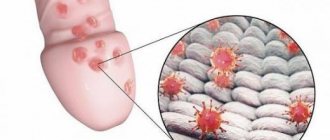
What it is
Cystic lesions of the gums can proceed for a long period without causing any discomfort to the person. Because of this, the patient often seeks help with the inflammatory process. A benign tumor occurs in both adults and children. Moreover, this disease is widespread.
The tumor affects the area of the tooth root. A cyst is a cavity filled with dead cells, various bacteria, and pus. The capsule has an oval or round shape.
The granuloma is composed of connective tissue, while the inner surface consists of multiple epithelial layers. Large defects reach several centimeters in size.
The pathological process begins with an inflammatory focus in soft tissue structures. After the cyst comes to the surface, inflammation affects nearby areas. The neoplasm gradually destroys the molar, roots, and bone tissue.
Types of cysts on the gums
Both adults and children develop different types of gum cysts. Among them are the following:
Radicular cyst
- cyst of the eye teeth, its main cause is sinusitis;
- paradental cyst;
- follicular, which is located near diseased teeth;
- radicular, the location of which is the dental roots.
There is also a cyst on the gum during teething in children (we recommend reading: photo of a growth on the gum of a child during teething). It usually occurs in children during the period when baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth.
Features of the disease
As stated above, the disease develops at a slow rate. It is difficult to notice, which often occurs during the treatment of another disease in the oral cavity. The lack of proper and timely therapy leads to its greater spread. In addition, as a result of untreated disease, cracks and fractures may appear in the jawbone. This is why treatment is so important, especially when it comes to a child. As you know, bones in children (in this case, jaw bones) are more fragile than in adults, so lack of treatment will lead to their rapid destruction.
There is often pain throughout the entire oral cavity, and noticeable swelling of the gums along with the cheek appears. Due to the formation of a large amount of purulent fluid, the neoplasm often bursts - pus rapidly flows out of the diseased gum, forming a fistula.
Where is the cyst located?
As a rule, the tumor is located opposite the tooth root. In children, it often appears above the front incisors during teething, less often around the chewing teeth. Spontaneous opening of a cyst on the gum anywhere will reduce swelling, however, if left untreated, the tooth bone will begin to rapidly deteriorate. After this, the diseased tooth is often removed. The appearance of alarming symptoms of the disease should be a reason to consult a doctor, namely a dental surgeon.
What does a neoplasm look like: photos and symptoms
The photo accompanying the article will help you recognize the disease in a child and an adult. As for the symptoms, at the beginning of the disease they are hardly noticeable, so they practically do not go to the doctor about them. In the initial stages of the disease it is practically invisible. We are talking about such unexpressed signs as barely noticeable swelling of the gums and discomfort on it. Due to the fact that no measures are taken to get rid of the cyst, it begins to progress - in place of the slight swelling, a granuloma slowly grows, taking the form of a vesicle, inside of which a yellow liquid is clearly visible. After some time it becomes a cyst. The diameter of the cyst is usually no more than 5 mm, but if it is not treated, it will grow to a large scale.
Read also: How to treat gumboil at home
Often the patient learns about the presence of a problem only during the period of a cold. As a result of decreased immunity, pain in the area of the tumor increases, as does the amount of pus in it. At the same time, the gums along with the cheek swell noticeably, and body temperature rises. The patient may attribute this last sign to a cold. An x-ray is required to confirm the diagnosis.
If a cyst suddenly appears in a child’s mouth, it should be treated as soon as possible. The specific type of therapy directly depends on the cause that caused it. Dentists recommend treating a newly appeared cyst at an early stage at home with frequent rinsing with a solution of kitchen salt. In general, medications are almost always used to get rid of these types of cysts.
When is removal surgery indicated?
The method of surgical removal of the cyst is used only in cases where it has reached an advanced stage, where little can be done with the help of therapeutic treatment. Previously, along with the cyst, the tooth near which it grew was also removed, however, today a tooth is removed only when its root becomes unusable. Thanks to modern technology, cyst removal is not as scary a procedure as it used to be.
