Acute tonsillitis is a pathological process that is fraught with serious complications and often becomes chronic. To prevent this from happening, it is important to know the primary manifestations of the disease: how it progresses and how it can be prevented.
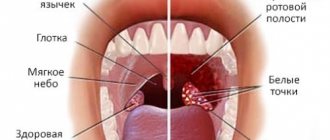
In the human throat, the tissue of several tonsils forms a lymphoid ring, which is a kind of protection against external pathogenic microorganisms. Sometimes, more often when immunity decreases, the tonsils cannot cope with numerous viruses and bacteria and begin to become inflamed. This is how tonsillitis or acute tonsillitis occurs.
Why does the disease occur?
The main reason is the entry of pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, fungi, bacteria) into the body through airborne droplets or household contact. Normally, lymphoid tissue should cope with them, but sometimes viral attacks are too frequent. Then the exhausted immune system fails, and the tonsils begin to increase in size, which leads to their inflammation and swelling.
In most cases of primary tonsillitis, a streptococcal infection is to blame. If fungal tonsillitis occurs, the cause is infection with fungi of the genus Candida. In rare cases, mold fungi are detected.
Factors that provoke the disease include:
- hypothermia of the body;
- frequent colds;
- decreased immunity;
- pathology or injury to the tonsils;
- untreated acute respiratory viral infections;
- problems with nasal breathing, including chronic runny nose;
- advanced caries and other pathological processes of the oral cavity;
- long-term use of chemotherapy drugs.
Conditions such as diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the circulatory system, cancer and gastrointestinal diseases can also contribute to the development of tonsillitis.
You can become infected with a sore throat through airborne droplets, for example, through communication with a sick person. The risk of infection is highest in the spring and autumn, when the body is weakened due to a lack of vitamins or frequent colds. The pathogen enters through the upper respiratory tract, and the first symptoms appear 1-2 days after infection.
Classification of the disease
Depending on the cause and symptoms, the following forms of acute tonsillitis are distinguished.
- Catarrhal - occurs easily. Usually painful symptoms disappear after 5 days. It rarely has complications, but can develop into other forms of sore throat. Characterized by slight swelling of the palatine tonsils.
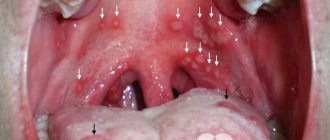
- Follicular - acute purulent tonsillitis - is characterized by soreness of the lymph nodes, and also purulent round formations (follicles) appear on the tonsils. The disease lasts up to 5-7 days.
- Lacunar - this form is characterized by the development of an inflammatory process in the recesses of the tonsils (lacunae) with the formation of pus.
- Ulcerative-membranous - symptoms include the formation of ulcers on the tonsils. Ulcers spread to the soft palate, oral mucosa, and also affect the larynx. Possible bleeding and inflammation of the periosteum.
These are primary forms of the disease that occur independently, but secondary ones can also occur. These types of tonsillitis occur against the background of another underlying disease. For example, acute tonsillitis is characteristic of leukemia, measles, scarlet fever or mononucleosis.
What causes purulent tonsillitis
The cause of damage to the palatine tonsils can be viral, bacterial, or fungal influences. But only bacterial infections can cause a purulent form of tonsillitis.
The purulent form of the disease is characterized by a more severe course and a high risk of complications.
Inflammation of the palatine tonsils occurs most often, compared to other tonsils of the pharyngeal ring.
The tonsils are the first organ to encounter bacterial infectious agents. They are involved in the fight against various infections and help produce protective antibodies.
With frequent massive infectious attacks, the tonsils may not cope with their function, and then inflammation of the lymphoid tissue develops.
If the process is chronic, then the inflammation is constant. The tonsils lose their ability to cleanse themselves.
Some negative factors contribute to the occurrence of inflammation in the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils:
- general and local hypothermia;
- decreased immunity, also general and local;
- frequent inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- poor nutrition;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- reduced content of vitamins;
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx, ears, sinuses;
- contaminated air;
- dental caries.
The purulent form of tonsillitis most often becomes chronic if the acute inflammation is not treated and preventive measures are not followed.
