A lipidogram is an analysis of the lipid spectrum, an extended blood test through which it is possible to track changes in the metabolic plan, disorders in the synthesis of certain fatty compounds; in addition to cholesterol, this includes another group of substances that have no less potential to provoke diseases.
Any deviations from the norm must be assessed professionally, but doctors avoid overdiagnosis. Changes in indicators do not always indicate a pathological process. Not everything is so simple. Therefore, the patient is examined repeatedly, or even several times, over time.
Treatment is carried out under the supervision of an endocrinology specialist, as needed. If there are reasons to start therapy. The issue is resolved on an individual basis, after a thorough assessment of all factors.
What the analysis shows
The lipid profile is examined to detect pathological processes in metabolism; based on the results of the analysis, the following deviations from the norm can be found:
- Atherosclerosis. Classic diagnosis in the context of fat detection. Almost always, high cholesterol and other similar compounds indicate the development of this condition. Even if the diagnosis was not previously confirmed. In any case, it is necessary to re-examine the patient.
The essence of the change is the deposition of cholesterol and other substances on the walls of the arteries.
These plaques interfere with blood flow, do not allow tissues to be properly nourished and provided with oxygen, and as the pathological process progresses, trophism decreases to a critical level, which can be fatal.
- Heart disorders. Among them, ischemic disease, a recent heart attack or precursors of one, angina pectoris, and a host of other options. The need to assess lipid concentrations is dictated by the high probability of provoking these conditions by metabolic disorders.
- History of stroke. Often, ischemic damage is caused by atherosclerosis. Blockage of the artery leads to problems with nutrition, and then to the complete impossibility of trophism in the local area.
- Diseases of the endocrine system. Diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders and other problems. This also includes excess weight. Excess body weight is almost always associated with high lipid concentrations.
- Disorders of the digestive tract.
Of course, jumps and smooth changes in the level of fatty compounds cannot unambiguously indicate one or another disease mentioned above. The sign is too general and nonspecific. However, assessment of the level can be a starting point for identifying the disorder.
Other diagnostic methods are also used to more clearly assess the condition; the question remains at the discretion of the specialist.
What deviations from the norm may there be?
A cholesterol test is often prescribed in the presence of pathologies of the heart muscle and blood vessels. While taking beta-blockers, the amount of total cholesterol may increase. Hormonal drugs, diuretics and tranquilizers can also further increase this indicator.
Total cholesterol may be below normal in those taking lipid-lowering drugs. Women who take contraceptives or hormonal drugs with antiandrogenic properties may also experience a decrease in cholesterol levels.
Sex hormonal drugs and corticosteroid medications affect not only the level of total cholesterol, but also HDL and LDL. For this reason, all three indicators will be higher than the normal value in the lipid profile table.
To know what a cholesterol test shows, you need to understand what ratios of indicators affect the development of a particular disease. The detailed analysis includes complexes of indicators, so the decoding should be done by the attending physician. While total cholesterol may be normal, other indicators may differ.
Total cholesterol
Normal lipid metabolism in the body may be disrupted, so total cholesterol will change. If total cholesterol is higher than normal, then there is a high probability of developing:
- pancreatitis,
- diabetes mellitus,
- obesity,
- alcoholism (if the patient abuses alcohol),
- ischemic kidney disease,
- liver cirrhosis,
- hepatitis A,
- renal failure,
- hypothyroidism.
In women, total cholesterol may rise during pregnancy.
If the indicator is below normal, then this picture can be observed when:
- severe physical exhaustion,
- sudden weight loss,
- prolonged fasting,
- anemia,
- hyperthyroidism,
- lung diseases,
- in a feverish state.
LDL
In the lipid profile table, LDL may be elevated for the following reasons:
- in the presence of Cushing's syndrome,
- excessive consumption of cholesterol foods, high in fat,
- development of hypothyroidism,
- diseases of the urinary system and liver,
- anorexia.
If the results are below normal, then there is a high probability of developing:
- lung diseases,
- hyperthyroidism,
- anemia,
- Tangier or Reye syndrome.
HDL
If the HDL level is not normal and it is below normal, then the doctor may assume that the patient has:
- atherosclerosis,
- the course of infectious inflammation in the acute phase,
- coronary heart disease,
- myocardial infarction,
- tuberculosis,
- stomach ulcers,
- urinary diseases.
