Hepatitis A, or Botkin's disease, is a viral liver injury that has an acute course.
Every year, 1 million cases of infection are reported worldwide. For timely medical treatment, it is important to know what hepatitis A is, the symptoms and treatment of the infection. The disease is most common in developing countries, where 9 out of 10 children develop the disease before age 10. Mostly does not lead to death, with the exception of the fulminant form, which in some cases becomes the cause of the rapid development of liver failure.
Transmission of the virus occurs through the fecal-oral route. Infection occurs through food, liquids or contact with an infected person. The virus is also known as “dirty hands disease”.
The disease does not become chronic. After an infection, antibodies remain in a person’s blood, forming immunity and preventing re-infection. However, the disease requires increased attention, especially when it comes to pediatric patients. To prevent infection, especially when traveling to developing countries, it is recommended to use the hepatitis A vaccine. If you have any symptoms of infection, you should immediately contact a specialist to receive competent advice and treatment.
Symptoms of hepatitis A in adults, how does the disease manifest in adults?
- Hepatitis A is perhaps the most popular liver disease that is viral. Its only difference is that when detected, it is quite easy to deal with because it is the mildest form and it does not bring practically any negative consequences to a person
- A feature of this hepatitis is the very resistance of the virus to various alkaline and acidic conditions. For this reason, infection most often occurs through dirty and “sick” water or poor quality spoiled and contaminated food.
- It is not surprising that this disease is quite common in countries where people are not accustomed to maintaining sanitary conditions. So-called “third world countries”: Bangladesh, India, Africa and so on
Hepatitis A occurs due to non-compliance with sanitary standards, consumption of dirty water and food.
Methods of transmission of the virus:
- Most often, people become infected with hepatitis A while traveling when minimum sanitary standards are not observed: washing hands, washing food, drinking poor-quality water, eating in dirty public places
- Drinking tap water is strictly prohibited, so even in normal home conditions, tap water is a source of the virus
- Fruits and vegetables that are purchased at the market and in supermarkets can also be carriers of the disease, so they should always be thoroughly washed with running warm water.
- The pathogen is hidden in products of sea and river origin. All these food products must be treated with temperature
a special type of hepatitis - A
How a person becomes infected:
- The virus enters the digestive system with food, where even increased acidity is not a hindrance for it
- The blood carries it throughout the body and thus allows it to end up in every cell of the body.
- It is in the liver that the virus itself multiplies, causing the liver to become inflamed
- As the entire immune system actively fights to destroy the virus, the liver becomes weakened and failure occurs.
hepatitis A virus, how to recognize the disease by symptoms?
Symptoms:
- similar to those characteristic of any inflammatory disease
- increased temperature, possible fever
- the temperature cannot be reduced for a long time
- muscles feel pain
- the body feels poisoned (intoxication)
- nausea
- vomit
- chills
- malaise
- lack of appetite
- weakness
- pain in the liver area
All symptoms are present simultaneously or occur progressively, but pain in the liver is present in each case.
It is simply impossible to accurately determine the disease in the “first couple of days” and doctors make an accurate diagnosis only when the patient’s urine turns dark brown and the feces turn white. But along with this symptom, the patient feels relief; as a rule, the temperature may subside and vomiting disappear along with nausea.
Children's hepatitis A differs from adult hepatitis A in that all the symptoms go away quite mildly and sometimes are not even noticeable. The disease proceeds spontaneously without complications.
Other methods
In addition to medicinal effects (or instead of it), other effective methods are also used, in particular, physiotherapy, herbal medicine, and nutritional therapy. Let's look at the basic principles of these methods and their effectiveness.
Physiotherapy
Properly selected physiotherapeutic methods are necessary to gently restore the functioning of the liver and biliary system. These methods increase immunity and improve blood circulation. However, it should be remembered that in some cases physiotherapy is prohibited:
- not used for acute development of pathology;
- prohibited in case of severe complications;
- used with caution in certain patient conditions: pregnancy, childhood.
