Ultrasound diagnosis of the thyroid gland is a modern, non-invasive and therefore effective method of examination. Deciphering the ultrasound picture of the thyroid gland quite often allows you to find out what is happening to the organ, whether there are signs of various pathologies, for example, cancer, thyroiditis and others.
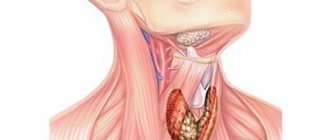
Briefly about the location, structure and function of the thyroid gland
The thyroid gland is the largest organ of the endocrine system. It is located on the front of the neck and consists of two lobes connected by an isthmus. Additionally, there is a pyramidal part, which is inferior in size to the main ones. It comes from the isthmus. The thyroid gland is formed in the fetus already at the 15th week of development and begins to work at the 18th.
The organ produces the most important hormones for the body - thyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are responsible for regulating metabolic processes through the release of energy and oxygen consumption. Hormones are produced in the thyroid gland and accumulate in the follicles, binding to thyroglobulin (protein).
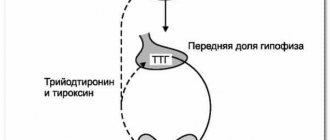
Then they enter the blood. They bind to plasma and are distributed throughout the body. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is involved in the control of the pituitary gland. The thyroid gland also produces calcitonin. It is responsible for calcium deposits in bone tissue (ostification process).
Features of thyroid size in women and men
In women, the thyroid gland is larger and is located more to the side of the cricoid and thyroid cartilage. In men, the organ is located below the upper edge of the sternum. For representatives of the fair half, the weight of the organ is 17-40 grams, the vertical size is 60-80 mm, and the size of the isthmus is from 7 to 15 mm. The diameter of the thyroid gland in the anteroposterior direction is approximately 20 mm. The volume of the organ in the fair half is slightly larger than in men.
We recommend reading: Laxatives for children: the best remedies for constipation
Throughout life, the thickness and length of the thyroid gland changes. In a newborn, the weight of the organ is about 2 grams, and at the end of the first year of life it reaches 14 grams. The most active increase in its thickness is observed in the interval of 5-10 years.
Involution of the thyroid gland begins at age 55. The reduction in size occurs due to follicle atrophy. In this case, the functionality of the organ is not impaired. Reserve reserves of hormonal tissue are maintained until the onset of menopause.
A fifth of people have an accessory thyroid gland located in the anterior part of the hyoid bone. It can be large in size and, in the absence or decrease in the activity of the main analogue, partially compensate for its lost functions.
The right lobe in humans is more developed than the left. The isthmus is normally fixed by a ligament to the cricoid cartilage. In 5% of people, the isthmus may be physiologically absent. In less than 1% of people, the thyroid gland may have abnormalities: bifurcation or the presence of additional lobes.
To correctly determine the size of the thyroid gland, you should take into account the anatomical features of the structure of the organ.
Most often, an overweight patient will have a larger thyroid gland.
Examination of thyroid nodules
If there are any concerns about the normal size and functioning of such an important component of the body as the thyroid gland, it is best to dispel doubts and undergo the necessary examination.
First of all, when visiting an endocrinologist, a detailed survey of the patient and palpation of the thyroid nodes are carried out, during which the doctor palpates the location and conducts a visual examination. If the thyroid gland is healthy, it will not stand out too much on the neck.
The palpation method allows an experienced specialist to determine both the lobes of the gland and the isthmus, and even determine the approximate size of the norm. In this case, the doctor is guided by the length of the nail phalanx of the thumb - each lobe of the thyroid gland should have approximately the same length. Deviation from this indicator gives rise to additional research, since this sign may indicate the presence of a first-degree goiter.
In the event that the thyroid gland can be seen on the surface even with the naked eye, then there is an assumption of the presence of a goiter of the second degree. The palpation method will also help to detect the presence of large nodes that are abnormal.
An ultrasound examination, of course, will give a more detailed picture of the condition of the thyroid gland. In particular, it will determine:
- the exact size of the thyroid gland compared to the norm;
- existing neoplasms;
- disturbances in the structure of the thyroid tissue of the thyroid gland;
- degree of parenchyma density;
- in the case of ultrasound using contrast, it is possible to additionally determine the quality of blood flow in the vessels in the thyroid gland area.
It should be taken into account that the presence of pathological processes in the thyroid gland is possible even when the volume and structure of the organ are normal and there are no nodes. That is why, along with ultrasound, it is imperative to undergo laboratory blood tests for hormones.
The best option is to perform an ultrasound of the thyroid gland using the same equipment and with the same doctor. This is due to both the existing error in different equipment and the different interpretation of the result by different doctors.
Particular attention should be paid to nodes that have increased density, as well as those that very quickly increase in size from the norm. Rapid growth of nodes is one of the properties of malignant tumors. With such nodular connections, there are pronounced symptoms, such as hoarseness in the voice, a feeling of constriction in the larynx, and an increased size of the lymph nodes from normal.
Another effective type of thyroid examination is scintigraphy using radioactive iodine. With its help, cold and hot node connections are detected:
- Hot thyroid nodules include: nodular toxic goiter or adenoma;
- to cold nodules of the thyroid gland - colloid goiter, thyroiditis, cyst, malignant neoplasm.
At home
You can detect abnormalities in the size of the thyroid gland by swallowing water:
- Stand in front of the mirror.
- Take a mouthful of water.
- Take several sips in a row.
- Look in the mirror and observe whether swelling appears in the thyroid area during swallowing.
If the test result is positive, it means the thyroid gland is enlarged.
The exact size and volume of the thyroid gland are of important diagnostic importance. Indicators are determined by ultrasound.
