Chlamydia is a very insidious disease that is sexually transmitted. The danger of chlamydia is that it can be asymptomatic for a long time, only later the consequences will be fully felt. Prevention of chlamydia in men is the main way to prevent the disease. As you know, the surest remedy is to use a condom. So, today I will tell you how to recognize the disease by the first signs, as well as who to contact if you suspect chlamydia.
Chlamydia in men
Chlamydia is one of the most common diseases among sexually transmitted infections. This pathology is caused by intracellular pathogens – chlamydia. According to the World Health Organization, chlamydia in men occurs in 50% of cases and mainly in sexually active ages - from 18 to 45 years. Chlamydia is most often transmitted sexually through unprotected intimate contact. Chlamydia is one of the most common diseases among sexually transmitted infections
Household infection is extremely rare, so there is no need to worry that the cause of infection may be public or household items such as shared dishes, towels, washcloths, toilet seats, etc. However, it makes sense to practice good personal hygiene.
Chlamydia is one of the most common diseases among sexually transmitted infections. This pathology is caused by intracellular pathogens – chlamydia. According to the World Health Organization, chlamydia in men occurs in 50% of cases and mainly in sexually active ages - from 18 to 45 years.
Chlamydia is most often transmitted sexually through unprotected intimate contact. Household infection is extremely rare, so there is no need to fear that the cause of infection may be public or household items such as shared dishes, towels, washcloths, and seats.
What does the causative agent of chlamydia look like?
Chlamydia is an intracellular bacterium - a parasite. Independently in the external environment, its lifespan is calculated in minutes. It contains a biological capsule and genetic material. Chlamydia is an intracellular bacterium - a parasite
When damaged, it finds itself inside the host cell and begins parasitism. Using the building material and energy of the host cell, chlamydia actively multiplies inside the host cell. After the end of the chlamydia reproduction cycle, the infected cell dies, and many daughter chlamydia are released into the intercellular space, which continue to infect more and more cells.
How is chlamydia transmitted?
Sexual transmission of infection. You can become infected with this infection only through sexual contact. Visiting the pool, sharing a toilet lid, sharing a towel, etc. cannot cause infection. In the external environment, chlamydia cannot maintain its viability. Therefore, household contact, airborne droplets and other methods of transmission of chlamydial infection are unlikely.
Infection can occur through any type of sexual contact: oral, genital, anal. Therefore, the only way to protect yourself from infection is to remain faithful to your sexual partner or to correctly use reliable means of protection. You can only become infected with this infection through sexual intercourse
Infection with chlamydia during each unprotected sexual contact occurs on average in a quarter of cases. However, women are more susceptible to this infection and are therefore more likely to become infected.
Causes of the disease
Infection with chlamydia usually occurs through sexual contact, but transmission does not occur in all cases: if 3 out of 4 people become infected with gonorrhea from a sick partner during sexual intercourse, then 1 out of 4 people become infected with chlamydia.
Sexual contact of any kind is important: vaginal, oral or anal. Women are more susceptible to chlamydia. Contact-household transmission is also possible. Children can become infected with chlamydia when passing through an infected birth canal, as well as in utero.
The incubation period (time from infection to the appearance of the first symptoms) is 2-3 weeks.
Signs of chlamydial infection in men
Chlamydia in men causes inflammation of the genitourinary organs, most often in the form of urethritis (inflammation of the urethra). Chlamydial urethritis in men in most cases is asymptomatic or has minimal manifestations. Patients complain of unpleasant or painful sensations, itching and burning during urination, as well as scanty discharge from the urethra like a “morning drop”.
In rare cases, spotting may occur, mainly at the end of ejaculation or urination. In some patients, local symptoms are accompanied by a slight increase in temperature to subfebrile levels, malaise and general weakness. When chlamydia gets on the membranes of the testicles (from the posterior parts of the urethra), inflammation of the appendages occurs (epididymitis)
When chlamydia gets on the membranes of the testicles (from the posterior parts of the urethra), inflammation of the appendages occurs (epididymitis).
