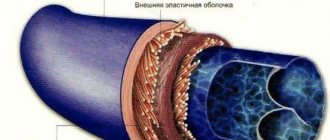
Intestinal atony is a condition in which the intestinal walls lose their tone. As a result, peristalsis weakens, which causes many unpleasant consequences that reduce a person’s quality of life. You will learn about the causes and methods of treatment and symptoms of intestinal atony from this article.
Intestinal atony leads to prolonged constipation
What it is?
Intestinal atony is a violation of the tone of the intestinal walls, as a result of which they cannot contract and relax normally to push feces to the rectum and subsequent exit.
With atony, intestinal motility (the contractility of the muscles of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract) is disrupted, which leads to constipation in humans, difficulty or impossibility of excreting feces.
In summary, atony is not constipation, but a dysfunction of intestinal motility, which leads to stagnation of feces.
Uterine tone and its features
The uterus is a muscular organ, which consists of several layers: the outer mucous membrane (perimetry), the middle muscular layer (myometrium) and the inner mucosa (endometrium). For example, the myometrium takes an active part during the period of childbirth and actively contracts. In its natural state, this muscle is completely relaxed. This condition is commonly referred to in medicine as normal uterine tone.
In practice, during the period before labor, the uterus begins to contract for no reason. Pathological activity becomes increased and can provoke various complications for human health. Western science pays special attention to this disorder. After all, a physiological process can be associated with various symptoms that create a certain discomfort and inform the attending physician about the occurrence of serious disorders. There is common sense in these discussions. Even a person’s tense psychological state can significantly affect the health of the body. Reductions may be short-term. Systematic tone can lead to disruptions in the development of the fetus and further termination of pregnancy. Why exactly is this rhythmic process dangerous?
Complications with uterine hypertonicity can have a variety of consequences for a woman. There are cases when the risk of miscarriage is simply possible (early stages of pregnancy). These circumstances may also arise in the second or third trimester of an interesting situation.
In most situations, contractions of the muscular organ occur in the early stages of fetal development. It is during this period that the process of implantation of the fertilized egg becomes significantly more difficult. There is a risk of embryo rejection and death (spontaneous miscarriage syndrome). If the period exceeds 28 weeks, then we will be talking about premature birth.
Uterine tone has a number of causes. With the development of technology, this list is updated every year. Let's consider the most obvious factors influencing the disorder:
- Generation of progesterone by the body. During pregnancy, the corpus luteum produces a large amount of steroid hormone in the ovary. This structure provokes division of the endometrium. Thus, successful implantation of the embryo occurs. In this case, the contractility of the uterus is significantly reduced. As a result, there is a threat of termination of pregnancy;
- Changes in the structure of the uterus of a chronic nature. This could be fibroids, endometriosis, various inflammatory infectious diseases;
- Significant overstretching of the uterine walls (multiple or large fetuses);
- Intestinal constipation + increased gas formation.
Causes
Atony is a functional state, and if the cause of its occurrence is eliminated, intestinal motility resumes. There is no single cause; it can manifest itself as an independent disease or be a manifestation of other diseases of the body.
There are several main causative factors leading to the development of intestinal atony:
- unhealthy diet - high-calorie foods with low fiber content lead to the development of intestinal atony;
- a sedentary lifestyle - leads to a decrease in the innervation of the muscles of the intestinal walls and a decrease in their peristalsis;
- medications (antispasmodics, morphine-like painkillers) - their long-term use in high doses leads to intestinal atony;
- constant stress - the regulation of intestinal function is carried out by the central nervous system, so excessive load on it can cause a failure in the innervation of the muscles of the intestinal walls (and in other organs too);
- some intestinal infections;
- intestinal dysbiosis - a change in the balance of normal intestinal microflora leads to digestive disorders and the production of toxins that reduce peristalsis;
- helminthiasis - parasitism of worms in the intestines occurs with the release of substances that reduce its peristalsis;
- alcohol abuse – due to the toxic effects of alcohol on the nervous system, its normal functioning is disrupted;
- intestinal tumors - malignant neoplasms in the intestine release toxins that affect the central and autonomic nervous system, disrupting their functioning;
- smoking - nicotine initially increases intestinal motility, but after a while it decreases;
- genetic predisposition - this condition can be inherited from parents to children.
