The human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV for short, is an infectious, slowly progressive disease that is characterized by damage to the human immune system. One of the achievements of modern medicine can be said with a clear conscience that today HIV-positive children have the opportunity to live healthy and full lives. But parents must know how HIV infection is transmitted in children in order to protect the life and health of their children.
Features of HIV
Presumably, the first carriers of HIV were monkeys on the African continent. Humans have also become infected from animals. Thanks to population migration, the infection spread across the planet. Now people already know how HIV infection occurs, but previously this was unknown, since the virus does not manifest itself in any way when it enters the body.
After infection, the body is affected in several stages:
- Acute phase. About 70% of patients complain of acute respiratory infections symptoms a month after infection. Diagnosing the virus is difficult because it requires a PCR test for every patient with a runny nose and fever.
- Asymptomatic period. After the symptoms of acute respiratory infections disappear, the person feels healthy and continues to do his usual activities.
- Seroconversion period. After 3-6 months, specific antibodies begin to form in the body. Sometimes they don't appear for a year. After 6-12 months, the concentration of the virus in the tissues of the body becomes sufficient to infect others. This period can last more than 10 years.
- Period of secondary diseases. At this time, the patient develops an immune deficiency, which is manifested by opportunistic infections. AIDS is the most severe stage of HIV, which is accompanied by the destruction of the immune system. The development of secondary infection leads to the death of the infected person.
To protect yourself, a person needs to know how AIDS is transmitted and methods for diagnosing the disease.
To detect the virus, the following studies are provided:
- Enzyme immunoassay - diagnoses HIV 3 months after infection. A false result occurs in less than 1% of cases.
- Immunoblotting - used to confirm a positive ELISA result.
- Polymerase chain reaction - used when the immunoblot result is indeterminate. The analysis allows you to examine the blood of newborns and sick people if more than 10 days have passed since infection. Because the test is highly sensitive, it reacts to other infections in the body.
- In emergency cases, a rapid test is used. But the result cannot be considered final; confirmation is required with the help of other additional studies.
What is HIV, HIV infection and AIDS
First, let's decide on the names.
HIV is a human immunodeficiency virus that infects cells of the immune system with CD4 receptors (T-lymphocytes (T-helpers), monocytes, macrophages, Langerhans cells, dendritic cells, microglial cells).
HIV infection is a slowly progressive disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus, as a result of which the human immune system sharply weakens and ceases to protect the body - AIDS develops.
AIDS is acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. AIDS is the final stage of HIV infection. People with HIV infection die due to manifestations of AIDS (infections and tumors).
HIV, or human immunodeficiency virus, was discovered in 1983, although the first mention of deaths of people of homosexual orientation caused by unknown immunodeficiency conditions appeared in 1981. A year later, it became obvious that in addition to homosexuals, this condition is common among injection drug users, hemophiliacs and citizens of Haiti. All this indicated the infectious nature of the disease.
HIV spread very quickly on Earth, becoming an epidemic. It was even called the “plague of the 20th century.” Over almost 35 years of observation, over 60 million people have become infected with HIV. Almost 30 million people have already died from AIDS; the rest are living with HIV.
An HIV vaccine has not yet been developed. At the same time, over the past 20 years, thanks to powerful public propaganda and widely introduced means of prevention, it has been possible to stabilize and even halve the level of HIV infection and morbidity.
Within 5-8 years (while the virus slowly destroys the immune system), HIV infection almost never manifests itself clinically. Once the number of T-lymphocytes falls below 200 cells/μl (6 times lower than normal), immunity is destroyed and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) develops. With AIDS, a person is attacked by infections that he would not have gotten with normal immunity (opportunistic infections) and tumors, in particular Kaposi's sarcoma and lymphomas. The patient dies within 1-3 years from infections and/or tumor.
After the onset of AIDS, a person can no longer be radically helped; just prolong life. At the same time, modern medicine is very successful in combating HIV infection detected in the early stages. Antiviral drugs and special protocols have been developed (long-term highly effective antiretroviral therapy), with the help of which it is possible to extend the life of an HIV-infected patient by several decades.
Prevention of HIV infection includes the use of condoms during any sex, the use of disposable syringes by injection drug addicts, mandatory HIV testing of donated blood, mandatory testing of expectant mothers in early pregnancy and other activities.
Ways of spreading the disease
How is HIV infection transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person?
- Parenteral route of transmission. Infection occurs when the blood of an infected person enters the bloodstream of a healthy person through direct contact or transfusion. There is also a risk of infection if instruments are reused in a healthcare facility without proper sterilization. The method of infection is common among drug addicts who use one injection syringe.
- Sexual contact. Sexual intercourse without a barrier contraceptive (condom) is the main cause of HIV infection. Heterosexual intercourse or oral sex can also cause infection if one of the partners is infected. The use of oral contraceptives, gels, suppositories and similar methods of contraception does not protect against infection with the immunodeficiency virus.