Infection occurs from a person with signs of acute inflammation of the tonsils, or a carrier of pathogenic bacteria.
When sneezing, coughing, sharing utensils, or household items, bacteria enter the mucous membranes. As a result, after the bacteria enter the mucous membrane, inflammation occurs.
Important to know: Chronic compensated tonsillitis
Acute tonsillitis: symptoms and diagnosis
The primary form of the disease is characterized by the following manifestations:
- sore throat of varying intensity;
- swelling, redness of the tonsils;
- sore throat;
- chills, fever;
- enlarged lymph nodes and their pain when pressed;
- difficulty in nasal breathing, possible purulent nasal discharge;
- the appearance of small formations or ulcers on the mucous membrane of the mouth, palate (in the follicular and ulcerative-membranous form).
Body temperature in the first days of illness can rise to 39–40 °C. However, in some cases, tonsillitis can occur with a slight fever, so a characteristic symptom of acute tonsillitis is severe pain when swallowing and inflammation of the tonsils.
If symptoms appear, you should contact an otolaryngologist or therapist. The doctor conducts a visual examination, studies the patient’s complaints and life history.
The standard set of diagnostic measures includes:
- Endoscopy of the nasopharynx - examination of the ENT organs using an endoscope.
- A swab from the throat, as well as from the surface of the affected tonsil. This is necessary to identify the causative agent of the disease.
- A clinical blood test allows you to determine the primary or secondary nature of tonsillitis.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe an immunoserological test, which allows you to assess the state of the immune system.
What is the difference between tonsillitis and tonsillitis and how to diagnose and treat the disease
What is the difference between tonsillitis and tonsillitis? A similar question can often be heard in the office of an otolaryngologist.
Patients try to understand which of the two diseases is more dangerous.
In reality, both diseases have the same roots. One of them is a more acute form of the other.
Signs of tonsillitis
The disease is characterized by inflammatory processes in the throat caused by certain viruses and bacteria. It is different from sinusitis. This is not the result of a complication from a respiratory illness or the flu.
The impetus for the development of the disease can be hypothermia, decreased immunity, prolonged stress or lack of vitamins.
During the course of the disease, inflammation localizes in the lymph nodes of the pharynx, and damage to the tonsils is observed.
Tonsillitis can be chronic or acute. The disease in its acute form is called tonsillitis. It is an infectious disease.
The inflammatory process is localized in the tonsils. Sore throat is characterized by bacterial etiology. A purulent plaque or caseous plugs form on the tonsils.
The disease is often accompanied by serious complications. Therefore, the issue of timely detection of the disease and its treatment becomes important.
Signs of a sore throat
The disease may be accompanied by:
- Headache;
- Pain when swallowing;
- Increase in temperature;
- Painful sensations in the joints;
- Difficulty breathing;
- General weakness and poor health;
- Reluctance to eat;
- Enlarged lymph nodes;
- Plaque on the surface of the tonsils and their enlargement.
Forms of chronic tonsillitis
When answering the question of how tonsillitis differs from tonsillitis, it is necessary to consider the various forms of the disease. The disease may have:
- A simple form, which is accompanied by symptoms of a local nature;
- Toxic-allergic form. After it, complications may occur in the kidneys, heart or joints.
The symptoms that characterize chronic tonsillitis are similar to the acute form (tonsillitis).
But the disease is not so pronounced. It is characterized by the presence of:
- Nasopharyngeal congestion;
- Unpleasant odor;
- Headache;
- Pain during swallowing;
- Enlarged red tonsils;
- General malaise;
- Plaque on the surface of the tonsils.
The symptoms that characterize chronic and acute tonsillitis include the following:
- The palatine tonsils are significantly enlarged;
- A white or yellowish coating forms on them, purulent plugs and ulcers may appear;
- The color of the tonsils becomes bright red.
The difference between a sore throat and tonsillitis
The diseases differ in the nature of the manifestation of the main symptoms. With angina they are pronounced. It becomes very painful to swallow, the pain immediately takes on an acute form. There is a sharp increase in temperature.
Plaque or purulent foci form on the tonsils. The joints begin to ache. The headache gets worse.