If LPV units are higher than normal values, then the patient may become a victim of neoplasms in the intestines and the development of liver cirrhosis. Also, this indicator can increase if a person constantly loads himself with hard physical work.
Triglycerides
Triglycerides must be included in the decoding of the results, since their excess of the norm may indicate:
- development of atherosclerosis,
- IHD,
- heart attack,
- hepatitis A,
- high blood pressure.
If triglycerides, on the contrary, are below acceptable levels, then this may indicate a poor diet, poor nutrition, the development of hyperthyroidism, and chronic lung diseases.
In what cases is examination indicated?
A blood lipidogram is a test designed to evaluate the concentration of fatty substances in fluid connective tissue.
There are several reasons for holding the event:
- Excess body weight. Weight gain is almost always associated with a change in fat concentration. It’s hard to say where the cause is and where the effect is. In any case, you can’t do without this technique.
- Age 45+. Over the years, the likelihood of developing one or more types of hyperlipidemia increases significantly. It is necessary to conduct a thorough assessment of the blood lipid spectrum in order to detect the problem at an early stage.
Caution:
Older people are at greater risk of complications, so treatment is required even if fat levels are slightly elevated.
- Preventive assessment of the patient's health status (screening).
- Burdened heredity. If there was one or several people in the family with pathologies caused by a violation of the concentration of lipid compounds. This is an increased risk factor for hypercholesterolemia.
- Deviations from the heart, central nervous system, digestive tract, endocrine structures. Those conditions that could potentially be associated with changes in the synthesis of fatty compounds.
The question is complex; additional examination methods will be required. If a primary factor is detected, its urgent correction is required.
- Therapy control. During treatment, it is necessary to focus on the level of cholesterol and other compounds in order not to miss the ineffectiveness or excessive results from the use of drugs. The challenge is to respond urgently and quickly to changing conditions.
- Having bad habits. Smoking, drinking alcohol. These factors increase the risk of developing cholesterol plaques. Giving up harmful addictions requires a re-evaluation of fat concentration, since even lifestyle correction does not always immediately result in the restoration of metabolism. Medical attention may be required.
- Physical inactivity. Insufficient physical activity. Risk factor for the development of pathologies based on metabolic changes and disorders. It is necessary to carry out the procedure after eliminating this provoking moment.
The list is approximate. The physician may order lipid testing at his own discretion when appropriate.
Preparing for research: on the way to reliable results
Assessment of the lipid spectrum is necessary to determine the state of fat metabolism in the body. To compile data, experts determine the following indicators:
- total cholesterol;
- triglycerides;
- high-density lipoproteins;
- very low density lipoproteins;
- low-density lipoproteins;
- atherogenic coefficient.
Blood lipid analysis helps prevent the risk of developing acute heart pathologies, heart attack, stroke, and other serious diseases.
As a rule, elevated cholesterol is detected in the examined patients. First of all, this disorder is due to age-related changes. In addition, elevated cholesterol levels are diagnosed in patients with the following conditions:
- alcoholism;
- gout, other diseases in which mineral metabolism is disrupted;
- obesity and diabetes;
- heart diseases;
- kidney diseases, liver and thyroid diseases;
- genetic predisposition;
- during pregnancy (in women);
- when taking certain medications.
A decrease in cholesterol levels also indicates the presence of problems in the patient’s body:
- liver or kidney pathologies;
- disturbances in the absorption of food;
- fasting;
- infectious diseases.
In addition, cholesterol levels may decrease when taking certain medications.
Cholesterol levels can be corrected by eating a diet high in animal fats.
With low levels of high-density lipoproteins, patients have a significantly increased risk of developing coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction. Men are more often susceptible to these diseases, especially those who suffer from the following pathologies:
- diabetes mellitus and obesity;
- liver diseases;
- atherosclerosis and cardiovascular pathologies;
- alcoholism and tobacco addiction.
- On the eve of the study. It is necessary to give up fatty foods, alcohol and smoking, avoid physical activity, and eliminate stress. If you had to drink alcohol, it is better to immediately reschedule the examination to another day.
