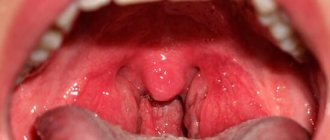
Causes, factors of occurrence and mechanism of development
Esophageal candidiasis is part of systemic candidiasis. The infection in humans is caused by bacteria of the genus Candida, a single-celled microorganism 6-10 microns in size. Depending on the conditions, they can form bud cells and threads of elongated cells.
In normal human health, candida is part of the natural microflora of the mouth, vagina and colon, as well as the environment - found in soil, water and food.
But if local immunity is impaired, the fungus multiplies uncontrollably, which leads to the development of candidiasis, in this particular case, esophageal candidiasis.
Doctors have proven that infection with candidiasis can occur in both ascending and descending ways. This disease is found in 5-10% of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and in 15-30% of patients with AIDS.
In the human esophagus there are ideal conditions for the reproduction and development of various microorganisms. But with candidiasis, not only the esophagus is affected, but also other organs that are associated with it.
Causes of esophageal candidiasis include:
- eating contaminated foods;
- use of contaminated personal hygiene and household items;
- weak immunity;
- contact with an infected person;
- long-term use of antibacterial agents;
- corticosteroid therapy;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- bad habits;
- poor nutrition;
- dysbacteriosis of mucous membranes;
- impaired intestinal motility;
- allergic reaction;
- lack of protein;
- increased activity of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands;
- unfavorable working conditions.
Factors that influence the development of esophageal candidiasis:
- hyperemia;
- toxic reactions of the body;
- diabetes;
- antacid therapy;
- tissue and organ transplantation;
- insufficient patency of the esophagus;
- chronic infections.
Symptoms of esophageal candidiasis
At the initial stage of candidiasis, the disease practically does not manifest itself at all and therefore requires extensive and detailed diagnosis. However, if a person monitors his health, he may notice some symptoms that indicate a violation of the microflora of the esophagus as a result of fungal activity:
- nausea and vomiting (there may be mucus in the vomit);
- pain, discomfort when swallowing;
- chest pain during or after eating;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- indigestion;
- irritability and weakness;
- loss of appetite and, as a result, weight;
- diarrhea with blood or mucus;
- discomfort in the pancreas;
- plaque in the mouth (optional symptom);
- the temperature rises.
Over time, mucus accumulates, which creates certain difficulties in the process of food passing through the passage. Lack of treatment only aggravates the situation, creating all the conditions for active forms of the fungus to penetrate the walls of the stomach and intestines.
Classification
Currently, there are 3 types of esophageal candidiasis:
- Catarrhal esophagitis. Redness (from mild to pronounced shade) and swelling of the mucous membranes occurs. They also find bleeding of mucous membranes upon any contact and a cobweb-like white coating. Erosion does not occur with this form of candidiasis.
- Fibrinous esophagitis. A loose, round-shaped coating with a diameter of up to 5 mm appears. Excessive hyperemia and pronounced contact vulnerability are determined.
- Erosive fibrinous esophagitis. The surface of the esophagus is covered with a fringed-ribbon coating of a dirty gray color. Most often, such lesions are located on the crest of longitudinal folds. Erosion up to 5 mm in diameter appears, and the mucous membranes become very painful and swollen. Sometimes the doctor is unable to perform an endoscope examination due to changes in the esophagus.
Manifestations
Manifestations of esophageal candidiasis come in various forms. At first, the affected areas on the walls of the esophagus look like yellowish or whitish spots that are raised above the mucous surface. Afterwards, such formations can merge and form plaques with the introduction of fungal colonies into submucosal surfaces or pseudomembranous deposits. Fungi penetrate into blood vessels and muscle membranes. Plaque films consist of desquamated epithelial cells that are mixed with fungal bodies, inflammatory cells and other bacteria. Microscopic examinations reveal the characteristic threads of Candida mycelium, which have a yeast-like structure and uniform color.