Focal formations, analysis of their size and structure ↑
In the conclusions, endocrinologists indicate the presence (present or absent) and their characteristics. If nodes or cysts are detected, they speak of focal lesions.
The classification is carried out according to their sizes:
- less than 1 centimeter are focal formations;
- more than a centimeter - a knot.
The occurrence of cysts is indicated by the results of an ultrasound of the thyroid gland when round, fluid-filled formations with clear edges are detected.
Nodular goiter is associated with the appearance of a compaction of dense consistency.
The presence of foci of compaction indicates an adenoma (benign tumor) or cancer. Benign tumors can be distinguished from malignant ones: they are limited to other tissues, and malignant ones are dark in color without clear boundaries. To accurately identify a malignant tumor, it is recommended to undergo a biopsy procedure.
Normal sizes and degrees of enlargement of the thyroid gland: tables
Before the advent of ultrasound, deviations in the thyroid gland from the norm were determined visually and by palpation.
According to WHO classification
In 2001, the World Health Organization approved the following classification of goiter according to severity and palpability:
- Zero degree - normal volume of the thyroid gland.
- The first is that the goiter is not noticeable, but is palpable.
- Second, deviations from the norm are clearly visible along the deformed contours of the neck, the organ can be clearly palpated.
According to Nikolaev
In the middle of the 20th century, deviations in size from the norm were verified according to Nikolaev:
- I degree - the organ is palpable and has normal dimensions.
- II - becomes visible when swallowing.
- III - the “thick neck” effect is observed.
- IV - the contour of the neck is deformed.
- V - the thyroid gland enlarges so much that it makes breathing and swallowing difficult.
What indicators are considered normal: tables of values
| Normal values | The thyroid and parathyroid glands are of the correct shape, no changes |
| No change in size | |
| No symptoms of tumor growth |
| Deviations from the norm | The thyroid gland is enlarged (goiter), tumor growth or cyst is noticeable |
| The parathyroid gland is enlarged |
Taking into account the patient’s weight, the optimal sizes of the thyroid gland in adults are as follows:
| Weight, kg | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | More than 100 |
| Volume, cm^3 | 15,5 | 18,8 | 22 | 25 | 28,5 | 32 |
In children:
| Child's age, years | 5-6 | 7-8 | 9-10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| Volume, cm^3 | 4-5,4 | 6-6,8 | 7,5-9 | 9-10 | 10,5-11,8 | 12-13,5 | 14-15 | 15,5-16 |
Formula for calculating volume:
V lobes = height*length*width*0.479,
where 0.479 is the elliptic coefficient.
V of the thyroid gland = V of the right lobe + V of the left lobe.
Normal size of the thyroid gland and signs of pathology
Normally, in men its size is 23-25 cm^3, in women it varies from 16-18 cm^3. The shares must be equal in size. The size of normal lobes is usually 4*2*2 cm. The normal thickness of the isthmus is 4-5 mm (in 7% of people there is no isthmus). The optimal size of the parathyroid glands is 4*5*5 cm. The weight of a healthy thyroid gland in a woman is 17-19 grams, in men – 18-20 grams.
In children under 16 years of age, the volumes are correspondingly smaller. The size of the thyroid gland in girls is always smaller and varies by 1-2 cm^3.
When is ultrasound diagnostics necessary?
The examination will be recommended if there are patient complaints or symptomatic manifestations detected by the attending endocrinologist during consultation and examination, such as:
- pain when swallowing and sore throat;
- general weakness, fatigue, lethargy, apathy, drowsiness;
- loss of strength, depression, increased sweating;
- anxiety, insomnia, fatigue, difficulty breathing;
- irritability, nervousness, sudden mood swings;
- noticeable weight loss or rapid weight gain;
- hair loss, fragility, dry skin;
- prolonged increase in temperature to 37–38 ºС for no reason.
It will be necessary to recommend diagnosing the thyroid gland during hormone therapy and identifying deviations from normal values in the results of hormone tests. For preventive purposes, the procedure is carried out:
- when planning pregnancy;
- congenital anomalies of the gland;
- the onset of 40 years of age;
- living in an area with low iodine content;
- professional activities in hazardous industries;
- control after long-term treatment or surgery;
- genetic predisposition to thyroid diseases and diabetes.
The importance of each of the symptoms or factors that require checking the functioning of the thyroid gland cannot be underestimated, since its role is very important for the entire body. And any disease can cause a decrease in both physical and social activity.
Ultrasound is used when performing a puncture of the thyroid gland, allowing you to monitor the process
Some organ pathologies
You cannot be completely sure that the study will reveal the norm of all indicators without exception.
It often happens that ultrasound reveals a number of problems with the thyroid gland that require urgent treatment.
Correct decoding of the data, which is carried out immediately upon completion of the diagnosis, helps to draw conclusions about the condition of this organ.
Photo:
All results and indications are recorded in a protocol, on the basis of which the attending physician makes a conclusion and also makes a diagnosis.
Thus, this study makes it possible to identify with a high probability the so-called nodular goiter. Using ultrasound, doctors learn about pathologies such as hypothyroidism, as well as the appearance of a cyst.
READ Some features of preparation for ultrasound of the thyroid gland
Diagnostics shows various types of tumors, both benign and malignant.
In addition, the study makes it possible to timely determine the development of thyroiditis, as well as diffuse toxic goiter.
The latter pathology is quite common and is associated with an increase in the volume of the organ itself. Meanwhile, to make this diagnosis, ultrasound alone will not be enough.
The disease itself must have pronounced symptoms, namely: high fever, excessive thinness, as well as regular attacks of palpitations.
If the transcript of the study coincides with all of the above symptoms, the doctor will diagnose “nodular goiter”.
As a result of an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, the presence of various diffuse changes in the internal organ can be detected. In this case, we can talk about hypothyroidism.
