Symptoms of chlamydia in women - diagnosis and treatment Symptoms of chlamydia in women may not be noticeable for a long time, and only become apparent during pregnancy. Chlamydia is a dangerous disease that is transmitted primarily through sexual contact. Chlamydia is a pathological process in the body, the causative agent of which is chlamydia. They can cause a whole range of damage to various organs in humans. Chlamydia cannot be classified as either a bacteria or a virus, but these microorganisms have the amazing ability to damage not only the external genitalia, but also the internal ones, disrupt the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, damage blood vessels and the heart, teeth and joints, and also cause conjunctivitis and otitis media. The disease has a clear clinical picture only in the case of acute chlamydia, but in other cases the disease...
Review
0
Result: Did you get an answer to your questions? Please rate the usefulness of this article!
User rating 0.52 (9 votes)
Symptoms of chlamydia in women may not be noticeable for a long time, and only become apparent during pregnancy. Chlamydia is a dangerous disease that is transmitted primarily through sexual contact. Chlamydia is a pathological process in the body, the causative agent of which is chlamydia. They can cause a whole range of damage to various organs in humans. Chlamydia cannot be classified as either a bacteria or a virus, but these microorganisms have the amazing ability to damage not only the external genitalia, but also the internal ones, disrupt the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, damage blood vessels and the heart, teeth and joints, and also cause conjunctivitis and otitis media. The disease has a clear clinical picture only in the case of acute chlamydia; in other cases, the disease has general symptoms characteristic of diseases of the genitourinary system.
basic information
Chlamydia in women is the most common causative agent of sexually transmitted diseases, especially in developed countries. Genitourinary (urogenital) and ophthalmological symptoms of chlamydia in women can also be accompanied by systemic signs of infection - arthritis, perihepatitis, proctitis. The consequence of infection may be infertility (sterility). Due to the excessive use of antimicrobial drugs (antibiotics) in the population, and the oligo- and even asymptomatic course of infection, a short-term therapeutic regimen leads to the fact that the treatment of chlamydia in women is not effective.
Chlamydia infection in women and diseases caused by Chlamydia trachomatis are expensive to diagnose and treat. They can cause serious health problems and negatively affect your overall quality of life.
Rational diagnosis, especially of the acute uncomplicated form, treatment of chlamydia in women and prevention based on sexual hygiene can reduce rising costs.
The high prevalence and often asymptomatic course (the course of the disease in which chlamydia does not show symptoms or the manifestation of the disease is relatively mild) of infection causes the progressive emergence of diseases among the population.
Who are chlamydia
Chlamydia is a pathogenic gram-negative obligate intracellular bacteria. Chlamydia has a size of 250-300 nm and during primary infection it affects the cells of the main barrier systems of the body.
Chlamydia has all the main signs of bacteria, such as:
- contain two types of nucleic acids - DNA and RNA (deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid, which carry genetic information and information about protein synthesis, respectively);
- ribosomes;
- muramic acid (this is a cell wall component similar to the cell wall component of gram-negative bacteria).
Chlamydia reproduces by binary fission and is sensitive to some antibiotics. Based on these facts and some others, chlamydia was classified by scientists as bacteria.
For a long time after the discovery of chlamydia, in the process of closely studying them, the question arose as to what type of parasite to classify chlamydia as a virus or a bacteria. The size of the chlamydial cell is such that it occupies an intermediate position between bacteria and viruses. From the perspective of evolution, all microorganisms are conventionally considered in the following sequence: bacteria - rickettsia - chlamydia.
Symptoms of chlamydia. Today it is believed that chlamydia are the smallest bacteria, and according to the modern classification, chlamydia are placed in the same group with the so-called rickettsia, with which they are united, in addition to size, by intracellular parasitism. Chlamydiae were isolated into an independent order due to their unique intracellular development cycle, which distinguishes them from all other bacteria.
Like viruses, chlamydia have outer shells built like elementary membranes. And in the development cycle of chlamydia there are, along with stages characteristic of cellular organisms - rickettsia, and stages characteristic of viruses, especially in the initial period of development.
At the same time, the two-phase life cycle of chlamydia itself significantly distinguishes them from bacteria themselves. It occurs in the cytoplasmic vacuole in the host cell and consists of a natural replacement of vegetative reproducing large non-infectious chlamydia cells (reticular bodies - RT) and small dense elementary bodies (ET) - infectious forms of the microorganism.