Acute epididymitis is characterized by the appearance of redness and swelling of the scrotum on the side of the inflamed appendage, accompanied by quite severe pain in the testicle, penis, radiating to the lower back and sacral region, as well as a violation of the general condition and fever above 38.5 ° C.
In the chronic course, general symptoms are most often absent, and the disease manifests itself in the form of a slight enlargement and hardening of the epididymis, while pain is mildly expressed, and in some cases may be completely absent.
How does chlamydia manifest?
The period of introduction of fungal spores and their further spread throughout the fertile environment takes from several days to several months, depending on the individual characteristics of the organism. At the end of the incubation period, the first signs of the disease begin to appear in the form of unpleasant itching and pain when urinating. However, this is not always the case. The peculiarity of chlamydia is that the disease may not have any symptoms.
As mentioned above, the infection propagation period ranges from several days to several months. On average, this period takes from five to thirty days. In this case, no pronounced manifestations are observed.
Symptoms of chlamydia are as follows:
- Morning glassy discharge from the urethra at an early stage of the disease;
- Mild itching and pain during urination;
- Weakness appears in the body, the temperature rises.
How does chlamydia manifest in women? Vaginal discharge takes on a mucopurulent form with a characteristic odor. The color of the discharge also changes - from transparent to pale yellow. Pain occurs in the internal and external genital organs, including during menstruation. Bleeding may occur mid-cycle. During urination, a woman feels itching and burning.
Chlamydia in pregnant women manifests itself as periodic purulent discharge and pain in the genitals. Untimely treatment can lead to natural abortion in the early stages and premature birth. A child becomes infected with chlamydia during childbirth, which subsequently results in inflammation of the mucous membrane, conjunctivitis, and pneumonia. A new mother may be at risk of postpartum fever.
Chlamydia in men manifests itself in the form of urethritis or inflammation of the urethra, which is characterized by glassy discharge. This period can last several months. During urination, a man also experiences discomfort. Periodic pain in the genitals occurs. Also, the presence of chlamydia is indicated by cloudy urine with purulent and blood impurities, including in semen.
Fans of anal pleasures, both men and women, can get an infection of the rectum. The disease may occur without symptoms or pain, itching, and discharge from the anus may appear.
What risks does untreated chlamydia entail?
- Chlamydia in men leads to the formation of adhesions, which in turn leads to blockage of the seminal flow. As a result, a man may become infertile;
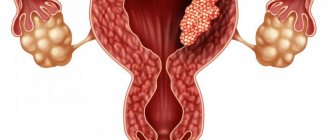
- In women, chlamydia leads to similar results (adhesions appear in the reproductive system, obstruction of the fallopian tubes occurs, and then the inability to get pregnant);
- Treatment of chlamydia should only be comprehensive (only then will a positive result appear);
- Damage to the body by chlamydia can affect not only the reproductive system, but also, for example, the organs of vision.
Symptoms of chlamydia
Patients may complain of white, yellow, or clear discharge from the urethra (men), vagina (women). They may differ from normal discharge by an unpleasant odor or a yellowish tint. Sometimes there is pain, burning during urination or sexual intercourse, redness and itching at the external opening of the urethra.
When complications develop, patients complain of pain in the perineum, scrotum, rectum; women are bothered by pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region. Chlamydia differs from many other sexually transmitted infections in that it affects not only the genitals, but also the lower parts urinary system.
The clinical picture is often blurred; the disease can be asymptomatic for a long time and diagnosed only when complications develop.
Symptoms of the infectious disease chlamydia
Symptoms of chlamydia appear only three weeks after infection. At this time, the incubation period of the disease occurs. In its acute form, it is almost impossible to identify signs of chlamydia.