A characteristic phenomenon for this pathology is a sharp decrease in both the volume and size of the internal organ itself.
Video:
Also, during the study, you can notice the appearance of fibrous fibers directly in the internal space of the organ.
The readings after decoding will not correspond to the norm even if various edemas are detected.
An ultrasound of the thyroid gland may show cavities filled with pus, which will indicate the presence of a pathology such as thyroiditis.
It often happens that, according to the results of the study, the thyroid gland is normal, but all sorts of round cavities are found that have fairly clear boundaries and contours.
In some cases, these cavities are filled with liquid. This formation is called a cyst and poses a serious health hazard.
Ultrasound is the diagnostic method that allows you to find out about health problems in a timely manner.
Preparing for the examination
The procedure is completely safe and painless and does not require any special preparation. However, there are some recommendations that will help make the examination as accurate and comfortable as possible:
- It is not recommended to take hormonal and iodine-containing medications for several days;
- Children and the elderly should refrain from eating for several hours. To avoid the gag reflex that may occur when pressing on the gland;
- If similar studies have been conducted before, you should take their results with you. By comparing the new results with previous ones, the diagnostician will be able to determine whether changes have occurred in the condition of the thyroid gland.
What can the results show? ↑
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is a reliable way to diagnose disorders, as it allows you to detect changes in its structure, detect lumps, cysts, and even changes no more than 1-2 millimeters in diameter. The procedure does not require special preparation. If you have previously undergone the procedure, take your previous reports with you; no other preparation is required. If the person is elderly, preparation may include undergoing an ultrasound scan on an empty stomach to avoid the gag reflex.
The results of an ultrasound of the thyroid gland allow:
- estimate the value;
- uniformity and density in all departments;
- the presence of formations, including their characteristics;
- determine the condition of blood vessels and lymph nodes;
- identify pathologies, which will help prepare for the necessary therapy.
How does the procedure work?
During the examination, the patient lies on his back, with a towel placed under his neck. This position is the most comfortable for diagnosis, since there is convenient access to the gland. A special gel is applied to the surface being examined, which increases the permeability of ultrasonic waves. Then the specialist conducts diagnostics from different angles. The procedure takes on average no more than fifteen minutes. How accurate the results will be depends, first of all, on the experience and qualifications of the diagnostician. The sensitivity of the device also affects the accuracy. Usually the transcript is issued after the examination is completed.
What does deciphering the results include?
Interpretation of an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, like all other organs, consists of assessing the parameters and their compliance with normal indicators. The description of the received materials itself does not last long in most cases - no more than 10 minutes, and only in particularly complex or controversial situations can it take longer.
When decrypting it is assessed:
- location;
- structure;
- dimensions;
- volume;
- contours;
- echogenicity;
- structure;
- additional characteristics of the gland.
Then all parameters are correlated with normal values, and on the basis of this, the specialist writes a conclusion with which the subject will go to the attending physician for further recommendations.
Results of diagnosing the structure of the thyroid gland
A significant indicator when interpreting ultrasound is the echogenicity of glandular tissue. It directly depends on its structure and density. During the examination, the ultrasound signal is reflected from the tissues and, depending on their density, colors the picture with gray color of varying intensity.
Normally, the thyroid gland consists of small, homogeneous structural elements - follicles; there are no signs of compaction in a healthy gland. The uniformity of the gland in this case is reflected on the monitor in light shades of gray over the entire surface of the gland.
But the structure of the gland may be heterogeneous. During the study, the signal is reflected unevenly and shows areas on the monitor screen that are colored dark gray to black. A sign of an inflammatory process are areas with a dark gray color. Black areas may indicate the presence of malignant tumors.
Cysts and nodes on ultrasound of the thyroid gland
The ultrasound transcript normally indicates echogenicity without any features. In deciphering an ultrasound with a heterogeneous structure of the gland, it may be indicated that echogenicity:
- local (individual areas of heterogeneity);
- diffuse (heterogeneity of the entire glandular tissue);
- mixed.
It is recommended that women planning pregnancy undergo an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland. Disturbances in the functioning of this important organ can negatively affect the course of pregnancy and the gestating fetus.
Normal thyroid gland and its possible deviations
Assessing each area of the thyroid gland is very important, since even the smallest detail that has eluded the diagnostician can, after some time, manifest itself as a serious disease that requires careful treatment. Therefore, when interpreting, all characteristics of the organ being studied are taken into account.
Location
The thyroid gland is located in the lower or middle anterior region of the neck. Its location can be typical (normal) or pathological (aberrant) - the organ is sometimes located very close to the larynx or even near the root of the tongue. In other cases, individual small parts of the gland may be attached to the trachea itself, not far from the organ itself.
Structure
The gland in its normal state consists of two equal lobes connected by a small isthmus. One of the most common deviations from the norm is the formation of an additional lobe and growths on the lower part of the gland. Also considered pathological is a shift of the gland to one side, which often occurs during intrauterine development.
Image obtained by ultrasound of the thyroid gland
Dimensions and volume
The results provided by ultrasound indicate the exact size of the gland. When calculating the size of the gland, only the lobes of the gland are taken into account - the isthmus is not taken into account when determining them. In some cases it may be absent altogether. But in the normal state of the thyroid gland, the isthmus acts as a strong ligament.
During the procedure, the diagnostician determines the size of the isthmus by measuring its thickness. This action is performed from front to back. As a person grows and throughout life, these parameters change. The normal size of the thyroid gland is (cm):
- length – from 2.5 to 4;
- width – from 1.5 to 2;
- thickness – from 1 to 1.5.