Routes of transmission of chlamydia in women
Symptoms of chlamydia. The causative agent of the disease is the highly contagious gram-negative bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis, which is tropic towards cylindrical and transitional epithelium.
Chlamydia is an obligate intracellular parasite and exists in two cellular forms (bodies) - highly infectious extracellular elementary and reproductive intracellular reticular. The full development cycle of the microorganism takes from 1 to 3 days and ends with the complete destruction of the affected epithelial cell. There are two main ways of becoming infected with chlamydia:
- Contact-sexual
. The source of infection becomes a sexual partner with clinical manifestations or an asymptomatic course of the disease. Infection occurs during vaginal, anal or oral sexual intercourse. - Vertical intrapartum
. Chlamydia can be transmitted from mother to newborn baby when passing through an infected birth canal. Cases of antenatal (intrauterine) spread of the disease have not been recorded.
Chlamydia in women. The possibility of infection with chlamydia through household contact is unlikely, but not excluded. The bacterium is characterized by extremely low resistance to destructive environmental factors: drying, ultraviolet radiation, high temperature, alcohol and antiseptic solutions.
At the same time, on natural fabrics at temperatures up to +18 ° C, the microorganism can maintain its viability for up to two days. Therefore, in families with a low level of hygiene, if there is a person actively secreting chlamydia, transmission of infection through bedding or toiletries is theoretically possible.
Predisposing factors for chlamydia infection are prostitution, frequent change of sexual partners, sex without the use of barrier contraceptives, and substance abuse.
The risk of infection is increased in women with low socioeconomic status.
Causes
Chlamydia can be infected in four main ways. Establishing the route of entry of the pathogenic microorganism will allow the doctor to make the most accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy.
The causes and routes of infection with chlamydia are as follows:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse . Any form of contact is dangerous - oral, anal, genital. Sperm or vaginal discharge from a sick sexual partner is a source of infection. When a pathogen enters the genital tract, damage to the mucous membranes and tissues of the genital organs begins, and an inflammatory process develops.
- The birth process . Childbirth occurring in an infected woman is dangerous to the health of the fetus. When passing through the birth canal, chlamydia can penetrate the mucous membranes of the eyes and even the lungs.
- Airborne path. This method of infection is rare. Transmission of the virus is possible when a patient with pneumonia caused by chlamydia coughs.
- Contact-household infection. Occurs when personal hygiene is not observed, using someone else’s towels, or wearing someone else’s clothes.
The danger of chlamydia
Symptoms of chlamydia. The special insidiousness of chlamydia is that they come in different types. Chlamydia differ from each other only in special structures on the cell surface that help them attach to a certain type of human cell. Depending on this, they are designated by Latin letters: A, B, Ba, D-K, I-3. For example, chlamydia I-3 causes the tropical disease lymphogranuloma venereum; the most studied chlamydia D-K - affects the genitals, and there are also chlamydia that cause trachoma - a serious eye disease.
Chlamydia is caused by Chlamydia trachomatis D-K. It can live and actively reproduce inside the human body, and also tolerates being in the environment quite well.
Chlamydia is one of the few sexually transmitted diseases that can be transmitted through household contact: through a handshake, cups, spoons, washcloths, towels and shared underwear. However, the surest way to become infected is to have sex (genital, oral or anal) with a sick person. Pregnant women need to be especially careful - they can easily transmit chlamydia to their unborn child.
Reasons for appearance
Chlamydia in women (symptoms will help determine the degree of development of pathological processes) are intracellular organisms that resemble viruses and bacteria. They live and develop from internal cells in the human body.
There are certain causes and provoking factors that contribute to the development of the inflammatory process:
- bad habits (abuse of alcohol, tobacco products, narcotic substances);
Chlamydia in women
- poor nutrition;
- promiscuous sex life without the use of protection;
- poor environmental conditions;
- weak immunity due to hypothermia, stress, after taking antibacterial drugs or as a result of vitamin deficiency;
- early sexual activity;
- medical manipulations in the reproductive system;
- installation of an intrauterine device;
- non-traditional sexual acts.
