Sexually transmitted diseases are characterized by the absence of symptoms. Sometimes this may indicate their aggravation. There are several main methods of transmission of infections and bacteria, among which sexual intercourse should be noted. Many sexually transmitted diseases cause serious health problems. At the same time, difficulties also apply to the treatment process. That is why diseases transmitted through sexual contact are classified as a separate group.
Definition of STD
STDs are a group of infections that can be transmitted through sexual contact. As a rule, all pathogens are sexually transmitted infections. Diseases that are sexually transmitted are often characterized by the absence of symptoms; this may also indicate their exacerbation.
Other features include the following:
- Most often, STDs are transmitted through unprotected sex. However, some viruses that are part of the STD group also enter the body through contaminated blood.
- Almost all sexually transmitted infections affect the development of the fetus and are transmitted to children through mother's milk.
- In women, sexually transmitted infections can cause the development of serious pathologies. In this case, a disease may develop that will cause infertility.
Sexually transmitted diseases may be incurable, while others can be treated, which can take many years. Let's look at a detailed list of what diseases there are that are transmitted sexually.
Sexual infections and pregnancy
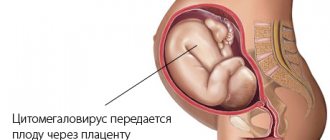
Since STDs have a negative impact on the course of pregnancy and the development of the fetus, before conceiving a child, sexual partners should be tested for sexually transmitted infections.
A disease detected in a woman must be treated before pregnancy occurs.
Many sexually transmitted infections can lead to both intrauterine infection of the fetus and at the time of birth.
As a result, the child may develop severe damage to the genitals, mucous membranes of the eyes, and respiratory organs.
Intrauterine infection may contribute to the development of fetal abnormalities.
Common diseases
There are several diseases that are included in the group of STIs:
- Chlamydia.
- Trichomoniasis.
- Gonorrhea.
- Herpes infection.
- Papilloma virus.
- Syphilis.
- Genital candidiasis.
- Mycoplasmosis.
- Ureaplasmosis.
- HIV infection.
Syphilis infection, a sexually transmitted infection, is one of the most common and well-known. According to studies, the number of people infected is increasing every year. Some of these diseases have no symptoms at the first stage of development, others cause serious health problems immediately after infection. Some viral diseases, for example, AIDS, cannot be cured at all. Let's look at the features of STDs in more detail.
What diseases are classified as STDs?
STDs, in addition to the well-known syphilis, gonorrhea and chlamydia, include:
1) AIDS,
2) both types of hepatitis (B and C),
3) trichomoniasis,
4) ureaplasmosis,
5) mycoplasmosis,
6) papillomavirus,
7) molluscum contagiosum and a number of other, less common diseases (there are about 20 sexually transmitted infections in total).
It is these diseases that are transmitted primarily through sexual contact, although in the minds of the majority, STDs include only sexually transmitted diseases - “shameful diseases”. And that is why they are doubly dangerous.
If the majority of the population is more or less informed about the first three diseases, then for all the others there is either complete ignorance or half-knowledge, which is more dangerous than ignorance.
However, to talk about sufficient awareness in relation to syphilis would be an exaggeration. According to mandatory medical examinations of the population, patients are often identified as having a syphilitic rash (i.e., advanced syphilis).
The asymptomatic course of syphilis is generally a special topic. Many people miss such obvious symptoms as a rash because they do not associate its appearance with a developing disease, especially since this rash goes away on its own without any treatment, marking the transition to the next stage of syphilis.
Even chancre - a one hundred percent confirmation of syphilis - many call it “just a blister” and even skip this stage without attention - after all, chancre really doesn’t hurt either.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection. Routes of spread: sexual contact, transmission of the pathogen from mother to fetus during childbirth and pregnancy itself. The following can be highlighted:
- The incubation period lasts 2–6 weeks.
- When an infection enters a woman’s body, damage occurs to the fallopian tube, cervical canal, urethra, and liver capsule. Diseases of the genitourinary system in many cases lead to severe discomfort. Complications can cause infertility.
- If the pathogen enters a man’s body, a disease may develop that affects the prostate and urethra.