Check out this article: First signs of developing thrush
The morphological classification of esophageal candidiasis allows us to distinguish the severity of the development of the process, which depends on the depth of damage to its walls:
- group. There are individual whitish plaques with the manifestation of the introduction of pseudomycelium of fungi between epithelial cells;
- group. Film deposits merge with each other and create vast fields. Threads of pseudomycelium penetrate not only into the mucous membrane, but also into the submucosal tissue;
- group. Pseudomembranous deposits are formed, which are combined with a deep phase of changes in which threads of the fungus penetrate into the thickness of the muscle tissue.
Why is esophageal candidiasis dangerous?
At the initial stage of the pathology, plaque appears only on the mucous membrane and causes local inflammation. But if there is a sharp jump in the development of candidiasis, then the disease begins to spread to all neighboring organs, which causes burning, pain and swelling. Plaque - a film of cheesy consistency - closes the lumen of the esophagus, which makes a person want to vomit.
If candidiasis is not diagnosed in time and treated, the risk of developing various types of complications increases (this especially applies to people with weak immunity):
- tissue necrosis;
- bleeding;
- chronic inflammation of the esophagus;
- inability to swallow food;
- spread of candidiasis to other internal organs;
- ulcers
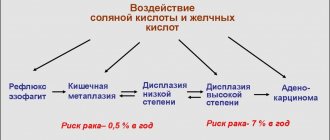
Three degrees of disease
How esophageal candidiasis will proceed depends on the spread of infection throughout the mucous membrane, the area of the affected surface, and the penetration of Candida deep into the epidermis and other tissues. The combination of these factors determines the severity of the disease.
| Degrees of candidiasis | Localization and manifestations of infection |
| 1st degree | The fungus invades the surface epithelial cells, forming sparse whitish cobwebs, spots and islands scattered throughout the esophageal mucosa |
| 2nd degree | Pathogenic forms of Candida (elongated cells, pseudomycelium) grow deep into the mucous membrane, one after another capturing its layers Extensive, overgrown films and a coating of fungus appear on the inner surface |
| 3rd degree | The fungus invades vessels and tissues located outside the esophagus The process is accompanied by the appearance of necrotic ulcers (areas of dead tissue), complicated by the addition of a bacterial infection (phlegmon), bleeding from blood vessels and ruptures of the damaged mucosa In the lumen of the organ, in addition to the fused plaque and islands of fungus protruding above the surface, numerous films (pseudomembranes) are formed, blocking the lumen of the esophagus and making swallowing difficult. |
Phlegmon
How to diagnose esophageal candidiasis?
Diagnosis of candidiasis begins with collecting anamnesis from the patient, who must tell the doctor about all the symptoms and changes in his health. After this, he is prescribed one of the following diagnostic methods:
- X-ray examination of the esophagus with contrast allows you to see fibrous formations of different shapes and sizes.
- Endoscopy is an examination of the walls of the tubular organ through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach. A bronchoesophagoscope tube is inserted into the person's esophagus through the mouth. Endoscopy can be diagnostic (various diseases of the esophagus are identified) and therapeutic (treatment procedures are carried out, which are also divided into two types - planned and emergency).
- Microbiological studies of mucus - take a sample of the mucus by introducing special instruments through the nasal passage.
- Immune system research.
Diagnostics
Recognition of the disease begins with a history of data, where the patient describes complaints about the disease that have arisen recently. The main instrumental method for detecting esophageal candidiasis is esophagoscopy.
To establish a diagnosis, the following diagnostic studies are performed:
- esophagoscopy (a special tube with an optical device is inserted into the esophagus, thanks to which the doctor can assess the current condition of the organ’s mucosa);
- X-ray examination using a contrast agent;
- culture of mucus from the esophageal tube;
- histological examination of the taken biomaterial.
Methods of treating the disease
Therapy for esophageal candidiasis must be carried out properly and be comprehensive - medications, diet, folk remedies.
