Chlamydia is a disease caused by chlamydia. There are several ways of becoming infected with chlamydia: they can be transmitted sexually, from mother to child, during sexual intercourse, and also through airborne droplets. Chlamydia is dangerous to human health: if it affects the genitals, it can lead to serious complications, such as infertility. The next article will provide detailed information on how chlamydia is transmitted. You will also learn about methods of treatment and prevention of chlamydial infection.
Characteristic
Chlamydia is an infectious disease that is sexually transmitted. It is caused by chlamydia. This is one of the most common pathologies transmitted through intimate relationships. One hundred million people are infected with this infection every year, while the number of those infected with chlamydia is about a billion. Every year the number of victims of the disease increases, which is due to the absence of its specific symptoms, which do not appear at the initial stage. Many people wonder whether chlamydia is transmitted through kissing. This is possible if you kiss immediately after oral sex.
Infection at home
Most people are interested in the question of whether chlamydia is transmitted through household contact. In some cases this is quite possible. An infection such as chlamydia is very insidious and secretive . Everyone needs to know how this disease is transmitted in everyday life. Although chlamydial bacteria are almost not viable in dry or cool air, they can survive for quite a long time in a humid and warm environment.
If a family member has chlamydia, the household route of infection may include infection through personal hygiene items. Therefore, you should always use only your own toothbrush, towel and razor.
Chlamydia can also remain on the bedding and clothing of an infected person. The household route of transmission of infection in this case is through the use of other people's personal belongings and bedding. This can also occur during sexual intercourse while using a condom. The contact itself was protected, but the infection remained on the bed.
Many people are afraid of contracting a chlamydial infection when visiting a pool or swimming in bodies of water. This fear is not justified, since in large quantities of water the concentration of bacteria is very low, so infection cannot occur.
To avoid becoming infected with chlamydia, you need to remember the risks of contracting this infection and how it is transmitted. It is also necessary to be regularly examined for the presence of chlamydial infection in order to detect the disease in time and take treatment measures.
Chlamydia
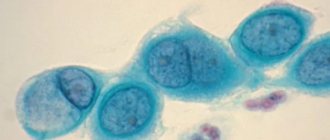
Chlamydia are coccoid, gram-negative, nonmotile organisms that primarily affect the genitourinary system. These organisms are capable of parasitizing the cells of the human body for a long time. This possibility is reinforced by the fact that they can “hibernate” under the influence of colds, antibiotics and hypothermia. In addition, dormant chlamydia are transmitted to daughter cells during cell division. In this case, exit from the sleeping state is carried out only with absolute suppression of the protective forces of the human body. So how is chlamydia transmitted?
Complications
- Reiter's disease (urethro-oculo-synovial syndrome) is characterized by a triad of symptoms: arthritis. Also with the syndrome, various types of skin lesions and circinar balanoposthitis occur.
- Urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra due to scarring of the urethral mucosa, the only treatment for which is surgery.
- Orchiepididymitis, leading to narrowing of the sperm ducts and death of Leydig cells, which leads to the cessation of spermagenesis (sperm production) and male infertility.
- Chronic prostatitis, leading to the death of glandular tissue of the prostate gland, narrowing of the prostate ducts, changes in the quantity and quality of prostate secretion, which leads to immobilization and rapid death of sperm.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women - chlamydial infection can penetrate the uterus, uterine appendages, fallopian tubes of a woman causing an inflammatory process there - endometritis, salpingoophoritis, salpingitis. A distinctive feature of chlamydia is the formation of scars and adhesions in the fallopian tubes, which is the cause of ectopic pregnancy and tubal infertility.
The presence of chlamydia often leads to premature termination of pregnancy (miscarriages); the danger is infection of the fetus during childbirth (up to 40%). The main forms of manifestation of chlamydia in newborns (congenital chlamydia):
- Ophthalmochlamydia (20%) - conjunctivitis with inclusions.
- Chlamydial pneumonia of newborns (20-25%).
- Generalized chlamydia with damage to the lungs, heart, liver, and gastrointestinal tract.
- Encephalopathy with convulsions, apnea.
- Chlamydial pneumonia of newborns - infection of a newborn with chlamydia during childbirth from a sick mother often leads to pneumonia (pneumonia) with an extremely severe course and high mortality.
- Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome (English) - it is considered an early complication of chlamydial infection. It manifests itself as acute peritonitis and perihepatitis, accompanied by ascites and can occur without the manifestation of PID.
Methods of infection
This infection is transmitted through sexual contact, but unlike gonorrhea, where an infected partner can infect three out of four partners, chlamydia can be transmitted to one partner out of the same number. Women are the most susceptible to this pathology.
The main route of infection with chlamydia is through anal or vaginal intercourse. The incubation period for this disease can vary from two weeks to a month. A child can also be infected during passage through the birth canal if the woman is sick. There is a possibility of infection through contact and household methods. According to the tests, chlamydia can survive on household items or fabrics for up to two days at a temperature of 19-20 degrees Celsius. You can check with your doctor about how chlamydia is transmitted.
How can you become infected with chlamydia?
Among the factors that are taken into account when determining the routes of transmission of chlamydia are:
- resistance of bacteria in the external environment,
- state of immunity,
- types of causative agents of chlamydia.
Most often, patients encounter the urogenital form of the disease, which is transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse. For many, it is asymptomatic. Patients learn about infection when undergoing preventive examinations or when secondary infections occur, in which the symptoms are pronounced.
The genitourinary system is predominantly affected by chlamydia trachomatis, but the routes of transmission vary depending on the antigenic serotypes:
- trachoma (conjunctivitis) is caused by subtypes A, B, C, Ba,
- urogenital infections and conjunctivitis are caused by subtypes E, F, D, G, H, I, J, K,
- Lymphogranuloma venereum is provoked by serotypes L1, L2, L3.
