What is ferritin
What is ferritin, which is determined in blood serum? This is an indicator by which you can judge the amount of iron stored by the body. Ferritin is a protein that binds iron and delivers it to internal organs for storage.
In addition to blood, ferritin is found in internal organs, mainly the liver and bone marrow.
If placental ferritin is detected in a non-pregnant woman or man, this is a sign of a malignant tumor.
A high level indicates an excess of iron, while a low ferritin indicates a lack of iron. By assessing this indicator, one can distinguish between absolute and relative iron deficiency.
With a lack of iron, the following symptoms are observed:
- excessive fatigue;
- irritability;
- dizziness and headaches;
- dyspnea;
- seizures in the corners of the mouth;
- unusual taste preferences.
Excess iron manifests itself in different symptoms, depending on the underlying disease that caused it.
Macronutrient functions:
- oxygen transfer;
- maintaining immunity;
- participation in the synthesis of hormones;
- formation of blood cells.
Ferric iron is quite toxic. To reduce toxicity, the protein ferritin binds it.
Indications for ferritin testing:
- assessment of iron reserves;
- diagnosis of anemia;
- determination of hidden iron deficiency.
The analysis is prescribed to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment with iron supplements.
How to downgrade?
Hemochromatosis is a disease in which excess iron accumulates in the body. It usually accumulates in organs and tissues such as the liver, pancreas, spleen, and skin.
- It is important to reduce your consumption of red meat. It contains the most digestible type of iron (heme-iron, hema-iron).
- Reduce vitamin C intake to 200 mg per day.
- Alcohol enhances iron absorption and should be avoided.
- Whole grain flour contains phytic acid, which removes iron from the body. It is also found in wheat bran, beans, almonds, and soy flour.
- Rice helps to quickly remove ferritin from the body.
Iron content in meat and fish:
| Type of fish or meat | Iron level, mg | Heme iron, mg | Heme iron,% |
| Venison | 4,5 | 2,3 | 51 |
| Lamb | 3,1 | 1,7 | 55 |
| Beef | 3,2 | 1,6 | 50 |
| Pork | 1,3 | 0,3 | 23 |
| Chicken | 0,6 | ||
| Cod | 0,2 | ||
| Mackerel | 0,7 | ||
| Salmon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 17 |
| Shellfish | 4,6 | 2,2 | 48 |
| Lobster | 1,6 | 0,6 | 40 |
| Shrimps | 2,6 | 1,0 | 40 |
As can be seen from the table, meat contains about 40-50% heme iron.
Drugs: Drugs such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid or deferoxamine also remove iron from the body. These medications should not be taken without consulting a doctor and can be toxic and dangerous if consumed in excess or incorrectly.
Another way to lower ferritin levels is to become a blood donor. Donating blood several times a year can significantly reduce your iron levels. To diagnose the results, it is necessary to do a blood test both before and after the donation.
Ferritin Facts:
- Men require 8 mg of iron per day, women - 18 mg (until menopause, after which the required amount of iron drops to 8 mg).
- Iron levels in men tend to be higher than in women.
- Pre-made formulas (such as muesli or muesli cereal) typically contain high amounts of iron;
- Taking various mineral supplements can enhance and speed up iron absorption. For example, vitamin B12 promotes the rapid formation of blood cells.
- Smoking is contraindicated at any level (high or low) of iron.
What does a ferritin test show?
A blood test for ferritin means, first of all, the ability to differentiate anemia of different origins. In addition, with the help of protein, you can evaluate iron reserves in the body: the norm, deviations upward and downward, the effectiveness of the therapy, and identify latent iron deficiency.
Indications for prescribing a ferritin test are: fatigue, chronic fatigue syndrome, pallor or pigmentation of the skin, alopecia, brittle nail plates, groundless nervousness, tachycardia, immunodeficiency, nausea, myalgia without exercise, arthralgia, heavy periods, decreased potency, various bleeding etiology.
A ferritin test is usually prescribed together with other laboratory tests, since alone this test gives an idea of the concentration of iron in the bloodstream, and together with others it helps to determine the root cause of the pathology.
With a blood test for ferritin levels, the following are tested: serum iron, transferrin, TLC, hemoglobin, red blood cells, folic acid, cyanocobalamin, thyroid hormones, liver and kidney tests, C-reactive protein.
If ferritin is elevated, what does this mean in an adult?
The causes of consistently high protein levels include a hereditary disease - hemochromatosis. With this pathology, iron in the human body is absorbed and accumulates in excess quantities. What causes the manifestation of secondary pathologies: cirrhosis, diabetes, arthritis and heart disease. The prognosis of the outcome is determined by the timeliness of diagnosis and the age of the patient. The earlier the fact of hemochromatosis is established, the faster supportive and preventive treatment will be selected.
An excessive amount of the test value is also observed after multiple transfusions of donor blood to the recipient. And also against the background of long-term use of iron-based medications and their intramuscular administration.
An upward deviation of the criterion from the norm is recorded in patients against the background of some infectious (severe pneumonia, osteomyelitis, purulent arthritis, pyoderma) and autoimmune (SLE, rheumatoid arthritis) diseases. It is important to understand that high ferritin values mask a severe lack of iron in the human body.
Causes of excess amounts also include liver pathologies, in particular alcohol abuse. When the normal functioning of the thyroid gland is disrupted, when the amount of hormones it secretes exceeds the norm, ferritin also increases.
A similar condition is also characteristic of hemolytic anemia, when red blood cells begin to actively break down, releasing their contents into the systemic circulation.
If the above reasons are excluded, the patient should undergo extensive diagnostics for malignant neoplasms. In case of oncological lesions of the bone marrow, mammary glands and lymphatic system, the value of the described criterion will significantly exceed normal values.