- 12 hours before the examination. You can't eat. You are allowed to drink only clean water.
- In the morning before the analysis. It is advisable to completely relax and calm down. It is imperative to warn medical professionals about the medications you take regularly, as they can greatly affect the results.
What indicators are included in the blood lipid spectrum?
The lipid profile includes: total cholesterol, triglycerides and lipoproteins of varying densities. This results in only six indicators that are examined during the diagnostic process:
Total cholesterol
Total cholesterol (TC) or cholesterol (CH) is the most important indicator in the entire analysis. With an increase, there is almost guaranteed to be a deviation in the volume of other substances, however, not always. Decryption required. A special formula for calculating this is used, this is an integral indicator.
Low density lipoproteins
Also called bad cholesterol, abbreviated LDL or LDL. There is some confusion in terms.
These connections are small in size and easily attach to the walls of blood vessels and large arteries. Therefore, they are considered one of the most atherogenic, capable of provoking the formation of plaques.
This indicator should be adjusted as quickly as possible, because there is a real danger of developing atherosclerosis.
High density lipoproteins
Good HDL cholesterol. Due to the significant size of individual particles of the substance, they are not only unable to settle on the walls of blood vessels, but also mechanically cleanse the arteries of layers of bad fatty compounds.
Most foods contain both forms of cholesterol. There is no need to fight this type of substance, even if it increases.
Triglycerides
Found in the bloodstream in minimal quantities. The lipid profile includes TG indicators since changes in these are always indicative and indicate endocrine diseases.
These substances need to be dealt with, since under the influence of third-party reactions, triglycerides are quickly converted into low-density lipoproteins. The consequences are clear.
Atherogenic index
AI is used as a generalized coefficient that takes into account all the above compounds for calculation. The value of the coefficient (AK) is normally 2.2-3.5. If the number is increased, we can talk about a varying degree of risk of developing or worsening atherosclerosis.
The use of the atherogenicity index is a mandatory item in laboratory assessment.
Very low density lipoproteins
VLDL is not always studied, as many doctors believe, there is no practical point in this. Therefore, such diagnostics are rarely carried out, depending on the laboratory. In some cases, including a layer in the protocol is mandatory. A question about a specific situation.
The lipid profile includes a spectrum of compounds: LDL, VLDL, HDL, TG, CA and TC. Low-density lipoproteins and triglycerides can provoke disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous and cardiovascular systems.
What it is?
A blood test such as a lipid profile is the taking of a person’s biological fluid from his venous circulatory system and its further study in the laboratory using a certain method. This is done by deposition and photometry, which are somewhat labor intensive and provide an accurate result.
A lipidogram allows you to determine the following indicators of human blood:
- The level of total cholesterol in the body.
- The amount of high-density lipid proteins, which are also called HDL or alpha-cholesterol.
- The amount of low-density lipoproteins, also called LDL or beta-cholesterol.
- The amount of triglycerides, abbreviated as TG.
The attention of specialists is most often drawn to low-density lipoproteins. This is due to the fact that it is their high number that determines the patient’s risk of developing such a rather dangerous disease as vascular atherosclerosis. This is why doctors call an elevated LDL fraction atherogenic. At the same time, substances such as high-density lipoproteins indicate a decrease in the possibility of the formation of an unfavorable disease. Because of this, HDL is designated in the medical literature as antiatherogenic.
Triglycerides are only an intermediate transport form of cholesterol. Therefore, their high levels in a person’s blood may also suggest that the patient is at high risk of developing atherosclerosis.
Every substance in the human body should be within normal limits. This applies to both cholesterol and various lipids. Their standard values are provided in the following list:
- Normal total blood cholesterol, for both men and women, should range from 3.1 to 5.2 mmol/l.
- Low-density lipoprotein levels should normally be below 3.9 mmol/L.
- The normal level of high-density lipoproteins in women should be higher than 1.42 mmol/l.
- The normal level of high-density lipoproteins in men should be higher than 1.68 mmol/l.
- The amount of triglycerides in a healthy person ranges from 0.14 to 1.82 mmol/l.
- The atherogenic coefficient should not exceed 3 units. It is calculated using a formula that takes the difference between total cholesterol and HDL cholesterol, and then divides the result by the LDL level.