Infection of the female body occurs in the following ways:
| Name | Description |
| Sexual | The main method of transmission of infection, which is confirmed in most cases. The risk of infection increases if partners do not use protective equipment. Chlamydia enters the mucous membrane of the external genitalia or the vagina, from where it affects the intracellular space through the membranes. The infection also enters a woman's body during anal and oral sex. |
| Contact and household | The causative agents of chlamydia can survive in an environment at a temperature of 20°C for up to 2 days. You can become infected through household contact by touching handrails on public transport, through a towel, bathrobe or dirty hands. |
| Intrauterine | Infection of the fetus occurs after infection of the amniotic fluid with chlamydia. Bacteria enter the baby's body through skin that is not fully formed. It is guaranteed that a child will become infected by swallowing amniotic fluid. |
| Airborne | Pulmonary chlamydia is transmitted this way. |
In some cases, the disease occurs without clinical signs. But if the first symptoms appear, it is important to make a timely diagnosis and undergo treatment in order to avoid serious consequences.
What happens with chlamydia
Symptoms of chlamydia. During the first two to three weeks after infection, no signs of illness are observed. The person feels healthy and full of energy. At this time, chlamydia integrates into the cells of the new host and multiplies. After the lull period ends, patients begin to experience the first signs of chlamydia, but the disease is often asymptomatic.
Chlamydia in men:
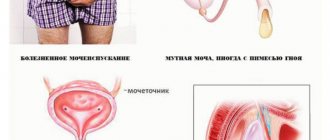
- in the morning, glassy discharge appears from the urethra, the first drop of urine may be very cloudy;
- there is itching and burning when urinating;
- Some men experience spotting at the end of urination or during ejaculation;
- Patients feel weak and their temperature may rise slightly.
Chlamydia in women:
- mucous discharge from the vagina appears, differing from normal in an unpleasant odor or yellowish color;
- there is itching and burning when urinating;
- General weakness is noted, and the temperature occasionally rises.
Even without treatment, after a couple of weeks, all of the above symptoms completely disappear. At the same time, chlamydia itself does not disappear, but becomes chronic. At the same time, chlamydia acts on the immune system, on the one hand causing it to weaken, and on the other hand, as if turning it against certain tissues of the body. This can damage internal organs, joints and eyes.
In women, chlamydia causes inflammation in the fallopian tubes and abdominal cavity. As a result of inflammation, adhesions and fusion of the fallopian tubes can form. This leads to infertility.
In men, chlamydia can also cause infertility. Another complication of male chlamydia is inflammation of the prostate gland (prostatitis).
Remember: a pregnant woman with chlamydia is a source of infection for the unborn child. Chlamydia does not cause congenital deformities, but can damage internal organs (intestines, lungs), joints and eyes.
Perihepatitis (Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome)
In exceptional cases, perihepatitis, which was previously considered typical of gonorrhea, may develop, but chlamydia is equally often the cause.
Women complain of sudden severe pain below the right costal arch, and sometimes in the right shoulder, but the disease is often characterized by an asymptomatic course.
The examination determines the presence of adhesions in the abdominal cavity, especially around the appendix. These conditions are known as Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome).
With an infection such as chlamydia in women, symptoms and treatment are interrelated. If the presence of chlamydia is diagnosed, treatment is based on the clinical picture and the serotype of the bacterium.
Symptoms of chlamydia in women
Symptoms of chlamydia. This disease can be asymptomatic for many years; signs of the disease are found in only 30–40% of women. However, the hidden course of the process is not at all safe: chlamydia, even without any symptoms, can cause many complications, including infertility. The incubation period of the disease is 2–4 weeks, so the appearance of any symptoms is often not associated with past sexual contact.
If a patient has an acute form of chlamydial infection, then, as a rule, the symptoms of chlamydia are glassy discharge from the urethra, often in the morning. The color of the discharge may be yellowish; as a rule, the discharge appears in small quantities. Possible itching or discomfort when urinating, pain and cutting sensations in the urethra, sticking of the urethral sponges.
The general condition changes to a lesser extent - weakness, signs of intoxication, a slight increase in body temperature. However, much more often chlamydia occurs without pronounced symptoms or does not manifest itself at all - asymptomatic.
Chlamydia, like other sexually transmitted infections, does not have specific symptoms, so to identify the true cause of the disease, an examination by a gynecologist is necessary. The following signs may indicate a chlamydial infection:
- burning sensation, itching in the vagina;
- the appearance of light yellow or white discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- frequent urination, accompanied by a burning sensation at the beginning or end of the process, may indicate the addition of urethritis;
- pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region may appear when the process spreads to the overlying organs of the reproductive system;
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile values (37–37.5 C).