The most effective method for removing a toothless cyst is laser excision. This procedure is not carried out in every clinic. It is for this reason that surgery becomes the solution to the problem.
Therapy methods
In the treatment of cysts in children, the endoscopic method is often used: the purulent fluid located in the cyst is removed using an endoscope. This method is most suitable for treating late stages of cysts in children.
Often, pus is removed from a cyst by drilling the tooth, through which it comes out.
Home remedies
For many years, various folk recipes have been used to treat cysts, which you can do yourself at home. Note that they are used only when the disease is in the initial stages. The effectiveness of prescriptions is quite high, so even doctors often prescribe them.
The following remedies are used at home:
- saline solution, to which you need to add 1 drop of iodine for greater effectiveness;
- tinctures of plants such as calendula or aloe;
- herbal decoctions for rinsing;
- garlic, which should be applied well to the sore gum;
- homeopathic remedies.
Ointments and compresses are often used to resolve cysts. Lotions, for example, made from sesame oil, are considered no less useful.
How to get rid of a cyst during pregnancy?
The disease often occurs in women during pregnancy. During the period of bearing a child, taking most medications is prohibited, and X-ray examinations are prohibited.
Cyst therapy during pregnancy is a mandatory procedure, because the presence of a purulent infection in the mother’s body is dangerous for the baby. The decision to treat the disease should be made by the attending physician on an individual basis. The best option in this case is treatment with folk remedies in the initial stages of the disease. If surgery or another method of surgical intervention is required, those anesthetics that do not contain adrenaline are selected.
Kinds
Granuloma can affect any part of the oral cavity. Capsules are divided into the following types:
- Paradental , localized on the molars. The third molar is almost always affected.
- Follicular , appearing on the roots. Such cysts arise due to advanced caries and mechanical damage.
- Radicular , located on the gum near the root.
- Residual , resulting from amputation or restoration of a tooth.
A congenital cyst should also be highlighted. This pathology is formed when the first primary molars emerge.
Types and symptoms
A person often recognizes that a cyst has formed in the mouth by the sensation of the presence of a foreign object on the soft tissues.
As the formation grows, it begins to cause inconvenience while eating, talking, or even sleeping.
Next, pain occurs, which at first is only recurrent, worsening with hypothermia, eating hot or cold food. In advanced cases, swelling develops and the pain becomes throbbing. At the same time, the lymph nodes may become enlarged.
Patients usually do not rush to see a doctor after noticing a small lump. Perhaps a cyst in the gum of a front tooth becomes an aesthetic defect, forcing you to see a specialist.
The main thing to remember is that you cannot try to remove a cyst at home on your own. It can grow to a considerable depth, and removal without following the rules of disinfection and inflammation relief will lead to extensive infection.
Granulomas are treated and removed by first determining their type:
- Root – formed when pulp tissue dies and is located in the root of the tooth.
- Residual – formed after the removal of a diseased tooth
- Follicular – appears in a sac that covers an unerupted tooth, and quickly spreads to adjacent incisors.
- Eruption cyst – occurs during teething if the process occurs slowly.
- Keratocyst – is formed from the incisor rudiment due to pathologies in its development, often involving molars and “sevens”.
There is also lateral periodontal and calcifying granuloma. Today, the causes of these problems have not been fully identified.
However, experts say that if left untreated, they can transform into malignant tumors.
The more important it becomes to visit a doctor in a timely manner, whose task is not only to help get rid of the cyst, but also to examine it for potential danger to humans.
Causes
Provoking factors are considered to be the presence of an inflammatory process in the gums under the crowns, chronic diseases of the nasopharynx, a weakened immune system, insufficient oral hygiene, and difficult eruption of wisdom teeth. In this case, a cyst on the gum develops for four reasons.