Determination of a lipid profile is necessary for diagnosing certain diseases, mainly associated with the human cardiovascular system, as well as for monitoring the treatment of diseases.
Preparing for the test
Preparatory measures for obtaining accurate results do not differ from those when conducting a biochemical blood test.
If we talk about specific recommendations:
- You should not consume food rich in animal fats within 24 hours. This can artificially increase the levels of lipid compounds, the result will be false. It’s clear what this entails.
- You shouldn’t physically overwork yourself during the day. Inadequate mechanical activity is almost guaranteed to affect the concentration of fats, and this in turn will lead to incorrect interpretation of the results of the lipid profile.
- Alcoholic drinks should not be consumed the same day before the test.
- Within 8 hours, food is completely abandoned. You can drink water.
- Blood donation occurs on an empty stomach. This is a mandatory condition so that the body does not begin biochemical processes that distort the final picture.
- You can't smoke for about an hour. Emotionally overloaded. Both of these affect the concentration of the substances in question.
If the doctor has suspicions about the results, the test may be ordered again. The question remains at the discretion of the treating specialist.
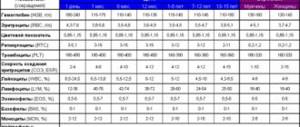
Standard tables
Mainly, the degree of deviation is studied by total cholesterol, other indicators are assessed within the framework of an expanded interpretation.
In men
| Age (years) | Level in mmol per liter of blood |
| 14-25 | 2.7-5.5 |
| 26-35 | 2.7-5.6 |
| 36-45 | 2.7-5.9 |
| 46-55 | 2.9-6.2 |
| 56-60 | 2.9-6.4 |
| After 60 | 3.5-7.1 |
Among women
| Age (years) | Cholesterol level (mmol/l) |
| 14-25 | 2.5-5.3 |
| 26-35 | 2.6-5.5 |
| 36-45 | 2.6-6 |
| 46-60 | 3.1-6.2 |
| 60 and older | 3.3-6.8 |
In children
| Age | Normal value (mmol/l) |
| Up to 1 month | 1.2-4.3 |
| Up to 1 year | 1.5-4.7 |
| 1-6 years | 2.5-4.9 |
| 6-18 years | 2.8-6 |
During pregnancy
During gestation, cholesterol levels increase 1.5-2 times depending on the age norm (see above). This is not considered an anomaly.
The numbers given are approximate. Deviations in one direction or another are possible depending on health status and many other factors.
The question of interpretation is decided by the treating specialist.
Attention:
When assessing, it is also necessary to take into account the reference values (normal range) accepted in a particular laboratory. Some discrepancies are possible, everything is determined by the methodology for calculating indicators.
Lipid spectrum: detailed transcript
It is recommended to trust your doctor to interpret the lipid profile. Indeed, in order to answer the question why this or that indicator is lowered/increased, it is necessary to take into account the patient’s medical history data, as well as the results of other tests. This is impossible without practical experience and specific clinical knowledge. It is important to understand that different laboratories use different methods to determine the same indicators. Therefore, their standards may differ.
Normal indicators
Most lipid profile indicators depend on gender and age. VLDL and atherogenic coefficient are insensitive to gender differences. The CA norm is:
- 2.0-2.8 – for young people (under 30 years old);
- 3.0-3.5 – for patients over 30 years old.
The ratio of total cholesterol to HDL should not exceed 1-3.5.
With age, the level of total cholesterol, LDL, triglycerides, and HDL increases. It is higher in men than in women. This is due to the low content of female sex hormones in their bodies, which inhibit the growth of cholesterol. When determining VLDL concentration, age and gender are not taken into account. The normal level is considered to be in the range of 0.26-1.04 mmol/l.
Table 1. Lipidogram of a healthy person.
Reasons for the increase
An increase in lipid concentration occurs in several cases. If we talk about the most common points that provoke an increase in cholesterol in the blood:
- Excess body weight. Significant weight does not always provoke changes in the lipid profile, but this is the most likely scenario.
- Hereditary forms of pathological processes. Usually these are not accompanied by any symptoms.
- Disorders of the coronary arteries. Up to a heart attack or at least transient myocardial ischemia.