Functions of ferritin
Ferritin is a protein whose main function is the accumulation of non-toxic iron in the body. The molecule consists of the protein apoferritin, a phosphoric acid residue. Fe (iron atom) is attached in the form of colloidal ferrous hydroxide.
For normal functionality, the human body aged 15-45 years uses 3-4 mg of iron. But the body contains about 4 g. About 20% is concentrated in the protein ferritin. The main places of concentration: liver, spleen, brain tissue near the duodenum.
In infectious diseases accompanied by inflammation, up to 25% of ferritin is redistributed to macrophages (antibodies that die after the destruction of a harmful virus, bacteria, from the Greek macro - large; phagos - to devour).
The main functions of ferritin:
- deposition (iron storage);
- transfer of iron from a toxic 3-valent form to a 2-valent form absorbed by the body;
- conversion from 3-valent to 2-valent form for macrophages, removal of excess Fe from the body, for brain cells - rarely.
- transferring iron obtained from food to transferrin;
- protection of tissues from the destructive effects of free iron.
In critical situations with severe iron deficiency, ferritin takes over the transport function of transferrin. With severe inflammation, a sharp decrease in immunity, the protein concentrates in the affected tissues.
Characteristics of ferritin and iron content
A globular protein complex found in almost all cellular structures of the body. Particularly concentrated in liver, spleen cells, and brain cells. It is the direct executor of the process of processing and preservation of iron cells. The characteristics of the distribution of iron within normal limits in the body can be found in the table.
| Protein complex | For women (mg.kg) | For men (mg.kg) |
| Hemosiderin | About 2 | About 4 |
| Ferritin | About 4 | Around 8 |
Attention! This protein complex is a depot of Fe. Additionally, functional and transport iron are isolated.
Ferritin
| Type Fe | For women (mg.kg) | For men (mg.kg) |
| Transport Transferrin | Less than 1 | Less than 1 |
| Functional Hemoglobin | Within 28 | Within 30 |
| Functional Heme enzymes | 1 | 1 |
| Functional Myoglobin | No more than 4 | No more than 5 |
| Functional Non-heme enzymes | 1 | 1 |
This is precisely the normal level of iron concentration, and any deviations from these indicators require urgent normalization.
Norm and stages of anemia
If Fe is in free form, it is dangerous for the body. Safety is guaranteed only thanks to ferritin. Consequently, iron is contained in a soluble and completely safe form.
It is important! The main function assigned to ferritin is its direct participation in the formation of hemoglobin, which is vital. Additionally, ferritin performs the function of transporting Fe from mother to fetus during pregnancy.
Blood ferritin levels by age
Ferritin concentrations correlate with age and gender: age differences are more pronounced. The normal level of ferritin in the blood is presented in the table.
Children
In children - no gender differences.
| Age | Norm in µg/l |
| Up to a year | 10-325 |
| Up to 4 years | 5-65 |
| Up to 7 years | 4-66 |
Men
| Age | Norm in µg/l |
| Up to 12 years | 15-125 |
| Under 18 years old | 14-150 |
| Over 18 years old | 15-152 |
Women
| Age | Norm in µg/l |
| Up to 12 years | 7-85 |
| Under 18 years old | 14-67 |
| Over 18 years old | 12-150 |
A blood test for ferritin in adults shows a reduced level of protein in a woman’s body in relation to a man, which is associated with her physiological characteristics: menstruation.
The level of ferritin during pregnancy decreases physiologically due to the consumption of iron reserves for the formation of internal organs and tissues of the fetus. The norm of ferritin in the blood for women during pregnancy is presented in the table.
| Trimester | Minimum in µg/l | Maximum in µg/l |
| I | 50 | 95 |
| II | 22 | 77 |
| III | 9 | 15 |
Iron deficiency in pregnant women provokes intrauterine defects in fetal development, miscarriages, and premature birth. If a woman's body is constantly deficient in iron, this can cause infertility. An increased level of ferritin in the blood of women during pregnancy indicates a latently developing pathology and requires a full examination.
Ferritin concentration standards
The norm of ferritin from birth has different indices according to the age of the child, but from adolescence, normative indices begin to be divided by gender.
| person's age | ferritin concentration, mcg/liter |
| infants up to 28 days of life | 25,0 — 200,0 |
| 1 calendar month after birth | 200,0 — 600,0 |
| up to 12 calendar months | 25,0 — 85,0 |
| from one year to 10 calendar years | 25,0 — 55,0 |
| from 10 years to 15 years of age | 30,0 — 140,0 |
| girls under 20 years of age | 10,0 — 40,0 |
| women from 20 calendar years to 50 years of age | 15,0 — 100,0 |
| boys under 20 | 20,0 — 100,0 |
| men from 20 to 50 calendar years | 20,0 — 300,0 |
| both sexes after 50th birthday | 20,0 — 300,0 |
| In pregnant women | |
| 1st trimester of pregnancy | 56,0 — 90,0 |
| 2nd trimester of fetal development | 25,0 — 74,0 |
| 3rd trimester of pregnancy | 10,0 — 15,0 |
From the very period of birth, the baby has a high hemoglobin index, and the concentration of red blood cells in the blood plasma is also high. Enhanced protection from hematopoiesis, as well as an increase in the content of ferritin in erythrocytes.
These indicators correspond to a new load for the baby’s body, because he has to adapt to the external environment and new conditions, and there is no protective dome in the form of the mother’s body.
Gradually, from the moment of birth, red blood cells disintegrate, hemoglobin (fetal type) is replaced by red cells, as in the body of an adult, the entire hematopoietic and blood flow system is being restructured, and as a result of these biological processes, the ferritinin index decreases.