Normal volume indicators do not exceed 18 cm³ for women and 25 cm³ for men. In children, this parameter does not exceed 15 cm³, but completely depends on the gender and age of the child. To determine compliance with its standard, a special table is used. The volume of the adult gland can also fluctuate, and all these deviations will be taken as normal. Only this indicator will be influenced by body weight, which can also be determined in a table with generally accepted values.
Table of normal thyroid volume indicators depending on body weight
Thyroid size in children
Pathologies of the thyroid gland occur in children due to iodine deficiency in a woman during pregnancy, tumors, autoimmune pathologies; diseases in a child are much more severe than in an adult. It is recommended to regularly do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, especially if the child lives in an unfavorable region; close relatives have had problems with the thyroid gland.
Complications with the thyroid gland in children occur due to maternal health problems during pregnancy
Normal thyroid volume in children
| Age | Thyroid volume in boys (cubic cm) | Thyroid volume in girls (cubic cm) |
| 1 | 0,84–1,2 | 0,84–1,2 |
| 2 | 1–1,5 | 1–1,5 |
| 3 | 1,4–2 | 1,3–1,7 |
| 4 | 1,8–2,5 | 2–2,6 |
| 5 | 2,1–2,7 | 2–2,7 |
| 6 | 2,3-3 | 2,1–2,9 |
| 7 | 2,8–3,8 | 2,4–3,4 |
| 8 | 3,1–4,3 | 3.1–4,3 |
| 9 | 3,2–5,2 | 3,2–5 |
| 10 | 3,6–5,5 | 4–5,8 |
| 11 | 4,2–6 | 4,5–6,5 |
| 12 | 5–6,5 | 6,3–7,6 |
| 13 | 7,1–10 | 6,7–10 |
| 14 and older | 9–10, 5 | 8,1–10.8 |
Important! The main signs of thyroid dysfunction are apathy, increased excitability, sudden changes in weight in any direction, changes in body temperature, increased sweating, and tremors of the limbs.
Outlines
Characterization of the contours or boundaries of the thyroid gland during their visualization immediately makes it possible to detect the presence or absence of neoplasms and inflammatory processes. Normally, an organ has clear boundaries, and vice versa, unclear ones - a clear sign of the presence of the above pathologies. During the examination, the doctor distinguishes between different degrees of blurred contours, and based on their characteristics he can draw a conclusion about the nature of the disease. For example, blurred boundaries indicate the occurrence of an inflammatory process or the spread of a cancerous tumor to areas of nearby tissue.
4 types of echogenicity
The echogenicity of the “thyroid gland” on the monitor has a gradation from dark gray tones to light gray. If black is present, this indicates the presence of a malignant tumor.
The interpretation of the results of ultrasound of the thyroid gland contains the following descriptions of the echogenicity parameter:
- Isoechogenicity. This indicates that the tissue is normal.
- Hyperechogenicity. This is a light area with no diffuse tissue.
- Hypoechogenicity. There may be dark areas with an inflammatory process.
- Anechoicity. The black zone of the organ is interpreted as cysts or tumors.
This video explains what symptoms you should pay attention to first when self-examining your thyroid gland. Provided by the Boris Uvaidov Health channel.
Structure
This is one of the most significant characteristics when diagnosing. In a normal state, the gland has a uniform granular structure, consisting of small follicles, and, accordingly, the detection of heterogeneity in the organ is a cause for concern. These are signs of the presence of pathological processes, such as inflammation, which are of an autoimmune nature.
Only in very rare cases, the presence of a heterogeneous structure does not confirm the occurrence of diseases, but is an individual feature of the thyroid gland. The normal state of the follicles is very important for the organ and the human body as a whole, since they produce hormones. A healthy person's thyroid gland contains approximately 30 million follicles.
Extra options
When making a diagnosis, the characteristics of additional parameters must be taken into account, such as thyroid nodes, regional lymph nodes, their size and structure, as well as blood flow in the organ and nearby tissues.
Nodes
In the normal state of the gland, there are no nodes. The presence of small tumors not exceeding 4 mm is considered acceptable. In the image they appear as black uniform inclusions, and they are classified as follicles - the cells that make up the thyroid gland. Formations exceeding 4 mm are classified as nodes considered pathological formations. Since a healthy gland has a homogeneous structure, the presence of nodes is taken as a deviation from the norm.
Regional lymph nodes
Normally, the lymph nodes of the neck have clear, even boundaries. Their length should exceed twice their width. The entrance site of the lymphatic vessel is clearly visible. Blood flow does not exceed normal. The presence of cysts in regional lymph nodes is also considered a pathology. Often, abnormalities in these areas indicate the presence of a malignant tumor.
Ultrasound indicators
An ultrasound of the thyroid gland is normal - this is the diagnosis the patient will receive if, according to the results of the study, no pathological changes in the organ are detected. This means that the tissues and cells of the organ are not in an altered state. Normal ultrasound indicators exclude the presence of tumor formations, as well as cysts, diffuse goiter, etc.
The organ must be correctly physiologically located, have clear contours and be characterized by the absence of echogenic structures. Ultrasound tests of the thyroid gland must demonstrate the volume of the gland. In men, the volume of the thyroid gland is 25 cubic cm, and in women - 18 cubic cm.
The thyroid gland is normal - a conclusion of this kind indicates that the lymph nodes of the cervical region, as well as the subclavian and submandibular lymph nodes are within the permissible value.
Normal thyroid volume
Having received ultrasound tests, the first point that the patient will see is the contours of the gland and its normal volume. What does it mean?
As a rule, the thyroid gland contour indicator can be the first bell that will indicate a malfunction of the organ or the onset of an inflammatory process in it. If the contours are blurry and difficult to read on the monitor screen during an ultrasound, this indicates that the organ is affected by a malignant neoplasm. In case of poor visibility of the structural outlines of the thyroid gland, it can be argued that its tissues have begun to grow into organs located nearby.