The mechanism for the development of intestinal atony is a decrease in the tone of the muscles of the intestinal walls, a decrease in peristalsis and the movement of food masses. This leads to digestive disorders, the development of putrefactive processes in the intestines, and the production of toxins that aggravate this condition.
Causes of development and provoking factors
The main cause of dyskinesia is stress. Signs appear a couple of weeks after psychological trauma, such as the loss of a loved one.
The disease also develops under chronic stress - in difficult living conditions or obstacles in activities, an unpleasant team, regular quarrels.
Provoking factors:
- the patient's inability to distinguish whether a person is experiencing physical or emotional pain;
- emotional instability manifests itself more often as somatic symptoms;
- inability to have emotional release;
- increased anxiety (even worries, for example, about a child, relatives, property, can be affected);
- predisposition to allergies;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics, anesthetics, anticholinergics;
- lack of movement;
- habit of fatty, high-calorie foods;
- genetic predisposition;
- viral or bacterial intestinal infections;
- diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, endocrine pathologies;
- lack of fiber in the diet.
Symptoms of atony
The main symptom of atony is indigestion, causing regular constipation. If periodic stool retention occurs for more than two days, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Other symptoms of intestinal atony are:
- flatulence - when digestive processes are disrupted, gases begin to be actively released;
- the stool has a dense consistency, the stool is dark in color, it does not contain liquid elements, since all the water is sucked out in the intestines;
- increased fatigue, constant weakness in the body;
- sleep disorders;
- anemia - occurs due to the fact that the body does not absorb iron well;
- general psychological depression;
- Discoloration of the skin.
After three days of constipation, the patient experiences nausea, heaviness in the stomach, and lack of appetite. Body temperature becomes higher, unstable blood pressure appears, and facial color changes.
Consequences and complications
Constant constipation caused by intestinal atony seriously impairs the patient's quality of life. Patients become lethargic and apathetic or, on the contrary, irritable and touchy; the patient’s emotional lability prevents full communication and social life. The patient’s appearance also leaves much to be desired: the complexion deteriorates, skin rashes and bad breath appear, and skin diseases may worsen.
Putrefactive processes caused by coprostasis disrupt the balance of intestinal microflora and suppress the immune system, provoke allergic and atopic conditions, and due to disruption of the absorption process in the intestine, people prone to atonic constipation often experience vitamin deficiencies and iron deficiency anemia. In the absence of adequate treatment, intestinal obstruction may develop against the background of intestinal atony, causing severe intoxication of the body.
Diagnostics
If an intestinal disease is suspected, the patient should visit a proctologist and gastroenterologist. Research and diagnosis is not difficult and is preliminarily established based on the patient’s complaints according to the main symptoms.
During diagnosis, it is important to determine the cause that led to the development of pathologies in order to prescribe effective treatment.
Your doctor may order the following tests:
- bacteriological examination of stool;
- colonoscopy (examination of the intestines with possible removal of tissue for biopsy).
Sometimes an X-ray may be performed to reveal the accumulation of stool, which often leads to the appearance of intestinal adhesive blood clots.
The examination takes into account the patient’s lifestyle, heredity and nutrition.
What symptoms indicate uterine hypertonicity?
In the first trimester of pregnancy (up to 12 weeks inclusive), when the uterus is not yet visible above the womb, the doctor can find out about the presence of hypertonicity by assessing the woman’s complaints. As a rule, the expectant mother complains of nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back of a long or short-term nature, and sometimes cramping, which may be accompanied by bloody discharge from the genital tract of varying intensity. The woman’s condition is aggravated by physical activity and the presence of aggravating factors during pregnancy.
In the second and third trimesters, when the uterus is visible to the naked eye, hypertonicity can be seen and felt by palpation. The uterus shrinks, its contour is clearly defined, the organ hardens under the hands. The woman's complaints remain the same.
How to treat intestinal atony
Let's consider treating intestinal atony using traditional methods - pills and proper nutrition. When a number of pharmaceutical drugs are prescribed, they must be taken in conjunction with a diet.
Drug therapy involves the use of laxatives along with substances that increase the tone of the intestinal muscle tissue along with peristalsis:
- Metoclopramide (tablets and injections). The drug has an antiemetic effect and enhances intestinal motility.
- Pancreatin and its analogs. This is an enzyme preparation that helps improve food digestion.
- Espumisan. A remedy that prevents intestinal bloating by reducing the formation of gases.
