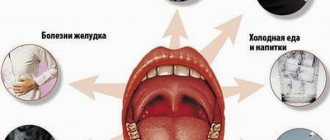
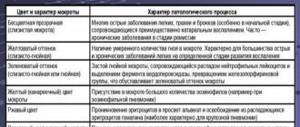
If inflammatory processes affect the throat, this most likely means an acute viral disease. To understand this, you need to know the symptoms of inflammation and all the features of this process. How does inflammation of the back of the throat manifest? What modern methods of treating this disease exist?
Causes
If the back of a child's throat is red, the condition is called pharyngitis, although it can easily be confused with a sore throat. In this case, the lymphoid tissue or mucous membrane becomes inflamed. The causes of the pathology can be different:
- the baby has inhaled cold, hot or polluted air;
- the child had contact with chemical irritants, for example, tobacco smoke, gases, dust, paint;
- exposure to bacteria and viruses;
- fungal infection;
- predisposition caused by genes;
- avitaminosis;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- abnormal development of the nasopharynx;
- low humidity of the room in which the baby is located;
- disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, heart, liver.
Depending on the degree of exposure to the irritant, acute and chronic pharyngitis are distinguished. In acute cases, the disease is just beginning and can be cured with medication.
At a later stage, the disease becomes chronic and may require surgery. So the sooner parents notice the symptoms, the better.
Features of the inflammatory process that affects the back wall of the throat
Experts associate inflammatory processes affecting the back wall of the throat with infections by viruses and pathogenic microorganisms. A number of factors contribute to such infection:
- reduced immunity;
- violation of all hygiene standards and rules;
- constant drafts;
- period of seasonal exacerbation of epidemics - influenza, ARVI, etc.
People who are constantly in large groups are especially susceptible to infection. These are mainly children of kindergarten and school age.
Signs of the disease
Pharyngitis, tonsillitis, tonsillitis - all these diseases are characterized by inflammation of the larynx. Parents may think that the child has problems with the bronchi or lungs, but this is not the case. An inflamed larynx has very specific signs:
- the throat feels sore, burns, and the sensation becomes stronger when swallowing;
- the voice becomes hoarse;
- cough is dry, but not deep;
- temperature can rise to 38 degrees;
- sores, redness in the larynx;
- the bacterial form of the disease may have complications in the form of a pharyngeal abscess or purulent otitis;
- with atrophic pharyngitis, the vessels on the back wall of the pharynx are clearly visible and crusts are visible;
- with a fungal infection, wounds appear in the corners of the mouth, a cheesy coating appears on the wall of the pharynx;
- with granulosa pharyngitis, red plaques and ulcers appear on the throat, the mucus becomes viscous and dry.
With tonsillitis, the nasopharynx becomes inflamed, sore throat is accompanied by high fever and severe redness of the throat.
In infants, it is much more difficult to diagnose inflammation, since they cannot talk about their feelings. That is why parents should be attentive to additional signs of disease:
- intestinal disorder;
- conjunctivitis;
- fever;
- disturbed sleep;
- rash;
- increased salivation.
If you suspect a disease, you should call a doctor. Sometimes parents, noticing inflammation of the larynx, begin to treat the baby incorrectly, as a result of which the disease drags on and becomes chronic. So it is better to trust the doctor's prescription.
How to treat?
Any doctor, dear readers, will prescribe you, first of all, drug treatment. It may consist of the following activities:
- Taking antibiotics. Relevant for infectious lesions of the larynx. As a rule, local medications such as Bioparox, Biseptol or Hexoral are sufficient to relieve inflammation. In severe forms of the disease, oral antibiotics are prescribed.
- Sprays with antiseptic effect. They relieve pain and inflammation well. Such medications include Septolete, Doctor Theis, Imudon, Strepsils. The sprays taste good and are well accepted by children.
- Antifungal medications such as Diflucan, Nizoral.
- Miramistin. This medicine is recommended for children from three years of age. It is used to lubricate diseased areas of the pharynx to relieve inflammation. Miramistin is not an antibiotic, but it enhances their effect on the body.