The normal thyroid gland appears on ultrasound as two small areas connected by a thin strip. Visually, the organ normally resembles a butterfly in its outline and contour. If the patient, trying to decipher the research tests, sees that the organ has acquired a rounded shape or has completely become of an indeterminate structure, then this indicates the presence of thyroid dysfunction.
Violations in the functionality of this organ can primarily be a deficiency of iodine entering the body, as well as a decrease in the functioning of the pituitary gland. The anterior part of the brain - the pituitary gland - is an important element in the synthesis of thyroid hormones - triiodothyronine, thyroxine and thyroid-stimulating hormone. As stated above, the normal size of the gland is 18 cubic centimeters.
Structure
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland should include indicators such as tissue structure and echogenicity. The structure of iron can be either homogeneous or heterogeneous. But, if we apply the concept of homogeneity to an organ of the endocrine system, it will be slightly different from the standard one. The homogeneous structure of the organ implies its granularity.
If the thyroid gland is affected by diseases such as Hashimoto’s goiter, diffuse goiter, as well as various types of cysts or malignant tumors, then an examination of the organ with an ultrasound machine will show you a “honeycomb” on the monitor. Visually, it seems that the thyroid gland is corroded by some microorganisms. But, in fact, this means that the organ needs urgent medical or surgical treatment.
You should know that indicators of gland heterogeneity are also characteristic of an absolutely healthy organ. An entry in the ultrasound protocol of the following nature: “moderately heterogeneous structure of the thyroid gland” appears in those patients whose blood tests showed an increase in the titer of antibodies to the substances thyroglobulin and thyroid peroxidase.
Echogenicity of the thyroid gland
The thyroid gland norm includes indicators of the echogenicity of the tissues of the organ or the “tone” of the thyroid gland. The endocrine system is examined using an ultrasound machine, which is capable of recognizing and analyzing the rays reflected by the gland. These ultrasonic beams line up on the monitor screen as a grayscale image.
Echogenicity in this case means a gradation of gray shades over the entire area of the thyroid gland. That is, inflammatory processes occurring in tissues will be presented in a dark gray shade, bordering on a black tone. If the study showed “black” echogenicity, then this should alert not only the ultrasound operator, but also the patient. Since such tests may indicate the first stage of malignancy. Normally, echogenicity will be expressed in light shades.
If we decipher ultrasound tests according to the “echogenicity” indicator, then:
- An isoechoic zone means that the organ tissue is normal, without pathologies;
- The hyperechoic area is a light zone in which the tissues are not diffusely changed;
- Hypoechoic zone means the presence of dark areas in which the inflammatory process presumably takes place;
- The anechogenic area is a black zone in which cysts and malignant neoplasms are observed.
How to calculate the volume of the thyroid gland using ultrasound?
To calculate the volume of the thyroid gland, you need to know the basic parameters of each lobe of the organ.
Formula:
- Multiply the length, width and thickness of the right lobe.
- Multiply the length, width and thickness of the left lobe.
- Add both obtained values to get the total volume.
- Multiply the result by the ellipsoidal correction factor, which is 0.479.
Important! A simple test to identify iodine deficiency - before going to bed, draw 3 stripes on the inside of your wrist. The first is very thin, the second is slightly thicker, the third is at least 1 cm wide. If the iodine level is normal, only the first strip will disappear in the morning; if there is a lack of the microelement, all 3 stripes will disappear.
To treat thyroid pathologies, hormonal, thyrotoxic, and iodine-containing drugs are prescribed, and the doctor prepares a special diet. If the volume of the organ significantly exceeds the permissible norms, the nodes grow rapidly, a biopsy shows the presence of cancer cells, the lumps do not produce hormones, surgery is prescribed.
If you have hoarseness, sore throat, neck pain, increased fatigue and nervousness, do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland. This research method will make it possible to determine the volume of an organ and the size of its component parts, and to promptly identify malignant neoplasms.
Structure (including uniformity and granularity) ↑
Normally, the organ consists of homogeneous follicles without compactions. As a rule, doctors, if there are no changes, indicate in the conclusion of an ultrasound of the thyroid gland that the echogenicity is unremarkable.
Changes in ultrasound of the thyroid gland are noted when the signal is reflected unevenly, which makes it possible to identify areas that differ in their echogenicity. In this case, the conclusion indicates that acoustic access is difficult or heterogeneous, and the echogenicity is mixed, local or diffuse, which indicates the occurrence of inflammation.
Normally, an ultrasound of the thyroid gland should not reveal changes in healthy tissues to connective or fibrous tissue; if this happens, then they speak of the disease hypothyroidism (Hashimoto's goiter), which is characterized by a decrease in the functions of the organ.
Reasons for organ changes on ultrasound
Pathology of glandular tissue most often develops against the background of genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalance, autoimmune and endocrine diseases.
Resizing
Both deficiency and excess of iodine in the body can lead to enlargement and reduction of the thyroid gland. Often the size of the thyroid gland changes under the influence of antibodies of the immune system, which destroy its cells.
Enlargement or hyperplasia
The volume of the thyroid gland increases due to the proliferation of its follicular cells. Hyperplasia can be autoimmune and compensatory in nature. The latter case is inherent in hypothyroidism (iodine deficiency state). When the thyroid gland enlarges, it tries to capture more iodine from the bloodstream. With hyperthyroidism (excess of iodine-containing hormones), hyperplasia occurs against the background of increased thyroid function.
Reduction, or hypoplasia
If underdevelopment of the endocrine gland appears immediately after birth, the pathology is considered congenital. The reasons for this hypoplasia are associated with a lack of iodine in the pregnant woman’s body and her existing thyroid problems.
Acquired hypoplasia is diagnosed as atrophy. The gradual death of thyrocytes leads to shrinkage of the thyroid gland.