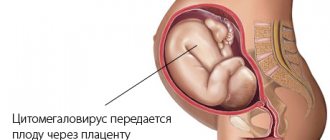
- Vertical transmission path. This method involves the transmission of the virus from mother to fetus during pregnancy. Doctors have figured out how children become infected in the womb and are taking measures to ensure the safety of the unborn child. According to statistics, 70% of newborns from an HIV-positive woman are not infected. When it is established that the mother is infected, it is recommended to stop breastfeeding. Diagnosis of the virus in a child is possible after he reaches the age of three; until this moment, antibodies transmitted from the mother remain in the body.
Symptoms
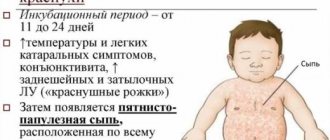
Symptoms of HIV depend on the stage of development of the disease. During the incubation period and the first stage of the disease, no changes in the human body may be observed. Typically, people seek medical help at the second stage of the disease, when persistent damage to internal organs, skin and mucous membranes appears. Symptoms of HIV in women are the following:
- severe headaches;
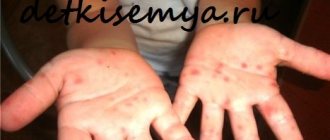
- rash on the body;
- pain in the throat, muscles and joints;
- fever;
- constant fatigue;
- increased sweating;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- mouth ulcers.
Symptoms may not appear until several years after infection. Their manifestation is individual and usually lasts no more than 2 weeks. After they disappear, the asymptomatic period of infection begins. The person leads a normal lifestyle and does not feel any discomfort. But the virus remains active and is transmitted to other people, gradually destroying the immune system.
Without treatment, after a few years, HIV develops into AIDS. This means that the immune system is severely damaged and susceptible to any infections from the outside. As a result, a person begins to suffer from constant colds, fungal diseases and flu. The main signs of AIDS are the following symptoms:
- causeless weight loss;
- diarrhea, indigestion, nausea and vomiting;
- vaginal infections;
- neurological disorders;
- persistent enlargement of lymph nodes;
- shortness of breath;
- inflammatory pathologies of the small pelvis;
- recurring chills;
- persistent rash on the body;
- feeling of constant fatigue.
In men, HIV is slow to manifest itself, so a person may not know about his serious illness for many years. If the immune system is weakened, then a few months after infection he experiences a condition as if he had the flu, which goes away in 1-2 weeks. There is a persistent increase in body temperature up to 39 ° C, severe sore throat, enlarged lymph nodes, constant fatigue, chills and active sweating.
Subsequently, the disease becomes asymptomatic and appears only after a few years. Symptoms will depend on how damaged the immune system is and how damaged the internal organs are. Most patients lead a normal lifestyle and see a doctor only at the last stage. When HIV turns into AIDS, a person lives from six months to 2 years.
At-risk groups
Certain categories of people are at risk of contracting HIV. Among medical personnel, surgeons, dentists, and laboratory workers are especially susceptible to this. For them, knowing how AIDS is transmitted is especially important.
Other categories include:
- persons with drug addiction;
- persons who have promiscuous sex without using barrier contraception;
- prisoners in colonies;
- law enforcement officials in contact with prisoners;
- women with reduced social responsibility;
- medical workers who, due to their occupation, have direct contact with sick people or biological fluids;
- people who are indicated for internal organ transplantation or blood transfusion;
- children whose mothers have been assigned HIV-positive status.
Symptoms
Symptoms of HIV depend on the stage of development of the disease. During the incubation period and the first stage of the disease, no changes in the human body may be observed. Typically, people seek medical help at the second stage of the disease, when persistent damage to internal organs, skin and mucous membranes appears. Symptoms of HIV in women are the following:
- severe headaches;
- rash on the body;
- pain in the throat, muscles and joints;
- fever;
- constant fatigue;
- increased sweating;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- mouth ulcers.
Symptoms may not appear until several years after infection. Their manifestation is individual and usually lasts no more than 2 weeks. After they disappear, the asymptomatic period of infection begins. The person leads a normal lifestyle and does not feel any discomfort. But the virus remains active and is transmitted to other people, gradually destroying the immune system.
Without treatment, after a few years, HIV develops into AIDS. This means that the immune system is severely damaged and susceptible to any infections from the outside. As a result, a person begins to suffer from constant colds, fungal diseases and flu. The main signs of AIDS are the following symptoms:
- causeless weight loss;
- diarrhea, indigestion, nausea and vomiting;
- vaginal infections;
- neurological disorders;
- persistent enlargement of lymph nodes;
- shortness of breath;
- inflammatory pathologies of the small pelvis;
- recurring chills;
- persistent rash on the body;
- feeling of constant fatigue.
In men, HIV is slow to manifest itself, so a person may not know about his serious illness for many years. If the immune system is weakened, then a few months after infection he experiences a condition as if he had the flu, which goes away in 1-2 weeks. There is a persistent increase in body temperature up to 39 ° C, severe sore throat, enlarged lymph nodes, constant fatigue, chills and active sweating.