The described symptoms of the acute stage of the disease (if any) disappear on their own after some time, but this only means that the disease has become chronic (self-healing is impossible). With an exacerbation of chlamydia, which most often occurs against the background of immunodeficiency, the above-described signs will appear.
Symptoms of chlamydia. Modern diagnostic methods are used to diagnose sexually transmitted infections; a smear on the flora is not enough in this case. In addition, chlamydia is often combined with other sexually transmitted infections. Also, when identifying the causative agent of the disease, it is necessary to determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. Treatment in each case is selected by the doctor individually.
Symptoms of fresh urethritis practically do not occur; more often they are subacute, low-symptomatic forms, in which discharge from the urethra in men and from the vagina in women, white, yellow or transparent, is noted. Nonspecific symptoms of chlamydia include signs of dysuria - pain, burning during urination or sexual intercourse, redness, itching of the external opening of the urethra. Chronic inflammation of the urethra caused by chlamydia leads to the development of stricture (narrowing). One of the most common signs of chlamydia in women is cervicitis, characterized by specific mucopurulent discharge from the genital tract, without a strong odor, swelling and hyperemia of the cervix.
Symptoms of chlamydia in girls include vulvovestibulovaginitis with characteristic frequent urination, itching in the genital tract, and discharge. Subsequently, with the further development of the disease, complications of chlamydia appear and patients complain of pain, lumbago in the perineum, scrotal organs, rectum, women are bothered by pain in the lower abdomen, in the lumbar region, and possible pain during sexual intercourse.
In approximately 60% of cases, chlamydia is asymptomatic. With the further development of chlamydial infection, the symptoms manifest themselves in complications of chlamydia: prostatitis, epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis, fever), endometritis, salpingoophoritis (inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages), which are one of the main causes of female infertility. A systemic symptom of chlamydia is Reiter's syndrome, which includes the triad: urethritis, conjunctivitis, reactive arthritis.
Diagnostics
Chlamydia in women (symptoms appear 14 days after infection of the body) requires a full medical examination based on existing complaints. Diagnostics will allow you to determine the degree of the inflammatory process, the affected area and the causative agents of the disease in order to select the most effective antibacterial agent.
For chlamydia, the following examination methods are prescribed:
| Name | Description |
| Vaginal smear | The study will allow us to identify the causative agents of pathological processes. |
| Blood test for antibodies | The results indicate the type of pathogen. The ELISA method can determine the development of chronic or acute chlamydia. |
| Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) | The results help determine the genetic characteristics of pathogenic flora. |
| Bacterial culture | The study allows us to determine with maximum accuracy the type of causative agent of the inflammatory process and its sensitivity to antibiotics. |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the pelvic organs | During diagnosis, the doctor determines structural changes in the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. |
It is important to differentiate chlamydia, since many inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system are accompanied by similar clinical signs.
Treatment of chlamydia in women
Symptoms of chlamydia. When treating any sexually transmitted infections, it is necessary to prescribe antibiotics; for chlamydia, various groups of antibacterial drugs are used, depending on the presence of concomitant infections and the sensitivity of the pathogen to them. The course of treatment is up to 14 days. It is important to strictly follow the medication regimen prescribed by your doctor; under no circumstances should you interrupt therapy on your own. This will lead to the fact that the causative agents of the disease will become resistant to the effects of the drug, and treatment will have to be started first with other drugs.
Correction of immunity is necessary for all women who have been diagnosed with chlamydial infection. Multivitamin complexes are used (Vitrum, Biomax, Alphabet, etc.), as well as adaptogens (Eleutherococcus, Echinacea purpurea, Schisandra, etc.)
For local treatment, tampons impregnated with medicinal substances and external ointments are used.
After antibiotic treatment is completed, it is necessary to restore the normal microflora of not only the intestines, but also the vagina. Normal microflora in the vagina creates local immunity and prevents the colonization of pathological microflora. It is recommended to take prebiotics (Linex, Bifidumbacterin, etc.) and probiotics (Acipol, Hilak forte, etc.) internally. Vaginal suppositories with lactobacilli (Lactonorm, Acylact, etc.) are used locally.