What diseases can ultrasound help detect?
During ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor can detect a number of abnormalities. They are determined depending on the size, volume, tissue structure and echogenicity. Changes in these parameters may be a sign of diseases such as:
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a disease associated with a reaction to low levels of thyroid hormones. A symptom may be reduced organ size. There are several degrees of this disease.
Primary hypothyroidism is caused by the following factors:
- hypoplasia or hyperplasia of the thyroid gland;
- congenital disorder of thyroid hormone synthesis;
- thyroiditis;
- nutritional characteristics (iodine deficiency, excess thiocyanates present in cabbage, rutabaga, turnips, turnips and cassava, excess calcium and lithium ions that block iodine uptake);
- medical actions (gland removal, radiation therapy, taking medications).
Secondary hypothyroidism is associated with hypopituitarism or a defect in the synthesis and transport of thyroliberin from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland.
Tertiary is associated with inactivation of circulating in the blood:
- T3 and T4 autoantibodies;
- TSH autoantibodies;
- proteases in sepsis.
There may be a connection with a decrease in the sensitivity of target cell receptors to hormones.
Hyperthyroidism
Unlike hypothyroidism, this syndrome is associated with an increased level of thyroid hormones in the blood. Its degree depends on their number. One of the symptoms of this disease is a severe enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Euthyroidism
According to external manifestations, this is the normal functioning of the thyroid gland, the absence of symptoms of hypo- and hyperthyroidism. Euthyroidism does not mean that the thyroid gland is healthy. Most often, this diagnosis is made in conjunction with goiter - euthyroid goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland with normal organ function). This condition is usually associated with iodine deficiency.
Nodular goiter
Tissue proliferation syndrome, or nodular goiter, occurs:
- uniform (diffuse);
- uneven;
- focal with the appearance of formations (colloid).
In this case, the pituitary hormone does not cope with the complete elimination of iodine deficiency, which leads to the appearance of nodes.
Thyroiditis
Inflammatory diseases caused by viruses and bacteria occur in acute and subacute forms and develop as a complication of acute respiratory viral infections, bronchitis, and tonsillitis.
Thyroiditis is accompanied by a sore throat when swallowing and headaches, manifested in ARVI
The disease is characterized by fever, frequent headaches, frequent or prolonged sore throat, and discomfort when swallowing.
Diffuse toxic goiter
This disease is associated with hereditary autoimmune abnormalities. It is characterized by a symptom such as exophthalmos - a forward displacement of the eyeball (bulging of the eyes).
Since thyroid hormones have different physiological functions, this disease can manifest itself in the following pathologies:
- Various heart disorders. Symptoms may include arrhythmia, tachycardia, high blood pressure, and chronic heart failure.
- Disruptions in the endocrine system, namely weight loss regardless of diet, heat intolerance, menopause or cycle disruptions in women.
- Dermatological problems such as increased sweating, changes in the shape and structure of nails, erythema, swelling of the extremities.
- Neurological problems. They may manifest themselves in the form of tremors, weakness, headaches, myopathy, anxiety and restlessness, and insomnia.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms, which manifest as diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
Cyst
On ultrasound, the cyst looks like a formation filled with fluid.
If there is an inflammatory process in the patient, the following may be detected:
- pain in the front of the neck;
- temperature increase;
- hoarseness of voice.
If a cyst is suspected, the puncture method is used together with ultrasound. It is used to analyze for the presence of cancer cells to exclude the presence of cancer.
The disease is accompanied by inflammatory viral or bacterial processes. In patients suffering from this disease, the volume of the “thyroid gland” increases, and the cyst can grow into the surrounding tissues and merge with them.
Neoplasms
Benign tumors on ultrasound are visualized as compacted foci with clear boundaries, while with malignant ones, their growth into other tissue structures is clearly visible. Enlarged lymph nodes are considered one of the signs of malignancy of the process. A timely diagnosed disease is the key to a quick cure!
Adenoma is a benign tumor of the thyroid gland (round spot on the right)
Ultrasound diagnostics of the thyroid gland is an easy and quick method of examination, allowing one to detect even the smallest nodular formations ranging in size from 1–2 mm. This makes it possible to immediately determine their nature and prescribe the necessary therapy, as a result of which, in all likelihood, the cure will take place quickly and effectively.
Carrying out the procedure for preventive purposes is also considered an important point, allowing timely tracking of pathological changes in the organ and taking appropriate actions. In addition, the procedure itself is carried out absolutely painlessly and quite quickly - you do not need to devote a lot of time to it. There is no preparatory process - the patient will not need to limit himself in food, drink and even smoking. You just need to sign up at any convenient clinic, take a towel with you, and, if available, the results of past studies.
What diseases are detected by ultrasound of the thyroid gland?
Thyroid dysfunction leads to a decrease or increase in the production of the hormones thyroxine (T4) or triiodothyronine (T3). If the synthesis of these hormones is disrupted, the risk of developing quite serious diseases increases, including:
Diffuse toxic goiter – increased production of thyroid hormones. The disease is characterized by an increase in the volume of the thyroid gland, as well as symptoms such as increased irritability, periodic increases in body temperature, weight loss with good appetite, heart rhythm disturbances and other ailments that become the reason for visiting an endocrinologist.
Nodular goiter is a disease of the thyroid gland in which the appearance of compactions in the tissues of the gland is noted. Such seals can be single or multiple and have different sizes.
Hypothyroidism is a decrease in the production of thyroid hormones, which leads to a reduction in the organ and the appearance of connective (fibrous) tissue.
Thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid tissue. The cause of this condition is considered to be bacteria and viruses. The disease is characterized by pain in the anterior surface of the neck, enlarged thyroid gland, increased body temperature and other symptoms indicating intoxication of the body. On ultrasound, you can notice a slight enlargement of the thyroid gland, as well as the focus and localization of inflammation. It is not uncommon for limited cavities with purulent content to be present.
