
- Patients with an open form of the disease are contagious and, upon contact with other people, can infect them, which leads to damage to the kidneys and urinary structures.
- Eating meat or milk from infected cattle, as well as other food products.
The main factor contributing to the development of tuberculosis of the kidneys and urinary system is damage to the lungs by mycobacteria.
Experts rarely diagnose the disease after contact with contaminated dairy products.
The entry of Koch bacilli into the human body does not always lead to the development of the disease. The immune system in some cases can independently prevent their spread.
The main risk factors for damage to the urinary system by mycobacteria include:
- decreased immunity;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra;
- poor social and living conditions;
- the use of medications that help reduce the body’s immune defense;
- poor nutrition.
Phthisiatricians identify several forms of spread of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from a patient or household items to other people:
- Airborne. In this situation, the source of infection is the patient's sputum or saliva.
- Contact and household path. You can become infected with Koch bacilli by shaking hands, hugging or communicating with a patient, as well as through the use of household and personal hygiene items.
- Penetration of mycobacteria into the urinary system by hematogenous or lymphogenous route.
- Transfer of infectious agents between kidneys.
To prevent infection upon contact with the patient, gauze dressings should be used. Also, after completing a visit to such patients, you should thoroughly wash exposed areas of the body and wash clothes.
These precautions will significantly reduce the risk of contracting tuberculosis.
Symptoms of tuberculosis of the genitourinary system
The symptoms of this disease largely depend on which organ of the genitourinary system is affected. For example, with kidney tuberculosis, both local and general symptoms are present. Patients complain of deterioration in general condition, fatigue, increased sweating, sleep disturbance and shortness of breath. They are also bothered by dull pain in the lumbar region, which develops as a result of stretching of the kidney capsule. Along with this, there is also a violation of urination in the form of delay or, on the contrary, increased frequency. Patients may also experience pain or discomfort when urinating.
When the bladder is affected by tuberculosis, the main symptom is increased urination. In addition, due to ulceration of the mucous membrane of the bladder, there may be pain at the end of urination and the release of a small amount of blood in the urine. Another symptom that occurs due to kidney damage from tuberculosis is increased blood pressure. It has the same character as with other kidney pathologies - due to increased secretion of renin, arterial spasm develops, which leads to increased blood pressure.
If a patient experiences similar symptoms, he should go for a consultation with a urologist so that he can confirm the urological pathology or send the patient for a consultation with a phthisiatrician.
Kidney with tuberculosis
Causes
The causative agent of the disease is Mycobacterium tuberculosis or, more simply, Koch's bacillus.
The main carrier of the infection is humans. In addition, the bacterium can live in the organs of fish, birds and farm animals.
- By airborne droplets. The bacterium enters the body during breathing, and then moves through the bloodstream or lymph to the genitourinary organs.
- Nutritional. The stick penetrates food through the digestive system.
- By contact method. Infection occurs through the skin or mucous membranes.
- Intrauterine infection. The fetus becomes infected from an infected mother.
- By sexual method. Infection can occur during unprotected sexual intercourse.
A third of the world's population is a carrier of the tuberculosis bacillus. But only in 10% of cases does the disease enter the active stage.
In the latent (inactive) phase, tuberculosis is not transmitted from person to person.
Most often, urogenital tuberculosis develops as a secondary disease. The lungs are first affected, and then the bacterium travels through the bloodstream to the kidneys. Then the infection spreads down the urinary tract: to the bladder, urethra.
Diagnosis of tuberculosis of the genitourinary system
When conducting general clinical studies, urine analysis can reveal a large number of leukocytes, an increased content of red blood cells and protein, as well as a high titer of bacteria. After conducting a bacterioscopic examination of the patient’s urine, in most cases, it is possible to detect the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which looks like red rods on a blue background.