In 90% of cases, signs of infection appear in a latent form or in a silent form that the infected person will not always notice these signs. Symptoms are expressed in:
- discharge of a transparent color, viscous consistency, sometimes yellow in color;
- itching in the perineum, urethra, near the anus and vagina;
- pain in the genital area;
- bleeding between periods;
- pain and burning at the time of urination, pain when pumping urination;
- general weakness of the body;
- elevated temperature.
After the infection has entered the body, and 7 to 10 calendar days have passed, the person develops a fever, general malaise, and muscle weakness. After these signs, the person did not consult a doctor, chlamydia adapts to being in the body and the symptoms decrease, which makes it very difficult to identify them.
At the time of colds, decreased immunity, and the development of diabetes, chlamydia begins to worsen.
Basically, these diseases are associated with the human urinary system and the reproductive system of the body. Diseases that cause chlamydia:
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- paraurethritis;
- cystourethritis;
- orchitis;
- vulvitis;
- funiculitis;
- chronic prostatitis;
- vesiculitis;
- orchiepidimitis;
- cooperite;
- colpitis;
- endocervicitis;
- erosion.
Diagnosis of chlamydia
If you suspect you have chlamydia or any other sexually transmitted infection, you should consult a doctor as quickly as possible (chlamydia in men is treated by urologists, in women by gynecologists). Diagnosis of chlamydia is difficult, since Chlamydia trachomatis is an intracellular parasite. For analysis, depending on the research method, scrapings from mucous membranes, blood, urine and semen in men can be used.
Currently, it is possible to detect the pathogen itself or antibodies to it in the blood. The doctor will advise you on the most suitable research method.
Methods for laboratory diagnosis of chlamydia
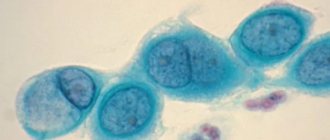
Diagnosis of chlamydial infection of the genital organs is a rather difficult problem. The difficulty of identifying this pathogenic microorganism is associated with the peculiarities of its life activity and functioning. First of all, it should be noted that chlamydia is an intracellular microorganism. Diagnosis of chlamydial infection of the genital organs is a rather complex problem
This means that chlamydia is able to enter cells and live in the host cell. The host cells most often are the epithelial cells of the mucous membranes of the genital organs of men and women.
It is with this intracellular form of life that numerous relapses of chronic diseases of the genitourinary organs are associated. That is, chlamydia remains inside the cells, and when favorable conditions arise for it, it again leaves the host cell, causing an exacerbation of the chronic inflammatory process.
Numerous attempts to treat chronic infections of the genitourinary organs, including those caused by chlamydia, lead to chronicity of the process and the emergence of resistant forms of the pathogenic microorganism. Very often, other infections caused by opportunistic microorganisms are combined with chlamydial infection.
Opportunistic pathogenic microorganisms are present in the human body normally, but with a decrease in immune defense they can cause the development of infectious inflammatory diseases. Opportunistic microorganisms are present in the human body normally, but with a decrease in immune defense they can cause the development of infectious inflammatory diseases
A decrease in immune defense can be caused by a variety of factors, including chronic persistent intracellular chlamydia.
So, conditionally, all methods for diagnosing chlamydia can be divided according to the principles underlying this or that method. Today the following methods are used:
- rapid tests
- smear
- immune fluorescence reaction (RIF)
- serological methods (complement fixation reaction - RSK)
- enzyme immunoassay (ELISA)
- cultural method (bacteriological culture)
- DNA methods (polymerase chain reaction - PCR, ligase chain reaction - LGC, transcription amplification - TA, DNA probe method)
Let's look at each of the methods in more detail. Today it is impossible to single out the best method for diagnosing chlamydia, since each method has advantages and disadvantages. And for maximum efficiency in identifying the pathogenic microorganism - chlamydia - the most appropriate methods in a particular clinical situation should be combined.