The first is advanced caries or pulpitis. In this case, periodontitis occurs, and an inflammatory focus forms in the upper zone of the molar root. The purulent mass gradually accumulates, resulting in a new formation.
The second reason is poor-quality root canal filling. Inaccurate processing leads to the formation of granuloma at the top of the passage. An infection penetrates the capsule and affects the gum tissue. The pathological process develops both immediately after filling and after a long time.
In addition, the cyst appears as a consequence of perforation of the molar canal. Improper treatment provokes inflammation in soft tissue structures. Because of this, favorable conditions arise for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
Another neoplasm develops as a result of developing periodontitis. In this case, the gums are affected by periodontal pockets with purulent contents. If the fluid does not find an outflow path, then a capsule with an abscess appears.
In childhood, pathology appears after injuries, infectious lesions of the oral cavity, and improper treatment of dental problems.
Often a cystic tumor occurs in a child during teething. This disease in infants is dangerous as the outbreak spreads throughout the body, as a result of which internal organs suffer and immunity decreases.
Causes of cysts
If you suspect the development of a disease, you must urgently consult a doctor to identify the source of the problem, make a diagnosis and prescribe therapy in order to negate the identified and provoking factors of the disease.
- There are several reasons for the appearance of gum cysts, and the most common of them is the negligence of the attending physician, who, during dental procedures, did not comply with the required rules for the sterility of instruments. As a result, the onset of infection along with suppuration, and then a cyst.
- Another equally common cause of the disease is incomplete treatment of dental problems such as pulpitis or caries. The development of any disease in the oral cavity always requires full treatment, to avoid new diseases and aggravation of existing ones. Note that the disease often manifests itself in a child’s body, and a cyst in a child’s mouth can form precisely as a result of untreated caries.
- The main thing in the treatment of caries is thorough cleaning and filling of the canals. If these rules are not followed, an inflammatory process may develop under the filling placed after dental procedures, during which a cyst is formed. Gum cysts can also occur after tooth extraction.
Clinical picture
At the initial stage, a cyst on the gum does not cause any discomfort, which is why the pathology is often detected when complications arise.
The prolonged course of the neoplasm causes pain when pressing on the affected molar, and slight swelling.
A weakened immune system can lead to frequent colds and worsening infections. In this situation, the patient’s body temperature rises and acute pain appears.
On this topic
- Oral cavity
Complications after removal of a dental cyst
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 5, 2020
The disease is also recognized by the following manifestations:
- Difficulty opening the mouth.
- Feeling of heaviness, tingling in the molar root area.
- Painful sensations while eating.
- The appearance of hyperemia on the gums , a growing and fluid-filled elevation.
- General weakness, fatigue.
- Loss of appetite.
- Headache , swollen lymph nodes.
- Change in color .
- Loss of stability, tooth displacement.
As inflammation progresses, the amount of purulent mass increases. The cystic substance tends to break out, which is why it approaches the gum. As a result, swelling develops followed by the appearance of flux or fistula.
Causes, consequences and treatment of cysts on the gum of a tooth
Content:
A cyst on the gum is a neoplasm of a certain size that is filled with purulent fluid. It can be localized in absolutely any area of the gums, without distinguishing between the basal or remote location.
It is noteworthy that the filling of the cyst with pus occurs a little later. Initially, you feel an unpleasant tingling sensation on the gum in a certain place. And don't attach any importance to it. But this may just be the first symptom of a cyst.
Symptoms of a cyst on the gum
If you experience discomfort in your mouth, be sure to pay attention to the symptoms. They can signal the appearance of such an unpleasant thing as a cyst.
- Focal redness of the gums.
- Tingling sensation in this area when eating.
- Swelling of the gums around the tooth(s).
- Slightly elevated body temperature.
- Mild headache.
A cyst on the gum is such an “insidious” disease that it may not appear for a long time. That is, the symptoms described above deserve special attention, since it is at this time that the cyst begins to rot in the middle. Outwardly, it has not yet manifested itself in any way, but internal processes are already taking place.