- In severe cases, surgery is prescribed to remove ulcers and inflamed areas of the mucous membrane with a laser.
Causes
If the back of a child's throat is red, the condition is called pharyngitis, although it can easily be confused with a sore throat. In this case, the lymphoid tissue or mucous membrane becomes inflamed. The causes of the pathology can be different:
- the baby has inhaled cold, hot or polluted air;
- the child had contact with chemical irritants, for example, tobacco smoke, gases, dust, paint;
- exposure to bacteria and viruses;
- fungal infection;
- predisposition caused by genes;
- avitaminosis;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- abnormal development of the nasopharynx;
- low humidity of the room in which the baby is located;
- disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, heart, liver.
Depending on the degree of exposure to the irritant, acute and chronic pharyngitis are distinguished. In acute cases, the disease is just beginning and can be cured with medication.
At a later stage, the disease becomes chronic and may require surgery. So the sooner parents notice the symptoms, the better.
How to make the correct diagnosis?
Pharyngitis has a good prognosis with timely treatment; the main task is correct differential diagnosis.
Table 1: Differential diagnosis of pharyngitis:
| Sign | Pharyngitis | Catarrhal tonsillitis |
| Most common pathogen | Viruses (adenovirus, enterovirus) | Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus |
| Pharyngoscopy | The mucous membrane of the pharynx is swollen, hyperemic (somewhat spreading to the palatine arches, tonsils) | Both palatine tonsils are primarily affected - enlarged, swollen, bright red in color. There is a serous secretion on the mucous membrane. The posterior surface of the pharynx is usually unchanged |
| Regional lymph nodes | Slightly increased | Significantly increased |
| Duration of the disease | Up to 5 days | Up to 5-7 days |
The photo shows a pharyngoscopic picture of the pharynx with tonsillitis and pharyngitis.
Signs of the disease
Pharyngitis, tonsillitis, tonsillitis - all these diseases are characterized by inflammation of the larynx. Parents may think that the child has problems with the bronchi or lungs, but this is not the case. An inflamed larynx has very specific signs:
- the throat feels sore, burns, and the sensation becomes stronger when swallowing;
- the voice becomes hoarse;
- cough is dry, but not deep;
- temperature can rise to 38 degrees;
- sores, redness in the larynx;
- the bacterial form of the disease may have complications in the form of a pharyngeal abscess or purulent otitis;
- with atrophic pharyngitis, the vessels on the back wall of the pharynx are clearly visible and crusts are visible;
- with a fungal infection, wounds appear in the corners of the mouth, a cheesy coating appears on the wall of the pharynx;
- with granulosa pharyngitis, red plaques and ulcers appear on the throat, the mucus becomes viscous and dry.
With tonsillitis, the nasopharynx becomes inflamed, sore throat is accompanied by high fever and severe redness of the throat.
In infants, it is much more difficult to diagnose inflammation, since they cannot talk about their feelings. That is why parents should be attentive to additional signs of disease:
- intestinal disorder;
- conjunctivitis;
- fever;
- disturbed sleep;
- rash;
- increased salivation.
If you suspect a disease, you should call a doctor. Sometimes parents, noticing inflammation of the larynx, begin to treat the baby incorrectly, as a result of which the disease drags on and becomes chronic. So it is better to trust the doctor's prescription.
How to treat?
Any doctor, dear readers, will prescribe you, first of all, drug treatment. It may consist of the following activities:
- Taking antibiotics. Relevant for infectious lesions of the larynx. As a rule, local medications such as Bioparox, Biseptol or Hexoral are sufficient to relieve inflammation. In severe forms of the disease, oral antibiotics are prescribed.
- Sprays with antiseptic effect. They relieve pain and inflammation well. Such medications include Septolete, Doctor Theis, Imudon, Strepsils. The sprays taste good and are well accepted by children.
- Antifungal medications such as Diflucan, Nizoral.
- Miramistin. This medicine is recommended for children from three years of age. It is used to lubricate diseased areas of the pharynx to relieve inflammation. Miramistin is not an antibiotic, but it enhances their effect on the body.