Diagnostics
To detect chlamydia, as a rule, several variants of diagnostic procedures are used. This is due to the fact that chlamydia has a unique biological cycle, in which these microorganisms can be confused with other pathological bacteria that provoke diseases of the genital organs.
If symptoms of chlamydia infection appear, you should seek the help of a urologist. The diagnostic complex begins with a survey for the presence of characteristic signs of the disease, as well as an external examination. If necessary, the patient is redirected to a gynecologist or venereologist.
Diagnostic methods:
- general urine analysis
- enzyme immunoassay
- polymerase chain reaction
- bacteriological culture
- transcriptional amplification
A suitable diagnostic method is prescribed individually, depending on certain factors, including the gender and age of the patient, the particular course of the disease, the presence of pregnancy, and other sexually transmitted infections.
It is important to note that when signs of the disease appear, not only the patient, but also his partner needs to be diagnosed. Also, the possibility of infection of immediate relatives through non-sexual means cannot be ruled out. It should be remembered that even the absence of symptoms in loved ones does not exclude the possibility of the disease and associated complications.
Features of chlamydial infection in men
Most often, urogenital chlamydia in men is asymptomatic as a chronic infection and does not manifest itself clinically for a long time. In this case, the pathogen not only parasitizes the mucous membrane, but also penetrates the submucosal connective tissue layer and spreads to other organs of the genitourinary tract.
The severity of inflammatory phenomena depends on local protective and general compensatory mechanisms. It has been established that under the influence of stress, hormonal disorders and other unfavorable factors, the chlamydial process can be activated, leading to an exacerbation of the infection and the appearance of the symptoms listed above, as well as the development of complications.
In some cases, carriage of chlamydia may occur - a condition in which even minimal signs of inflammation are not observed, despite the fact that the pathogen itself can persist for a long time on the mucous membranes of the urogenital tract.
This condition can only be diagnosed using modern high-precision laboratory diagnostic methods, such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction).
Types of chlamydia or chlamydial infection
Chlamydial infection is divided into types of chlamydia, depending on the damage to a specific organ:
- Chlamydia psittaci - this chlamydia causes the disease conjunctivitis;
- Chlamydia trachomatis - this infection in newly born children causes eye diseases, conjunctivitis, otitis and nasopharyngitis, Chlamydia trachomatis in adults causes venereal lymphogranulmatosis and genital chlamydia;
- Chlamydia pneumoniae - this chlamydia infects the cardiac system, blood vessels, respiratory system with the transition to pneumonia, acute and chronic bronchitis, cardiac and bronchial asthma;
Chlamydial infection or chlamydia can be acute or chronic and without symptoms of disease development.
Treatment of chlamydia in men
Immunological disorders play an important role in the development of chlamydial infection. Immunity to chlamydia is unstable and short-lived and does not protect against subsequent introduction of pathogens. All this requires complex therapy with the mandatory inclusion of drugs that correct and increase the body’s protective functions. In addition to antibacterial agents, immunomodulatory drugs are prescribed that can activate the immune system to fight infection and increase the body’s resistance to infectious agents.
Moreover, the use of antibimicrobial drugs alone leads to the emergence of chlamydia strains resistant to them.
In the complex therapy of chlamydia, drugs from the group of recombinant alpha-interferons can be used, in particular VIFERON® Suppositories, which, in addition to the immunomodulatory effect, also has an anti-chlamydial effect. In the complex therapy of chlamydia, drugs from the group of recombinant alpha-interferons can be used
Clinical studies have shown that the use of the drug in a combined treatment regimen allows the majority of men infected with chlamydial infection to normalize the immune status and block the reproduction and spread of the pathogen. Against the background of such therapy, there is a significant improvement in the outflow of stagnant secretions in the prostate gland, an increase in the efficiency of the lymphatic and blood vessels in the prostate gland. genitourinary organs and reducing the incidence of complications.