With timely treatment, which is represented by taking prescribed antibiotics, the likelihood of complications can be eliminated.
What diseases are considered STIs?
There can be any disease, but they all have one common path of transmission. Typically, human-to-human transmission occurs through direct sexual contact. At the initial stage of development, the disease manifests itself on the genitals, anus or rectum, and oral mucosa. Over time, infections attack multiple systems, affecting the bones, central nervous system, liver, heart and other organs.
Sometimes STIs are also transmitted through non-sexual contact: from mother to child, through kissing, blood transfusion, use of contaminated instruments, and household contact.
The causative agents of sexually transmitted diseases are bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. Most of them have been known to science for hundreds and even thousands of years. In women, their treatment is complicated by the structure of the genital organs.
List of bacterial infections
During sexual contact, partners can exchange pathogenic bacteria that provoke STIs. The list of infections in women includes:
- Syphilis
. The causative agent is Treponema pallidum. 3 weeks after infection, a hard chancre (round ulcer) appears at the site of penetration of the bacterium. Women may not notice it on the genitals because it does not cause discomfort or pain. With the proliferation of treponema, characteristic rashes appear on the skin and mucous membranes, and the lymph nodes become enlarged. The first signs are replaced by systemic damage to all organs: hair may fall out, bald spots may form, and the voice becomes hoarse. - Chlamydia
. This is the most common sexually transmitted infection: chlamydia is diagnosed in 1 billion people. Women are especially susceptible to it. Microorganisms usually damage the genitourinary system and can cause trachoma, conjunctivitis and lymphogranuloma venereum. Symptoms such as mucopurulent vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor, pain, itching and burning, and less commonly, low temperature and weakness are observed. - Gonorrhea
. The cause of the disease is gonococcus, signs of infection with which appear after 3-7 days. Mucus and pus begin to be released in the genitals, and urination becomes frequent and painful. If gonorrhea is not treated, it spreads to the bladder, kidneys and even the uterus, causing infertility. - Mycoplasmosis
. Mycoplasmas most often affect the organs of the genitourinary system. - Ureaplasmosis
. The most controversial sexually transmitted disease, because ureaplasma lives in the vagina of 60% of healthy women. Microorganisms do not manifest themselves in any way for years, so their hostility towards humans is questionable. Inflammation begins when immunity decreases and the normal microflora of the vagina is disrupted. - Lymphogranuloma venereum
. When the pathogen enters the body, the inguinal and femoral lymph nodes begin to become inflamed. - Soft chancre
. The incubation period of the pathology is 3-7 days. During this time, women develop a purulent ulcer on the labia minora and labia majora.
Lymphogranuloma and chancroid are most typical for tropical countries; they occur rarely in Europe.
In women, STIs are almost always asymptomatic, so you need to undergo regular screening and smear testing.
Treatment of bacterial infections begins with antibiotics. But some microorganisms do not die, but go into hibernation until better times. As soon as a person’s immunity fails, they will begin to gain strength.
Features of viral infections
A number of sexually transmitted diseases are caused by viruses. The list of STIs in women includes:
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
. Over time, it completely destroys human immunity. The last stage is known as AIDS. But with antiretroviral therapy, the life expectancy of patients can reach up to 70-80 years. - Herpes
. How a sexually transmitted infection causes genital lesions. It poses the greatest danger to infants born from an infected mother. - Genital warts
. As a result of infection, small flesh-colored growths appear on the genitals and around the anus. - Papillomavirus
. Most of the varieties cause cancer. - Hepatitis B
. The virus is highly resistant to adverse factors. - Cytomegalovirus
. Refers to the herpes virus. - Molluscum contagiosum
. After the virus penetrates, nodules grow on the labia majora, thighs and buttocks, raised above the skin. They are round, with pressure in the middle, and flesh-colored.
Antiviral drugs are prescribed for treatment.
How do simplest infections work?
This type of STI includes trichomoniasis. Once in the human body, protozoa immediately cause inflammation of the genitourinary tract. Then they become the cause of dangerous complications - infertility, pregnancy pathologies, and so on.