Subsequently, the disease becomes asymptomatic and appears only after a few years. Symptoms will depend on how damaged the immune system is and how damaged the internal organs are. Most patients lead a normal lifestyle and see a doctor only at the last stage. When HIV turns into AIDS, a person lives from six months to 2 years.
How not to get infected with AIDS
There are many myths about how the virus can be infected.
Doctors focus on how you can’t get infected with HIV:
- Infection does not occur in a household manner, since virus cells do not survive contact with the environment. There are no recorded cases of such infection in statistics.
- Saliva is not a source of infection. Viral cells are found in it, but their number is not enough to infect the body.
- Tears and sweat will also not harm a healthy person.
- Airborne transmission is not a method of infection.
- HIV is not transmitted through contact in public places, for example, by shaking hands or through handrails in transport.
- There is no hereditary predisposition to the virus.
- The disease is not transmitted through food and drink.
Infection with AIDS is considered almost impossible, since such a disease is the last stage of the development of HIV infection. If you seek help in time and follow the recommendations of a specialist, the development of infection will not lead to aggravation of the disease.
Symptoms of HIV infection and AIDS
HIV infection can be divided into 3 stages:
- incubation stage (1-7 years) - asymptomatic or accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy). At the beginning of this stage, the number of T-lymphocytes is close to normal, but progressively decreases as immune cells are destroyed;
- manifest stage, or the stage of clinical manifestations, which is characterized by acute infections (frequent ARVI, otitis, sinusitis, rhinitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, bacterial pneumonia, furunculosis, streptoderma, acne, lymphadenitis, abscesses, meningitis, oral candidiasis (fungus), stomatitis, periodontitis, herpes zoster, infectious mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus infection, measles, toxoplasmosis, staphylococcal infection, listeriosis, etc.), seborrheic and ulcerative dermatitis, cervical erosion, cervical dysplasia, cervical cancer, menstrual disorders, mastopathy, peripheral neuropathy, idiopathic thrombocytopenia (decreased number of platelets in the blood), anemia; leukoplakia (damage to the mucous membrane of the cavity, mouth, respiratory system, genitourinary system and anus), chronic diarrhea, etc.;
- AIDS, which manifests itself as infections (pulmonary candidiasis, cytomegalovirus infection, herpetic lesions of the esophagus, pneumonia, mycobacteriosis, salmonellosis, sepsis, etc.), tumors (Kaposi's sarcoma, skin cancer, lymphoma, cervical cancer, rectal cancer, kidney cancer, cancer brain, etc.), encephalopathy, dementia. AIDS ends in the death of the patient.
Prevention of infection
Population infection by the virus remains an important issue worldwide. To avoid the penetration of an infectious agent, people need to know whether it is possible to become infected with AIDS in life situations, and what rules need to be followed.
Prevention includes taking the following measures:
- gain knowledge about risk groups;
- avoid indiscriminate unprotected sexual intercourse;
- stop using drugs;
- be careful in the postoperative period;
- Maintain sterile conditions when administering injections.
For people with diabetes, COPD, hepatitis, cancer and pathologies of the lymphatic system, preventive measures involve taking antibiotics and antiviral medications.
AIDS prevention is aimed at sanitary and information education of the population. If the recommendations are followed, a healthy person can come into contact with infected people without the risk of infection.
Treatment of HIV infection and AIDS
There are no ways to radically eliminate HIV from the body yet. The most effective treatment for HIV infection is antiretroviral therapy, which slows the progression of HIV infection (delays or prevents the onset of AIDS), allowing a person to live a full life for decades.
Highly effective antiretroviral therapy requires many years of regular (without omissions) taking three (four) drugs under the supervision of an infectious disease specialist or virologist.
An HIV-infected patient must maintain his body through a healthy lifestyle (proper nutrition, healthy sleep, avoiding stress, etc.)
Clinical manifestations of AIDS (infections, tumors, encephalopathy, etc.) are treated by specialists in clinics and hospitals. Precautions are required to avoid HIV infection of medical personnel and other patients.
Is it possible to become infected with HIV from one act during therapy?
Partners are also interested in what is the chance of becoming infected with HIV after a single contact if a person is taking medications for a retrovirus that causes immunodeficiency. Antiviral drugs slow the progression of the disease by inhibiting viral replication in the host cell. This means that the viral load of people receiving therapy is significantly lower, and the chance of infecting someone is reduced by 96%.
But at the height of the disease, when a person has symptoms, the contagiousness increases sharply. Considering that you can become infected with HIV even at the first sexual contact, it is important for a person with a negative status for the virus to take a course of prevention after any unprotected sex. If antiviral medications are started within 72 hours of condomless sex, infection can be prevented. When using a condom, the chances of transmitting the virus are reduced by almost 80%.
If you are unlucky and you become infected with HIV the first time, unfortunately this happens, then you immediately need to undergo a course of retroviral therapy. Check out this range of HIV medications. There you will definitely find a suitable drug and will not have to worry about the development of HIV.