The columnar epithelium that lines the urethra is most susceptible to chlamydia. In 2nd place is the mucous membrane of the eyes. Therefore, these organs are most often affected.
The main routes of transmission of chlamydia:
- sexual,
- domestic,
- airborne,
- intrapartum,
- antenatal.
Despite the fact that chlamydia is considered a sexually transmitted disease, it is not transmitted through every unprotected contact. You can become infected through vaginal sex, as well as oral or anal sex.
During oral sex, bacteria can enter the throat from infected genitals and cause the development of chlamydial pharyngitis. This method can infect women and homosexual men with chlamydia. But this form of pathology rarely develops; the likelihood of infection is higher during normal vaginal contact. During anal sex, rectal cells can be affected.
One of the rare ways of transmitting chlamydia is infection through kissing through saliva. But for this the following conditions must be met:
- increased concentration of bacteria in saliva,
- infection in the mouth,
- weakened immunity of the partner.
Comment! The risk of infection through saliva exists only if the patient has a generalized form of chlamydia, and the pathogen penetrates all biological fluids and tissues of the body through the blood. Only a few such cases have been described in the history of medicine.
Airborne transmission of chlamydia is also possible. This is how the respiratory form of the disease can be transmitted. The source of infection will be a person suffering from chlamydial pneumonia. When coughing and sneezing, pathogens are released into the air through mucus. But it is difficult for a healthy person to become infected; only people with weakened immune systems are at risk.
The most dangerous methods of infection with chlamydia are considered to be intrapartum and antenatal routes. Intrapartum infection occurs when a baby passes through the mother's birth canal contaminated with bacteria. As a result, the newborn baby becomes infected with chlamydia. In the absence of necessary prevention, the risk of infection reaches 70%.
A child may develop the following chlamydial pathologies:
- conjunctivitis,
- pneumonia,
- proctitis,
- urogenital chlamydia.
The antenatal method of infection means that the bacteria reach the fetus in utero. Chlamydia is transmitted through the placenta and amniotic fluid in cases where the mother's infection during pregnancy affects the lining of the uterus (endometrium). With such infection there is a high risk of premature birth, developmental defects and intrauterine fetal death. Complications can be prevented if you plan your pregnancy and treat infections in advance.
Main manifestations in women
Chlamydia often occurs either without symptoms at all, or they are not clearly expressed. There are specific manifestations that are characteristic of men, and those that occur in women. So, how does chlamydia manifest?
Patients suffering from chlamydia, in some cases, complain of the appearance of mucopurulent or mucous discharge from the vagina. They have a purulent yellowish color and an unpleasant odor. In some cases, pain is observed in the area of the external and internal genital organs, and this may intensify before the onset of menstruation. Often patients complain of itching and burning of the external genitalia. In some cases, women experience pain during urination, and sometimes they experience bleeding between menstrual periods. Often there are signs of general intoxication, expressed in an increase in body temperature to 37.5 degrees and general weakness.
Below are the symptoms of chlamydia in men.
What is chlamydia
Urogenital (genitourinary) chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection caused by chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis). The problem of urogenital chlamydia is very acute today. In recent years, there has been an increase in chlamydia both among the sexually active adult population (men and women from 20 to 40 years old) and among teenagers.
Early sexual relations, unprotected sex with casual partners, and lack of awareness about the possible consequences of such relationships place chlamydia at the top of the list of sexually transmitted infections. Almost 90 million people become infected with chlamydia every year.
Persons with reduced immunity are especially susceptible to chlamydia. In 40% of cases, chlamydial infection causes various gynecological diseases, and in 50% – tubo-peritoneal infertility.
The combination of several infections aggravate each other and prolong treatment. Women are more susceptible to chlamydia. The most common route of transmission of chlamydia is sexual.
Infection of a newborn is possible during childbirth; it is accompanied by the development of congenital chlamydia in the child. Much less common is the household route of transmission of chlamydia in the family through bedding and toiletries, underwear, etc. Typically, 1-2 weeks pass from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first symptoms of chlamydia (rarely up to 1 month).
The causative agent of urogenital chlamydia, Chlamydia trachomatis, is a small bacterium that parasitizes inside human cells. Chlamydia can exist in the human body for a long time and not manifest itself.
When the defenses are suppressed and the body is weakened, they begin to actively multiply and cause clinical manifestations of chlamydia. There are 15 different types of chlamydia known to cause damage to the eyes, lymph nodes, genitourinary organs, etc.
Characteristic signs in men
In men with chlamydia, at the beginning of the disease, the urethra - the urethra - becomes inflamed. Often representatives of the stronger sex are disturbed by slight glassy discharge from the urination channel. In addition, itching, burning and pain appear. As in women, the temperature may rise slightly and general weakness is observed. Some men complain of spotting during ejaculation, as well as at the end of urination. Often, a person can be a carrier of the infection if microcolonies of chlamydia remain on his mucous membranes, the detection of which is possible only during the implementation of high-precision research methods. This situation may be due to the fact that the human immune system inhibits the reproduction of these microorganisms.
Can you get chlamydia through a condom? If used correctly, infection is impossible.
Sexual route of infection
There are different ways of transmission of chlamydial infection. The most common way to become infected with chlamydia is through unprotected sex with an infected partner. With one-time contact, chlamydia is transmitted in approximately 60% of cases, with repeated contact - 100%.
People with reduced immunity are most at risk of contracting a sexually transmitted infection. In this case, the virus almost instantly invades human cells. A strong immune system will prevent the infection from developing quickly, thereby smoothing out the possible symptoms of the disease. But in any case, an infected person without proper treatment and protection will become a spreader of chlamydia.