Diet therapy
Proper nutrition significantly speeds up the healing process. First of all, it should be taken into account that the fungus likes to live in an environment of mold, sugar and yeast, so the patient needs to remove products that may contain these substances:
- sweets;
- jam;
- honey;
- baking;
- alcohol.
It is also advisable to give up milk, since it contains lactose, which fungi also love.
The diet should include natural products:
- yogurt;
- fermented baked milk;
- cottage cheese;
- foods high in fiber.
You can drink kombucha - it has a beneficial effect on the treatment of esophageal candidiasis.
In the first days of the diet, people may feel weak and tired, which is associated with food restrictions, since simple carbohydrates have stopped entering the body, but soon the situation improves and they feel much better.
Taking medications
Candidiasis is treated with antifungal drugs and immunostimulants. The first group of drugs is prescribed after the fungus is detected based on the results of laboratory tests, and the second group is prescribed if a violation of the immune system is detected.
Antifungal drugs can be divided into three groups:
- Polyene antimycotics:
- Amphotericin B is the only polyene antibiotic that is administered intravenously. It is practically not absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract, can penetrate into many tissues and organs, but does not pass well through the blood-brain barrier and is excreted from the body through the kidneys. It is a toxic drug with a large number of side effects - allergic reactions, fever, nephrotoxicity, anemia, phlebitis, hypotension, etc. The drug should not be used by people with diabetes mellitus and liver and kidney disorders. Therapeutic dose is an average of 1 mg/kg/day. It is necessary to dilute 5% glucose in 400 ml and administer intravenously at a rate of 0.2-0.4 mg/kg/hour.
- Natamycin acts on a larger number of fungi and is applied topically and orally. Adults should take 0.1 g every 6 hours, and children - every 12 hours.
- Nystatin is similar in chemical structure to Amphotericin B, but is more toxic. It is used topically and orally, and is practically not absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract. Ineffective as a preventive measure, as it only works through direct contact with the fungus. It should be used every 6-8 hours after meals.
- Azole antimycotics:
- Pimafucin has a strong fungicidal effect, which affects the source of infection without entering the bloodstream. Take 1 tablet 4 times a day for 7 days. The drug is non-toxic, it combines well with other drugs, and the only contraindications are the presence of individual intolerance.
- Clotrimazole is a broad-spectrum drug, available in different forms - suppositories, solutions, etc. The drug disrupts the activity of pathogenic fungi. It should not be used in children under 12 years of age or in cases of indigestion. The disadvantages of the drug include its effectiveness and speed of action.
- Fluconazole is an effective drug for the treatment of gastrointestinal candidiasis. The course of treatment can last about a month, provided that therapy was started at an early stage of the disease. The drug is used both as a primary treatment and as a prophylactic. The daily dose ranges from 150 to 400 mg. Take the capsule as a whole, regardless of food intake.
- Ketoconazole is a fast-acting drug. The active substance is instantly absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract if there is an optimal acidity level there.
- Levorin is an effective antifungal drug, available in different forms - tablets, ointments, granules or powder. The duration of treatment is from 10 to 12 days. Adults should take one tablet at any time, four times a day.
- Echinocandins are inhibitors of glucan synthesis:
- Caspofungin is effective against various forms of pathogenic fungi. It is used only in the form of injections, since for internal use the bioavailability is 1%.
- Micafungin is prescribed for severe forms of digestive candidiasis and is administered intravenously.
- Anidulafungin - the drug is at the stage of clinical trials, but the results are already showing good results. It is available for intravenous administration only.
Immunostimulating drugs:
- Anaferon is an immunomodulator, the advantage of which is its natural composition and pronounced antiviral effect. According to buyers, it has no shortcomings.
- Immunal , in addition to its immunostimulating effect, also has antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties. The key component is echinacea. The advantage of Immunal is its versatility in the treatment of various types of pathologies and the fact that it can even treat small children. The downside is that it is prohibited for people with AIDS and autoimmune diseases, as well as the price.
ethnoscience
To restore the body as quickly as possible, use traditional medicine recipes. With their help you can get rid of the initial stages of candidiasis.