- In severe cases, surgery is prescribed to remove ulcers and inflamed areas of the mucous membrane with a laser.
Treatment with folk remedies can be carried out along with drug therapy:
- compress with honey on your feet for half an hour;
- gargling with infusions of herbs (mint, oregano, sage, eucalyptus, raspberry leaves, oak bark);
- compress with vodka on the neck for 2 hours;
- inhalation over boiled potatoes;
- baths with mustard, for which 100 grams of powder must be diluted in 5 liters of warm water (for infants, you can make a dry compress by pouring mustard into socks).
All the remedies described will help you quickly cope with inflammation of the back of the throat. But you shouldn’t use them without a doctor’s advice if you don’t want to harm your child.
Did you like the article? Recommend her to your friends on social media. networks. The information is provided for informational purposes only.
A little about what we understand by the term “throat”
To select effective treatment, it is important to first understand the terminology. When we say that the back wall is inflamed, anatomically we mean the pharynx. The pharynx is the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract, located between the mouth and the upper third of the esophagus.
In addition to the digestive function, it also performs a respiratory function, ensuring the passage of air warmed in the nasal cavity into the larynx. It consists of four walls, of which, upon objective examination in daylight, only its far side is easily visible.
Oroscopy refers to the direct examination of both the oropharynx (middle part of the pharynx) and the contents of the oral cavity using external lighting and a spatula.
Symptoms and diagnosis of pharyngitis
The standard way to diagnose pharyngitis is to examine the throat under artificial light with a pharyngoscope.
They resort to examination if there are symptoms:
- sore throat, sore throat;
- runny nose, nasal congestion;
- hoarse voice;
- cough.
Pharyngoscopy requires nasopharyngeal speculum, a frontal reflector, and a spatula, with which the local anesthetic lidocaine is applied to the root of the tongue.
A diagnostic tool is a laryngopharyngoscope with an optical system , which allows the doctor to carefully examine the mucous membrane of the throat.
Additional research methods include bacterial culture of microflora taken during pharyngoscopy and biopsy.
What kind of disease is this?
If upon examination it is discovered that the back of the throat is inflamed, this is a criterion for diagnosing pharyngitis.
Important! With pharyngitis, the mucous layer of the organ is affected.
Cause of illness
As an independent disease, it develops through the interaction of an infectious agent and various physical or chemical factors (cold air, alcohol abuse, smoking, food irritation, etc.).
What infection should you suspect:
- adeno-, entero-viruses; parainfluenza;
- bacteria (streptococcus, staphylococcus, mycoplasma, etc.).
Attention! The disease is predisposed by general hypothermia, pre-existing diseases of the nose or paranasal sinuses, smoking and alcohol abuse.
What are we complaining about?
Exacerbation of the disease occurs in the spring-autumn period. Usually, if you just have a sore throat, the symptoms are quite mild.
- Painful sensations have different characteristics - soreness, discomfort in the throat, rawness, burning. These symptoms are aggravated by swallowing. Sometimes patients describe the condition as the presence of a foreign body in the throat.
- Additional complaints include noise and congestion in the ears, hoarseness. A headache may occur as a manifestation of general intoxication syndrome.
- The temperature varies depending on the ability of each organism to fight infection, and, in fact, the type of infectious agent itself. For example, the influenza virus directly affects the temperature center in the medulla oblongata, causing hyperthermia that is resistant to antipyretic drugs. With pharyngitis, body temperature ranges from 36.6 to 38.0°C.
Attention! If the first priority is an increase in temperature above 39.0°C, it is imperative to exclude a sore throat, since its improper treatment can lead to severe consequences.
The back wall of the throat is inflamed and hurts, if it is red in an adult - how to treat pharyngitis in a child
The throat can hurt in different ways: sometimes the side walls become inflamed, sometimes the palate, tonsils, and sometimes the back wall. Complaints about the last symptom quite often have to be listened to by local therapists and ENT doctors. Inflammation of the back of the throat is usually caused by pharyngitis and its varieties, but other causes are possible.