In addition, it was found that the interaction of the components of the drug VIFERON® Suppositories (alpha 2b interferon, vitamins E and C) makes it possible to reduce the course doses and duration of antibiotic use, as well as significantly reduce the side effects associated with the action of the latter.
What can you do
If you have a chlamydial infection, you should strongly encourage your sexual partner to get tested. Explain to her/him that the infection may be asymptomatic and may not cause any clinical manifestations. If you have a chlamydial infection, you should strongly encourage your sexual partner to get tested
Unfortunately, maintaining constant contact with the infection can lead to re-infection and treatment failure. During the treatment period, you should abstain from sexual intercourse or use a condom.
How can a doctor help?
In the treatment of chlamydial infection, antibacterial drugs from the group of macrolides, tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones are currently used. The choice of antibiotic depends on the severity of the infection. Do not self-medicate. Only a doctor can choose the right drug.
After completing the full course of treatment, you may be recommended to undergo repeated examinations to confirm the cure. As a rule, blood is tested for this using ELISA or PCR.
Antibiotics in the treatment of chlamydia
Since chlamydia is a parasite that lives inside cells, their treatment requires the use of antibiotics that can penetrate and accumulate in the affected cells. In each case of chlamydia, ONLY AN INDIVIDUAL treatment regimen should be drawn up
In each case of chlamydia, ONLY an INDIVIDUAL treatment regimen should be drawn up, which will take into account the nature of chlamydia, the sensitivity of chlamydia to antibiotics (determined based on the culture indicator for sensitivity to antibiotics), the presence of concomitant infections, the severity and duration of chlamydia, its localization - which organs are affected by the infection. Taking into account all these factors, the doctor calculates individual doses of antibiotics for you and the duration of the treatment cycle - a course of several cycles of chlamydia development will be required in order to be able to talk about the effectiveness of treatment.
It is especially worth noting that if, along with chlamydia, other sexually transmitted infections are detected - mycoplasma, ureaplasma, cytomegalovirus, gonococci, etc., then treatment also becomes more complicated. The doctor will have to develop a regimen, taking into account the sensitivity of each infection found to the prescribed drugs.
During the treatment process, medications are also prescribed to prevent the proliferation of fungal infections in the body exposed to antibiotics.
Treatment of chlamydia disease
If chlamydia does enter the body, then treatment of chlamydia requires a long time, this is a rather complex process.
Urogenital chlamydia is treated jointly by an immunologist and a gynecologist for the female body, and an immunologist and a urologist for the treatment of the male body.
The main drugs used in treatment are antibiotics of different groups and directions:
- macrolites;
- tetracyclines;
- fluoroquinolones.
Along with antibiotics, the following are involved in the treatment process:
- multivitamins;
- immunomodulators;
- drugs karsil, festal;
- antifungal drugs;
- probiotics.
Women who have chlamydia in the genital area are prescribed douching and vaginal antiseptic tampons along with medications.
In men, local treatment of the disease is used using iontophoresis, enemas, suppositories and prostate massage.
To treat chlamydia trachomatis in the body, the following medications are prescribed:
- Azithromycin 500 mg once a day;
- Doxycycline 0.1 mg 2 times a day;
- Levofloxacin 500 mg once a day;
- Erythromycin 500 mg 4 times a day;
- Ofloxacin 300 mg 2 times a day;
- Roxithromycin 150 mg 2 times a day;
- Spiramycin 3 mg 3 times a day.
If necessary, the patient is prescribed extracts of medicinal herbs that strengthen the immune system: echinacea, eleutherococcus, aralia.
To normalize the microflora in the body, multivitamins and always probiotics are prescribed.
Women who have chlamydia in the genital area are prescribed douching and vaginal antiseptic tampons along with medications.
The treatment regimen is drawn up by a specialist and in this case self-medication is contraindicated. During treatment for chlamydia, sexual intercourse, smoking and drinking alcohol are prohibited, and you must also exclude spicy foods from your diet.