There is an infection inside the gums. A cyst can have a destructive effect on both bone tissue and tooth roots; it can even promote inflammation of the lymph nodes. Further, the external manifestation is the final stage of the development of a cyst on the gum mucosa, when pus tries to find its way out and manifests itself in the form of a purulent sac on the gum mucosa.
Therefore, as soon as you experience primary symptoms, it is better to immediately consult a specialist. Initially, seek the necessary advice from a dental clinic. Further, when the diagnosis is confirmed, it is likely that you will need to consult a dental surgeon.
Causes of cysts on the gums
When faced with a certain disease, we delve so deeply into the issue of its treatment that we do not think about the causes at all. But if you understand what was the initial cause of the disease, there is a great chance of eliminating its occurrence in the future. What is the main cause of this disease? There are several of them.
- Untreated pulpitis or caries. Dental diseases and problems with teeth require very careful treatment, since there are many pathogenic microbes in the mouth that can become active if any problem is neglected or undertreated. Both caries and pulpitis are processes of decay in different places of the tooth. If this pus is not stopped, it will begin to grow and develop into a more serious condition called a cyst.
- Poor quality dentistry. If the treatment process for any dental disease has been disrupted (unscrupulous attitude of the doctor, careless handling of the instrument, poor sterilization of the instrument), this can contribute to infection and a purulent process that gradually develops into a cyst on the gum.
- Poorly sealed canals. When treating caries, the canals must be filled very well. Otherwise, pus from the damaged tooth through these channels can flow into the soft tissue of the gums, where there is fertile ground for further decay.
Consequences of a cyst on the gum
As soon as this disease is discovered, you need to immediately begin treatment. The cyst cannot be started. There are two options for the development of the event.
If you ignore this problem, there is a chance that the cyst with pus will burst on its own. A gap or, in medical parlance, a fistula, forms at this site. However, this does not mean that the problem is solved. No, the process of decay continues and if it is not stopped, the consequences can be disastrous. This includes the loss of several teeth or decay of bone tissue.
If you start treatment even at the stage of external manifestation of the cyst, there are high chances that there may be no consequences at all. During surgery, the cyst is cut out and for some time there may simply be a scar on the gum. But if the cyst is large in size and a significant part of the tooth is affected, then a specialist on an individual basis may decide to remove the tooth.
Surgery to remove a cyst on the gum
A timely visit to the dentist about a cyst gives the doctor more options in choosing treatment. Indeed, today it is possible to use both therapeutic and surgical methods of treatment.
Since patients mostly turn to dentists at later stages of cyst development, sometimes surgery is the only right solution. Before the procedure, the patient undergoes a series of tests and, most importantly, an x-ray to determine the extent of the tooth’s damage to the cyst.
Based on the results of the x-ray, the doctor determines which procedure is required. When treating cysts with surgery in dentistry, there are two types of surgical intervention.
- Cystectomy. This manipulation involves complete removal of the cyst, as well as partial removal of the apex of the damaged tooth.
- Hemisection. This procedure involves removing the cyst, as well as parts of the tooth root and parts of the tooth that were damaged by the cyst. The tooth itself is restored using a crown.
If the x-ray does not show damage to the tooth or roots, but simply the presence of a cyst, then superficial surgery is used. That is, the gums are chipped with an anesthetic, an incision is made into the cyst and all the pus is sucked out. The wound must be treated with a disinfectant solution. If there is a need for sutures, then this procedure is also performed.
Treatment of cysts on the gums with folk remedies
There are also folk remedies to treat this disease. But we can talk not only about treatment, but also about prevention. Which is much more effective and reduces the risk of tumor and cyst formation significantly.
The most important requirement for the prevention of any infections in the mouth is personal hygiene. That is, this means using dental floss, mouthwash and, of course, brushing your teeth in the morning and before bed.