Effective ways to influence these mushrooms are the following recipes:
- Decoction instead of tea. Mix calendula, chamomile, St. John's wort and oak bark in equal proportions. Mix all ingredients and grind in a blender. Brew 1 teaspoon of the resulting mixture with 0.5 liters of boiling water and let it brew for an hour, after which you can drink half a glass before each meal.
- Garlic. Eat one slice in the morning and evening for a week. This vegetable not only very successfully fights pathogenic fungi, but also strengthens the body as a whole.
- Pour 1 teaspoon of chamomile flowers into a glass of water and leave for 20 minutes, after which the infusion can be taken.
- Oat decoction. Take 2 kg of oats, chop and add 6 liters of water. Place the mixture on the fire and cook for 2-3 hours. Allow the medicine to cool, after which it can be strained. Take 100 ml of decoction before meals for 2-3 hours, take a break for a month and repeat the course again.
- Take one lemon and two oranges, squeeze the juice out of them and mix. Add 10 tablespoons of honey and a paste of 4 onions to the resulting mixture. Mix everything and pour into a glass container. Take the balm every day before meals.
- Juniper infusion. Take 15 grams of juniper per glass of boiling water and let it brew for 4 hours.
- Herbal tea. Take one part each of bergenia root, walnut leaf, birch leaf, bird cherry fruit, 3 parts each of thyme herb, cladonia, fireweed and cetraria. Pour 2 tablespoons of the mixture into 1 liter of water and boil over low heat for about 25 minutes. Let the drink brew for about an hour. Drink half a glass up to 5 times a day for 1-2 months, regardless of meals.
Treatment regimen for esophageal candidiasis
If esophageal fungus has developed, symptoms, treatment and prognosis depend on the form and stage of the disease. Treatment is carried out in several directions:
- Impact on all foci of infection present in the body with antifungal drugs.
- Anti-slag therapy: Enterosgel, Polysorb.
- The immune system must be strengthened.
The duration of antifungal therapy is at least a month. When the esophagus is affected, the treatment regimen differs from the treatment of other organs. For example, local irrigation of the pharynx in this case is ineffective, and from Fluconazole, taken once, Candida only acquires resistance (resistance to antifungal agents). Medicines and doses are selected taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen to the drugs. An approximate scheme for treating esophageal candidiasis is presented in the table.
Attention! Therapy must be prescribed by a doctor. If the medication regimen differs from the one below, then you must use the one prescribed by your doctor.
| Drug name | Dosage | How to use |
| Fluconazole | 150 mg (1 tab) | Once a day for at least a month |
| Diflucan | 150 mg (1 tab) | 1 time per day for 2 weeks |
| Itraconazole | 100 mg (1 tab) | 1 time per day after meals for 15 days |
| Ketoconazole | 200 mg (1 tab) | 1 time per day during meals for 3 weeks |
| McMirror | 200 mg (1 tab) | 3 times a day, duration – 10 days |
Nystatin in tablet form is rarely used for the treatment of esophageal candidiasis. It can be taken according to an individual regimen when combined with mycotic lesions of the oral cavity, intestines or vagina. Other drugs act in a complex manner, for example, taking Macmiror can effectively fight Helicobacter (the causative agent of stomach ulcers). When choosing any drug and determining the dose, the patient’s weight and age, as well as symptoms of concomitant diseases, are taken into account.
Prevention measures
Preventive measures reduce the risk of esophageal candidiasis. To do this, follow the following recommendations:
- eat yogurt every time after taking antibacterial drugs;
- antibiotics can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor;
- Get regular dental checkups;
- drink vitamin premixes;
- reduce the amount of sweets;
- spend more time outdoors;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Don't eat foods that contain jitters.
By approaching the treatment of esophageal candidiasis responsibly, you can be sure that you will not encounter any complications. Therapy must be comprehensive, and if you do not know the treatment methods, be sure to go to a doctor, who will not only prescribe an adequate treatment regimen, which will rid the body of pathogenic microorganisms.