It is very important to maintain hygiene when treating this disease.
Immune stimulation
First of all, normalization of immunity is achieved through a reduction in neuropsychic stress and a rational daily routine. An active lifestyle, healthy nutrition and a positive attitude have a significant impact on the body. An active lifestyle, healthy nutrition and a positive attitude have a significant impact on the body
However, in the treatment of an infectious-inflammatory process, these recommendations are supplemented by the prescription of immunostimulating drugs: vitamins from the group of antioxidants (A, C, E). These vitamins reduce the toxic effects of infectious agents on the body.
Timely and adequate quantitative intake of these vitamins into the body contributes to the active restoration of damaged tissues. Immunal - this herbal preparation stimulates the activity of immune cells. Thanks to this, the processes of eliminating infection from the body and restoring damaged tissues are more active.
Immunostimulating therapy is prescribed by the attending physician according to an individual regimen. The use of these drugs is possible only after eliminating possible contraindications.
Enzymes in the treatment of chlamydia
The administration of special drugs - enzymes - also plays an important role in the treatment of chlamydia. How do enzymes “help”? And enzymes provide invaluable help. Firstly, they return membrane permeability in diseased cells to normal. Thus, higher concentrations of antibiotics enter the cell with lower doses of their use. The administration of special drugs - enzymes - also plays an important role in the treatment of chlamydia
Enzymes also help reduce the body’s allergic sensitivity to medications. Thirdly, enzymes provide anti-edematous and analgesic effects.
Enzymes enhance the action of antibiotics not only inside the cell, but also increase their concentration in the blood by an average of 20–40%, which makes it possible to transfer large doses of antibiotics to diseased organs with a lower dosage. And finally, enzymes help restore peripheral circulation.
Treatment
Antibiotic Azithromycin
Chlamydia therapy is carried out using predominantly antibacterial drugs. To destroy and remove harmful bacteria from the body, various groups of antibiotics are used, as well as antibacterial drugs characterized by high penetrating ability, which is necessary to influence chlamydia, which parasitize inside cells.
In addition to bacterial therapy, patients are often prescribed medications whose action is aimed at activating immune functions. During the acute course of chlamydia, bacteria suppress the immune system, making the body much more sensitive to other infectious pathologies. When choosing medications, the individual characteristics of a particular patient, as well as the localization of infection, are taken into account.
To improve the effect of treatment, topical medications can be used. They have an antiseptic effect on the affected areas of the genital organs, prevent the proliferation of chlamydia, and also eliminate some symptoms of the disease.
Hardware procedures can also be used for therapeutic purposes. In particular, exposure to ultrasound, magnetic fields and infrared radiation is considered an effective treatment method.
Symptoms of worms in children 2 years old: causes of occurrence, general signs, drug treatment
The effectiveness of treatment directly depends on the methods of drug administration and the correct choice of dosage. In addition, the presence of concomitant sexually transmitted infections has a significant impact. The course of treatment for chlamydia is from 20 to 25 days, after which re-diagnosis is carried out.
In general, treatment of chlamydia is carried out by carrying out antibacterial therapy followed by taking immunostimulants, vitamins, and symptomatic medications.
Complications of chlamydia
In men, the most common complication is inflammation of the epididymis epididymitis. Women have inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages. It should be understood that the presence of a chronic inflammatory process in the organs responsible for reproductive function can cause the development of infertility in men and women, lead to the development of various pregnancy pathologies (frozen pregnancy, miscarriages, premature birth, developmental pathology fetus).
This is why it is so important to undergo treatment on time.