For hepatitis A, the following types of physical therapy are used:
Diathermy
Diathermy. This technique is based on heating, which is performed in the area of the affected organ. The procedure is performed during the recovery period using high-frequency currents daily.
- UHF therapy. With this hardware method, the effect of heat is carried out using a high-frequency electromagnetic field.
- Magnetotherapy. A static magnetic field is used. The procedure is performed five to seven times in cases of protracted acute hepatitis A. Thanks to it, blood flow improves and metabolic processes are normalized.
- Ozone therapy. Thanks to ozone, viruses are destroyed, the activity of liver cells is increased, and humoral immunity is activated. Ozone is applied to the liver area. In the case of severe forms, ozone infusions are used in a daily amount of up to 400 ml of solution. When toxic forms develop, rectal administration of liquids containing this active element is used.
Herbal medicine
Since hepatitis A is effectively cured using traditional methods, alternative medicine methods have not become particularly widespread. The only exception is folk methods that can improve the functioning of the liver, as well as speed up the effects of medications.
Traditional medicine acts as a “helper” for drug treatment and is not the main type of therapy.
The following recipes can be used at home:
- Herbal infusion:
- valerian root, barberry bark, hawthorn flowers and mint leaves, taken in equal parts (two small spoons each). This collection must be filled with 200 grams of hot water. The product sits for 24 hours. You should drink half a glass of the decoction during the day and evening before meals;
take one small spoonful of herbs such as horsetail, yarrow, St. John's wort and the same amount of chicory root. They are poured with a glass of boiling water. You should drink the mixture before meals - one teaspoon in the afternoon and evening.
Berry infusion. You need to mix one small spoon of rosehip and rowan. Pour a glass of boiling water. Take the product in the morning, at lunch and in the evening. You can add honey.
People who have had hepatitis actively share their experience of treating the pathology:
Victoria: “I know one recipe that is used for hepatitis. You need to take three large onions. Rub them through a sieve. You need to add two tablespoons of dry wormwood and 4 tablespoons of honey to the mixture. Pour this mixture with dry white wine (0.7 l). Leave the product for three weeks in a dark place. It is advisable to shake it every day. Drink the prepared tincture three times a day before meals in an amount of 50 ml. Helps very quickly."
Andrey: “For hepatitis A, I drank a decoction of immortelle. To prepare it, you need to take 25 g of the plant and add a liter of water. Bring to a boil and cook until half has evaporated. You should drink a decoction of 50 mg half an hour before meals. They were discharged from the hospital literally on the fourth day, as all indicators returned to normal.”
Polina: “Doctors recommend, as an additional treatment for hepatitis, to drink half a glass of clove decoction half an hour before meals, at least twice a day, the optimal option is three times. Dandelion juice is also used. Dilute one tablespoon with half a glass of water (boiled). That's exactly what I tried. Maybe my body is strong, but I think these remedies also helped.”
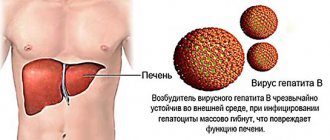
Symptoms of hepatitis B in adults, how does the disease progress?
Hepatitis B is a serious viral disease that can be transmitted from person to person and the most serious consequence of such hepatitis is liver damage. In particular, this virus is the main and most common cause of cirrhosis - liver cancer, a serious and incurable disease.
It is known that this disease exists in two forms and can be:
- acute - occurring suddenly
- chronic - consequences, occurrence of acute hepatitis
hepatitis B is a serious disease that destroys the liver and impairs its function.
Acute hepatitis is a disease that occurs with pronounced symptoms: fever, chills, pain in the liver, vomiting, nausea. Fortunately, the majority of patients (more than 90%) are successfully cured of this disease and only about 10%-7% become chronic. But this applies only to an adult; if the virus affects a newborn, then the situation is exactly the opposite - only 10% of children are able to cope with this disease safely and not become chronic.