Infection is also possible through oral and anal contact. In such cases, its effect is even more harmful, since the infection affects the intestines and respiratory organs.
Using condoms during sexual intercourse significantly reduces the risk of infection. But with any defect or improper use, infection remains almost inevitable.
The most reliable way to protect yourself from chlamydia is to avoid promiscuity and have a regular sexual partner.
Diagnostic methods
Detecting the presence of chlamydia is quite difficult, because such microorganisms are parasites inside the cell, and to diagnose this disease, it is necessary to analyze scrapings of the cells of the inflamed organ. Semen, urine and blood are also examined. The simplest diagnostic method is a mini-test for chlamydia, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. But the accuracy and reliability of this method is only 20%, that is, you should not rely on its results.
In many gynecological departments and public clinics, a smear is taken from the cervix, vagina and external opening of the urinary canal, all at once. In men, a swab is taken from the urethra and then analyzed. But the accuracy of such a study is 15%.
It is recommended to use a diagnostic method such as RIF - immunofluorescence reaction. With this method, material taken from the urethra or cervical canal is examined and analyzed under a fluorescent microscope. Chlamydia reveals its presence by glowing in the microscope lens. The RIF study provides an accuracy of up to 50%. But it will be useful only when the disease is already in its most active stage.
The most accurate method for detecting the presence of chlamydia is the polymerase chain reaction, or PCR. The accuracy of this method reaches one hundred percent.
We now know what causes chlamydia.
Symptoms, causes and treatment of chlamydia disease
Special pathogenic microorganisms - chlamydia, penetrating inside the human body, cause a disease such as chlamydia. They can affect any internal organ, but the most vulnerable place is the genitourinary system. Chlamydia symptoms are not pronounced, so it is difficult to immediately identify the disease.
Have you been trying to get rid of PARASITES for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of parasites by taking every day...
Read more "
Routes of introduction into body cells
What is chlamydia? This intracellular parasite infects any mucous surface inside the human body. They are small microorganisms with a round shape. A common cause of chlamydia is unprotected sex with a sick partner. Chlamydia becomes the causative agent of chlamydia.
What is chlamydia? Chlamydia chlamydia is a group of infectious diseases that can occur in acute and chronic stages.
Chlamydial infection manifests itself in different ways. When infected with chlamydia, the further course of the disease depends on the main route of penetration of microbes into the body. There are several ways of infection.
The most common and main route of transmission of chlamydia in humans is sexual.
Initially, the vagina begins to suffer. Gradually, the infection spreads to other organs of the reproductive system, which causes adhesions. The situation threatens the development of infertility, cystitis, and inflammatory diseases of the uterus. Any unprotected sexual intercourse becomes a source of infection. Infection can occur from a sick mother to a child during its passage through the birth canal. Chlamydial conjunctivitis or pneumonia occurs very often. There is a possibility of transmission of infection during gestation.
Transmission of chlamydia infection through contact and household contact cannot be ruled out. Using other people's personal hygiene items, dirty unwashed hands, or visiting public toilets can cause illness. Bacteria can maintain pathogenic activity outside the human body for up to two days.
The rarest route of infection is the airborne type. The source of infection is a patient who has been diagnosed with chlamydial pneumonia.
Variety of species
For chlamydia, symptoms and treatment depend on the type of bacteria identified. The following types of chlamydia are distinguished.
- Where does Chlamydia psittaci come from? This type of bacteria is transmitted by airborne droplets or through dust from birds. They are the ones who become carriers of the disease. The patient may develop inflammatory processes in the joints (arthritis), respiratory organs (pneumonia, bronchitis), kidneys (pyelonephritis), and heart disease.
- Chlamydia pneumoniae is transmitted by airborne droplets from an infected person to a healthy person. It most often provokes respiratory infectious diseases.
- Chlamydophila felis mainly affects cats, causing runny nose and conjunctivitis. Can also be transmitted to humans.
- Most people become infected with Chlamydia trachomatis. This type of chlamydia leads to diseases of various body systems. Most often, the result of chlamydia trachomatis is damage to the urogenital organs.
Identifying the type of bacteria will help further determine how chlamydia can be treated.
Manifestation of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease is difficult due to the fact that chlamydia symptoms are almost always absent. But this does not reduce the danger to the body. The latent course of the disease leads to severe consequences. Only a small percentage of the infected population exhibits symptoms of chlamydia.
For chlamydia, the incubation period can last from two weeks to a month. After this time, unpleasant symptoms may appear. How long does it take for chlamydia to appear after sexual intercourse with a sick partner? Signs may appear after 10-14 days, provided that a condom was not used during sexual intercourse.
The life cycle of chlamydia will look like this.
- Contact of microorganisms on the mucous surface of internal organs.
- Penetrating inside the cells, chlamydia begins to actively multiply. After a couple of days, the cell in which the bacterial activity took place dies.
- After the cells die, new microorganisms enter the space between the cells. The short cycle of chlamydia development continues here. After this, they begin to invade new cells. In place of the dead cell, an inflammatory process occurs.
Chlamydial infection in women can manifest itself in the form of inflammatory diseases associated with the reproductive system.
If chlamydia trachomatis is detected in women, the following diseases may develop.
You will be surprised how many parasites will come out if you drink a glass of regular...
Parasites will leave the body in 3 days! You just need to drink on an empty stomach...
Inflammation of the vaginal mucosa leads to the development of colpitis. The main signs of colpitis are painful, unpleasant sensations in the vaginal area. The disease can manifest itself as a burning sensation, discomfort, itching, discharge, pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. Body temperature rises slightly.