In the female body, the ferritin index is lower than in men.
This is due to the fact that after puberty, women lose blood monthly (during menstruation), and the concentration of red blood cells and hemoglobin protein in a woman’s body is also lower.
These indicators are based on the biological structure of the female body.
During the period of intrauterine gestation, a woman also experiences a decrease in plasma ferritin concentration. This is due to the fact that most of the iron ions are spent on the intrauterine formation of the child’s body. During this period, control over the level of hemoglobin and ferritin protein is mandatory.
Reasons for the increase
Ferritin in the blood can be elevated when there is excessive intake of iron into the body from the outside or when iron accumulates in tissues for pathological reasons. This happens when:
- prolonged fasting;
- hemochromatosis;
- malignant tumors, including blood;
- osteomyelitis;
- systemic collagenoses;
- disorders of the liver and biliary system:
- renal failure;
- infections of various origins:
- alcoholism;
- taking hormones, cytostatics, antibiotics, NSAIDs.
A persistent increase in protein concentration of more than 1000 mcg/liter indicates the development of a serious pathology, but more often an increase in ferritin in the blood occurs in combination with other indicators:
- an increase in ferritin against the background of low hemoglobin indicates hemolytic or folate deficiency anemia, or a viral infection, ulcerative colitis or oncology;
- an increase in ferritin with normal iron levels in the blood or its decrease indicates the development of inflammation;
- a simultaneous increase in ferritin and iron in the bloodstream indicates an excess of iron in the body, which occurs with hereditary hemochromatosis.
Elevated numbers and cardiovascular disease
Diseases of the cardiovascular system associated with hemochromatosis most often affect men. In women, the risk of developing heart disease as a result of hemochromatosis occurs only during menopause. And this is understandable: excess iron is removed from the female body during menstruation.
If hemochromatosis is not eliminated, this condition can lead to dysfunction of the cardiovascular system: coronary heart disease, arrhythmia, heart failure, heart attack, and even sudden cardiac arrest.
Due to elevated levels of ferritin, cardiac hemochromatosis can develop, a disease in which the heart muscle acquires a characteristic rusty-brown color, thickens and increases in size.
In this case, cardiosclerosis occurs - the proliferation of fibrous tissue. Subsequently, the contractile function of the myocardium decreases due to atrophic or dystrophic changes in muscle fibers.
Typically, after detecting an elevated ferritin concentration, the doctor prescribes the following tests:
- to determine the total iron-binding capacity of serum;
- genetic test for hemochromatosis;
- ECG and Holter study of the heart.
If there is a risk of coronary heart disease, the analysis will show an increase in the level of ESR and leukocytes. Other characteristic changes will be noticeable:
- an increase in the amount of serum iron to 54–72 µmol/l;
- decrease in the total iron-binding capacity of serum;
- low transferrin content;
- hyperglycemia;
- dysproteinemia;
- increasing the coefficient of transferrin saturation with iron to 60–90%.
If you have cardiovascular diseases, you need to keep the level of iron in your body under control. Your doctor will prescribe appropriate therapy to maintain ferritin levels between 70 and 80 mcg/L.
This will have a positive impact on the dynamics of treatment of identified heart or vascular disease, reduce the risk of stroke or heart attack, increase the duration and improve the quality of life.
Cardiovascular diseases can be both a consequence and a cause of increased iron levels in the body. For example, with circulatory disorders associated with heart attacks and strokes, patients experience a sharp increase in serum ferritin.
What does an increase in ferritin in the blood say in combination with other indicators?
If ferritin is high, other indicators need to be assessed in a blood test - hemoglobin, serum iron, folic acid, vitamin B12. Based on combinations of results, a person’s disease is judged.
Ferritin is elevated with low hemoglobin
Elevated ferritin against the background of low hemoglobin is an indicator of folate deficiency or hemolytic anemia. These diseases develop:
- due to a lack of folic acid and/or vitamin B12;
- accelerated destruction of red blood cells.
The iron content does not change.
This combination also means that the person has an acute viral infection, ulcerative colitis, or pneumonia. Long-term registration of this condition is a reason for examination for cancer.
Ferritin is elevated, but iron is normal or low
High ferritin in the absence of other factors of anemia means the presence of an inflammatory process. If iron is normal or gradually decreases, it means that the body is getting rid of it in order to suppress the inflammatory process. The patient needs to be examined for chronic infections, systemic inflammatory pathologies, and cancer.
Elevated serum iron and ferritin
Serum ferritin shows only the content of microelement reserves. He does not talk about the level of free iron in the blood. If both of these factors are too high, there is an excess of iron in the body. This happens with the hereditary disease hemochromatosis.
When standards are raised
An increase in ferritin is observed in the case of hemochromatosis - the name sounds so complicated in medical scientific language, to put it simply - this is a process of impaired iron storage. The disease can be hereditary in nature; it is a genetic disease when the body accumulates iron 5 times more than normal (about 20 g instead of 4 g of the normal amount). A high excess of iron can primarily accumulate in the liver, heart and joints (in the male body, the testicles are storage sites). It is worth noting that the male body accumulates iron faster than the female body - women waste a significant portion of the substance during the natural process of blood loss (menstruation).
Other reasons for high levels are inflammatory processes accompanying lupus erythematosus, osteomyelitis, urinary tract infections, burns, as well as more dangerous and serious oncological diseases of the liver, breast, and Legionnaires' disease. Some forms of acute leukemia and lymphogranulomatosis also contain elevated ferritin (a tumor marker will help to detect).