In the female body they settle in the vagina. The first signs of the disease begin to appear after 1-4 weeks. Trichomoniasis reveals itself:
- itching and burning of the labia;
- pain during urination;
- discomfort during sex;
- “fishy” smell;
- yellowish and greenish discharge;
- reddened vaginal mucosa.
Preparation for testing begins 2 days in advance. But for diagnosis it is not enough to take a smear; a more reliable result is shown by scraping and in vitro culture.
STIs and fungal infections
Even in gynecology, candidiasis is called thrush. White vaginal discharge in women is so abundant and thick. They look like cottage cheese and cause severe itching.
Painful sensations may occur during sexual intercourse.
Usually, when the vagina is affected by candida, antifungal suppositories are prescribed, but in difficult cases, medications for internal use are recommended.
But the disease cannot always be called a sexually transmitted infection - yeast fungi are everywhere. That's why they are called opportunistic. If a person is healthy and full of strength, then candida does not make itself felt. But when immunity decreases, they begin to actively reproduce.
What are sexual parasites?
During sexual contact, lice pubis, or phthiriasis, is transmitted. The louse attaches to the base of the pubic hair, feeds on the host's blood and begins to reproduce.
The first larvae hatch after about a week, and after two they turn into adult lice. After 2-3 weeks from the moment of infection, the patient begins to experience severe itching.
HIV infection
When considering viral diseases, special attention should be paid to HIV infection. Its features include:
- After entering the body, the pathogen remains in it until death. There are no effective drugs that stop or slow down the replication of the virus.
- The infection is almost asymptomatic. For several weeks after infection, minor symptoms may appear, which some people confuse with a cold or other illness.
- The disease, which develops when infected with HIV, affects the immune system. As a result, infectious diseases that develop after damage to the immune system manifest themselves in the most severe form.
- The last stage of development of the virus leads to the appearance of AIDS. With this disease, even a common cold provokes symptoms that can cause death.
With proper treatment, life expectancy increases significantly. There are many cases where people live with the diagnosis for more than 10 years. However, this is only possible with strict adherence to medical recommendations.
Herpes virus
Among the sexually transmitted infections is herpes. Many people are familiar with it, since when the immune system is weakened, various types of rashes appear, most often on the lips. After the pathogen enters the body, it can reach the spinal cord, where it is localized and becomes immune to the effects of antibiotics.
There are types 1 and 2 herpes viruses. Both are sexually transmitted and have only a few differences in the symptoms they present. Infection occurs through direct contact with the infected area, as well as through genital secretions. The incubation period lasts from 2 to 21 days.
Features of the manifested symptoms include:
- The clinical manifestation of the disease, which consists of the formation of blisters.
- After some time, the bubbles burst and a large number of virus cells are released. Viral cells infect healthy tissue, which leads to the appearance of even more bubbles.
- At the site of the rupture of the vesicles, erosion forms, which sometimes takes at least a month to heal.
It should be noted that after the disappearance of clinical symptoms, the virus again enters an inactive phase. Stress and excessive physical activity cause many diseases, including those caused by the herpes virus.
The microorganism that causes the development of herpes can be transmitted through sexual secretions and normal contact. Prevention in case of manifestation of the herpes virus consists of abstaining from contact until the erosion passes.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea can be transmitted through sexual contact, as well as from a pregnant woman to her fetus. The incubation period in this case is 10 days. In this case, a defeat occurs:
- Urethra.
- Rectum.
- Joint bags.
- Conjunctiva.
- Cervical canal.
When the virus enters the body of a woman and a man, symptoms manifest differently. An example is bleeding from the rectum, discomfort and a burning sensation. Gonorrhea is one of the most common sexually transmitted pathogens.
Human papillomavirus
Sexually transmitted papilloma infections are included in a separate group. At the same time, there are pathogens of low and high oncogenicity. The most dangerous is the highly oncogenic papillomavirus, as it causes the development of cancer cells that affect the cervix. The pathogen is sexually transmitted and affects the body of women and men equally. Examples include the following symptoms:
- The appearance of painless rashes in the anal and urogenital area.
- Women may develop rashes in the vagina or cervix.
- Men may develop rashes in the urinary tract.