Damage to the cervix leads to cervicitis. During the examination, a specialist may note the increased size of the cervix, its swelling and inflammation. A complication is the development of erosion.
These inflammatory processes can be accompanied by endometritis and salpingitis. Very often, together with the disease chlamydia, other sexually transmitted diseases are found, for example, herpes, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea.
There are several distinctive features of how chlamydia manifests itself.
- The acute period of the disease is characterized by the fact that the body temperature remains at 37.5 degrees for a long time.
- Pain of varying intensity appears, periodic or constant, in the lumbar region and tender part of the abdomen.
- The symptoms are associated with a disturbance in the functioning of the urinary organs. There is a frequent, painful urge to urinate, pain and tension at the end of urination.
- Purulent vaginal discharge may appear. Sometimes the discharge may be yellowish or white. Accompanied by an unpleasant pungent odor.
Chlamydial infection in men is characterized by pain not only in the abdomen, but also in the scrotum or testicles. Pain and burning during urination. Discharge may be detected, especially in the morning. With chlamydia trachomatis, body temperature rarely rises above 37 degrees.
The appearance of all these alarming symptoms should be a reason to visit a venereologist-infectious disease specialist.
Diagnostic measures
How to identify chlamydia? The disease cannot be detected using conventional tests. Most often, a scraping is taken in the laboratory, but other diagnostic methods can be distinguished.
- There is a mini-test for the presence of chlamydia, which can be bought at the pharmacy. You can do the test at home. But the reliability of the results is low, only 15-20%.
- A general smear, which is taken from the urethra in men, and from the cervix, vagina and urethra in women.
- Chlamydia in the blood is detected by ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). The detected titer allows us to judge what stage of the disease is occurring at the time of the test: chronic, acute or remission.
- The PCR detection method is the most reliable (polymerase chain reaction).
The interpretation of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent blood test is determined by the number of titers that are indicated in the form. Blood should be taken from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach.
- If chlamydia is detected in the blood of the IgM group, it means that the disease is just beginning to gain momentum, and the acute phase begins.
- IgA titers indicate that the disease is progressing.
- If chlamydia is detected in the blood of the IgG group, one can judge the beginning of the chronic stage.
The research takes on average 5 days. Based on the test results, one can judge the stage of development of the disease. Accordingly, the doctor prescribes treatment for chlamydia.
Therapeutic actions
The treatment regimen for chlamydia depends on the state of immunity, intestinal microflora, and the presence of concomitant diseases. Chlamydia is curable with the right treatment approach.
Chlamydial infection is a bacterial disease, so antibiotics will be the mainstay of treatment. You need to choose only the treating antibacterial drug that acts at the intracellular level.
Treatment regimens for chlamydia depending on the prescribed medication.
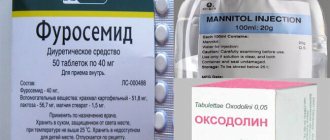
- How to get rid of chlamydia using the drug Doxycycline? The medicine is used for uncomplicated forms of the disease. On the first day, take 0.2 g. Then, for 7-14 days, take 0.1 g twice a day.
- Treatment of chlamydia with Azithromycin is effective if the disease occurs in a sluggish form. On the first day of treatment, 1 g is prescribed, on the second and third days the dosage is reduced to 0.5 g. From days 4 to 7, it is enough to drink 0.25 g.
- Erythromycin helps against chlamydia. Prescribed 500 mg up to 4 times a day. The duration of treatment is at least a week.
- Ofloxacin is prescribed at a dosage of 300 mg twice a day. The course of treatment is a week.
- During chlamydia treatment, the drug Roxithromycin may be prescribed. It is prescribed 150 mg twice a day.
- Spiramycin is prescribed at a dose of 3 million units three times a day for 7 days.
- If chlamydial infection occurs in a complicated form, the drug Ciprofloxacin can help. For the first dose, the dosage is 500 mg; for the remaining nine days, 250 mg are taken.
Both partners should be treated for chlamydia at the same time. It is possible that one course of treatment will not be enough. Two months after the end of treatment therapy, the PCR analysis should be repeated.
Is it possible to cure chlamydia forever? If the disease was detected in the early stages, then with effective treatment, after three weeks you can forget about the disease.
Is chlamydia permanently curable if the disease is chronic? If treatment was started late or was carried out incorrectly, the immune cells become depleted and stop fighting the infection. In this case, in addition to antibiotics, it is necessary to use immunomodulators (Interferon, Immunal), vitamins and anti-inflammatory drugs.
How to cure chlamydia requires an integrated approach. Often, along with antibiotics, antifungal drugs, such as Nystatin or Fluconazole, are needed for complete cure. Local antiseptics are prescribed. To eliminate the symptoms of dysbiosis, prebiotics (Bifidumbacterin, Linex) are prescribed.
You should not self-medicate or make changes to your doctor’s recommendations. Modern medications can permanently cure the disease. Don't forget about preventative measures.
Treatment
Currently, there are many different safe and effective antibiotics that make it possible to reduce the duration of therapy to 2-3 weeks, which is significantly different from the previous period of two months.
To cure chlamydia in women, it is necessary to use drugs that have the ability to enter cells, for example, macrolides. These drugs include Erythromycin and Oleandomycin. At this stage, new generation drugs are used that do not differ in the spectrum of influence from the well-known “Erythromycin”. At the same time, new drugs have improved pharmacokinetics and a high level of safety. The drugs prescribed for the course of treatment for chlamydia are Azithromycin and Doxycycline.