At elevated levels, there is a danger of cardiosclerosis (an increase in fibrous tissue), when the heart muscle becomes dense, grows, acquiring a brownish tint. High levels often result from repeated blood transfusions.
Reasons for the downgrade
A reduced ferritin content in a blood test is recorded during gestation and with iron deficiency anemia. Iron deficiency increases gradually: first, the reserves of the element in the liver and bone marrow are depleted. The hemoglobin concentration does not change. Then, the formation of hemoglobin is disrupted, resulting in iron deficiency anemia.
For a short time, ferritin levels may fall under conditions that require high iron consumption: active child growth, mental or physical stress, blood donation. For a long time, ferritin levels fall when iron absorption is impaired: diseases of the digestive system, menopause, veganism, celiac disease.
A false decrease in ferritin in the blood occurs after taking testosterone drugs, statins, hypoglycemic agents, and allopurinol.
Association of low concentrations with cardiac pathologies
Iron deficiency and, as a result, anemia, can be caused by heart failure. Moreover, in addition to reduced ferritin, tests show a low level of hemoglobin; when examining red blood cells, it turns out that they are small in size compared to the norm and are less saturated with hemoglobin.
As anemia progresses, low levels of transferrin saturation may be detected. There is also constant low blood pressure.
But most often, a lack of ferritin is not a consequence, but a cause of cardiovascular diseases.
Iron deficiency leads to the following disorders in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels:
- carditis;
- vascular damage;
- metabolic disorders in the myocardium;
- tachycardia.
Since the heart does not receive sufficient nutrition, it works at an unusual pace and quickly wears out. Due to constant load, it expands and hypertrophies. And this leads to the fact that the myocardium needs increased oxygen supply, which the body is not able to provide.
Sooner or later, hypoxia of myocardial cells occurs. The consequence of this condition is small focal necrosis, heart murmurs, mitral and aortic valve insufficiency.
A low or high serum ferritin concentration indicates that a person is suffering from hemochromatosis or anemia. These conditions have a negative impact on the health of the heart and blood vessels and lead to the development of heart failure, heart attacks and strokes.
How is the test performed?
The test requires a small amount of blood.
Doctors recommend not eating for 8-12 hours before the test. According to the American Association for Clinical Chemistry (AACC), the test will be most accurate if taken in the morning on an empty stomach. You can drink water. It is necessary to ensure that the patient is not taking any medications that can change or correct the ferritin levels in the test. If it is impossible to discontinue the medications, you should notify your doctor. Before donating blood, it is important not to engage in heavy physical labor, drink alcohol, fatty, fried or spicy foods.
If tests such as ultrasound, fluorography, radiography, laser or physiotherapeutic procedures, anoscopy or sigmoidoscopy were performed before the analysis, the results of the analysis may also change. You must notify your doctor about this.
The healthcare professional will carefully draw blood from the vein.
No serious side effects were identified after the test.
There are no other special instructions or precautions for taking the test. Often after donating blood, symptoms such as slight bleeding, weakness, dizziness, and bruising were noticed. They pass within an hour.
Symptoms
Symptoms of low ferritin:
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- tachycardia;
- aching muscle pain without physical activity;
- dyspnea;
- increased sweating;
- pale skin;
- apathy;
- diarrhea;
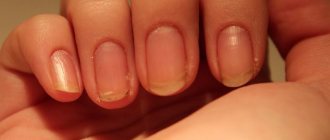
- hair loss;
- peeling of nails;
- chest pain;
- itching
Symptoms of elevated ferritin:
- decreased sex drive;
- pain in bones, joints;
- weight loss;
- characteristic ferrous taste in the mouth;
- constipation;
- swelling of the face is possible;
- frequent palpable pulsation of blood vessels.
Irritability, muscle spasms, and nosebleeds are symptoms of both high and low ferritin levels. Bleeding can occur both due to thin blood and fragility of blood vessels with low ferritin, and due to thin walls of blood vessels and high pressure with increased ferritin.
With low Fe, contractility and muscle volume decrease, and with increased Fe, muscle hypertension and an increase in muscle protein myofibril molecules occur. Brain cells with low amounts of iron replenish the metal component with calcium.
With low ferritin, short-term irritability alternates with long-term apathy, and with elevated ferritin, long-term irritation may not alternate with melancholy.
High level
Symptoms:
- stomach ache;
- rapid heartbeat or chest pain;
- weakness;
- joint pain.
Ferritin levels may increase if the liver or kidneys are damaged.
Ask your question to a clinical laboratory diagnostics doctor
Anna Poniaeva. Graduated from the Nizhny Novgorod Medical Academy (2007-2014) and Residency in Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics (2014-2016).Ask a question>>
The results of the analysis can be taken into account when assessing your overall health.
Diagnostic methods
Regardless of the method used, the sample used is venous blood.
Determination methods:
- Klochkov's method - cadmium sulfate is used as a reagent - high speed of obtaining results, low accuracy;
- histochemical method (Pels reaction) - the formation of the so-called Prussian glaze - the sample turns blue with high ferritin, the concentration is determined by the output amount of iron oxide - the most common method;
- latex immunological test (reaction with antibodies of a test sample) using the method, you can determine both the concentration of Fe and the general level of immunity.
Rules for preparing for the test
The main goal of preparation is to minimize possible distortions in the analysis:
- Do not take iron supplements for a week.
- For 5 days, do not take penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics, antifungal medications, hepatoprotectors that contain aluminum or silymarin.
- 3 days before the test, stop drinking alcohol; if the daily dose of alcohol in terms of ethanol exceeds 300 ml, do not test for ferritin for 7-10 days.
- Stop smoking one day before and eliminate red meat from your diet; liver, except chicken, 3 days in advance; Do not consume chicken liver the day before.