- Regulax. Natural herbal preparation based on senna herb. It has a mild laxative effect, helping to remove feces from the intestines.
- Amiridine. The drug improves the transmission of neuromuscular impulses, thereby enhancing the contractile function of the intestine. Use only under medical supervision.
- Prozerin. The drug has a pronounced effect, enhances gastrointestinal motility, facilitates the transmission of nerve impulses and restores neuromuscular conduction. For use only in hospital settings.
An important role in the treatment of intestinal atony is played by following recommendations for proper nutrition and lifestyle.
Forms
Since muscle hypotonia in children is included in the symptom complex of various diseases, the following are distinguished:
- depending on the degree of damage, generalized (diffuse) and local (isolated) hypotension;
- depending on the onset - acute and gradually developing;
- according to the nature of the course - episodic, intermittent (with periods of rise and fall), recurrent and progressive hypotension.
Depending on the reasons that provoke the development of hypotension, there are:
- Congenital hypotension. It develops in the presence of genetic diseases and is part of the overall clinical picture.
- Acquired hypotension. May be associated with neurological diseases (cerebral palsy, obstetric trauma, etc.), exposure to toxins (mercury poisoning), infectious diseases at an early age (previous meningitis, encephalitis, sepsis, etc.), metabolic disorders (observed with rickets, hypervitaminosis of vitamin D, secondary hypothyroidism), autoimmune diseases (observed with myasthenia gravis and post-vaccination complications).
According to the level of origin, muscle hypotension is divided into hypotension:
- Central level (divided into cerebral and spinal levels).
- Peripheral level (motor units are affected). Occurs in diseases of the peripheral neuron (neuronal and neural level), diseases of neuromuscular transmission (synaptic level), congenital structural myopathies, myotonia, myodystrophy and myoplegia, metabolic and inflammatory myopathies (muscular level).
Treatment of atony with folk remedies
At home, the simplest and most accessible means of normalizing digestion and eliminating constipation is to take vegetable oil, 1 tablespoon three times a day. Beet salad seasoned with vegetable oil perfectly cleanses the intestines. It is better to eat it at lunchtime and in the evening. Dried apricots and prunes help well; they are soaked in hot water overnight and then eaten during the day.
In addition, treatment with medicinal herbs is popular:
- A decoction of string is also effective. Two large spoons of the plant are poured with half a liter of water, the container is placed on the stove and wait until the product boils. After this, remove the container from the heat, cover with a lid, and leave for 30 minutes. The liquid is filtered, drunk in the morning and evening, 200 ml for each dose.
- Treatment with honey and aloe. Take the fleshy leaves of aloe, peel them from the skin and thorns and grind them thoroughly. One and a half glasses of honey are heated in a saucepan, and care must be taken that the honey is not heated above 40°C, otherwise its medicinal properties will disappear. Add crushed plant leaves to the heated mass and mix everything thoroughly. The resulting product is left to infuse for 24 hours. Before use, you will need to slightly warm the mixture of honey and aloe. Take one tablespoon one hour before breakfast. At the end of the course, a seven-day break is taken and the treatment is repeated.
- Roast pumpkin and beans: cut a quarter of the pumpkin into cubes, chop the onion, mix with the pumpkin and simmer in a frying pan in vegetable oil. When the pumpkin becomes soft, add the boiled beans and simmer for another 5 minutes.
- Tea with oregano. For intestinal atony, tea with the addition of oregano herb is effective. To prepare it, pour one tablespoon of oregano leaves into a glass of boiling water and leave for 15 minutes. It is recommended to drink a cup of this tea in the morning before meals and in the evening; it will not only have a strengthening effect on the intestinal muscles, but will also improve its functioning, relieve spasms and calm the nerves.
- A tincture based on calamus and rhubarb will help with chronic constipation and atony. It is necessary to chop the rhubarb root, add crushed calamus leaves and ground gentian to it. All components are mixed in equal parts. The resulting mixture must be filled with 70% alcohol in a ratio of 1:10. The product is infused for 14 days in the dark, filtered, and taken in the morning and evening before meals. A single serving is one small spoon.
- Buckthorn infusion. To prepare it, two tablespoons of buckthorn bark are poured into 200 ml. boiling water and place in a thermos for two hours. The finished infusion is filtered and drunk 1/3 glass twice a day.
All these recipes are quite effective, but before using them you should definitely consult with your doctor and use folk remedies under his supervision.