- Diabetes. A classic pathology, which is characterized by disorders of lipid metabolism: concentration, synthesis, deposition and excretion of fatty compounds.
Accompanied by a lot of changes, not only an increase in cholesterol and other lipids. If a deviation is detected, urgent medical attention is required to avoid dangerous complications.
- Pancreatitis. Inflammatory process of the pancreas. Usually does not have an infectious origin.
- Hepatitis. Liver damage. Occurs against the background of viral invasion. We are talking about a whole group of strains that can provoke a disorder.
In some cases, a toxic form occurs. Including abuse of alcohol and drugs. Since fatty compounds are processed precisely in this organ, one should not be surprised at the critical increase in indicators.
- Cirrhosis of the liver. Acute tissue necrosis, cell death.
- Disorders of the urinary tract.
- Hormonal imbalances.
We are not talking about changes as a result of natural factors. That is, about pregnancy, excess nutrition the day before.
Indications for use
A lipidogram is recommended not only for people with obvious diseases, but also as a preventive measure. To control fat balance, this examination must be completed from the age of 20. Doctors recommend checking the amount of cholesterol from a young age, since blood vessels are characterized by gradual changes.
Obesity
There are a number of indications:
- people over 45 years old,
- overweight,
- smoking,
- inactive lifestyle,
- high cholesterol in the past,
- diabetes,
- hypertension,
- long-term treatment with lipid-lowering drugs,
- increase in total cholesterol,
- heredity (if there were cases of cardiovascular diseases or atherosclerosis in the family).
In women, it is advisable to monitor lipid metabolism from the age of 50, and men should check their blood for this indicator from the age of 45. It is often appropriate to take the test after a certain treatment. The doctor will be able to see how effective the prescribed therapy was.
Reasons for the downgrade
A drop in level indicates several possible violations.
- Malignant processes. Tumors of any location. Mainly when located in the digestive tract and organs of the reproductive system. Kidneys.
- Starvation. A long-term lack of adequate nutrition leads to an understandable result. Lipids simply do not enter the body in sufficient quantities. If there is a fat layer, this phenomenon can be delayed.
- Infectious lesions. Up to sepsis.
- High concentration of thyroid hormones. Accompanied by poisoning of one's own systems.
- Pulmonary diseases of different types.
- Burns. The larger the affected area, the more significant the problem.
A blood test for the lipid spectrum shows changes in organs and systems indirectly; in any case, auxiliary techniques will be required for clarification.
How to prepare for analysis
In order for the result to be accurate, you need to follow some rules for preparing to donate blood for a lipid profile:
- do not radically change your diet;
- if you are not feeling well, the analysis should be postponed until better times;
- It is not allowed to do the test after an X-ray examination and physical procedures;
- when treating atherosclerosis, you need to continue taking medications;
- training should be postponed for a day, or even better - for several days;
- do not drink alcohol for a day or two;
- do not smoke immediately an hour before the test;
- adjust yourself to calmness;
- last meal – 8-10 hours before the procedure;
- if thirst occurs on the eve of a lipid profile, you can only drink clean water in small quantities. But instead, it is advisable to rinse your mouth.
Decoding
Lipid profile analysis provides detailed information necessary for future treatment, showing five main values.
Total cholesterol
This indicator is not a “horror story” for a patient undergoing a blood test for a lipid profile. This substance, essential for the body, is involved in the formation of tissue cells, cell membranes, sex hormones, human growth and development. Cholesterol is produced by liver cells, and a fifth of the total amount (subject to normal nutrition) enters the body through food.
A feature of cholesterol, like any lipid (fatty substance), is its inability to dissolve in a liquid medium and move in it. The function of transporting cholesterol through blood vessels is performed by lipoproteins, which are able to combine with lipids due to the mixed protein-fat shell.
Additional examinations
Among the activities that may be needed:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Depending on the specific diagnosis, the results reveal certain deviations. The structures of the digestive tract are examined first.
- Study of kidney tissue. Through the same ultrasound or using endoscopic methods, depending on the case. A general urine test is also practiced.
- Dopplerography of blood vessels, duplex scanning. Typically, the structures of the heart, brain, neck, and limbs are subject to evaluation if there is a suspicion of obliterating atherosclerosis.