- Do not eat food 12 hours before.
- Do not drink liquid 1 hour before.
- Don't worry for half an hour.
Decoding the results
A blood test for ferritin in children and adults is not performed very often. Such a study is often carried out when it is necessary to monitor the level of total iron reserves in the body. In addition, this type of study may be required to determine the causes of anemia, as well as to identify hidden anemia. Another reason for conducting the analysis is to monitor the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy in the patient.
A decrease or, conversely, an increase in this specific protein may indicate various diseases in the child.
Treatment for abnormal ferritin levels
How to increase the ferritin level in the blood is of interest to everyone who is faced with this problem. It must be understood that it is impossible to separately increase the content of the carrier protein. First you need to determine the reason for its decrease. If this is a physiological reason, it is enough to include iron-containing foods in your diet. To identify the disease, they are tested for ferritin and a number of other indicators.
Traditional treatment
Treatment will depend on the underlying disease. Taking iron supplements can increase ferritin levels in the blood. Depending on the severity of the condition, they are prescribed orally or intravenously. During treatment, biochemical parameters should be monitored to prevent an excess of macronutrients.
The question of how to lower ferritin is more difficult. This indicator increases with serious diseases - hereditary, systemic, oncological. The main way to reduce it is to remove excess iron from the body. It is necessary to treat the underlying disease and against this background the protein content returns to normal.
Diet when ferritin levels change
A healthy diet is important to increase protein. Iron-containing products are:
- beef and pork liver;
- seafood;
- buckwheat grain;
- prunes;
- green apples;
- eggs;
- nuts.
A person needs 12-17 mg of iron per day. Only 10% of the macronutrient contained is absorbed from food. Ascorbic acid increases its absorption. It is found in citrus fruits, gooseberries, currants, potatoes, and sauerkraut.
Ferritin is a protein that ensures the preservation of iron for the body's needs. Its increase or decrease reflects a disorder of iron metabolism. Ferritin analysis is used to diagnose anemia, inflammatory diseases, and malignant tumors.
Ferritin levels change throughout a person's life. With its deficiency, typical clinical signs occur, but an accurate diagnosis can only be established through laboratory testing. If you identify symptoms of iron deficiency, it is recommended to consult a doctor, as various disorders can provoke it. Depending on the level of serum iron, the specialist prescribes a special diet and, if necessary, drug treatment.
Ways to reduce ferritin
It is important to discuss the situation with your doctor if the test shows elevated ferritin. Your doctor should identify the cause of the elevated ferritin and prescribe treatment.
You may also try the additional actions listed below if you have discussed them and agreed with your doctor, provided that such actions may be appropriate for reducing ferritin levels in your case. Remember that none of the additional options for lowering ferritin should be used instead of the recommendations and prescriptions of a doctor.
Green tea and coffee
Tea and coffee contain tannins and polyphenols, which reduce iron absorption. However, tea does not appear to affect ferritin levels in healthy adults. It can only lower ferritin in those who have iron deficiency or, conversely, excess.
Blood ferritin concentrations were not associated with black, green or herbal tea consumption in healthy adults in a study of more than 2,600 subjects.
However, ferritin showed a negative correlation (the more tea, the less ferritin) with tea consumption in old age (over 80 years).
Tea consumption was associated with lower ferritin levels in groups of people with iron deficiency. On the other hand, in those people who show increased iron levels, tea consumption may reduce ferritin concentrations.
The green tea catechin, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), markedly inhibits heme iron absorption in the intestine (by reducing iron export in Caco-2 cells).
Coffee interferes with the absorption of additional iron, such as that taken in supplement form.
Pregnant women who frequently drank coffee showed lower levels of iron in the body.
Cellulose
Fiber impairs iron absorption . Consumption of fiber-poor fruits, vegetables and juices was associated with higher ferritin concentrations in premenopausal women.
Phytic acid
Phytic acid is found in almost all plant foods, including whole grains, beans, nuts and seeds. It is a potent inhibitor of iron absorption.
In healthy people, a dose-dependent inhibitory effect of phytic acid on iron absorption is observed.
In one study, iron absorption in humans increased 4-5 times when the amount of phytic acid was reduced to about 4-5 times the normal amount in soybeans.
Calcium
Calcium-rich foods such as dairy products may reduce iron absorption. Ferritin levels were negatively associated with cow's milk intake and calcium intake in a study of 18-month-old children.
Pregnant women who consumed cow's milk at least 3 times a week showed lower levels of ferritin and iron in the body. A diet rich in milk and yoghurt increased the risk of low iron levels by 50% in women in New Zealand.
However, despite some short-term effects, it has been noted that long-term dietary calcium supplementation does not have a negative effect on iron status and blood ferritin concentrations.
The importance of tissue accumulation of iron in inflammatory and infectious, oncological, genetic, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases is constantly increasing (source)
Exercise stress
Ferritin rises sharply immediately after exercise, but returns to baseline levels within a few hours.
On the other hand, long-term, sustained exercise reduces ferritin along with other acute-phase reactants.
Regular physical activity, especially intense running, increases iron loss. With significant physical activity, moderate iron deficiency and sometimes true iron deficiency anemia can even occur, especially with insufficient iron nutrition and an increase in iron requirements due to growth (in children, adolescents) or additional iron loss (during menstruation).
Iron deficiency is common in athletes involved in endurance sports. In female marathon runners, the prevalence of this disease reaches 28%, while in the general female population the rate of iron deficiency is 11%.
Endurance athletes need more iron because their training causes their red blood cell count to increase. This means their hemoglobin levels may appear normal, but their ferritin levels (a marker of iron stores stored in the body) may be low.