General information
Intestinal atony is a functional condition characterized by a sharp decrease in the tone of the smooth muscles of the intestinal wall and a disruption in the process of emptying it. Normally, contractions of the intestinal muscles (peristalsis) ensure the movement of food mass to its final sections. Within a minute, each section of the colon makes about fifteen peristaltic movements. If the tone is impaired, peristalsis is weakened, in severe cases it is absent.
The pathology is accompanied by prolongation of the intervals between acts of defecation and the appearance of difficulties during bowel movements. Constipation is an extremely common complaint, but in most cases, patients do not consult a gastroenterologist for a long time and take laxatives and traditional medicine on their own. However, the symptoms persist because the cause of the condition is not identified and eliminated, and improper treatment only aggravates the tone disorder. Intestinal atony can be a symptom of other diseases, so the appearance of constipation requires a visit to a doctor for adequate diagnosis and treatment.
Diet and nutrition
The absence of the following products in the diet also helps to normalize intestinal function and motility:
- Peas, beans;
- Rice;
- Mushrooms;
- Garlic;
- Canned food;
- Salty fish;
- Rich broths;
- Chocolate, coffee;
- Pomegranates, quince;
- Smoked meats;
- Blueberries, pears.
When making this diagnosis, the patient must include in his menu products that facilitate the passage of feces through the colon:
- Vegetable juices, fruit compotes, jelly;
- Cauliflower, zucchini, tomatoes, carrots;
- Barley, millet and buckwheat cereals;
- Pasta;
- Sea kale, greens;
- Baked apples;
- Curdled milk, yoghurts, sour cream, kefir;
- Stale bread, dry biscuits;
- Vegetable soups, borscht, cabbage soup;
- Lean meat, poultry, veal;
- Prunes, dried apricots;
- Lingonberries, oranges, peaches;
- Pumpkin;
- Rhubarb.
It is advisable to eat small portions - 5 times a day, at the same time, combine proper nutrition with walks and exercises. It is advisable to eat food not dry, cook or bake food, and not smoke or fry. By adhering to this treatment, you can improve gastrointestinal motility.
Proper drinking regime is also of great importance. Every day you need to drink about one and a half or two liters of water, which will improve bowel movements. In the morning on an empty stomach you should drink 200 ml of non-carbonated mineral water to enhance peristalsis.
Main types of constipation
The occurrence of atonic constipation occurs as a result, in fact, of intestinal atony. Meanwhile, there are other types of constipation, a concomitant factor for which is intestinal atony. For example, the most common is nutritional constipation, which occurs as a result of a poor-quality approach to nutrition. In addition, constipation is classified as psychogenic, toxic, endocrine and neurogenic. They do not exclude such a variety as constipation, which occurs due to weakening of the muscles and anorectal area.
Constipation also occurs due to the presence of an influencing factor in the form of a mechanical obstacle, due to which the movement of its contents through the intestines is significantly hampered. This kind of interference includes tumors or polyps, as well as adhesions and some other anomalies that form during the development of the large intestine.
Physical exercise
Physical activity that strengthens the abdominal muscles is of great importance. Even half an hour a day has a significant effect. A certain set of exercises is recommended to help improve peristalsis in intestinal atony:
- Lying on your back, raise your legs and perform circular movements, as when riding a bicycle. Exercise helps strengthen the abdominal muscles, normalize and accelerate blood flow in the abdominal cavity.
- Lying on your back, grab your legs bent at the knees and press them to your stomach. Stay for 2-3 seconds in this position and return to the starting position
- In a kneeling position, alternately stretch your legs back. Exercise promotes the outflow of blood from the pelvic organs.
- Lying on your back, legs together, lift and throw behind your head, return to the starting position.
- Standing on your knees and resting your elbows and palms on the floor, squat alternately on your right and left buttocks. Exercise enhances intestinal motility and promotes the passage of gases.
Each exercise should be repeated 10 times.
Causes of increased uterine tone during pregnancy
Briefly and painlessly, the uterus can respond to external stimuli by increasing its tone. Such irritating factors can be: sexual intercourse, laughter, sudden movement of the mother, movement of the fetus itself, vaginal examination, coughing and others. This tone should not bother a woman.
The reasons for this dangerous symptom:
- Hormonal, primarily ovarian and placental insufficiency. Lack of progesterone is the most common cause of hypertension. Excess prolactin (hyperprolactinemia) can also contribute to abnormal uterine tone.