Thyroid cyst - the cavity is filled with fluid. Small formations do not cause discomfort to a person, but when they grow there is a risk of suppuration. Ultrasound for cystic formations of the thyroid gland allows you to determine the size and roundness of the formation. To determine the nature of the cyst, the patient is prescribed additional tests - thyroid puncture.
Benign or malignant tumors. Quite common diseases that can be detected using ultrasound diagnostics. Most often, adenomas or cancer are found. Such neoplasms can have both a benign and malignant course. Using ultrasound, you can determine the size of the tumor, its location, and assess the condition of the lymph nodes and other surrounding tissues.
Any of the above diseases are quite dangerous for humans, but if they are diagnosed in the early stages of development, the prognosis for treatment is always favorable.
Symptoms in the presence of nodes
If the node has a size below normal - less than 1 cm, then its presence will not make itself felt as unpleasant sensations in either men or women.
When thyroid nodules become larger than normal (over 3 cm), a person may experience a number of symptoms:
- pain and discomfort in the neck;
- difficulty swallowing;
- pain in the respiratory organs and in connection with this a cough and a sore throat appear;
- voice changes are observed;
- an increase in the size of the lymph nodes from normal.
If nodal connections produce thyroid hormones, then thyrotoxicosis (with increased secretion of hormones): protrusion of the eyeballs, tachycardia, irritability.
The most common pathologies encountered during ultrasound interpretation
Analysis of deviations from the norm of the main parameters during ultrasound examination makes it possible to diagnose common pathologies of the thyroid gland.
- A nodular goiter in an ultrasound transcript is described as a high-density focus with clear boundaries between it and healthy tissue. Usually determined by palpation of the neck as compaction of organ tissue. The diagnosis is made when one or more lesions larger than 1 cm are present on ultrasound.
- It happens that an ultrasound reveals only an increase in the size of the gland. The structure of the thyroid gland is homogeneous and has no deviations from the norm. Then the endocrinologist may assume that the patient has a diffuse toxic goiter. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a blood test for thyroid hormones, the excess of which above the norm accompanies this disease.
- On the contrary, hypothyroidism is characterized by a smaller than normal volume of the thyroid gland. In this case, a blood test reveals decreased levels of hormones.
- With thyroiditis, patients experience swelling and pain in the neck, fever and headaches. The disease starts in the presence of inflammatory or viral processes in the thyroid gland. The ultrasound image reveals heterogeneity of the structure; the interpretation indicates increased echogenicity of the organ.
- A thyroid cyst in an ultrasound image is a round-shaped cavity that is filled with fluid and has clear contours. If it is detected, it is advisable to prescribe a puncture and exclude cancerous pathology.
- Benign tumors on ultrasound are defined as areas of tissue compaction. With a clear delineation of the lesion, endocrinologists make a conclusion about the presence of an adenoma. In malignant tumors, areas of compaction are also identified. But in this case, growth deep into the tissue is observed, and the doctor comes to the conclusion about the possible presence of a malignant formation (cancer). In addition, enlarged lymph nodes may also indicate the presence of a malignant tumor.
Due to the obvious advantages of the ultrasound research method (safety, accessibility, accuracy), it has become the main tool for endocrinologists in diagnosing thyroid diseases.
Correct interpretation of information obtained by ultrasound allows specialists to identify developmental anomalies in the early stages and prescribe subsequent examination and treatment.
Important to remember! The correct diagnosis in the presence of abnormalities in the ultrasound of the thyroid gland will be made only by a doctor during your examination!
Some thyroid ultrasound results can be deciphered independently. Ultrasound of the thyroid gland - the normal indicators in the table are given in the following material.
We will look further into the reasons for the increase and decrease of the T4 hormone in a woman’s body. How does the concentration of this hormone affect women's health?
Treatment methods
The endocrinologist draws up an individual treatment regimen taking into account the physiological state of the person, age, and the degree of deviation of the thyroid gland size from the norm. An important place in complex treatment is given to proper nutrition. With different types of goiter, patients require different menus.
Drug therapy
If the normal size of the thyroid gland is changed due to hypothyroidism (decreased function), replacement therapy is prescribed. Treatment consists of taking (often lifelong) thyroid hormones.
To combat increased thyroid function (hyperthyroidism, thyrotoxicosis), medications are prescribed that suppress the functioning of follicular cells. This is Mercazolil, Methimazole.
If deviations from the norm in the functioning of the thyroid gland are provoked by viruses or bacteria, then antibiotics (Ceftriaxone, Penicillin) are included in complex therapy. Treatment lasts 7-10 days.
Treating thyroid disease with home remedies is dangerous. You can drink decoctions and infusions based on medicinal herbs only with the permission of an endocrinologist.
Deviations from the norm in the structure and functions of the thyroid gland are treated only with medication. Folk remedies cannot replace therapy prescribed by a doctor.
When does a thyroid nodule mean surgery?
Should you be scared when your doctor tells you that a nodule has been found in your thyroid gland? In order not to succumb to groundless panic, let's figure out what thyroid nodules are, why they occur and what threat to health they can pose. What are the indications for thyroid surgery and when can surgery be avoided?
Problem out of nowhere
Usually, a message about neoplasms in the thyroid gland, and nodes are called any formations other than the main tissue of this organ, plunges the patient into shock. It seems that the problem arose suddenly and there were no prerequisites for this, because the formation of nodes is not accompanied by any pronounced symptoms, and the neoplasm itself can only be detected by ultrasound.