Chronic hepatitis can be a complication of an acute disease, or it can simply remain in the body of a person for a long time, unaware of it. The virus can remain silent for a long time and destroy the body from the inside. Symptoms may be present, or they may appear when the disease takes a serious form. In cases where people do not suspect they have this disease, the virus can develop quickly and in a short time can turn into cirrhosis.
Liver cirrhosis is a common consequence of hepatitis B. This disease is characterized by disruption of the structure of the internal organ, the formation of scar tissue on it, and disruption of the liver. Cirrhosis also occurs for other reasons, in case of organ intoxication with alcohol and drugs.
hepatitis B virus, a serious disease that affects the liver and leads to cirrhosis
The difference between this virus is that it is poorly susceptible to environmental conditions:
- Stores for a long time at room temperature (up to three months)
- if the virus is frozen, it can survive in such an environment for up to twenty years
- the virus can withstand boiling, which lasts no more than an hour
- the virus is quite resistant to bleach and can survive in it for up to two hours
- formalin solution is also not a strong obstacle to the virus and allows it to live in its environment for up to seven days
- in a solution of ethyl alcohol (80%), the virus does not die immediately, but in two minutes
Ways of infection with hepatitis B virus:
- The virus can be stored in all human biological fluids: saliva, blood, urine, semen, vaginal secretions, sweat, tears and feces. The most concentrated amount of the virus is found in the blood and secretions from the human genital organs
- infection with the virus occurs only when the biological fluid of a sick person touches an open, affected area of skin (scratch, wound, cut)
Be sure that hepatitis B cannot be contracted by:
- cough
- sneezing
- shaking hands
- friendly kiss
- hug
- during a common meal
- during breastfeeding (if the integrity of the mother’s nipples and the baby’s oral cavity is not compromised)
When the virus enters the liver, it does not infect it; the body tries to develop protection and infects the cells in which the virus is located. It is this process that leads to inflammation of the liver.
It is possible that for the first two weeks a person may not feel any unpleasant symptoms at all. And only after this time he notices:
- lack of appetite
- lethargy
- nausea
- fatigue
- vomiting
- increased temperature and fever
- joint pain
- muscle pain
- migraine
- cough
- sore throat
- runny nose
These symptoms are typical at the initial stage and occur because the person’s immune system is weakened.
After this, other very telling symptoms come:
- yellowing of the skin
- yellowing of the eyeballs
- yellowing of the mucous membranes of the mouth
- darkening of urine
- stool lightening
- pain in the liver area
Once treatment for the disease begins, it only goes away completely after more than three months; a third of patients may feel symptoms much longer.
Symptoms of hepatitis C in adults, how does the disease progress?
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease that primarily affects the liver. The symptoms of all brands of hepatitis are almost the same, brand “C” differs in that the virus can quietly remain in the human body for up to several years, without giving any signs, and only after a while does it manifest itself in the last stage - cirrhosis of the liver.
Most often, the first signs of the disease appear only a month or two after infection with the virus, but it is not uncommon for this virus to remain in the human body asymptomatically for up to 180 days.
Symptoms of this disease manifest themselves in:
- Fatigue
- weaknesses
- drowsiness
- apathy and reluctance to work
- nausea
- vomiting
- lack of appetite
- belching constantly
- bitterness in the mouth
- abdominal pain on the right
- discomfort in the right side of the abdomen
- dark urine
- light feces
- joint pain
- temperature rise
- body aches
Over time, you can notice characteristic changes:
- yellowing of the eyeball
- yellowing of the skin in different parts of the body
Typically, the disease is diagnosed only when a person begins to experience liver problems. It has been noticed that men suffer from this disease much more often because they are able to drink more alcohol than women, which significantly worsens the functioning of an already weakened and damaged liver.
hepatitis C, course of the disease and its symptoms
The main specific symptoms of hepatitis C are everything that can be associated with intoxication (poisoning) of the body:
- migraines and weakness
- digestive dysfunction
- decreased performance, lethargy, weakness
- abdominal pain, especially on the right
- itching on the skin (most often on the palms, around the mouth, ears, on the legs)
- changes in blood test values
A more detailed examination and ultrasound makes it clear that the liver is becoming covered with frequent fibrosis, it is even possible to observe an enlargement of the abdomen on the right side. The patient’s body is covered with a noticeable capillary network, the person’s hormonal background is not stable, weight can rapidly disappear.