- Gynecological diseases: infantilism - congenital underdevelopment of the genital organs, in which the small uterus is overstretched by the growing fetus, which provokes hypertonicity;
- endometriosis, the foci of which can contribute to the development of uneven tone;
- uterine fibroids localized in the myometrium also provoke uneven tone, which jeopardizes the development of pregnancy.
Proper treatment of large intestinal dyskinesia
In gastroenterology, the term intestinal dyskinesia defines a symptomatic complex of disorders of the digestive organ that occurs as a result of a violation of its motor and functional activity.
Most often, intestinal dysfunction occurs in the colon, representing the so-called irritable bowel syndrome with a predominance of functional constipation.
According to statistics from the World Health Organization, colon dyskinesia is diagnosed in every third inhabitant of the planet, with a predominance of frequency in women of childbearing age.
Large intestine in humans
Types and causes of intestinal dyskinesia
Dysfunction of the colon (according to ICD10 - K59.8.1) is divided into several classification characteristics:
- Hypomotor dyskinesia of the large intestine is a functional disorder of the muscle layer, leading to constant relaxation and contraction, resulting in difficulties in the movement and evacuation of feces.
- Spastic dyskinesia of the large intestine is caused by constant tension of the organ of the digestive system, leading to disruption of its peristalsis.
- The hypertensive form of large intestinal dyskinesia is characterized by increased hypertonicity, leading to the development and progression of persistent constipation and painful sensations (colic).
- Hypotonic or atonic dyskinesia of the colon is a sharp weakening and disruption of wave-like contractions in the intestinal walls, accompanied by constipation, dull bursting pain in the abdomen and a feeling of heaviness.
In gastroenterology, primary and secondary forms of intestinal dyskinesia are determined. The probable cause of primary colon dyskinesia, according to medical experts, is considered to be a psychogenic factor - intrapersonal conflict, negative emotions, mental or nervous diseases.
Among other probable cause-and-effect factors in the formation of symptomatic disorders of the intestinal system, excessive consumption of low-fiber foods is considered, that is, those food components that are not digested by the digestive enzymes of the human body, but are processed by the intestinal microflora.
In addition, the causes of intestinal dyskinesia may be due to the occurrence of an acute infection in the colon.
Along with the primary disorder of the large intestine, a cause-and-effect relationship can be provided by secondary factors in the occurrence of dyskinesia:
- chronic gastritis;
- cholecystitis;
- peptic ulcer;
- diabetes;
- disorders of the pancreas and/or endocrine system.
Slow transit of intestinal contents through the large intestine may be due to myopathy and neuropathy of various origins.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xIOXj0hJhyQ
Colon function
Symptoms of intestinal disorder
Intestinal dyskinesia provides the patient with various discomfort sensations, including pain symptoms, which vary in intensity. Acute, dull, aching or cutting pain in the abdomen can bother a person from several minutes to several hours until he receives qualified medical care.
The localization of pain with dyskinesia of the colon affects almost the entire abdominal cavity, and the painful sensations do not subside until gas is released or a complete bowel movement occurs. The pain intensity subsides for a while during sleep and resumes after waking up.
All these factors of impaired intestinal motility cause emotional overload and stressful situations in a person.
Also, the emerging spastic colitis or irritable bowel syndrome with dyskinesia, leading to stagnation of feces, can provoke an allergic reaction or general intoxication of the body.
Regardless of the type of food consumed, the main symptoms are rumbling and bloating with dyskinesia of the large intestine, as well as bowel dysfunction.
General symptomatic characteristic signs, regardless of the degree of neglect and type of intestinal disorder, are as follows:
- constipation;
- nausea and frequent persistent vomiting;
- unmotivated increase in body temperature;
- weight loss or gain, regardless of a person’s appetite;
- increased gas formation and flatulence;
- changes in the general blood test, for example, an increase in ESR, leukocytosis;
- pain in the abdominal cavity without local localization, which goes away after defecation;
- dizziness and general weakness of the body.
Differential diagnosis
Patients with dyskinesia of the large intestine present complaints with strictly specific syndromes of digestive system disorders. However, it is necessary to clearly differentiate symptomatic signs from other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract that occur with similar clinical indicators:
- nonspecific ulcerative or post-infectious colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- intestinal polyposis;
- colon cancer or tuberculosis;
- diverticulitis and so on.