In the article we will look at the features of this symptom: we will find out what the signs of this kind of inflammation are and why it appears. In addition, we will learn how to treat this unpleasant and life-complicating symptom.
Causes of inflammation of the posterior pharyngeal wall
Let's find out what diseases can cause inflammation of the back wall of the larynx. Find out how to treat a sore throat and painful swallowing from this article.
Pharyngitis
The most common cause of this symptom. Most often, this disease appears as a result of a cold infection during the cold season. In this case, the mucous membrane of the posterior wall of the larynx suffers: it becomes inflamed, it is irritated by accumulated mucus, causing pain - the first signs of pharyngitis in adults and children.
Upon visual examination, the doctor sees that the back wall of the throat is red and slightly swollen. You can often notice mucous discharge flowing down the throat. Typically, the discharge leads to the fact that a patient with pharyngitis begins to cough and sneeze frequently, trying to get rid of mucus.
Foreign body entry
This reason is more common in children: while playing, the baby can put a small part of a toy in his mouth, which then gets into his throat. In addition, it is also possible that the back wall can be injured by a fish bone - this fact is more common in adults.
Teething
If this process is difficult, inflammatory symptoms may appear on the back of the throat.
Acute tonsillitis: white plaque and red throat
This common disease may also well cause an inflammatory process in the posterior part of the larynx. Accompanied by pus and plaque on the tonsils, high fever, severe pain when swallowing.
Symptoms of acute tonsillitis.
Provoking factors
What points can accelerate the occurrence of an inflammatory process on the back wall of the larynx.
Reduced immunity. One of the main provoking factors. And, as you understand, weak immunity is a vulnerability not only for the respiratory system, but also for everyone else.
Period of seasonal respiratory epidemics. Every year at a certain time, mainly in winter and spring, the likelihood of “catching” an infection increases markedly.
To minimize the risk of contracting viral and bacterial infections, it is necessary to avoid crowded places, or appear “in public” in a medical fabric mask.
Lubricating the nasal mucosa with oxolinic ointment before leaving the house also gives good results, protecting against infection.
Hypothermia as a result of inappropriate choice of clothing for weather conditions.
Being in a draft also does not add to your health. It is especially dangerous to be in a draft wind if you have recently had a cold, or your immune system is simply weakened.
Vitamin deficiency and abuse of bad habits are also complicating factors that provoke diseases of both the respiratory tract and any others.
Symptoms
It should be noted that a sore throat can manifest itself in different ways. Pain in the back of the larynx can be:
- sharp, sharp;
- aching (dull);
- weak;
- intense;
- localized in a specific area;
- spilled all over the back wall.
An experienced doctor, based on the type of pain, can already make the correct diagnosis simply by listening to the patient’s complaints. In order for the diagnosis to be made as correctly as possible, it is necessary to collect all the information about additional symptoms.
So, in addition to pain in the back of the throat, the following signs of inflammation are possible:
- heat;
- rhinitis;
- swollen tongue;
- sore throat, burning sensation, scratching;
- sometimes a foreign body is felt in the larynx, although it is not there;
- painful swallowing is one of the most common signs of throat diseases;
- sneezing and coughing;
- headache:
- sometimes, along with a sore throat, unpleasant sensations appear in the ears, head, neck, and even in the muscles.
- cervical lymph nodes enlarge;
- Nausea and vomiting are possible.
Symptoms of cough due to thyroid gland are described in the link.
The posterior wall of the larynx becomes very red, this is noticeable to the naked eye upon examination. In addition, the mucous membrane in this area swells, the tonsils become inflamed and increase in size.
If the disease is caused by a fungal infection, stomatitis or some other diseases, a whitish or yellowish coating may appear in the throat.
In addition, the timbre of the voice may change: it becomes hoarse, hoarse. The mucous membrane swells, sometimes leading to difficulty breathing. Based on these symptoms, the doctor can more accurately make a diagnosis, narrowing the range of suspected diseases to a minimum.
Source: https://ProLor.ru/g/lechenie/vospalenie-zadnej-stenki-gorla.html