In addition to the mandatory prescription of antibiotics to the patient, antifungal drugs, for example, Fluconazole, and agents that have an immunomodulatory effect are used for treatment. If men have strong discharge from the urinary canal, antimicrobial medications are prescribed.
During treatment, partners need to limit sexual contact or use condoms. In addition, the consumption of dairy products and alcoholic beverages is excluded.
Treatment of pathology
Chlamydia is treated comprehensively. Prescribing one antibiotic does not bring a positive result. Preparatory measures must be taken to neutralize the harm of antibacterial medications.
At the preparatory stage the following is done:
- Normalization of intestinal microflora with eubiotics: Hilak Forte, Bifidumbacterin, Linex .
- The state of the digestive system is brought into order with the help of enzyme preparations: Festal, Creon, Panzinorm .
- A course of treatment with hepatoprotectors if there are liver diseases: Essentiale, Liv 52 , etc.
- A general blood test to detect and eliminate pyelonephritis. In case of illness, antibiotics and diuretics are prescribed, and urine is cultured for bacteria. If necessary, a urologist conducts a consultation.
Attention! Preparation is characterized by a different course for each specific case. It depends on the presence of chronic diseases in the body.
How to properly treat chlamydia
On average, the stage lasts about two weeks to a month. Preparation for treatment of chlamydia is necessary due to the duration, the use of various medical regimens and the toxicity of the medications used. Interrupting the treatment process is extremely undesirable, since with the resumption of chlamydia it becomes insensitive to antibiotics and other medications. Existing chronic diseases may also prevent you from taking medications. Therefore, stabilization of all human systems and organs is a necessity in the treatment of chlamydia.
Antibiotics in eliminating chlamydia
These drugs are the main ones in therapy. The effectiveness of fighting infection depends on a well-chosen regimen. The doctor selects only those antibiotics that are able to penetrate inside the cell, since chlamydia is located there. For this purpose the following are used:
- Macrolides : Azithromycin, Erythromycin, Midecamycin.
- Tetracyclines : Doxycycline, Tetracycline.
- Fluoroquinolones : Ofloxacin.
The dosage, regimen and other recommendations are prescribed only by the attending physician. On average, medication use ranges from 5 to 14 days.
Video - How to treat chlamydia?
Immunostimulating procedures
The patient’s immune defense is normalized through stress reduction, proper daily routine, proper nutrition, and positive thinking. Immunostimulants are used: Immunal, vitamins.
Preventive measures
The greatest effect comes from avoiding circumstances that lead to infection, as well as:
- Reducing the number of sexual partners.
- Use of contraception in casual relationships.
- Serological and bacteriological examination every year.
- Immediate treatment of an existing chlamydial infection.
- Stop any sexual intercourse during treatment.
- Checking for complete cure after completing the treatment period. Only if there is a complete absence of infection in the body can sexual intercourse be resumed.
Preparations for the prevention of chlamydia
Curability studies
To establish microbiological and clinical criteria indicating curability, the following studies are carried out.
- An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is mandatory, which detects the presence of antibodies in the blood to chlamydia - IgM, IgA, IgG. In this case, the blood is tested for the content of immunoglobulin A, that is, IgA. These antibodies are produced in the human body as a response to infection. Such a study should be carried out one and a half or two months after the patient is cured. If he has recovered, no antibodies will be detected.
- The next test needed to analyze curability is the polymer chain reaction, or PCR, test. This method is the most specific and sensitive for determining the presence of chlamydia in the human body. It is also the most preferable when conducting diagnostics.
Is it possible to completely get rid of chlamydia and how to treat it correctly? Many patients turn to their doctor with this question. This is not so easy to do, since these microorganisms are parasites inside the cell, and humans do not develop immunity to them. That is, infection can happen again. Often patients undergo several therapeutic courses using antibiotics at once, which naturally leaves its mark on the condition of their liver. That is why it is very important to fully undergo treatment and further examination for the presence of chlamydia.
How chlamydia is transmitted
How chlamydia is transmitted interests many people who care about their health.
Contrary to the established belief that you can become infected with an unpleasant disease only after sexual intercourse, there are different ways of transmitting the microorganism, in particular:
Sexual contact: is indeed the most likely cause of the development of an infectious disease, and it does not matter what kind of sex people have: oral (blowjob, cunnilingus), genital or anal. The risk of infection in women is higher than in men due to the fact that the mucous membranes The vaginal membranes contain more cylindrical cells than the male genital organ.
It should be taken into account that the partner can only be a carrier of dangerous microorganisms, that is, not have visible manifestations of the presence of chlamydia in the body. The only obstacle to infection can be a condom or sex with a regular healthy partner.
Airborne: using chlamydia, which affects the respiratory system, causing pneumonia. How is chlamydia transmitted in this case? A person becomes infected when a patient coughs or sneezes near him. However, infection in this way occurs very rarely, since the sputum of a sick person must contain a huge amount of pathogenic agents.
Contact-household route: much less often than the previous one, it becomes the cause of the development of an infectious disease, but such a possibility exists. In this case, the microorganism attaches to the mucous membranes of the organs of vision, throat, and genitals. Chlamydia can enter the body from dirty hands, shared towels, underwear, and personal hygiene items.
In rare cases, infection occurs after contact with food - poultry meat, unwashed vegetables and fruits. Chlamydia can linger briefly on various objects, door handles, and the toilet rim. Different types of infectious agents are transmitted through a handshake with a sick person or contact with an infected person
Different types of infectious agents are transmitted through a handshake with a sick person or contact with an infected animal, for example, if a dog or cat has chlamydial conjunctivitis.
From mother to fetus: chlamydia can be transmitted in utero, as the baby passes through the birth canal, or through household objects after birth.