Hepatitis during pregnancy: consequences of the disease in pregnant women
During the entire period of pregnancy, a woman undergoes a blood test several times to exclude the presence of any type of hepatitis virus “A”, “B”, “C” and others in her body. If this disease is detected, then going to a regular hospital maternity hospital is contraindicated for her. Hepatitis is a viral and infectious disease that has many unpleasant consequences and is transmitted by infected blood.
You should definitely know that the hepatitis virus has several varieties, which are marked with letters. However, having one virus in your life does not limit a person from becoming infected with another.
Moreover, it is important to know that some people and some types of virus are capable of acquiring a chronic form, that is, once they get sick, they suffer from the disease all their lives.
The virus attacks the liver in the human body and slowly leads it to cirrhosis. However, one of the viruses can still be prevented - hepatitis B, for which vaccinations are increasingly being given.
Of course, childbirth is a direct way of transmitting the virus to your newborn child, but if the doctor is experienced and the management of pregnancy is attentive and competent, then it is quite possible to avoid infection of the child.
hepatitis virus in pregnant women Hepatitis virus is, simply put, an inflammation of the liver, which in the worst case leads to liver cancer. Due to the fact that this organ is affected, several aspects of the human body suffer:
- the immune system
- hormonal background
- metabolism
A common symptom for each brand of the disease is yellowing of the skin due to insufficient liver function and production of enzymes necessary for the body. In addition, there is always intoxication - poisoning of the body and a number of accompanying symptoms.
Since the liver, one of the main internal organs, suffers, it is not uncommon to feel pain in the right hypochondrium and even swelling of this part of the body. The pain can be completely varied: from stabbing to cutting, alternating with aching. This disease is often called “insidious” because for a long time it can generally be asymptomatic and not make itself felt.
Hepatitis lives well in the environment, food and water and therefore can easily enter the body through any object that an infected person has come into contact with.
hepatitis during pregnancy, methods of obtaining the virus
Different types of hepatitis during pregnancy:
- “A” is often called “Jaundice” and even “the disease of dirty hands.” This disease is often transmitted in childhood only because children do not yet know certain hygiene measures and precautions. This is the mildest type of hepatitis that a pregnant woman can become infected with. Most often it is treated safely and does not affect the outcome of events
- “B” - comes from blood poisoning; a woman can catch such a virus in a nail salon, at the dentist, from a razor and a syringe, from a toothbrush that got someone else’s blood on it. To avoid this, every pregnant woman must be responsible when choosing clinics and ensure complete disinfection. This type of hepatitis is very severe during pregnancy and a quarter of women become chronic.
- “C” slowly destroys the human body at the cellular level, almost always it becomes chronic and fatally affects the liver
Complications after a woman becomes infected with hepatitis during pregnancy:
- If the baby did not catch the virus during childbirth, the woman nevertheless requires special monitoring after childbirth, because her body weakens and becomes susceptible to all unpleasant complications
- During pregnancy and hepatitis, the liver suffers a double or even triple load, its work is impaired and it is not able to produce the required amount of enzymes necessary for the baby’s development
- If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with hepatitis, then natural childbirth is contraindicated for her in order to avoid infecting the child. For this reason, she is prescribed a caesarean section.
hepatitis during pregnancy, treatment of hepatitis in pregnant women
Treatment of hepatitis in pregnant women:
- It is important to know that if the disease has acquired an acute form, then it is simply impossible to cure and destroy the pathogenic virus
- During pregnancy, if a virus is detected, all attention should be paid only to the immune system, which must independently fight the disease
- You can help the immune system only by supporting it in every way. It is for this reason that it is necessary in no case to allow dehydration, monitor your well-being and monitor the functioning of other internal organs.