Microscopic examination is good because it gives prompt results. Its only disadvantage is that with a small amount of bacteria in the urine, they cannot be seen under a microscope. In such a situation, a bacteriological method is used, during which the patient’s urine is sown on a Stein-Leventhal nutrient medium, where after two weeks colonies of microorganisms are formed. This method gives a 100% result even with a small bacterial count. The downside of the technique is that you have to wait 14 days to confirm the diagnosis.
Since nephrotuberculosis often becomes a complication of the pulmonary form of the disease, patients must undergo an X-ray examination of the chest organs. If the result is positive, the x-ray shows darkened fields, which are direct signs of tuberculosis.
In addition to confirming the diagnosis, the patient needs to determine the anatomical and functional state of the kidneys. This can be done using ultrasound examination of the retroperitoneal organs and excretory urography. The results of these methods completely depend on the stage of the disease. If at the initial stages there may be no changes at all, then in the later stages both structural changes and disturbances in the excretion of urine by one or two kidneys are noted.
Excretory urography for renal tuberculosis
Many parents refuse to have their children undergo an X-ray examination of the chest organs, citing a high dose of ionizing radiation. In such a situation, the child undergoes the classic Mantoux tuberculin test. The test result is considered positive if the papule that appears on the third day after the injection exceeds ten millimeters in diameter. In turn, a test up to 3 mm is considered negative, and in the range from 3 to 10 - doubtful and must be repeated.
There are other methods for diagnosing the tuberculous process of the genitourinary system, such as ascending cystography, radioisotope renography, retrograde pyelography, as well as CT and MRI. But due to their impracticality and high cost, they have not found widespread use in diagnosing tuberculosis of the genitourinary system.
Kidney tuberculosis
Kidney damage often accompanies urogenital tuberculosis. Symptoms of the disease are quite varied and may appear at certain stages of the disease. With such a lesion, tuberculosis bacteria are detected in the urine during a detailed analysis. Often the disease may not be noticed and the diagnosis made incorrectly. This type of kidney damage is often confused with:
- Pyelonephritis.
- Urolithiasis.
- Polycystic disease.
- Cystitis.
Symptoms of the disease may be identical to the listed diseases or not appear at all. In addition, the disease rarely affects the general condition of the patient. So, even with severe kidney damage, the patient’s general health remains normal. How severely the functioning of the organ will be impaired depends not only on the degree of damage to the kidney tissue.
Changes in the organ and its deformation also depend on damage to the ureter. Therefore, damage to the entire genitourinary system and kidneys is so connected. It is best to detect the disease in the initial stages of development and begin treatment aimed at restoring normal urine flow. Your doctor will be able to prescribe special medications for you after a complete examination.
Treatment of nephrotuberculosis
Depending on the clinical course and morphological state of the kidneys, nephrotuberculosis is divided into four stages. For the first two, conservative therapy is used, and for the other two, surgical treatment is used. As a conservative therapy, a classic combination of chemotherapeutic and antibacterial drugs is used: isoniazid, ethambutol, rifampicin and streptomycin. All these drugs are used once a day in the morning under the supervision of medical personnel for 6-9 months. These drugs are purchased under the state program and delivered directly to TB treatment facilities.
Since patients with nephrotuberculosis have been on powerful antibacterial treatment for a long time, they need the use of symptomatic drugs to improve the functional state of the liver and intestines. For this purpose, they are prescribed hepatoprotectors such as Karsil and probiotics such as Latium. Unfortunately, these drugs are not included in the state program for the treatment of tuberculosis, and patients are forced to buy them themselves.
Surgical treatment of tuberculosis of the genitourinary system is radical. For example, in the third or fourth stage of nephrotuberculosis, patients need to remove the entire kidney. True, in tuberculosis surgery there is a rule according to which the scalpel should not spread mycobacteria throughout the wound. That is why the operation is performed during the “cold” period of the disease, after a year-long course of antibacterial therapy.