The required scope of laboratory instrumental diagnostics includes:
- blood chemistry;
- scatology;
- analysis of stool for worm eggs and dysbacteriosis;
- bacteriological examination of stool;
- lactose tolerance testing.
In addition, the attending physician will conduct an ultrasound scan of the abdominal cavity and a study of the speed of colonic transit, a colonoscopy with a biopsy of the mucous contents of the colon, and a survey X-ray examination - irrigography, when the intestinal tube of the digestive system is examined.
If necessary, other medical specialists are involved in the diagnostic examination - gynecologist, psychiatrist, neurologist, endocrinologist, and so on.
Treatment and diet for intestinal dyskinesia
The widespread prevalence of the disease leads to the fact that most patients, following generally known information, self-medicate, increasing plant dietary fiber and the amount of fluid in their diet. Such treatment and preventive measures do not cause harm and are welcomed by official medicine.
However, in most cases, trying to get a quick result, patients with severe intestinal dyskinesia use laxatives or daily cleansing enemas, while ignoring visits to a medical facility.
Laxatives are quickly addictive
A critical disadvantage of pharmaceutical laxatives is the rapid addiction to them, as well as a gradual increase in the dose of the drug, which ensures degeneration of the receptor functions of the colon.
You should know that frequent use and increased dosage of a laxative cause osmotic pressure in the intestinal lumen and bloating, and the systematic use of cleansing enemas results in a loss of visceral sensitivity and defecation reflex in the colon.
The treatment program for symptomatic colon disorder includes basic therapy based on dietary recommendations and medication. For large intestinal dyskinesia, the patient is prescribed a special diet that excludes the consumption of foods that cause excessive gas formation:
- caffeine;
- lactose;
- vinegar;
- black and red pepper;
- pickled and smoked products.
Red pepper contributes to excessive gas formation
The predominant products in the diet remain vegetables and fruits with an increased fiber content, which contribute to the softening of feces and their high-quality transit through the intestinal tract. Sufficient amounts of fiber can be obtained from the following foods:
- carrot;
- white and cauliflower;
- beet;
- pumpkin;
- corn;
- avocado;
- flax seeds;
- banana;
- apple;
- pear;
- dried apricots;
- raisins, etc.
However, given the fact that the main clinical syndrome is abdominal pain, the primary task of medical workers is to eliminate pain through the use of pharmacological drugs. All efforts of the gastroenterologist should be aimed at reducing visceral sensitivity and normalizing intestinal motor functions.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5ZhgxIsAiUI
Among the most effective means of drug treatment are the following drugs:
- Cerucal® is a prescription drug in the form of a solution for intramuscular and intravenous administration from the German manufacturer AWD.pharma GmbH & Co.KG. The drug helps to increase the tone of the intestines and stomach, accelerates emptying, stimulates peristalsis and reduces hyperacid stasis. Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the active substance - metoclopramide, first trimester of pregnancy, children under 5 years old. Cerucal increases intestinal tone and improves its peristalsis
- Bellastesin® from the Russian manufacturer JSC Tatkhimfarmapreparaty is a prescription drug with the main active ingredients belladonna and benzocaine. The dosage form has a combined effect, providing antispasmodic and local anesthetic activity, and ensures the tone of smooth muscle cells of the intestinal tract. Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the active ingredients, chronic diseases of the genitourinary system, children under 12 years of age.
The course of treatment and dosage of these pharmaceutical combinations is determined by the attending physician.
Traditional medicine for intestinal dyskinesia
Along with official drug treatment, you can use proven methods of traditional medicine:
- Freshly squeezed potato or cabbage juice will improve the motility of the gastrointestinal tract and ensure high-quality transit of feces from the large intestine.
- Green tea with honey will have a relaxing effect.
- Watermelon rinds will help improve intestinal motility. Watermelon rinds help soften stool.
- Cleansing enemas with the addition of chamomile will help get rid of constipation.
Any actions to use folk remedies for the treatment of intestinal dyskinesia should be agreed with the treating medical consultant.
Forecast and prevention of intestinal disorders
In general, the prognosis for symptomatic intestinal disorder is favorable, provided clinical recommendations are followed.
The course of the disease will not develop complications in the form of intestinal obstruction, formation of fistulas, perforations or strictures if all the prescriptions of the attending physician are carried out by the patient in good faith.
Among the preventative measures, the following must be observed:
- Monitor your own weight and nutrition.