- It is impossible to help yourself during hepatitis, so you should definitely contact a clinic where the necessary inpatient treatment will be prescribed.
How to avoid infection
You can avoid getting this hepatitis after infection with viral cells only if you have previously received a special vaccination against this infection and the body has formed immunity to it.
If there are no bodies for protection, and the virus has already entered the blood, then hepatitis itself cannot be avoided. There is a specialized drug - immunoglobulin , which is introduced into the body immediately before a possible infection or in the near future after the infection. This makes it possible to protect yourself for a certain period from infection or the active development of the disease if infection has already occurred.
Remember that hepatitis type A cannot be re-infected.
If there is already a patient in your family, you need to examine absolutely all family members for the spread of antibodies in the body that work against hepatitis. When there are no antibodies in the body, vaccination is recommended. It is carried out on the direction of a doctor who checked your health.
Always follow the hygiene rules indicated everywhere, which will help you avoid illness when in contact with a sick person:
- After each visit to the toilet and even using the bathroom, you should wash your hands.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after routinely caring for a newborn or older child and before doing anything that touches them.
- It is also recommended to wash your hands before eating and preparing food.
It is worth paying attention to what you eat, never take food with dirty hands, which can carry not only hepatitis A, but also other dangerous ailments.
It is necessary from early childhood to teach children to wash their hands after going outside or having contact with animals. Food should be heat treated so that it does not contain any dangerous viral infections and their pathogens, which cause great harm to the body.
How are hepatitis A and B transmitted? Routes of transmission of the virus
As mentioned earlier, the hepatitis virus (of any kind) is very resistant to various environmental factors and lives in the biological fluid of an infected person.
hepatitis in the human body leads to cirrhosis of the liver, which in turn leads to cancer.
How the virus of this disease is transmitted in everyday life:
- during a blood transfusion, if an insufficient analysis of this biological fluid has been carried out
- during repeated use of a disposable syringe (most often occurs in drug addicts)
- through surgical instruments that have undergone insufficient sanitary treatment
- in the dentist's office, if the instruments are not sterilized enough
- in tattoo parlors when using the same needle for different people
- in nail salons where tools are not properly processed
- during sexual contact: regular sex, oral and anal (and non-traditional types of sex provide a greater likelihood of infection)
- during childbirth: from a sick mother to a child, when the tissues of two are affected and contact of biological fluids occurs
- when different people use the same toothbrush and razor
Sweat and saliva contain a minimal concentration of the virus and therefore it is unlikely to become infected through a kiss or a towel. However, the risk increases if there is blood in the saliva and you apply pressure to a fresh wound with a dirty towel.
How is hepatitis C transmitted? Ways of transmission of the disease
You can become infected with this disease if the blood of an infected person somehow enters the body of a healthy person. This can happen if:
- a person uses a disposable syringe several times (when using drugs that are injected into the veins)
- If the mother is sick during childbirth, she transmits the virus to the child through the birth canal
- through cosmetic, medical and surgical instruments that do not receive proper treatment
- through unprotected and sometimes protected sexual intercourse
- in everyday life, if the patient’s blood enters the mucous membrane of a healthy person
hepatitis C, hepatitis C virus, how does the disease progress?
Prevention
The most effective method of combating the disease is prevention. At the population level, the risk of HEV transmission and development of hepatitis E disease can be reduced through the following measures:
- compliance with quality standards of centralized water supply;
- Establishment of proper systems for disposal of human fecal waste.