Low ferritin with hemoglobin in the mid-upper normal range and low ferritin with hemoglobin in the low normal range are relative indications for iron supplementation in athletes.
Zinc
Zinc is an essential mineral and is important for the immune system. It may interfere with iron absorption due to similar chemical properties and common absorption pathways.
In human studies, zinc supplementation does not appear to have a clinically important negative effect on body iron status. But when zinc is taken along with iron, the iron content does not increase compared to when iron is taken without zinc.
Manganese
Manganese is an essential mineral that may interfere with iron absorption due to similar chemical properties and common absorption pathways. In humans, manganese inhibits iron absorption at a dose that depends on the types of iron solutions. Manganese has a strong direct competitive inhibition of iron uptake.
Magnesium
Some types of common magnesium supplements, such as magnesium oxide, impaired iron absorption in cellular studies.
Curcumin
Curcumin, a polyphenol found in turmeric, binds to iron and may cause iron deficiency in rats. It may also help rats with elevated blood iron levels.
In a model of borderline iron deficiency, those rats that received curcumin showed severe reductions in iron levels.
Peppermint, cocoa and chamomile
One study examined whether various plant polyphenols in beverages could inhibit iron absorption. The beverages studied contained various polyphenolic structures and were rich in either phenolic acids (chlorogenic acid in coffee) or monomeric flavonoids (herbal teas, chamomile (Matricaria recutita L.), verbena (Verbena officinalis L.), linden flower (Tilia cordata Mill.) , pennyroyal (Mentha pulegium L.) and peppermint (Mentha piperita L.), or complex polymerization products of polyphenols (black tea and cocoa).
Grape seed extract
Grape seed extract (GSE) markedly inhibits intestinal iron absorption (by reducing iron export in Caco-2 cells).
Regular intake of vitamin C may counteract the inhibitory effects of low concentrations of polyphenols on heme iron absorption, but may not counteract the inhibitory effects of high concentrations of polyphenols.
Chilli
Chili peppers were able to inhibit iron absorption in a study involving young women living in tropical regions of Asia.
Ginger
One of the main substances in ginger, 6-shogaol , caused a decrease in ferritin levels in 3 of 6 (50%) patients with early myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) whose ferritin levels were elevated at the beginning of the study.
The information on this site has not been evaluated by any medical organization. We do not seek to diagnose or treat any disease. The information on the site is provided for educational purposes only. You should consult your physician before acting on information from this site, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medications, or have any medical condition.
Indicators of low ferritin
When functional iron levels fall or rise, ailments and other signs of disease may occur. It is typical that with low ferritin, symptoms do not appear until anemia is confirmed. In the early stages, the following signs of decreased ferritin are observed:
- a person begins to get tired quickly even in the absence of increased load;
- there is constant weakness;
- the skin turns pale;
- decreased libido;
- decreased level of concentration;
- irritability and mood swings;
- increased heart rate;
- hair begins to fall out.
The danger of reducing ferritin is a decrease in the production of vital hemoglobin.
Decreased ferritin concentration
Attention! It is hemoglobin that performs the function of transporting and saturating all tissues and systems with oxygen.
When the iron depot is below the normal level, anemia begins to develop, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Pronounced pallor of the skin.
- The appearance of shortness of breath.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Fast fatiguability.
Functions of ferritin
What causes a decrease in ferritin?
There are several factors that influence the decrease in this protein complex, and, consequently, iron. These include:
- constant diets, fasting;
- insufficient consumption of iron-rich foods;
- loss of iron concentration due to bleeding;
- pregnancy period;
- problems with the absorption process of Fe during digestion.
Note! Most often, pregnant women, as well as women during menstruation (with heavy blood loss), suffer from anemia.
If ferritin levels decrease during pregnancy, the child may suffer from oxygen starvation, and after birth the baby will experience developmental abnormalities. And during anemia, premature birth or early miscarriage cannot be ruled out.
Ferritin concentration in the body
The main sign of a decrease in the level of the protein complex - ferritin - is hair loss. As you know, it is the hair follicles that actively consume Fe. With its deficiency, hair weakens and begins to fall out. If you experience uncharacteristic increased hair loss, it is recommended to consult a specialist and donate blood for analysis. Otherwise, significant hair problems are observed, including alopecia.
What needs to be done?
To normalize ferritin levels, it is necessary to review the diet and include foods high in iron. Additionally, you should visit a doctor to prescribe a mineral-vitamin complex. To keep all indicators normal, you must not forget about sports activities and proper healthy nutrition.
Iron content in foods
Video: Iron deficiency, how to replenish it
Features during pregnancy
The level of ferritin in the blood of women decreases during pregnancy. The standard values are different for each trimester.
| Trimester | Minimum permissible value μg/l | Maximum permissible value µg/l |
| I | 55 | 90 |
| II | 25 | 75 |
| III | 10 | 15 |
A decrease in ferritin value occurs due to an increase in iron concentration in the tissues of the placenta and fetus . Along with a decrease in serum ferritin, an increase and complete saturation of transferrin is observed. The main catalyst for accelerating Fe metabolism is estradiol (a component of estrogen).
The norm of ferritin in the blood of women during pregnancy is valid only when hemoglobin is not lower than 70. If hemoglobin is lower, ferritin can concentrate in the tissues.
If ferritin, hemoglobin and transferrin are low, and there are no signs of iron deficiency anemia - there is enough iron in the soft tissues - treatment should be aimed at increasing hemoglobin. If ferritin is low and signs of elevated levels are present, treat associated symptoms.
Table of changes in ferritin levels during pregnancy
Ferritin levels decrease during pregnancy; this is a physiological process. This happens because iron reserves from tissues are spent on the needs of the fetus.