The disease is characterized by the presence of serious complications. They affect the immune system and can affect the heart, kidneys and joints.
It is important to remember this and after recovery, conduct a general examination of the body.
Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by inflammatory processes that have a sluggish form. The inflammation may subside and resume again.
This material may also be of interest to you:
Chronic disease is not always accompanied by fever. Caseous plugs form on the tonsils.
The main difference between chronic tonsillitis and tonsillitis is the presence of a stuffy nose.
Distinctive features in the treatment of diseases
When deciding how tonsillitis differs from tonsillitis, you should consider possible methods of treating the disease.
To prevent serious complications from occurring after an illness, it is necessary to apply correct and timely treatment.
Outpatient methods are most often used to treat angina. Only in severe forms do they resort to hospitalization.
Complex therapy necessarily includes antibacterial drugs. It is usually recommended to gargle regularly using herbal decoctions and medications.
It is necessary to drink a lot and eat foods containing vitamins B and C.
The chronic form is treated using immunocorrective drugs, biostimulants and antiseptics.
Antibiotics are used only in cases where there is a risk of complications.
You should lead an active life, exercise, and maintain a proper diet. Physiotherapeutic procedures are used to improve the general condition.
Possible complications
The course of acute and chronic forms of the disease can lead to serious complications. The most dangerous is endocarditis. During the course of the disease, the inner lining of the heart and valves are affected.
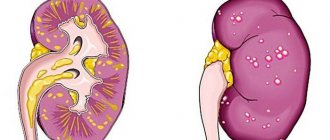
You should also be wary of rheumatic fever and kidney damage. Such complications are quite rare. More often, otitis media, laryngeal edema or abscess occurs.
It is important to prevent the infection from spreading to the chest area. In such a situation, mediastinitis may develop. Meningitis occurs when the meninges become inflamed.
This can occur as a result of infection entering the skull. As a result of the vital activity of streptococci, harmful toxic substances are formed.
How to diagnose and treat the disease
There are usually no difficulties in diagnosing the disease. The diagnosis is based on the patient’s complaints, external examination of the throat, and laboratory test results.
Symptoms of the illness may be similar to flu or respiratory illness. Sometimes they proceed the same way.
There may be an increase in temperature and pain when swallowing. But during the course of influenza or ARVI, enlargement of the lymph nodes rarely occurs.
To determine the specific pathogen, you should take a swab from the throat. The material is taken from purulent discharge from the surface of the tonsils or mucus.
This may also be useful to you:
For the most effective identification, PCR is used. In this way, DNA sections of the pathogen are determined.
In addition, it is necessary to inoculate the nutrient medium. This test determines sensitivity to the effects of a particular antibiotic.
Sore throat can be treated with conservative and radical methods. If bacteria are the causative agents, treatment is carried out using antibacterial drugs and antiseptics.
If there is a fungal etiology, medications that affect fungal formations are used. General and local therapy should be used.
The latter includes rinsing procedures with antiseptics and the use of sprays.
Antibiotics are discontinued only after the temperature has dropped and the full course of treatment has been completed. Complex therapy can be carried out using painkillers and antihistamines.
During treatment, bed rest is necessary. If decompensated tonsillitis is diagnosed, the tonsils are removed.
Based on the above, we can draw the following conclusion - the acute form of tonsillitis is practically no different from a sore throat.
If the latter occurs, serious complications are possible. In order to prevent this, antibacterial therapy is used.
Source: https://priangine.ru/chem-otlichaetsya-tonzillit-ot-anginy.html
Possible complications of the disease
If acute tonsillitis is suffered on the legs, it becomes chronic and difficult to treat conservatively. The main complications of the disease include:
- The spread of the infectious process into the chest or cranial cavity with the development of meningitis.
- Severe intoxication of the body, which can lead to shock and sepsis.
- Weakening of cardiac activity. Due to the high infectious load and a significant increase in temperature, the heart has to work to the limit, which subsequently leads to various malfunctions in the cardiovascular system.
- Kidney pathologies, up to renal failure.
- Pneumonia.