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Avoid nervous and mental stress.
- Comply with the sanitary and hygienic rules of the hostel.
- See a doctor promptly.
When performing intestinal prophylaxis, do not forget to teach children to do this.
Source: https://gastrogid.ru/pravilnoe-lechenie-diskinezii-tolstogo-kishechnika/
Prevention measures that improve peristalsis
Proper and balanced nutrition in combination with an active lifestyle will be an excellent prevention of the development of atony.
Walk in the fresh air more often, devote 30 minutes a day to physical exercise, light gymnastics, drink more water - this will be the key to health, smooth bowel function, and the need for taking medications will fade into the background.
Lack of fluid in the diet is one of the main causes of constipation. To get rid of it in 3 days, you need to drink a simple remedy every day.
Timely seeking medical help will avoid serious consequences in the gastrointestinal tract and the transition of intestinal atony to the chronic stage. Give up bad habits: alcohol and smoking are not the best “friends” for the peristalsis of the hollow organs of the digestive tract, as well as for all body processes.
Practicing gastroenterologist. Work experience – 9 years in a private clinic. If you haven't found the answer to your question, ask the author!
Treatment of the disease
Treatment involves more than just drug therapy. It is necessary to reconsider your diet, lifestyle, use of special exercises, and traditional medicine. During treatment, the patient is prescribed a number of laxatives, cleansing enemas, and drugs that increase peristalsis.
Important! Recommended remedies for the treatment of this dysfunction are freely available in pharmacies. But it is better to use them only as prescribed by a doctor!
Each medicine has a different composition. And only the attending physician can predict how the body will react to taking it. In pharmacology, there are several groups of drugs with laxative or sedative effects. This:
The first group of drugs is the most popular. They contain antiglycosides that help thin stool and irritate mucosal receptors. Usually these are medicines based on the following natural ingredients:
- senna leaves;
- rhubarb root;
- vegetable oils;
- glycerol.
Osmotic agents contain the prebiotic lactulose, which can stimulate motility. Natural ones include bran and seaweed.
It is important not to forget that you should completely change your diet, lifestyle, carry out preventive measures, and simple gymnastic exercises.
How to help your child with constipation
Unfortunately, this pathology does not spare even infants. This causes suffering to the baby and torment to his mother. The main reason lies not so much in the structural features of this organ, but in the mother’s diet. Everything she ate will be reflected in the child’s intestinal activity.
Many mothers, taking the advice of their grandmothers, insert pieces of soap into the baby’s anus. This is not only dangerous, but also causes discomfort for the child himself. In this case, it is best to use lactulose syrup, which is easy to find in any pharmacy. Lactulose itself in the form of a white powder can be kept in reserve at home.
Important! If signs of constipation appear in children, you should inform your pediatrician.
The syrup is not only harmless, it is also beneficial. After consuming it, the microflora in the intestines improves dramatically. But this does not mean that you should not consult with doctors.
Traditional medicine tips
Traditional medicine has a lot of recipes that can be used without fear at the first signs of atony. The advantage of this treatment is that it is not addictive and acts more gently on the intestinal walls.
- Flax seeds can be used in their pure form or ground in a coffee grinder. Consume in this form, simply with water.
- Rowan syrup, the preparation of which is not difficult. Red rowan berries must be washed, placed in a jar and covered with sugar. Place in a sunny place and leave for 4 weeks. Then squeeze, strain, pour into a container and take as needed.
- Wheat bran acts like lactulose. You can eat them in their pure form, simply with water.
- Mustard seeds have a positive effect. It is enough to eat 10 grains, and the effect is guaranteed in a couple of hours.
- Sauerkraut and fresh cabbage salads should be included in the diet as often as possible.
- Fresh juices from potatoes and beets are useful.
Traditional medicine also recommends using buckthorn infusion and decoctions of the following herbs:
These herbs are best used in collections. Often the cause of the disease is stress, so it is necessary to include sedative components in the preparations. They are all mixed, a certain amount is taken and steamed in a liter thermos, after which it is consumed throughout the day. The next day, a fresh decoction is prepared.
Elderberry leaves and aloe leaves will help improve digestion, improve intestinal function and eliminate constipation. Fruit infusions, olive oil, jelly, including oatmeal, will also help improve intestinal function.
Don't forget about such a helper as pumpkin. It is stewed, porridge is cooked from it, juices are squeezed out, baked and safely eaten.