At the individual level, the risk of infection can be reduced through the following measures:
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- refusal to drink drinking water and ice of unknown quality.
A recombinant subunit vaccine against hepatitis E was registered in China in 2011. This vaccine has not yet been approved for use in other countries.
In 2020, the WHO Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on Immunization reviewed the available evidence on the burden of hepatitis E and the safety, immunogenicity, clinical and cost-effectiveness of the authorized hepatitis E vaccine.
- Global prevalence of hepatitis E virus infection and population susceptibility: a systematic review
- Systematic review of the situation with hepatitis E in the world (in English)
Based on the work of SAGE, WHO published a position paper:
- WHO position paper on hepatitis E
The WHO activities section below provides a summary of the recommendations presented in this document.
Is it possible to treat hepatitis A, B, C? How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment of hepatitis A:
- As mentioned earlier, hepatitis A is the safest only because it is milder and leaves no consequences. Hepatitis of this label usually goes away on its own without requiring any serious measures to be taken
- Observation of the patient usually takes place in a hospital setting. People infected with hepatitis A require mandatory bed rest, a special diet and medications that protect the liver.
- To protect yourself from the disease, you should regularly observe hygiene measures, you can also get vaccinated
Hepatitis B treatment:
- This type of hepatitis is more serious and therefore requires a special approach and comprehensive treatment. Treatment depends only on the stage at which the disease is detected
- For the treatment of “B” hepatitis, immunostimulants, hormonal drugs and a number of important necessary antibiotics are mainly used
- There is 100% prevention against this type of disease - vaccination, which is carried out in the first year of a newborn child's life, however, a sufficient amount of time must pass after vaccination for immunity to the disease to develop - about seven years
hepatitis virus and its treatment depending on the type
Treatment of hepatitis C:
- The worst feature of this disease is that for many years it does not make itself felt at all, and only when the disease finally affects the liver does hepatitis C make itself felt
- If hepatitis C is detected at the initial stage, the patient should regularly check the functioning of his internal organs and carry out therapy aimed at destroying viruses
- Drugs that are administered to the patient for treatment have an antitumor effect and try to destroy the virus at the same time
In no case does hepatitis tolerate self-treatment or personal choice of any medication, because what suits one person does not suit another. If you carry out a number of incorrect actions, then it is quite possible to end up with a negative reaction and even worse development of the disease. Traditional treatment can significantly improve well-being and destroy the virus.
Who is susceptible to infection?
Hepatitis A is called a childhood infection. In most cases, this concerns countries that are developing and still have a reduced level of social and economic development. Many children suffer from the disease before the age of 10 and have a strong immunity to it for life.
Studies have shown that the number of patients who showed symptoms of hepatitis A is much less than the number of people who have antibodies to this virus. This fact suggests that the disease often does not manifest itself in any way and has no obvious signs.
In well-developed and stable countries, the “disease of dirty hands” is not so common, because personal hygiene is maintained at a high level there, and public utilities do an excellent job of their tasks.
Should adults be vaccinated against hepatitis A, B, C?
Hepatitis is a serious disease, which, depending on its specificity, is divided into several types. Each of these types is more dangerous than the other, and in order to protect oneself from this disease, vaccination was carried out.
You can get hepatitis at any age, because it is not at all difficult to do - just contact with any biological fluid of an infected person is enough. Moreover, the virus lives in this fluid (outside the body) for up to two weeks. It is for this reason that we can say with confidence that adults need vaccination just as much as children.
Many people are afraid of this vaccination, believing that they are being injected with the virus itself, but this is absolutely not the case. During vaccination, a protein is introduced that does not pose any danger to a person and cannot infect a person with hepatitis. Depending on the manufacturer, several effective drugs are available.
For vaccination to be effective, it must be done in the thigh muscle. If the substance is injected through the skin, the vaccination may be considered invalid.
vaccination against hepatitis virus
It is customary to vaccinate against hepatitis A and B; vaccination against C is not carried out for the reason that the virus is constantly changing.