It should be noted that the disease in question can be completely asymptomatic. However, in women, complications can cause the appearance of cancer cells. Therefore, if a sign of infection appears, a woman should undergo periodic examination as a preventative measure.
The first signs of sexually transmitted infections
Most women are interested in how signs of infection appear.
It should be noted that many of them have similar symptoms at the very beginning of the disease.
Therefore, no doctor can, as they say, “by eye,” say exactly what kind of disease we are talking about.
The incubation period for sexually transmitted infections is quite long and therefore the infection may not manifest itself in the early stages of infection.
The first symptoms appear at the moment of exacerbation of the process.
Most often, symptoms in women when infected with sexually transmitted infections look like this:
- a woman complains of increased vaginal discharge, which may differ from normal in smell and color;
- addition of painful sensations in the lower abdomen. In this case, pain can radiate to various areas: to the perineum, groin, etc.;
- it is possible that there is a menstrual cycle disorder characterized by heavy acyclic bleeding, delays or amenorrhea;
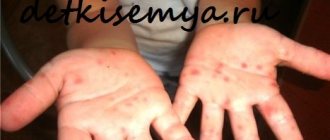
- a rash may appear on the genitals in the form of growths or ulcers, which differs in location, color, size, and other indicators;
- enlargement of nearby lymph nodes;
- frequent urination with pain;
- the presence of discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- complaints of burning pain in the genital area.
It should be understood that women may experience a rash on the genitals not only due to sexually transmitted infections.
It can also be non-infectious.
Syphilis
Syphilis infection, a sexually transmitted infection, is one of the most common and well-known. According to studies, the number of infected people is increasing every year. In this case, you should pay attention to the following:
- The long incubation period is 21 days, but it can last as long as 90 days.
- In some cases, symptoms practically do not appear, in others they cause a lot of discomfort. In severe forms, the manifestation of the disease will cause the development of serious complications.
- The disease causes many problems due to the fact that both partners must undergo treatment. Otherwise, it will be impossible to cure syphilis, since one partner will transmit the pathogen to the other.
- There are three main stages of disease development: primary, secondary and tertiary syphilis. Each stage has its own symptoms. Latent syphilis is also distinguished separately, in which symptoms are almost completely absent.
- When primary symptoms appear, ulcers form on the genitals, which lead to itching or burning.
Please note that sexually transmitted infections must be treated. This is due to possible complications. Syphilis, manifested in acute form, causes the development of pathological changes in the heart, brain and other organs. Often the acute form of the disease causes blindness. If treatment is not promptly carried out, there is a possibility of death.
Common STD symptoms
All diseases that belong to this group have similar symptoms. An example would be:
- Unnatural discharge from the genitals, which may have an unpleasant, concentrated odor.
- Unnatural redness of the genitals, swelling.
- Rashes of various types. It doesn’t really matter what type of pathogen: bacterial or viral. In most cases, the primary and most striking symptomatology is the formation of rashes of various types. Moreover, their localization can be very different: on the genitals, both inside and outside, on other parts of the skin of the body.
- Severe itching or burning sensation.
- The appearance of pain in the groin. In this case, pain most often occurs at the time of urination.
Rashes of various types.
However, there are infections that enter the body and do not manifest themselves for a long time, that is, the disease occurs in a latent form. In this case, an infected person can transmit the pathogen to his sexual partner.
Symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases
Signs of sexually transmitted infections in women
Due to the physiological characteristics of the body, a woman may experience the following symptoms of STI infection:
- Copious vaginal discharge (green, foamy, smelly, bloody);
- painful and frequent urge to urinate;
- pain and discomfort during sex;
- changes in the menstrual cycle;
- itching in the area of the external genitalia and perineum;
- rash on the labia or around the anus, mouth, or body;
- enlarged lymph nodes, etc.
If there are such symptoms of an STD, a woman must immediately go to see a gynecologist.
Manifestation of STDs in men
Men, after contracting a sexually transmitted disease, experience the following health abnormalities:
- unpleasant discharge from the urethra (white, mucous, purulent, with an odor);
- frequent and painful urination;
- blood in semen;
- various rashes on the genitals;
- problems with normal ejaculation;
- pain in the scrotum.