Table of ferritin levels in the blood for women during pregnancy.
| Trimester | Normal for non-pregnant women |
| First | 50% |
| Second | 30% |
| Third | 12% |
Lack of iron in a pregnant woman leads to impaired fetal development and premature birth. When preparing for pregnancy, you need to study ferritin. Its deficiency leads to disruption of the formation of sex hormones. This becomes the cause of female infertility.
Increased levels of ferritin in the blood of women during pregnancy require additional examination. This may indicate a developing disease.
Ferritin levels during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the mother's iron reserves are used up to meet the needs of the growing baby and placenta. It is imperative to replenish the loss of iron, which is necessary to increase the number of red blood cells in the blood, as well as to replenish iron losses during childbirth due to bleeding.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), during pregnancy, anemia is diagnosed when the hemoglobin level is less than 110 g/l, or the hematocrit level is less than 33%.
If a pregnant woman does not have anemia, then iron deficiency is diagnosed when the ferritin level is less than 15 ng/ml. In the presence of anemia during pregnancy (if other causes of anemia have been excluded), a ferritin level of less than 40 ng/ml indicates iron deficiency anemia. [1]
Norm of ferritin in a child
Ferritin standards for children differ from those for adults:
| Ferritin | ||
| Age | Reference interval (ng/ml) | |
| At birth | 25-200 | |
| 1 month | 200-600 | |
| 2-5 months | 50-200 | |
| 6 months – 15 years | 7-140 | |
Not all laboratories have the same range of reference values, so it is worth focusing on the indicators directly from the laboratory in which the study was performed.
Ferritin levels in men and children
The indicator under consideration depends on the patient’s age and gender. Therefore, when selecting acceptable values, the doctor will definitely take them into account. The maximum protein content is observed in infants. Thus, the level of ferritin in the blood in the first 2 months reaches 600 mcg/l.
Then its value gradually decreases. At the age of 2 months to six months, normal values range from 55 to 210 mcg/l.
After six months, the indicator is quite stable up to 15 years. Its normal value varies from 8 to 143 μg/l.
After the onset of puberty in a young man, the reference values are: 21 – 250 mcg/l.
Danger of deviation from the norm
Dangers of low ferritin:
- Fall in blood pressure – weakness – fainting.
- Kidney failure, fragility of blood vessels.
- Hardening, loss of elasticity of bone tissue.
- Uncontrolled muscle contractions.
- Decreased immunity – increased likelihood of an infectious disease; lack of reaction to viruses and bacteria that have entered the body.
- Dehydration of the body.
- Impaired intestinal motility.
- Blood thinning.
The dangers of elevated ferritin:
- Creating a favorable environment for the development of cancer cells.
- Reducing the life of cells - accelerating the process of division and premature wear and tear of the body.
- Tendency to arthritis, rheumatism and other collagen diseases.
- Heart attacks, strokes due to fragility of blood vessels.
- Thickening of the blood - the formation of blood clots.
- Formation of cholesterol plaques; sclerosis, atherosclerosis.
- Damage to soft tissues – 400 and above or above 250 for more than six months.
- High tendency to suppuration.
The likelihood of tumors, regardless of benignity, increases with both excess and deficiency of ferritin. In the first case, due to the high rate of oxidative reactions; in the second - lack of fluid in the tissues. Elevated ferritin leads to sepsis, and decreased ferritin leads to necrosis.
If ferritin is elevated during necrosis, necrosis is the cause of its increase, and not vice versa. During menopause, it is necessary to monitor the ratio of ferritin and estrogen levels: high estrogen with low ferritin, or vice versa - adjust the hormone level. If estrogen is normal, adjust ferritin.
Why is a high ferritin index dangerous?
An increased ferritin concentration index in the blood serum can provoke the cardiac pathology cardiosclerosis, in which an increase and proliferation of fibrous tissue cells occurs.
The muscle of the cardiac organ becomes dense in its structure, its elasticity disappears, and it cannot efficiently perform its functional duties.
Cardiosclerosis can develop into a complicated form of ischemia of the heart muscle, as well as myocardial infarction.
A low serum ferritin concentration is dangerous in a complicated form:
- Anemia of iron deficiency type, as well as hemolytic nature,
- Hypoxia of internal organs and the blood flow system, which can provoke coronary insufficiency and myocardial infarction,
- During pregnancy, it causes hypoxia and the risk of miscarriage in the 1st trimester; underdevelopment of the physical and mental state of the fetus in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters.
Reduced ferritin standards
A decrease in ferritin occurs when the level of iron ions in the blood serum is low and sufficient hemoglobin is not produced to fill red blood cell molecules.
In this condition, the transport of oxygen throughout the body is disrupted and a pathology occurs - anemia.
Serum iron and its low index indicate that iron reserves in the body are depleted, and drastic measures must be taken to replenish them.
A low index of this protein indicates the following causes of pathology and disorders:
- Deficiency of iron ions in food;
- Improper functioning of the intestines (pathology malabsorption syndrome);
- Iron deficiency anemia;
- Anemia of another etiology;
- Anemia of the hemolytic type, which develops together with the pathology of intravascular hemolysis;
- During pregnancy (especially in the 3rd trimester);
- Nephrotic kidney syndrome.
If the amount of hemoglobin is reduced and oxygen transport is impaired, then hypoxia of the cells of internal organs and tissues develops in the body.
If the hemoglobin index does not fall below 100.0 g/l, then the body does not feel a low ferritin ratio.