It should be noted that chlamydia is almost never transmitted through kissing, since there are not enough infectious agents in saliva for infection to occur. Chlamydia cannot remain in the oral cavity for a long time, and once it enters the stomach, it dies.
In order for infection to occur in this way, the infected person must have a very severe form of chlamydia. For the same reason, it is wrong to think that this infection can be contracted in water bodies, since the amount of chlamydia in water is too small for infection.
Folk remedies for chlamydia
Traditional methods can be used in combination with drug treatment under the supervision of a physician. They can increase the effectiveness of traditional therapy and lead to lasting positive results.
An infusion of parsley stems improves blood flow in tissues and has an antibacterial effect. 45 grams of finely chopped greens are poured with half a liter of boiling water for 5-10 minutes. Then filter and drink 2 tablespoons 3 times a day for 2 weeks.
Also used is a herbal mixture of wheatgrass, calamus, and bergenia roots (20 g each). Add elecampane and licorice roots (30 g), rhizomes of aralia and rosea radiola (10 g), and red rowan fruits (40 g). The mixture is poured into a 1 liter thermos. The raw materials are poured with boiling water, hermetically sealed and left overnight. The strained infusion is drunk one day between meals every day for 15 days.
Bird cherry fruits, wormwood seeds, yarrow herb, St. John's wort, celandine and dry walnut leaves are also very healing. Pour 35 g of the collection into 0.5 liters of boiling water and heat it in a water bath. After half an hour, the broth is removed from the stove, cooled and filtered to remove dry residue. Drink the infusion before meals up to five times a day. Several weekly courses will be required.
Trichomoniasis disease: symptoms in women and signs
Recently, the incidence of sexually transmitted diseases has been growing rapidly.
In terms of frequency of detection, it ranks almost second after the flu. Regardless of lifestyle, social status and personal hygiene, not a single person is immune from infections of the genitourinary system. This is due to the fact that such organs are covered with mucous membranes, which are an ideal environment for the existence and reproduction of microorganisms. Most often, bacteria, viruses, microbes and fungi become pathogenic. Trichomoniasis in women is a dangerous sexually transmitted disease, the causative agent of which is not just bacteria or microbes, but protozoa. They are equipped with flagella that affect the organs of the genitourinary system, the vagina in women and the urethra in men. The main route of transmission of this infection is sexual intercourse. In addition, you can become a carrier of Trichomonas by using personal belongings or underwear of an infected person.
Causes
Trichomonas are protozoan single-celled animals, which in medical science are classified into Trihomonas elongata or oral Trichomonas, Trihomonas hominis or intestinal Trichomonas, and Trihomonas vaginalis or genitourinary Trichomonas. The main cause of trichomoniasis infection is sexual contact with a Trichomonas carrier. And only under the condition of a strong immune system and an optimal balance of vaginal microflora, Trichomonas in a woman’s body immediately die.
The reasons that Trichomonas still take root in the organs of the woman’s genitourinary system are as follows:
- improper personal hygiene;
- many sexual partners;
- pregnancy;
- exploitation of personal belongings of the bacteria carrier;
- relaxation in a public sauna;
- poor hygiene during menstruation;
- HIV;
- diabetes.
First signs in women and photos
After infection with trichomoniasis, the disease has an expected incubation period of 5-28 days. At the end of it, characteristic phenomena begin to appear. Typically, the female body is characterized by an acute onset of an infectious disease with pronounced symptoms and signs. For men, the clinical picture is not of such significant severity.
The first signs of trichomoniasis in women:
- copious vaginal discharge of a foamy, greenish consistency with a specific odor;
- burning in the genital area;
- swelling, severe itching and redness of the vagina;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent and sometimes false urge to urinate;
- pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
The main symptoms of trichomoniasis in women
Despite the prevalence of this disease, few people know what symptoms of trichomoniasis in women can manifest throughout the entire period. Often, the manifestations of this disease are perceived as other diseases of the genitourinary system.
Symptoms of trichomoniasis in women are as follows:
- pain in the perineal area;
- yellow-green vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- painful urination;
- burning and itching in the vaginal area;
- infectious development in the urethra;
- infection of the bladder and anus.
According to statistics, out of 100 women, approximately half experience trichomoniasis without experiencing any clinical manifestations. If you identify at least one symptom from the above points, you should definitely visit a doctor.
Photo of discharge
Prevention
In order not to become infected with pathogenic protozoa Trichomonas, it is imperative to use contraception during sexual intercourse. Although doctors say that a condom is not capable of 100% protecting a person from such germs. You should avoid visiting public saunas, swimming pools and toilets, and if this is not possible, you need to strengthen your personal hygiene and sanitation.
You can also prevent trichomoniasis by refusing to use other people's personal belongings and underwear. A shower stall or bathtub needs periodic disinfection. To carry out drug prevention of trichomoniasis, both sexual partners should take appropriate medications. Also, every six months to a year, every woman should undergo a preventive examination by a gynecologist, which will allow timely detection of infection.
In terms of prevalence, toxoplasmosis is not inferior to herpes - every fifth Russian is among carriers of the disease. The main danger of the pathology is that it can occur for a long time without any special symptoms or is disguised as other diseases. How toxoplasmosis manifests itself: symptoms in women can be varied, since many internal organs are affected when infected. What traditional and folk methods are used in therapy?
How does infection manifest in women?
Toxoplasmosis is a dangerous infectious disease that develops after the microorganism Toxoplasma enters the blood. The main causes of infection are eating insufficiently cooked meat, eggs or seafood, and untreated water. The infection can enter the body through blood transfusion during organ transplantation. All these factors lead to the development of acquired toxoplasmosis. Congenital toxoplasmosis is diagnosed when a child is infected from the mother during pregnancy.