How is diagnostics carried out?
In order to completely cure the disease, the doctor should conduct a diagnosis, because it will help identify the type of disease, the type of pathogen, and also assess the condition of the affected organ.
When a person suffers from hepatitis A, they experience characteristic changes in their blood, namely:
- its general composition changes;
- bilirubin levels increase;
- markers of the viral course of the disease are formed.
Feces and urine also exhibit characteristic changes; changes in color and composition indicate liver inflammation.
To make a correct diagnosis, the patient is prescribed:
- blood donation;
- donating urine;
- donation of feces;
- performing ultrasound;
- general examination of the patient and palpation of the affected organ.
After receiving the test results, the doctor identifies the causative virus in each of them. If there is one, the doctor draws up a treatment plan for the disease. As a rule, already 7-10 days after the end of the incubation period of the virus, markers of hepatitis in the blood can be determined. Therefore, even if the patient does not have symptoms of the disease, laboratory tests will still show the presence of liver disease.
Hepatitis vaccine for adults, side effects
There are certain contraindications for vaccination:
- human allergy to yeast
- During a cold or infectious disease, vaccination is prohibited
- if body temperature is elevated
- Vaccination should not be done during lactation and pregnancy
- after suffering from meningitis
- in the presence of the disease itself
It is worth noting that side effects after vaccination in adults over eighteen years of age are rare.
The list of complications that arise includes:
- hives
- anaphylactic shock
- rash
- allergic reaction
- multiple sclerosis
vaccination against hepatitis, complications and consequences after vaccination
Indications and contraindications for hepatitis vaccination in adults and children
Hepatitis vaccination is considered a national health program. It affects all newborn children and adults, who are at a particular risk group. Vaccination is needed only to protect a person from infection and prevent the spread of the virus.
A person can become infected with the virus through:
- contact of an open wound with any biological fluid of an infected person: blood, saliva, tears, sweat
- violation of the integrity of the skin by a contaminated object
- blood transfusion
Particularly susceptible to infection are:
- people who live in hygienic and poor conditions
- people with a family history of chronic hepatitis
- children who live in boarding schools
- people with hemodialysis
- people who have a large number of sexual partners
- non-traditional people
- drug addicts
vaccination against hepatitis, indications and contraindications
Along with the indications for vaccination, there are certain contraindications:
- an allergic reaction in a person to any component of the drug
- vaccination during colds and flu
- vaccination during pregnancy and lactation
- presence of hepatitis - such vaccination will be completely useless
Treatment
There is no specific treatment that can affect the course of acute hepatitis E. The disease usually resolves spontaneously, usually without hospitalization. It is very important to avoid unnecessary drug treatment. Acetaminophen/paracetamol and anti-vomiting medications should not be given. Hospitalization is necessary in case of a fulminant course of the disease; Hospitalization should also be considered in pregnant women with severe symptoms.
For patients with chronic hepatitis E who are immunosuppressed, treatment with ribavirin (an antiviral drug) is indicated. In special cases, the use of interferon may be effective.
Revaccination of hepatitis in adults, why is it needed?
Nowadays, revaccination is a way to protect against the disease. Of course, in childhood a person is vaccinated against hepatitis A and B, but in adulthood the need for it becomes more and more important. This is because the virus is constantly mutating and a person’s ability, decades after the first vaccination as an adult, is much higher than that of a child.
Most often, people become infected with hepatitis only because they believe that they do not need this vaccination at all. Once vaccinated, it will not produce antibodies forever and sooner or later its effect will end. In addition to the fact that the risk of the disease increases with age, it is quite difficult to endure all the complications at this stage.
Why do adults need revaccination against hepatitis?
In childhood, of course, it is quite possible to become infected with hepatitis. The child has contact with other children at school and kindergarten. But an adult does not lose this opportunity in the same way by visiting medical institutions, beauty salons and other establishments.