During treatment for chlamydia, a woman is advised to avoid sexual intercourse, limit physical activity, and avoid drinking alcohol, fatty, spicy, salty and fried foods.
Treatment
When deciding how to treat chlamydia in women, the first choice drugs are antimicrobial substances, i.e. antibiotics with expected intracellular penetration and antichlamydial effect. These include:
- Doxycycline,
- macrolides,
- systemic fluoroquinolones.
In order to cure chlamydia in the acute phase, a short-term treatment regimen can be used; with it, drugs from the group of azalides, macrolides, fluoroquinolones or tetracyclines are administered once. Chronic infections or infections with systemic manifestations require long-term treatment.
The second therapy for the disease chlamydia, the symptoms and treatment of which are also interrelated, is carried out by changing the person’s treatment group, just like the third therapy. the latest version of the treatment approach involves a combination of Azithromycin and Ciprofloxacin, i.e., a combination of bacteriostatic and bactericidal antibiotics that have a significant post-antibiotic effect.
The question remains unanswered: how to treat the remaining approximately 12% of patients who do not respond to standard treatment. The toxicity of antibacterial therapy should not be overlooked because... it is significant. The clinical symptoms of such people are usually insignificant. Their ability to adhere to a strict protective regime is then limited. Thus, there is a high risk of further spread of infection among the population. Is it possible, despite the toxicity of the treatment, to use the drugs at the maximum dose in an attempt to eradicate the infection? The future may provide an answer to this question.
To improve the response to treatment, it is enhanced by supportive therapy, especially enzyme therapy (for example, Wobenzym) or probiotics. Depending on the person’s condition and symptoms of infection, anti-inflammatory drugs, suppositories for chlamydia and COX-2 inhibitors are used.
Before using suppositories for chlamydia, it is advisable to consult a doctor, despite the fact that most of them can be bought without a prescription!
Immunological screening and testing is part of the care of a significant percentage of patients with chronic infection.
Control sampling for microbiological testing is carried out at intervals of at least 4-6 weeks.
If the treatment results are positive, another antimicrobial substance is administered. The success rate of the second and third therapy within one year reaches 92% in women and 86% in men.
Drugs for the treatment of chlamydia in women
Symptoms of chlamydia. The choice of drug for chlamydia is the most important process. Entrust it to a specialist; choosing the right medicine for such a dangerous disease is possible only through direct interaction with the patient. We will give recommendations on choosing a drug; your task is to coordinate them with your doctor and begin timely use.
- Antibiotics. All types of tetracyclines, macrolides and cephalosporins. They respond to most strains of chlamydia. But it is better to find out the type of chlamydia before taking it.
- Immunomodulators. Viferon, Lysozyme or Timalin. They increase the body’s defenses, prevent complications from appearing, and speed up the treatment process.
- Prebiotics. Duphalan, Lactusan. They are used to enhance antibiotics and create comfortable conditions for the development of antibodies against chlamydia. The infection itself does not cure.
- Multivitamins. Vitrum or Supradin. They are prescribed during treatment and after completion. They normalize the functioning of the female reproductive system and increase the overall tone of the body.
Try to take a comprehensive approach to treatment, combining all four classes of medications. Then you can not only get rid of the infection, but also create a favorable environment for the development of the immune system after recovery.
After completing the course of treatment, it is necessary to undergo examination again in order to ensure the positive results of therapy.
Treatment regimen for chlamydia in women
Symptoms of chlamydia. To cure chlamydia, you need to be diagnosed and receive prescriptions for medications from a doctor. Deviations from the algorithm should not be allowed, since chlamydia is a strong microorganism. They are able to resist most antibacterial and antiviral drugs, since they are neither viruses nor bacteria in full. Folk remedies, classical antibiotics of different generations, immunomodulators in their pure form - all this is useless against chlamydia. Therefore, therapy should begin with identifying the type of parasites, as we discussed earlier.
- Laboratory tests to identify the type of chlamydia and search for chemical reactions with various drugs.
- The doctor prescribes a special antibiotic, which reacted with the infection during the study and overcame it.
- A week after prescribing and using an antibiotic at home, the woman undergoes control tests to identify the dynamics of recovery.
- If the prescribed medicine does not produce results, then another drug is prescribed.