For prevention using folk non-medicinal remedies, you can use herbal ingredients, which primarily help disinfect the oral cavity. For example, a few grams of sesame oil, held in the mouth for 3-5 minutes, helps regulate the bacterial balance. This product is also suitable for use when a cyst has already formed. In combination with sesame oil, you can also use a gauze swab, after soaking it in a drop of clove oil. This tampon is applied to the tumor site in order to reduce it. Perform the procedure 2 times a day.
There are also a number of useful herbal substances that are used to treat abscesses on the gums at home.
- Warm water with lemon juice added.
- Tea tree oil.
- Cranberry juice.
- Essential oils of almond and mint.
- Bergamot oil.
All this is used for rinsing in order to reduce the cyst itself. The antiseptic (antibacterial) properties of these plants will help reduce pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity that cause rot and cysts.
But before you start treating a cyst with folk remedies at home, it is still better to first consult a specialist at the clinic.
Author of the article:
Alekseeva Maria Yurievna |
Therapist Education: From 2010 to 2020 practicing physician at the therapeutic hospital of the central medical unit No. 21, the city of Elektrostal. Since 2020 he has been working at diagnostic center No. 3. Our authors
Diagnostics
In most cases, granuloma is discovered accidentally during a dental examination.
To clarify the diagnosis, radiography is used, which shows the presence of cystic formations and determines the condition of the dental canal.
Based on the information received, the specialist assesses the degree of damage to the molar and selects the type of treatment. Sometimes it is not possible to save a tooth.
This occurs with a long-term infection of the periodontal canal or in the presence of a vertical crack in the molar. If the tooth is partially destroyed, it is also removed.
How dangerous are dental cysts, what are the consequences of untimely treatment and complications?
A dental cyst is dangerous because the patient may not be aware of its presence for a long time. At the same time, the formation grows, which causes pain and discomfort. In children and adults, serious complications are possible after untimely or unskilled removal of a dental cyst. Among them:
- gradual destruction of the roots of incisors, wisdom teeth, molars;
- headaches and toothaches;
- purulent inflammation;
- sepsis and phlegmon;
- periostitis;
- holes in bones;
- osteomyelitis;
- oncological degeneration;
- destruction of the jaw.
A dental cyst is considered a benign formation, but it should not be taken lightly as it will not go away on its own. You should contact a reliable clinic with experienced staff who have positive reviews from patients. With poor quality dental care, the following are possible: nerve paresis, formation of fistula canals, injuries to the alveolar processes, death of the pulp of adjacent teeth, infection and abscess.
There are no special measures to prevent periodontal cystic formations. Following simple hygiene rules will reduce the risk of its occurrence and development. It is important to regularly treat your teeth, undergo preventive examinations and x-rays.
rated 4.80 out of 5) Loading...
Risk of degeneration into cancer
Like any other cyst, granuloma on the gum is prone to malignant degeneration.
On this topic
- Oral cavity
Laser removal of dental cyst
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 5, 2020
Malignization occurs when the neoplasm rapidly enlarges, as a result of which the capsule compresses adjacent healthy tissues and has a detrimental effect on nearby teeth.
Cystic formation goes unnoticed for a long time, while symptoms signal the development of complications. Degeneration into a cancerous tumor is considered one of these consequences.
What is a cyst
A cyst in the gum is an inflammatory neoplasm localized on the surface of the periodontium. As a rule, inside a dense sac there is purulent exudate, causing a dull aching pain. When there is a lot of purulent content, a fistula is formed, through the channel of which pus comes out. In dental practice, a cyst-like formation on the surface of the periodontium is a form of periostitis.
Treatment
Cystic lesions of the tooth root are eliminated by several methods.
Conservative therapy
The essence of this technique is to open and clean the molar. This treatment is used in the initial stages of pathology, when the purulent sac does not exceed 1 cm in diameter. However, the traditional method is dangerous for relapse of the disease.