- If necessary, MRI diagnostics of individual areas of the body that are susceptible to the main lesion is carried out.
- ECG.
- ECHO-CG to detect heart problems through tissue imaging.
These methods are aimed at identifying the consequences of elevated lipids. It is also necessary to discover the root cause of the pathological process. For this purpose, additional diagnostic methods may be prescribed.
Treatment methods
Therapy is carried out with medications. When deciphering a lipid profile, all possible indicators are taken into account; an increase in even one, as well as a decrease, requires in-depth analysis.
If there is reason to suspect a disease, extensive diagnostics are performed. Then a course of therapy is prescribed.
What medications are used:
- Statins. Atorvastatin, Atoris and similar. To eliminate excess concentration of fatty compounds. Prescribed in short courses, as it can provoke negative effects. The risk of side effects is high, which is considered a reason to use them as carefully as possible.
- Fibrates. They are used in combination with statins, especially when they are insufficiently effective. The doctor selects the names.
- A nicotinic acid. Effectively reduces some types of lipids, used with great caution.
In addition, correction of body weight, changes in diet, and cessation of bad habits are indicated: smoking, drinking alcohol.
Lipidogram: the essence of the analysis, what it shows, the norm and deviations, how to take it
Have you been struggling with CHOLESTEROL for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to lower your cholesterol just by taking it every day...
Read more "
Cardiovascular diseases lead in the number of cases worldwide, and their main cause is considered to be disorders of fat metabolism with atherosclerosis affecting the vascular walls. Laboratory examinations, including a lipid profile, help to objectively assess the degree of risk of atherosclerosis.
You can find out about the amount of total cholesterol from a biochemical blood test, but this indicator alone does not make it possible to reliably judge the presence or absence of pathology. The study of the lipid spectrum involves determining the concentration of not only cholesterol, but also other fatty fractions of the blood. These indicators are very important in assessing the degree of risk of pathology of the heart and blood vessels, therefore they are indicated for people predisposed to atherosclerosis, myocardial ischemia, and diabetes.
For the analysis, venous blood is taken, and the patient must know some of the features of preparation for it and the conditions that may affect the result. The lipid profile is deciphered by a general practitioner, cardiologist, or endocrinologist.
Lipid profile indicators
The pathology of fat metabolism plays a key role in the genesis of a variety of diseases and, above all, vascular lesions. There is no longer any doubt about the influence of lipid metabolism disorders on the development of atherosclerosis, and this disease is a path to myocardial infarction, stroke, and dangerous damage to the aorta, kidney vessels, and limbs.
Timely detection of abnormalities in cholesterol and lipid fractions is necessary not only for early diagnosis of pathology of the cardiovascular system, but also for the prevention of severe complications of atherosclerosis.
Many people know that cholesterol level is the most important indicator of fat metabolism, so its increase is always a cause for concern. However, this indicator alone is not enough for correct conclusions, because cholesterol can increase in absolutely healthy individuals without provoking atherosclerosis. To assess fat metabolism, it is important to establish the concentrations of lipid fractions, the fluctuations of which are more characteristic of pathology or normality.
A lipidogram with the study of all fatty components of blood plasma makes it possible to more accurately assess the risk of atherosclerosis. The analysis may reveal abnormalities even when the total cholesterol concentration is within normal limits.
Cholesterol is an integral component of cell membranes; it is part of bile, necessary for proper digestion, and is a precursor of sex hormones, without which development, puberty and functioning of the adult body do not occur. In plasma, cholesterol is found bound to lipoprotein proteins.
In addition to cholesterol (CH), a lipid profile - a blood test for lipids includes indicators such as triglycerides (TG) and high, low and very low density lipoproteins - HDL, LDL, VLDL. They make up the total cholesterol, but their role is different, so the disease is not judged by total cholesterol. Based on the content of these components, the plasma atherogenic coefficient is determined, which serves as a prognostic factor for cardiovascular diseases.
Cholesterol is formed by liver cells and enters the body from the outside with food, and its excess is excreted. VLDL is not saturated with cholesterol and is able to bind it, becoming LDL. High-density lipoproteins capture excess cholesterol from the blood and deliver it to hepatocytes, where cholesterol is converted into fatty acids or included in very low-density lipoproteins, thus being “neutralized.”