Important! Most often, infection occurs from cats; stray and domestic animals can be carriers of the disease. Parasitic cysts are excreted along with feces, and the animal may look completely healthy.
If a person has a strong immune system, the disease can be asymptomatic. The first signs may occur when the body's protective functions are weakened during pregnancy or against the background of a chronic disease. The intensity of the disease depends on the stage of the pathology - acute, chronic, latent.
The cause of exacerbation of the disease in women may be the use of hormonal contraceptives, a sedentary lifestyle, or abortion.
Symptoms of the acute stage of toxoplasmosis:
- a sharp increase in temperature above 38 degrees, chills, fever;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the armpits, neck, back of the head - severe pain is felt when pressed;
- weakness and pain in the muscles, every movement causes discomfort;
- against the background of a sharp decrease in immunity, a woman often suffers from colds and seasonal diseases;
- change in the color of the eye sclera, clouding of the lens;
- migraine, nausea, vomiting, digestive disorders;
- deterioration in sleep quality, lack of appetite.
Against the background of exacerbation of toxoplasmosis, a woman may experience disruptions in the menstrual cycle, signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia may appear, unreasonable attacks of fear may occur, and an enlargement of the liver and spleen may occur.
Symptoms during pregnancy
Toxoplasma can penetrate the placental barrier, so infection during pregnancy is dangerous for a woman - there is a high probability of miscarriage and premature birth. Infected children have various physical and mental pathologies. But if the blood test is positive for toxoplasmosis, an abortion is not always done: termination of pregnancy is recommended if the infection is present in the amniotic fluid.
Important! Toxoplasmosis does not pose a danger to pregnant women who have had it before conception. Their bodies have antibodies that destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Through breast milk the risk of infection is minimal.
Toxoplasmosis manifests itself with various symptoms, many of which are characteristic of pregnant women - increased fatigue, irritability, apathy.
Signs in pregnant women:
- slight or sudden increase in temperature;
- nausea, lack of appetite;
- attacks of dizziness, headache, tachycardia;
- temporary impairment of vision and hearing.
Since the signs of toxoplasmosis are very diverse, only timely diagnosis can confirm or refute the diagnosis. It is better to test for the presence of antibodies to Toxoplasma before conception.
Toxoplasmosis in pregnant women is subject to mandatory treatment, but antibacterial therapy can be started from 12–14 weeks.
Toxoplasmosis in HIV
For HIV-infected people, toxoplasmosis can be a fatal disease. With the blood flow, the infection penetrates the brain, irreversible changes in tissues begin, and cerebral toxoplasmosis is diagnosed.
Symptoms of brain toxoplasmosis:
- muscle weakness, headache, which is localized in the temporal and occipital region;
- temperature above 38.5 degrees;
- decreased or increased sensitivity in some areas of the body, which is caused by damage to nerve endings;
- frequent sensation of “goosebumps” on the skin;
- paralysis, coma, cerebral edema.
Treatment for HIV-infected people is carried out depending on the size of the lesions, their number, and the degree of intensity of the disease. Oral antibacterial agents are used in therapy - Pyrimethamine, Fansidar, Sulfadiazine. Additionally, patients are recommended to take folic acid and B vitamins. Improvement occurs after 6–7 days, but the duration of therapy is at least 6 weeks.
Diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis, a woman needs to undergo a special test for toxoplasmosis. The study reveals the presence of immunoglobulins M and G in the blood: based on the results, you can see the presence of parasites and the duration of infection.
Analysis transcript:
- The presence of only IgM antibodies means the infection occurred recently and treatment is required.
- Immunoglobulins M and G are present in the blood - the infection occurred within the last year. It is necessary to do repeated tests after 3 weeks: if the number of class G antibodies increases, the disease is in an acute form.
- The presence of only G antibodies is an indicator of stable immunity to toxoplasmosis.
The presence of parasites in the body can be determined using a serological diagnostic method - a special Sabin-Feldman dye is used for this. A negative result indicates the absence of pathology. If the result is positive, additional examinations are performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Important! Toxoplasmosis can cause temporary infertility in women.
What to treat in women
Treatment of toxoplasmosis is not always required - therapy is mandatory in the acute form of the disease, when pathology is detected in children, HIV-infected people, and pregnant women. In the chronic and latent form, it is necessary to systematically strengthen the body’s protective functions - take vitamins, harden, lead a healthy and active lifestyle.
For treatment, antibiotics, antiparasitic and antihistamine drugs, and drugs with a wide spectrum of action are used. The treatment regimen is drawn up individually, taking into account various factors and indicators.
The most effective drugs for the treatment of toxoplasmosis:
- Pyrimethamine;
- Sulfadizine;
- Calcium folinate.
Fansidar is a complex antimalarial drug that effectively helps with toxoplasmosis. The medicine contains sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine, which destroy parasites. The product is not suitable for treating nursing women, but it can be used in the second half of pregnancy.
Rovamycin is an effective and relatively safe drug. It is approved for use in the treatment of toxoplasmosis in pregnant women - the absence of a negative effect of the drug on the fetus has been proven.
Important! It is impossible to completely destroy toxoplasma in the blood - a residual amount of parasites and antibodies will be present in the blood throughout life. In clinical practice, there are cases of complete recovery, but only if adequate therapy is prescribed within a few days after infection.
Treatment with folk remedies is ineffective in eliminating toxoplasmosis. Parasites quickly adapt even to modern antibiotics; herbs and bee products cannot kill them. Complex therapy can include products that will help strengthen the immune system - tincture of propolis, garlic, horseradish. But first you should definitely consult with your doctor.