Such first signs should alert a man and force him to see a urologist, since all sexually transmitted diseases can progress hidden and cause serious complications.
About HIV: symptoms in men, read the material of the same name.
In what situations should you consult a doctor?
There are certain situations in which it is recommended to contact your doctor for a referral for blood tests. An example would be:
- Casual sexual intercourse. An important point is that it is impossible to identify many diseases by external signs, since they do not have clinical manifestations. Any casual sexual intercourse, especially unprotected, is a big risk for both partners.
- When changing a permanent sexual partner. Seeing a doctor in such a situation cannot be called mistrust. Many people do not suspect that they are a carrier of a dangerous pathogen, since it may be in an inactive phase, or the disease may be latent.
- If any of these symptoms appear, if they coincide with unprotected sexual intercourse.
A common misconception is that antibiotics will reduce symptoms and prevent various complications from developing. Antibiotics of a certain group are most suitable for fighting infectious diseases. There are drugs that have a general antibacterial and viral effect. But in many cases they do more harm than good.
Recently, only a doctor prescribes antibiotics. This is due to the fact that when self-medicated, they can have a negative effect on the body, weaken the immune system, and cause exacerbation of chronic diseases.
What are the preventive measures?
Even if there is only one partner, there is a possibility of transmission of the pathogen during sexual intercourse.
Everyone should know about preventive measures to prevent the spread of infectious disease pathogens. This is due to the fact that some infections can enter the body not only through sexual contact, but, for example, through normal contact.
The most common recommendations for compliance with preventive measures include:
- Correct and systematic use of female and male contraceptives, namely condoms. It is important to purchase high-quality condoms that have not expired. This is due to the fact that the use of low-quality latex causes the condom to break during sexual intercourse.
- When used correctly, germicidal agents can also significantly reduce the likelihood of transmitting certain infections that are spread through sexual contact. However, they cannot, for example, prevent the transmission of syphilis or HIV infection.
- Even if you have sexual relations with only one partner, there is a possibility of transmission of the pathogen during sexual intercourse. Therefore, conducting periodic examinations eliminates the possibility that an infection will affect the body and cause various kinds of complications.
- If clinical signs or significant deterioration in health occur, you should refrain from sexual intercourse.
- If a disease is detected, you should definitely notify your sexual partner. There is a high probability that the disease will develop in a latent form. If the sexual partner conducts a timely examination and, if necessary, appropriate treatment is prescribed, then, in some cases, the disease will not cause harm to health.
- Vaccinations have recently been carried out against some infections. The administered drugs contribute to the development of immunity. This point means that even if infected, the disease will be mild and treatment will take place much faster.
Not the entire list of diseases in the STD group causes serious illnesses, but discomfort, pain and complications in relationships with a sexual partner are guaranteed. That is why unprotected sexual intercourse and sharing sexual toys are appropriate only if both partners trust each other, do not have other relationships and take care of their hygiene and health. Otherwise, it is recommended to resort to preventive measures.
In addition, we should not forget that some infections from this group can be transmitted not only through sexual contact, but also through household contact. An example is Trichomonas, which can remain active for a long time at high humidity. Therefore, it is recommended to use only personal towels. The causative agent of scabies is transmitted both through sex and through ordinary household means, for example, through household items. HIV infection and hepatitis can be transmitted through parenteral routes.
STI prevention
It is easier to prevent any disease than to cure it, so do not forget about preventive measures. It is advisable to abandon casual relationships and frequent changes of partners. If a person has sex regularly, he will need contraception. They will not only protect against STDs, but also prevent unwanted pregnancy. After contact with a potentially sick partner, you need to visit a dermatovenerologist and get tested. Self-medication is not recommended. This may make the situation worse.
If the patient consults a doctor early after infection, he may be prescribed emergency prophylaxis. Unfortunately, there are no universal means for carrying it out, so the regimen includes immunomodulators, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and agents that have an antiviral effect.
The population must be informed of the danger. For this purpose, educational work is carried out, in particular, the promotion of contraceptives. Pregnant women are required to be checked for torque infections and STDs. Any person can undergo examination in an anonymous office, and no one will know about the test results. People who are at risk due to their professional duties should regularly donate biomaterials.