High-density lipoproteins are classified as anti-atherogenic fractions, that is, these components prevent atherosclerosis by removing “bad” cholesterol from the circulation. When they decrease, the likelihood of atherosclerosis increases.
The bulk of blood fats are LDL, which are endowed with the ability to “stick” to the walls of blood vessels and participate in the formation of a fatty-protein plaque. They account for up to 70% of total cholesterol. If these substances do not go beyond the normal limits, then the risk of pathology is minimal, because the exchange occurs in the right way. In cases where LDL is elevated and settles on the vascular walls, we can talk about a high probability of atherosclerosis, even if total cholesterol retains normal values.
Triglycerides are a normal component of the blood, they are considered natural metabolites that are part of VLDL, are supplied with food and are excreted by the liver. Their main volume is concentrated in fatty tissue; they are the main energy substrate in the body. Being an integral part of metabolic processes, they, at the same time, can cause serious harm if normal concentrations are exceeded.
It has been established that TGs increase in atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, excess weight, hypertension and play an important role in the genesis of coronary heart disease and vascular changes in the brain.
So, a lipid profile consists of the definition:
- Total cholesterol;
- Triglycerides;
- HDL;
- LDL;
- VLDL.
The atherogenic coefficient, which makes it possible to quantify the risk of atherosclerotic damage to the vascular endothelium, is calculated using these indicators: the sum of the values of VLDL and LDL is divided by the level of HDL. (Normally - up to 3.5).
To correctly decipher a lipid profile, it is necessary to take into account some other conditions:
- Floor;
- Age;
- Heredity in relation to cardiovascular pathology;
- Presence of carbohydrate metabolism disorders;
- Presence and degree of obesity;
- Blood pressure level;
- Bad habits (smoking, alcohol).
Only an objective assessment of the lipid spectrum, taking into account these factors, provides the most accurate prognosis for atherosclerosis and heart and vascular diseases.
When is it necessary to study the lipid spectrum?
The study of the lipid spectrum aims not only to determine the risk of heart and vascular diseases, but also to assess the effectiveness of treatment for an already established diagnosis of myocardial ischemia, diabetes, and hypertension. It is important for dynamic monitoring of patients on a lipid-lowering diet and taking medications to lower cholesterol.
Indications for a lipid profile are:
- Examination as part of preventive measures for people over 20 years of age - once for five years;
- Increased total cholesterol in a biochemical blood test;
- The presence of changes in cholesterol concentrations in the past;
- Unfavorable heredity, when among close relatives there are patients with severe atherosclerosis, hereditary forms of fat metabolism disorders;
- Presence of risk factors – smoking, diabetes, excess weight, arterial hypertension, age over 45 and 55 years for men and women, respectively;
- Treatment with lipid-lowering drugs, prescription of a special diet (monitoring the effect).
How to take the test correctly and what affects the result?
When going for any research or analysis, we all want to get the correct and most reliable result, and in the case of a lipid profile, as with other tests, you need to know and follow some rules so as not to distort the indicators.
The blood lipid spectrum is very sensitive to external conditions. This doesn't just apply to food intake. The result can be influenced by anxiety, excessive physical effort, taking medications, recently performed other tests, infections, etc., so all these factors must be kept in mind.
Cholesterol will drop to normal! Will help on…
A tricky recipe for cleaning blood vessels from bad cholesterol! 4 drops and all plaques will disappear...
It is recommended to take blood samples for lipid levels in the morning, on an empty stomach, at least 12 hours after the last meal. Half an hour before the test, you should exclude physical activity and psycho-emotional experiences, as well as smoking. The analysis should not be performed in patients with acute myocardial infarction and during the first 3 months from the moment of its occurrence.
The result may change:
- Physical activity, injury;
- Infectious diseases in the acute period;
- Eating, alcohol, smoking shortly or immediately before the test;
- “Hungry” diet, exhaustion;
- Concomitant diseases with damage to the liver, kidneys, endocrine glands;
- Pregnancy.
Many medications can cause an increase or decrease in both total cholesterol and its fractions, so if you are taking any medications, you must notify your doctor.