Prevention of chlamydia
The main preventive measures to avoid chlamydia are the exclusion of fleeting sexual intercourse, as well as the use of protective equipment, that is, condoms. But this does not become a 100% guarantee that protects against infection. If a suspicious contact has occurred, you should not just wait for the first symptoms of chlamydia to appear. Within a few hours after intimate intercourse, the genital organs and areas adjacent to them can be disinfected with the latest antiseptic - Miramistin. Of course, it is much better to try to prevent the disease than to treat it after infection.
We looked at how chlamydia is transmitted.
Chlamydia in women: causes of the disease and its prevention
Chlamydia for the fair sex is primarily dangerous because it can lead to infertility. Chlamydia enters the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system from an infected partner during sex. The infection can also begin on the intestinal walls if you have had anal sex.
Chlamydia is not transmitted through kissing. However, it can be transmitted orally if a condom is not used. Barrier contraceptives can protect against infection, but even a condom is not a 100% guarantee of safe sexual intercourse. Much less often, chlamydia is transmitted through household contact.
Three out of a hundred people become infected due to the use of hygiene products from a chlamydia carrier. Chlamydia poses a great threat to women during pregnancy; the causes of infection are the same. You can also add to them the activation of “dormant” chlamydia.
A feature of these parasitic microorganisms is their high adaptability to the cells in which they live. That is, if they have not been completely eliminated from the body of the sick person, they can asymptomatically parasitize in the human body for up to several years, waiting for a “convenient” opportunity. Pregnancy and hormonal changes are a good time for infection to activate.
This venereal disease is curable, although with great difficulty. It is much easier to protect yourself from this disease. It is enough to use condoms, maintain personal hygiene and have sex with one partner. If you have unprotected sex, we recommend regularly getting tested for chlamydia.
The causative agent of chlamydia
It should be noted that experts distinguish between two types of bacteria that can cause chlamydia. One of the species affects only animals, but Chlamydia trachomatis causes human disease. There are 15 varieties of Chlamydia trachomatis, affecting different organs and systems. As an example, we can highlight, for example, urogenital chlamydia (genitourinary system) or lymphogranulomatosis venereum. Chlamydia, the causative agent of chlamydia, often causes serious illness.
It is also worth noting the rather small size of the pathogen (approximately 300 nm).
The causative agent of chlamydia is defined by doctors as an intermediate link between bacteria and viruses. It has clear signs of bacteria:
- DNA, RNA;
- muramic acid;
- ribosomes.
Division occurs in a binary manner; sensitivity to some antibiotics is noted.
On the other hand, if chlamydia is compared with a virus, then we can note the presence of an outer shell (similar to elementary membranes). Modern technologies have allowed scientists to consider chlamydia to be the smallest bacteria, intracellular parasites (like rickettsia).
Breeding order
Need to know! In chlamydia, the order of reproduction differs greatly from the bacterial cycle. All changes occur in the cytoplasmic vacuole, inside the cell of the human body.
At the initial stage, chlamydia attaches to the mucous membranes of leukocytes, monocytes, etc. After about four hours, the bacterium penetrates the human cell. Similar to the formation of viral colonies, the formation of chlamydia colonies occurs. Then DNA synthesis in infected cells is inhibited (approximately 10 hours).
After this comes the eclipse, or latent period. During this time, the infection cannot be detected, and its duration is approximately four hours. Complete infection of the body's cells and the logical end of this period occurs if the easily moving genetic material of chlamydia can emerge from the “sleepy” state.
After the latent (sleeping) stage, as with any viruses, there comes a period of rapid growth and maturation. Doctors call this time the peak of infectivity, the exponential phase. It ends at the stage of reducing the rate of infection propagation.
In simple terms, at the beginning of the development and reproduction cycle, chlamydia is very similar to viruses. But a little later, the first differences appear in the form of an increase in nucleic acids (for chlamydia there are two: DNA and RNA, for viruses there is one nucleic acid, which persists until the end of the entire reproduction cycle).
Both viruses and chlamydia do not produce their own energy (ATP) due to the lack of mitochondria, therefore all energy life processes are carried out at the expense of human cells. This parasitism is available to them, since they completely suppress cellular DNA synthesis. Among all the negative actions of the pathogen, there are also positive qualities, such as the ability to leave the affected cell without destroying it.
Factors influencing the survival of chlamydia in the environment
Chemical substances
How do women become infected and how can a man become infected? Sexual transmission routes. In this case, chlamydia trachomatis invades the body differently in men and women, at different speeds. The routes of transmission also differ. If pathogenic agents are found in the urethra or vagina in women, this means that the method of infection is vaginal contact.
If the presence of chlamydia trachomatis bacilli is noted in the rectum, this means that they were transmitted during anal sex, but if the infection is found on the surface of the respiratory organs or on the mucous membrane of the organs of vision, this means that the bacilli were transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person through oral contact.
Women and men can be protected from this route of transmission of chlamydial infection by using various methods. The most drastic of them (and unlikely) is a complete renunciation of sexual contacts. But you can protect yourself by other methods. For example, if your partner is permanent, if barrier contraceptives are constantly used during sexual contacts, if you have not cheated or cheated on your sexual partner, you can protect yourself from the danger of contracting not only this disease, but also from other sexually transmitted diseases, including immunodeficiency.
What other way can one become infected? A sick pregnant woman can transmit the disease to her newborn baby. Moreover, the disease is not transmitted through blood or the placenta, since the placenta in this case is a reliable barrier that protects the baby in the womb. Only in isolated cases, if there is leakage of amniotic fluid, can the disease be transmitted.
Household infection is rare. But certain sources of infection cannot be ruled out. If conditions in the external environment are favorable for the pathogen, it can maintain its viability for two days.