What is chlamydia - symptoms, treatment and prevention of chlamydia
Chlamydia is an infectious disease that can only be transmitted through sexual contact. It is caused by chlamydia - bacteria that are located inside the cell. Modern medicine successfully treats this disease, but doctors never cease to warn that its prevention is not so difficult and is accessible to everyone, and therefore there is no point in exposing yourself to the risk of becoming infected. In order to have a clearer idea of what chlamydia is and to seek medical help in time, it would not hurt to study theoretical information: what are the symptoms of the disease, how does it manifest itself, what should you pay attention to. It would not be amiss to consider the signs of chlamydia in the photo, which clearly demonstrate this; in this case, the disease can be detected much earlier, because the external manifestations, which are depicted in such photos, often appear before other symptoms. Chlamydia: what is it?
In medical practice, there are a huge number of diseases that are transmitted from one sexual partner to another under the condition of unprotected contact. However, many from this list are also dangerous because they can become infected not only through sexual contact, but also through everyday contact, which significantly complicates the prevention process. That is why those who are responsible about sexual hygiene are unlikely to ever face the need to treat chlamydia.
In order to understand what chlamydia is, you must first understand what causes it and how it develops after entering the body of a healthy person. It should be taken into account that this is a bacterium, i.e. The dimensions allow chlamydia to be seen only in photographs taken with a microscope. Although in order to understand what it is and how to avoid it, a photo is not required. So, chlamydia is an extremely small, round-shaped bacteria that affects all kinds of mucous membranes of the human body, but primarily the genitourinary system. in some cases (previously they were recorded extremely rarely, but now they have become more frequent) the bacterium penetrates the tissues located under the mucosa. As a result, the disease exists, but its symptoms are absent until a certain time.
There is one feature that clearly distinguishes chlamydia from other bacteria that cause sexually transmitted infections. What it is? This is a development cycle that is unique in its kind, in that these microorganisms have characteristics of both viruses and bacteria. That is why scientists decided to distinguish them into a separate class of microorganisms.
Once in the human body, forms of bacteria that can exist exclusively inside the cell are gradually replaced by others—adapted to environmental factors. Moreover, within 72 hours, which is how long the development cycle lasts, several forms of chlamydia can be detected at once, including atypical ones. What is it - atypical chlamydia? These are cells that do not reproduce and do not cause harm to the body, but are transmitted through sexual contact, infecting a healthy person. Such forms are poorly diagnosed and cannot always be treated with antibiotics. They are the cause of the most dangerous consequences of chlamydia, since they do not show symptoms and are resistant to conventional antibacterial therapy.
The most important thing that anyone who is wondering about chlamydia – what is it? – should remember is that a responsible attitude towards sexual life will help to avoid the disease. Symptoms of chlamydia
If we consider all the existing symptoms, then they can be divided into groups:
Symptoms in women Symptoms in men Common symptoms Common symptoms Symptoms that can be seen in the photo
The last group includes those external manifestations that are observed on the genital organs of women and men, accessible for photography without the use of a microscope. These include redness of the genitals, various rashes, etc. In addition, both women and men may have discharge from the genitals of varying colors and consistency. But infertility caused by chlamydia is diagnosed in women much more often than in men. Purely female symptoms include pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar pain, but men are more often concerned about discomfort in the groin and rectal area, as well as prostatitis.
It is possible that symptoms will be completely absent, however, manifestations such as itching, swelling, redness, discharge, increased urination, pain that worsens during urination and sexual intercourse are present in almost every patient diagnosed with chlamydia, and therefore are considered common.
Other less common manifestations of the disease include:
Cervicitis Urethritis Salpingitis Chronic diseases of the respiratory system Constantly worsening conjunctivitis Reiter's syndrome Proctitis Epididymitis
It happens that the same person, depending on the state of immunity at the time of infection, may not experience any symptoms at first, but later develop several of the manifestations described above. Treatment of chlamydia
Like any other infection transmitted through unprotected sex, chlamydia can cause significant harm to the human body, regardless of whether any symptoms are present or the disease is hidden. Unfortunately, the lack of timely treatment causes inflammation to occur in various parts of the genitourinary system, which can result in various diseases, including infertility. Also often, due to the lack of timely, comprehensive treatment for chlamydia, Reiter's syndrome can occur - a disease that combines symptoms of conjunctivitis, arthritis and inflammation of the excretory system.