Dietary features and lifestyle
Tuberculosis patients, as a rule, are asthenic. They need food with high calorie content. True, with nephrotuberculosis, unlike this disease of other localizations, it is necessary to take into account the functional state of the kidney. Therefore, all fried, smoked, sour and salty foods are excluded from the diet. Patients are prohibited from drinking alcoholic beverages, strong coffee and tea.
The diet of such patients should consist of high-calorie boiled meat, white bread, potatoes, various cereals and sweets. Cranberry juice is prescribed as a drink, which has a very good effect on kidney function.
Rehabilitation after illness
Since tuberculosis, regardless of its location, is an incurable disease, patients need lifelong rehabilitation. For this purpose, even year-round sanatoriums have been built along the sea coasts, where special conditions have been created for the treatment and prevention of various forms of tuberculosis infection.
If it is not possible to visit such resorts, patients are recommended to undergo periodic courses of physiotherapeutic treatment. For this purpose, special thermal irradiation of the lumbar region is used to create conditions unfavorable for the life and reproduction of mycobacteria.
As already mentioned, patients with tuberculosis of the genitourinary system undergo long courses of antibacterial and chemotherapy treatment, as a result of which the normal microflora of the gastrointestinal tract suffers. To restore it, you can take the previously mentioned drugs or eat foods containing lactic acid bacteria (kefir, fermented baked milk, sourdough).
Pathogenesis
Genitourinary tuberculosis is an extrapulmonary secondary disease. It spreads by hematogenous dissemination (the pathogen migrates with the blood). Bacteria from the primary focus are dispersed throughout the body through the bloodstream. Typically, the pathological process develops in the lungs or kidneys, then the infection spreads to the ureters and bladder. Tuberculosis develops in both men and women to the same extent.
The infectious agent is mycobacterium, it enters the body with inhaled air, enters the digestive system with food, and is not afraid of the acidic environment of the stomach.
Much less frequently, tuberculosis can be transmitted by contact and through mucous membranes. Infection of the fetus in the womb of a pregnant woman is possible.
The presence of a small number of mycobacteria in tissues is not immediately detected. Outside the cell, they multiply slowly, and the tissues have a normal structure. Over time, with the flow of lymph, the infection enters the lymph nodes and spreads throughout the body.
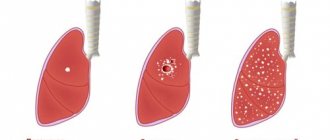
The classification of the disease is based on clinical signs and radiological data. The following forms are distinguished:
- parenchymal damage, multiple lesions in the underlying renal tissue;
- papillitis – tuberculosis of the renal papillae;
- formation of a fibrous capsule – cavernous tuberculosis;
- compression and overgrowth of the neck of the cups - fibrous-cavernous form;
- nephrolysis of the kidney - the proliferation of focal tissue impregnated with calcium salts.
Different forms of tuberculosis of the genitourinary system manifest themselves in different ways.
Complications of tuberculosis of the genitourinary system
For the Sami, a formidable complication of this disease is the development of chronic renal failure, which will soon require constant support with a hemodialysis machine. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to begin treatment measures in a timely manner.
Another complication, which, unlike the first, develops as a result of a positive outcome of treatment, is scarring of the kidney. It simply leads to a decrease in the functional capacity of the organ and an increased load on the second kidney. Also, with this complication, sclerosis of the renal artery may occur, which is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure.
In addition, renal tuberculosis is a good basis for the addition of a secondary infection or the formation of stones in the lumen of the renal pelvis.
Prevention of tuberculosis of the genitourinary system
To protect yourself from the development of the tuberculosis process, you must avoid contact with infectious patients. If it is impossible to get rid of this, for example, due to professional factors, then it is necessary to use personal protective equipment, for example, gauze masks.
The second direction in the prevention of tuberculosis infection is maintaining a normal lifestyle, avoiding smoking and alcohol abuse. Equally important in the prevention of tuberculosis is normal nutrition and satisfactory living conditions.