When the level of these two proteins is low, the following symptoms occur in the body:
- Dizziness;
- Dyspnea;
- Headache;
- Sudden attacks of apathy;
- Irritability;
- Increased heart rate;
- Weakness in the lower extremities;
- Painful sensations in the heart organ;
- Pale skin;
- Dry skin and hair;
- Insomnia;
- Fatigue of the whole body.
With such symptoms, it is necessary to undergo a diagnostic test to determine the concentration of these proteins in the body and visit a doctor for timely treatment.
When anemia develops in a deep state, a person experiences the following symptoms:
- Ulcers in the corners of the lips;
- Burning on the tip of the tongue;
- Changes in the nail plate;
- Desire to eat chalk, as well as red and white clay;
- Blueness in the eyeballs;
- Increased sensitivity to low air temperatures;
- Enlarged organ - spleen;
- Colds that occur systematically;
- Purulent lesions on the skin;
- Constipation or diarrhea;
- Partial loss of taste buds.
These signs characterize a deficiency in ferritin molecules and a deficiency in the accumulation of serum iron ions.
Ferritin index and pregnancy period
During the period of intrauterine gestation, a woman rapidly loses the concentration of ferritin in the serum fluid.
In the first trimester, the decrease rate is 50.0% (2 times), the second trimester is another 20.0% higher, and by the third trimester the loss amounts to 80.0% of the total concentration of this protein (10 times).
Factors that contribute to the rapid decline of this substance:
- Poor nutrition during pregnancy;
- Pathology hyperpolymenorrhea;
- More than 1 child develops at the same time;
- More than 4 pregnancies during life;
- Bleeding during intrauterine gestation;
- Diseases in the body that are caused by impaired absorption of iron;
- Chronic diseases;
- Worms;
- Neoplasms of a malignant nature.
Low iron index affects the baby in the womb.
Ferritin deficiency can provoke anemia, which causes intrauterine hypoxia, which threatens:
- The body's own termination of pregnancy;
- Intrauterine disorder in the fetus in the formation of hemoglobin protein;
- Anemia in the fetus;
- Physical intrauterine underdevelopment;
- Deviations in mental abilities;
- Hypoxia of body cells, which has entered the chronic stage;
- Low immunity.
When does hair fall out?
Many men, and especially women, experience hair loss (on the scalp). There is no positive result when taking anti-hair loss medications. The cause of this pathology is a violation in the concentration of ferritin in the serum.
In order to cope with this problem, you need to know at what level hair falls out and becomes dull.
Hair loss occurs with a reduced ferritin index and with hemoglobin below normal.
Low iron serum levels weaken the hair roots, follicles become weak and hair loss occurs. The body simply compensates for iron when iron ions are taken from the hair to supply vital organs and life support systems.
IDA treatment regimen
Preventive actions
With a low ferritin index, as well as with a high one, it is necessary to adjust the diet. You should also treat chronic pathologies that can affect ferritin levels.
Preventive measures include diagnosing the state of the blood composition and the concentration of iron in it, which affects the ferritin index.
Engage in moderate physical activity, give up alcohol and smoking.
During pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo laboratory testing in every trimester.
The protein ferritin has an impact on many vital processes in the body, so its concentration within the normative limits is the balance of all organs of the body and the uninterrupted operation of all its systems.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, which is related to the level of serum iron in the body, it is necessary to undergo a diagnosis to identify the ferritin index.
For laboratory testing, it is necessary to donate venous blood:
- In biochemical analysis for ferritin;
- Radioimmunoassay;
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA);
- Fluorescence test;
- Hemoglobin analysis;
- Transferrin test;
- General blood analysis.
The normal concentration of a ferritin molecule of 1 mcg/l is equal to 8 milligrams of serum iron in the body.
In addition to laboratory verification, when Ferritin is deciphered, deviations from the normal ferritin index are identified, it is necessary to undergo instrumental testing:
- ECG (electrocardiography);
- Ultrasound of the heart organ;
- Ultrasound of the liver;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- Ultrasound of the peritoneal organs.
The instrumental technique reveals the etiology of disturbances in the level of ferritin molecules in the blood serum, and the consequences of a high or low index of this protein on organs.
Price for ferritin diagnostic test
| type of study per indicator | price in Russian rubles | cost in Ukrainian hryvnia |
| iron | 20 | 45 |
| transferrin | 520 | 120 |
| ferritin | 540 | 150 |
| ceruloplasmin | 610 | 200 |
Life forecast
With a low ferritin index, the heart organ does not receive the required amount of nutrition, so the heart muscle is depleted. Working hard, the heart increases in size, its walls hypertrophy.
Therefore, in this state, the myocardium needs the necessary dose of nutrition for proper functioning. With timely diagnosis and correction of the ferritin and hemoglobin index, the prognosis for life is favorable.
If you do not pay attention to the level of ferritin protein, then necrosis occurs in the exhausted heart muscle.
In the bloodstream system, due to deficiency of iron and ferritin, hypoxia occurs, leading to anemia, improper functioning of the heart valves, which develops coronary insufficiency and myocardial infarction, the prognosis for life is not favorable.
How to interpret the results of the analysis?
| Indicators | Norm | Latent iron deficiency | Iron-deficiency anemia |
| Hemoglobin, g/l: | |||
| men | 132 – 180 | > 130 | < 130 |
| women | 120 – 160 | > 120 | < 120 |
| Serum iron, µmol/l: | |||
| men | 9,4 – 29,9 | < 7,5 | < 7,5 |
| women | 8,7 – 27,0 | < 6,0 | < 6,0 |
| THC, µmol/l | 44,7 – 71,6 | > 71,6 | > 71,6 |
| Ferritin, µg/l: | |||
| men | 30 – 400 | < 40 | < 12 |
| women | 13 – 150 | < 20 | < 10 |