If a diagnosis is not made in time and treatment is not started, tonsillitis can lead to the development of acute otitis media, laryngeal edema, purulent inflammation of the neck tissue (phlegmon) and the formation of an abscess. These are dangerous conditions that in most cases require hospitalization. When an abscess forms, surgical treatment is necessary, since this condition threatens human life.
Treatment of acute tonsillitis
In most cases, the disease has a favorable prognosis and requires home care. In severe cases or if complications occur, hospitalization is recommended. Drug therapy gives good results. However, sometimes surgery is required.
General recommendations include:
- Isolation of the patient from healthy family members, especially children and the elderly, is mandatory.
- Bed rest is required. It reduces the load on the cardiovascular system.
- Nutrition should be gentle and include more plant foods.
- Drink plenty of fluids to reduce symptoms of intoxication. Fruit juice, pure or mineral water, and compotes are recommended.
Depending on the cause of the disease, antiviral or antibacterial medications are prescribed. If complications arise, infusion therapy is carried out, that is, solutions with glucose are used. At high temperatures, you can take antipyretic medications and analgesics. Medicines are prescribed only by a doctor after laboratory diagnostics.
Local treatment
To reduce pain and inflammation in the throat, using various gargles and irrigations with medications is effective.
Recommended recipes:
- herbal decoctions of chamomile, calendula, sage;
- rinsing with soda or saline solution;
- a compress of dimexide solution on the area of the lymph nodes if there is no high body temperature.
Among pharmaceutical preparations, absorbable antiseptic lozenges or tablets provide a good local anesthetic effect. They contain menthol, which has a slight cooling and soothing effect. If a stronger effect is required, the doctor prescribes medications that include lidocaine. It has an anesthetic effect for a longer period of time.
Treatment is prescribed by an otolaryngologist. If necessary, for example, if an abscess develops or heart problems occur, other specialists are involved - a surgeon, a therapist, a cardiologist.
Differences in treatment
To combat chronic tonsillitis, it will take much more effort and time than to deal with its acute form. Important directions in the fight against this pathology should be considered:
- use of antiseptic drugs;
- physiotherapy;
- use of immunomodulators;
- prescription of antihistamines;
- vitamin therapy, etc.
Antibacterial drugs for chronic tonsillitis are prescribed during the period when various complications occur. The patient's condition improves significantly when physiotherapeutic measures are carried out: UHF, ultrasound, ultraviolet irradiation of damaged tonsils.
After recovery, a patient with chronic tonsillitis should lead an active life, eat right, play sports, and strengthen his body to get lasting results.
- antibacterial therapy to eliminate pathogenic microflora;
- use of local aerosol antiseptics;
- frequent rinsing with a solution of medicinal herbs;
- drinking plenty of water;
- consumption of foods containing vitamins B and C.
A special gargling solution based on medicinal herbs and iodine effectively cleanses a damaged throat from purulent plaque. This solution must be applied several times a day, especially in the morning and after each meal. Additional consumption of vitamins B and C will improve immunity and speed up recovery.
Treatment of angina is most often carried out on an outpatient basis with bed rest. If, after following all the doctor’s recommendations, there is no improvement in health for a long time, then the patient is urgently hospitalized in a medical facility for more radical treatment. He undergoes a simple surgical operation to remove his tonsils.
Thus, tonsillitis and chronic tonsillitis, being related diseases, have a number of differences in symptoms and treatment.
Preventive actions
Malicious microorganisms attack the human body every day. But not every person experiences acute tonsillitis. To prevent the development of the disease, you need to improve your health and take care of your immune system.
General strengthening recommendations include:
- hardening of the body, including local gradual adaptation of the larynx to cold temperatures;
- physical activity in the fresh air;
- to give up smoking;
- proper nutrition and taking multivitamin complexes;
- after-treatment of colds.
To reduce the risk of household infection, you need to follow hygiene measures, that is, wash your hands, vegetables and fruits with boiled water. In the autumn-spring period and during the epidemic, do not neglect safety measures.
- avoid crowds of people;
- use local antiviral agents;
- limit contact with sick people.
Also, to prevent tonsillitis, it is necessary to sanitize the oral cavity in a timely manner and not to cause diseases of the nasopharynx.