At the beginning of the procedure, the specialist removes fillings with a canal or removes the pulp. To eliminate the purulent mass, rinsing with an antiseptic solution is done.
Together with the drug, the dentist fills the canals with a temporary substance. The medicine must be replaced over several months.
After a control x-ray, a permanent filling is placed.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is prescribed when conservative treatment is not effective. During cystectomy, the anterior part of the granuloma is removed and the canal with the root apex is cleaned. After the procedure, the incision is sutured, antibiotics and antiseptic rinses are prescribed.
During cystotomy, the anterior wall of the growth is excised, where the capsule is connected to the oral cavity.
After such an operation, the patient will have to recover for a long time. During hemisection, the cyst and root are removed along with the affected area of the molar. Now a laser is used to eliminate the tumor.
This method is characterized by painlessness, quick duration, exclusion of infectious infection, possibility of tooth preservation, and reduced risk of complications.
What happens?
It all starts with periodontitis - inflammation of the periodontium - a thin layer between the tooth root and the jaw bone. If the disease is not treated, serious complications may arise: tissue will begin to grow around the root of the tooth - a small neoplasm up to 5 mm, it is called a granuloma. Gradually it enlarges, becomes covered with a membrane and turns into a cyst - a sac with semi-liquid contents from damaged cells. If treatment is not taken now, the cyst will grow further and capture more and more teeth. Sometimes the cyst spontaneously opens, forming a fistulous tract.
Consequences
In an advanced stage, a cyst on the gum leads to the loss of a molar. In addition, the pathology is dangerous due to the appearance of gumboil and periodontitis.
On this topic
- Oral cavity
Removal of tooth granuloma
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 4, 2020
Rupture of the filled capsule is dangerous due to the entry of purulent contents into the periosteum, as a result of which acute inflammatory phlegmon develops.
In some cases, the pathological process affects other parts of the skeleton. When the bone marrow is damaged, dangerous osteomyelitis occurs.
If the roots of the tooth are destroyed, the interaction with the periosteum is disrupted, as a result of which the molar falls out.
Deadly complications of the disease are considered to be malignant degeneration of the tumor and blood poisoning.
Emergency care for pain
If the pain is very strong, then quick first aid methods will help. There are several reliable drugs that will reduce pain:
- Tea bags. It is necessary to pour boiling water over them and let them brew for a while, then take them out and cool. Apply the bag to the area of pain and hold until the discomfort goes away.
- Soak a cotton pad in organic vinegar and apply. This method can be used up to six times a day.
- Sesame oil. This remedy effectively gets rid of bacteria that provoke pain. You need to drink a teaspoon of oil and rub a small amount of it around the mouth line clockwise for 10 minutes.
The choice between treatment or removal of a cyst on the gum of a tooth remains with the patient.
Symptoms of an emerging cyst
At the initial stage, the formation in the oral cavity does not manifest itself in any way. Most symptoms occur at a later stage, when the cyst begins to grow, increasing in volume.
Cyst treatment
When the immune system is weakened, the cyst begins to manifest itself from a latent state by suppuration and enlarged lymph nodes. The body, trying to destroy the source of infection, tries to isolate it from healthy tissue. An inflammatory process develops, which may be accompanied by fever and weakness; the following symptoms are also characteristic:
- pain when chewing food;
- pain in the mouth;
- the formation of a small tubercle on the gum;
- bad breath;
- the smell of pus in the nose (with sinusitis);
- the appearance of a fistula.
A fistula is a canal that appears during purulent formation as a result of the disintegration of an inflammatory focus. Through this channel, pus periodically comes out of the cyst. When the inflammation is removed, the canal heals. Most often, it is after the appearance of a fistula or periostitis (swelling of the gums with pain) that people turn to a dentist for help.
An example of a fistula on the gum
A cyst located on the upper jaw, having reached a large size, can grow into the maxillary sinus and thereby cause severe headaches.
Treatment of a dental cyst at the dentist