- Immunotherapy. Severe infections quickly impair immunity. In the process of getting rid of chlamydia, a woman needs to improve the protective functions of the body. To do this, you need to use immunostimulants of plant origin and synthetic structure. In addition to these, take interferon and vitamin and mineral complexes to stimulate the immune system. The better the immunity, the faster and easier the treatment will be.
- Taking antioxidants and hepatoprotectors. The final stage of treatment, but no less important. Hepatoprotectors are needed to protect the liver from the effects of antibiotics, and antioxidants cleanse the body of microorganism residues.
If the doctor initially selected the right medicine, then the patient is lucky, because chlamydia quickly adapts to medications that affect them but do not kill them. The more medications are tried, the stronger the immunity of chlamydia develops.
Diagnosis and treatment
When visiting a doctor, the woman will be prescribed an examination. For this purpose, the secretion secreted in the cervical canal is used.
Methods for diagnosing chlamydia are as follows:
- PCR;
- direct immunofluorescence method;
- cultural research.
If chlamydia is confirmed in women, treatment at home is excluded. Therapy is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor and includes powerful antibiotics that can penetrate tissue cells and destroy chlamydia.
The following types of antibacterial drugs are used for treatment:
- macrolides;
- tetracyclines;
- fluoroquinolones.
Medicines such as Azithromycin, Sulfanilamide, Penicillin, Tetracycline are effective.
The drugs are prescribed in large doses. The course of treatment lasts from 7 to 10 days and is necessarily comprehensive. In addition to tablets, antibacterial suppositories or ointments against chlamydia are prescribed.
The chronic course of the disease requires a longer course of treatment with antibiotics - up to 21 days. It is supplemented by the prescription of immunostimulating drugs, as well as physiotherapy.
During the treatment period, women are recommended:
- compliance with the diet prescribed by the doctor;
- use of multivitamin preparations;
- exclusion of alcoholic beverages;
- refusal of sexual activity.
Self-medication for chlamydia in women is unacceptable! Incorrect selection of drugs leads to the development of resistance in the pathogenic microorganism. Then chronic foci of infection develop, which are very difficult to treat.
Discharge before and after treatment for chlamydia
Before treatment, the disease is most often diagnosed by the appearance of mucous or mucopurulent discharge from the woman’s genital tract. They may differ from normal discharge by an unpleasant odor and a greenish tint.
Symptoms of chlamydia. If after completing the course the symptoms do not disappear (exactly the same vaginal discharge that was there before treatment remains, pain and discomfort are felt) or reappear after some time, you must consult a doctor again. The doctor will prescribe a second course of treatment and adjust it taking into account the patient’s sensitivity to the antibiotics used. It is also necessary to undergo treatment if an infection is detected in a sexual partner, even if you have no symptoms of the disease.
Complications and consequences of chlamydia in women
Inflammatory processes accompanying chlamydial infection can spread to overlying organs. Most often, chlamydia leads to the development of the following serious complications:
Adnexitis (inflammation of the uterine appendages) is a complication of chlamydia, which can lead to the formation of adhesions and scars in the fallopian tubes, as a result of which their patency is impaired. As a result, women suffer from infertility and the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy increases. Often surgery is necessary to restore the function of the fallopian tubes.
Endometritis (inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus) can also cause infertility, miscarriage, and premature birth.
Endocervicitis (an inflammatory process that occurs in the cervical canal) increases the risk of developing malignant tumors in the cervix. Rarely occurs in isolation; usually the infection involves the endometrium of the uterus.
Chlamydial peritonitis and perihepatitis in women can occur when the process spreads to the peritoneum. Although this is a rare complication, it still occurs and requires immediate surgical treatment.
Symptoms of chlamydia. Reiter's syndrome, which occurs in patients with chlamydia, includes the so-called triad: arthritis, conjunctivitis, urethritis. Most often it develops against the background of an acute form of the disease in young women and is accompanied by cervicitis and endometritis.
Chlamydia is a serious disease, the consequences of which can bother a woman for many years even after successful treatment. Oddly enough, it is chlamydia that, much more often than other sexually transmitted infections, leads to infertility, frozen and ectopic pregnancies. Infected women have a significantly increased risk of miscarriage and premature birth.
An increase in the incidence of perinatal mortality is also recorded. Women who have given birth and have chlamydia have an increased risk of developing postpartum complications. We should not forget about the consequences of chlamydia for newborns, who become infected while passing through the mother’s birth canal.