Fortunately, modern medicine does not see any particular difficulties in the treatment of this disease, especially if the patient seeks help in a timely manner. If you pay attention to the appearance of any abnormal symptoms, and do not try to find out on your own what it is, but seek medical help, most likely there will be no problems with treatment.
As a rule, chlamydia is treated under the strict supervision of a doctor, and the treatment period is expected to be three weeks or more. It is very important for both partners to take the course at the same time, despite the fact that the test results of one of them may be negative. Treatment consists of a course of antibacterial therapy plus a set of special procedures. Recovery is not established after the disappearance of symptoms, but only when an examination carried out two months after the start of treatment confirms the absence of bacteria in the body. Disease prevention
It is no secret that the prevention of any disease lies in the fact that all those factors that can provoke it should be avoided, i.e. causes of the disease. Since the main cause of the development of the disease is unprotected sexual intercourse, to prevent chlamydia, one should adhere to sexual hygiene: either have contact with a minimum number of partners, or use condoms. Since you can only be sure of the absence of contact with an infected person one-sidedly (in relation to yourself), it is highly recommended to use a condom that can protect against infection. Remember that even in the absence of active manifestations of the disease, the carrier infects every second sexual partner.
Considering that chlamydia can be transmitted to a newborn from a sick mother, the only way to prevent it is, again, a responsible attitude towards your life and health. So, when planning a pregnancy, it is best for a woman to be fully examined and, if necessary, undergo courses of treatment, and only then become pregnant. After conception, neither the woman nor her partner should be allowed casual sexual contact.
Despite the fact that treatment of chlamydia is quite possible, with virtually no consequences for the human body itself, it would be wiser to take care of its prevention, which will not allow the infection to enter the body.
Prevention of chlamydia in men
The basis for preventing chlamydia is avoiding promiscuity. The use of condoms does not prevent infection in all cases. It is very important to inform your sexual partners about the disease, even if nothing bothers them, and to convince them to undergo examination and treatment of chlamydia.
Remember that being asymptomatic does not reduce the risk of complications.
Recommendations for the prevention of chlamydia:
- For casual sex, it is necessary to use a condom.
- If maintaining marital fidelity is impossible or your regular sexual partner does not inspire trust, then it is necessary to conduct an annual bacteriological and serological examination for sexually transmitted infections.
- If you are diagnosed with chlamydia, you must begin treatment immediately.
- During the treatment period, all sexual contacts must be stopped. Using a condom does not provide 100% protection. Oral or anal sexual intercourse is no less dangerous for infection with chlamydia than genital intercourse.
- After a full course of treatment, it is necessary to carry out a mandatory diagnosis of cure. Only after chlamydial infection has been ruled out is it possible to stop treatment and resume sexual intercourse.
How is chlamydia treated?
It is strictly contraindicated to treat chlamydia on your own. Therapy is prescribed only by the attending venereologist or gynecologist or urologist.
Medications are selected in such a way that their pharmacological properties make it possible to treat the disease at the cellular level. Timely diagnosed chlamydia is treated with Azithromycin, a capsule of which is taken once. Longer therapy is carried out with Doxycycline for one week, one tablet twice a day.
Complex therapy, in addition to the above remedies, includes antifungal and immunity-boosting drugs. Local ointments and suppositories can be used if there is strong discharge from the urethra.
Tests and treatment are prescribed to all partners who had contact with the infected person. You cannot be sexually active during the period of treatment and medical examination, or you must use condoms.
Drinking alcoholic beverages during treatment is prohibited. The consumption of dairy products also needs to be reduced. One and a half to two months after treatment, it is necessary to repeat tests for chlamydia to confirm or deny their presence in the body.