Total cholesterol increases during treatment with beta-blockers, which, by the way, are often prescribed for pathology of the heart and blood vessels, which at the same time serves as a reason for a lipid profile. Hormones and some diuretics and tranquilizers also increase total cholesterol.
A decrease in total cholesterol is observed in individuals taking lipid-lowering drugs (statins, fibrates), as well as when prescribing estrogens, androgens, allopurinol and others.
Corticosteroid and sex hormones cause an increase not only in total cholesterol, but also in HDL and LDL. Hormonal contraceptives increase cholesterol, LDL and reduce HDL.
The ability of many drugs to influence lipid profile parameters makes it necessary not only to take it into account when interpreting the results, but also to closely monitor patients taking such drugs, because their risk of developing vascular and cardiac pathology may be increased.
Normal or pathological?
When deciphering a lipid profile in adults, a specialist first assesses whether there are deviations in the numbers of specific indicators. It is believed that the risk of atherosclerosis is increased if total cholesterol, LDL, VLDL and TG exceed normal values. Pathology is also indicated by an atherogenic coefficient of more than three and a reduced content of high-density lipoproteins.
The following values of lipid spectrum indicators are considered the norm:
- Atherogenic coefficient – 2.2-3.5;
- TG level up to 2.25 mmol/l;
- HDL – 1.03-1.55;
- LDL up to 3.3;
- VLDL – 0.13-1.63 mmol per liter;
- Total cholesterol – up to 5.2 mmol/l.
For high-density lipoproteins, different normal values are provided for women and men. Thus, an increased likelihood of atherosclerotic lesions and cardiovascular pathology is indicated by HDL levels below 1 mmol per liter of blood in men and less than 1.3 in women. Low risk is defined for both sexes if HDL levels exceed 1.55 mmol per liter.
The atherogenicity coefficient can also serve as a prognostic indicator. If it is below three, then the risk of atherosclerosis and vascular lesions is minimized. A coefficient level of 3-4 may indicate an increased risk of atherosclerosis, and with a value of 5 or higher, patients usually already have certain manifestations of atherosclerosis - coronary heart disease, discirculatory encephalopathy, kidney pathology, impaired blood flow in the extremities. With such numbers, vascular complications are quite likely.
A positive lipidogram result, that is, an increase in its atherogenic indicators, can be observed in a wide variety of pathologies:
- Familial, hereditary forms of dys- and hyperlipidemia;
- Cardiac ischemia due to atherosclerotic changes in the coronary arteries;
- Hepatitis, liver cirrhosis;
- Pathology of the urinary organs;
- Decreased production of thyroid hormones;
- Diseases of the pancreas (pancreatitis, diabetes);
- Overweight.
A physiological increase in cholesterol is possible during pregnancy.
Reducing total cholesterol and its fractions is possible with:
- Malignant tumors;
- Pulmonary pathology;
- Thyrotoxicosis;
- Infectious diseases, sepsis;
- Burn disease;
- Fasting.
High-density lipoproteins usually decrease in coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, diabetes, and stomach ulcers.
The nature of the food consumed has a great influence on the indicators of fat metabolism. Even if there is no atherosclerosis yet, changes in the lipid spectrum already create a risk of heart and vascular diseases. Abuse of quickly digestible carbohydrates, animal fats, fatty and fried foods, and alcohol creates an excessive load of cholesterol, which the body is not able to metabolize. Over time, increasing concentrations of its derivatives are deposited in the vascular endothelium.
If the doctor notices increased cholesterol in a biochemical blood test, he will refer you for a lipid profile study to rule out metabolic disorders. Patients whose cholesterol is normal still need such detailed analysis if they are exposed to risk factors. Persons who have an unfavorable heredity for dyslipidemia are examined regularly, at least once a year, regardless of age.
The price for studying the lipid spectrum depends on the level of the clinic and the locality, varying between 500 and 1500 rubles. The analysis is quite common, so there are usually no difficulties in finding a clinic or laboratory where it can be performed.
Video: lipid profile in the program “Live Healthy!”
Step 2: after payment, ask your question in the form below ↓ Step 3: You can additionally thank the specialist with another payment for an arbitrary amount ↑