In fact, there is always a root cause that provoked the formation of nodes. You may have had your neck X-rayed frequently as a child because of problems with your tonsils or thymus gland and were exposed to excess ionizing radiation. Scientists have already identified the genes responsible for the occurrence of such formations.
But most often, nodes arise due to prolonged chronic iodine deficiency in the body. It is no secret that in many regions of the country the content of this element in water and products is far from the norm. Unfortunately, this factor becomes one of the decisive ones when it comes to the prevalence of thyroid nodules in a given area.
If it's cancer
The detected node can be either a benign or a malignant tumor. Don’t panic – according to statistics, only 5% of tumors in the thyroid gland turn out to be cancerous. However, such encouraging statistics do not mean that you can forget about the nodule in the thyroid tissue as soon as it is discovered and refuse further diagnosis.
To finally make sure that the tumor is benign, you will have to do a fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNA), during which a tissue sample is taken from the tumor for analysis. If the analysis does not reveal malignant cells in the sample, the suspicion of oncology is removed. But even if the answer is positive, you should not give up - thyroid cancer, as a rule, is treatable.
What are the indications for thyroid surgery?
Typically, surgery to remove the gland is prescribed in the case of a malignant tumor after confirmation of the diagnosis. If the tumor is diagnosed as benign, they are first limited to its observation. The main thing is to visit an endocrinologist every six months and do an ultrasound to monitor changes in the size of the node. If it does not grow, no medical intervention is required.
But in the case when the nodes cause increased levels of thyroxine and triiodothyronine, treatment may be required. An excess of these hormones occurs due to the fact that they are produced by both the changed and unchanged parts of the thyroid gland. Usually the problem is solved with medication, without surgery.
Surgery for benign nodes is performed only as a last resort, when they grow so large that they begin to cause physical problems for the patient. Overgrown nodes can put pressure on the trachea and esophagus, causing a sensation of a lump in the throat, difficulty breathing or swallowing, and hoarseness in the voice. Usually, only large nodes whose size exceeds 3 cm lead to such consequences. But even in this case, most often only the neoplasm is removed, and not the entire gland.
Basic definition parameters
The ultrasound method allows you to make the most accurate conclusions about the condition of an organ such as the thyroid gland.
During the procedure, measurements are taken of the width and length of the internal organ, its structure is studied, and the presence of neoplasms is determined, which can cause the onset of a variety of diseases.
When performing an ultrasound, the doctor also looks at the volume of the thyroid gland, which is individual for each individual case.
Photo:
It is worth noting that for women and men this parameter cannot exceed 18 cubic centimeters.
In a normal state, no seals can be detected on this most important internal organ, and the structure itself is completely homogeneous.
All data that the doctor receives after the procedure is necessarily entered into a special protocol, on the basis of which the interpretation and diagnosis is made.
First of all, the most accurate location of the thyroid gland in relation to other internal organs is established. The nature of the contours and their general condition are examined in detail.
The structure of the organ, its homogeneity and maximum density are carefully examined. When performing an ultrasound, the overall dimensions of the right and left lobes are necessarily compared with each other.
All these data allow us to assess the condition of the thyroid gland in general terms and make a diagnosis with high accuracy.
READ Preparing for an abdominal ultrasound in a child
The norm is the absence of any deviations and suppuration in the internal space of the organ, as well as the absence of an increase in volume.
Video:
In its normal state, the thyroid gland should not only have cysts, but also all kinds of tumors that may indicate serious health problems.
Only the attending physician can prescribe an ultrasound diagnosis of the thyroid gland.
The reason for referral for the procedure may be poor blood tests, as well as pathologies discovered during an individual examination of the patient.
An ultrasound may also be recommended if a person complains of insomnia, severe nervousness and sudden mood swings.
It is extremely important to undergo this study even in the case where hormonal therapy was carried out. In some cases, the reason for ultrasound is a genetic factor.
It should be noted that, as a preventative measure, the study is recommended for all people over thirty years of age.
The diagnosis itself does not require any preparatory measures. The study does not take much extra time and effort and is considered completely safe.
What are the dangers of changing the size and structure of the thyroid gland?
If left untreated, the thyroid gland will gradually increase in size, which will subsequently lead to constriction of the throat and difficulty breathing. Against the background of oxygen starvation, the body begins to experience a lack of energy. First of all, the lack of oxygen affects the functioning of the brain. A person’s memory deteriorates, blood pressure drops, and diseases of the nervous and cardiovascular systems develop.
With normal functioning, a reduced thyroid gland is not dangerous to human life. But in unexamined patients, long-term hypoplasia can cause an acute lack of thyroid hormones in the body. Such a person gets tired quickly, he constantly wants to sleep, he has no desire for life.
Prevention
The thyroid gland needs constant care. For this purpose, doctors recommend following the rules of a healthy lifestyle. They include:
- balanced diet;
- daily walks in the fresh air;
- good sleep;
- rejection of bad habits;
- timely treatment of any diseases.
Periodic examination by an endocrinologist and compliance with all his recommendations is the key to ensuring that the thyroid gland will always be normal.v
How often should you get your thyroid checked?
Doctors advise undergoing an ultrasound of the thyroid gland once a year. In some cases, you need to undergo additional testing of the thyroid gland (even if the doctor has not given a referral for this):
- Pregnancy.
- Bad heredity. If your parents suffered from thyroid disease, you need to undergo ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland more often. Indeed, in the early stages of thyroid disease, it is easier to treat.
- Diabetes.
- Environmentally hazardous industries, as well as work in conditions of high radiation.
- Reaching the fortieth birthday.
- Taking hormonal drugs.
- Psychological disorders - nervousness, drowsiness, apathy, and so on.
- Severe obesity, as well as sudden weight loss.
- A prolonged increase in temperature by 1-1.5 degrees.
- Feeling of a foreign object in the throat.
- Suspicion of cancer.